Spring Security
认证
验证用户名和密码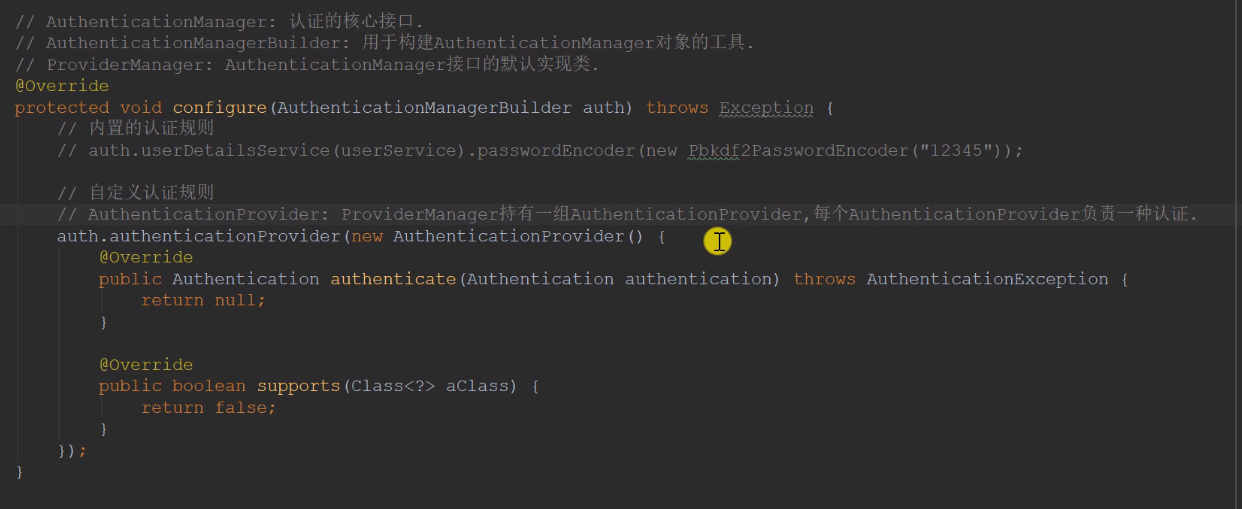
//AuthenticationManager:认证的核心接口//AuthenticationManagerBuilder:用于构建 AuthenticationManager 对象的工具//ProviderManager:AuthenticationManager 接口默认实现类@Overridepublic void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception{//内置认证规则//auth.userDetailsService(userService).passwordEncoder(new Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder("1234"))//加盐//自定义认证规则//AuthenticationProvider:ProviderManager持有一组 AuthenticationProvider 每个AuthenticationProvider负责一种认证//采用委托模式:ProviderManager 将认证委托给 AuthenticationProviderauth.authenticationProvider(new AuthenticationProvider() {//Authentication: 用于封装认证信息的接口,不同的实现类代表不同类型的认证信息@Overridepublic Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {String username = authentication.getName();String password = (String) authentication.getCredentials();User user = userService.findUserByName(username);if(user == null){throw new UsernameNotFoundException("账号不存在");}password = CommunityUtil.md5(password + user.getSalt());if(!user.getPassword().equals(password)){throw new BadCredentialsException("密码不正确");}return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user,user.getPassword(),user.getAuthorities());}//当前 AuthenticationProvider 支持哪种类型的认证@Overridepublic boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {//UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken: AuthenticationProvider 常用的实现类return UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class.equals(aClass);}});}
用户认证是我们自己写的逻辑(在LoginTicketInterceptor中),跳过了 Spring Security,那我们就需要把我们自己做的逻辑认证的结果通过SecurityContextHolder存入 SecurityContext,以便于 Spring Security 进行授权
// 构建用户认证的结果,并存入 SecurityContext, 以便于 Spring Security 进行授权Authentication authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user, user.getPassword(), userService.getAuthorities(user.getId()));SecurityContextHolder.setContext(new SecurityContextImpl(authentication));
授权

/*** 授权* @param http* @throws Exception*/@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {//授权配置http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers(//添加访问路径"/user/setting","/user/upload","/discuss/add","/discuss/publish","/comment/add/**","/letter/**","/notice/**","/like","/follow","/unfollow").hasAnyAuthority(//这些用户拥有访问以上路径的权力AUTHORITY_USER,AUTHORITY_ADMIN,AUTHORITY_MODERATOR).antMatchers("/discuss/top","/discuss/wonderful").hasAnyAuthority(AUTHORITY_MODERATOR).antMatchers("/discuss/delete","/discuss/delete/","/data/**").hasAnyAuthority(AUTHORITY_ADMIN).anyRequest().permitAll().and().csrf().disable();// 权限不够时的处理http.exceptionHandling()// 1. 未登录时的处理.authenticationEntryPoint(new AuthenticationEntryPoint() {@Overridepublic void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException e) throws IOException, ServletException {String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");if ("XMLHttpRequest".equals(xRequestedWith)) {// 异步请求response.setContentType("application/plain;charset=utf-8");PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();writer.write(CommunityUtil.getJSONString(403, "你还没有登录"));}else {// 普通请求response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/login");}}})// 2. 权限不够时的处理.accessDeniedHandler(new AccessDeniedHandler() {@Overridepublic void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException e) throws IOException, ServletException {String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");if ("XMLHttpRequest".equals(xRequestedWith)) {// 异步请求response.setContentType("application/plain;charset=utf-8");PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();writer.write(CommunityUtil.getJSONString(403, "你没有访问该功能的权限"));}else {// 普通请求response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/denied");}}});// Security 底层会默认拦截 /logout 请求,进行退出处理// 此处赋予它一个根本不存在的退出路径,使得程序能够执行到我们自己编写的退出代码http.logout().logoutUrl("/securitylogout");http.headers().frameOptions().sameOrigin();}
CSRF配置
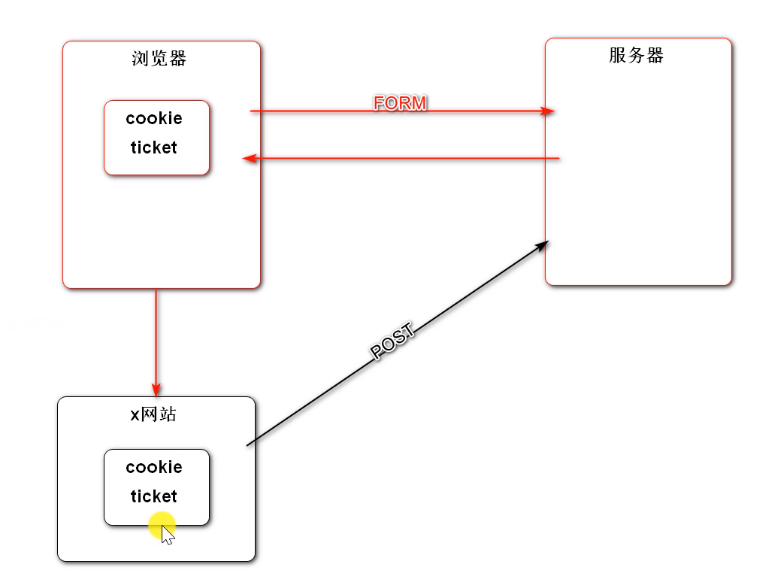
用户浏览器在发送表单请求时,访问x网站。x网站窃取cookie中的凭证,伪装用户向服务器发送post请求(修改数据)危害用户账户安全。
解决方式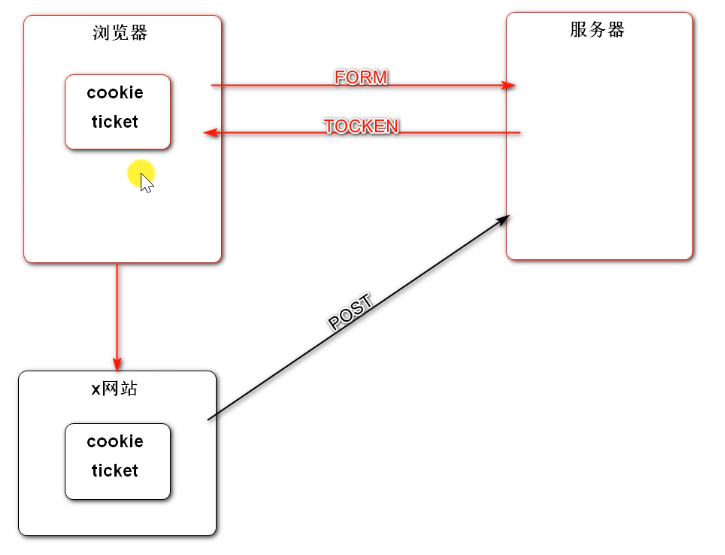
引入Spring Security后,用户在请求表单数据时,Security会在表单里默认加一个隐藏的数据 tocken,每次请求tocken都不一样。x网站能窃取到cookie,但是窃取不到tocken, x网站在提交数据时 cookie对,tocken不对,服务器则判断为非法请求,拒绝这样的请求。
Spring Security入门
spring security 的核心功能主要包括:
认证 (你是谁)
授权 (你能干什么)
攻击防护 (防止伪造身份)
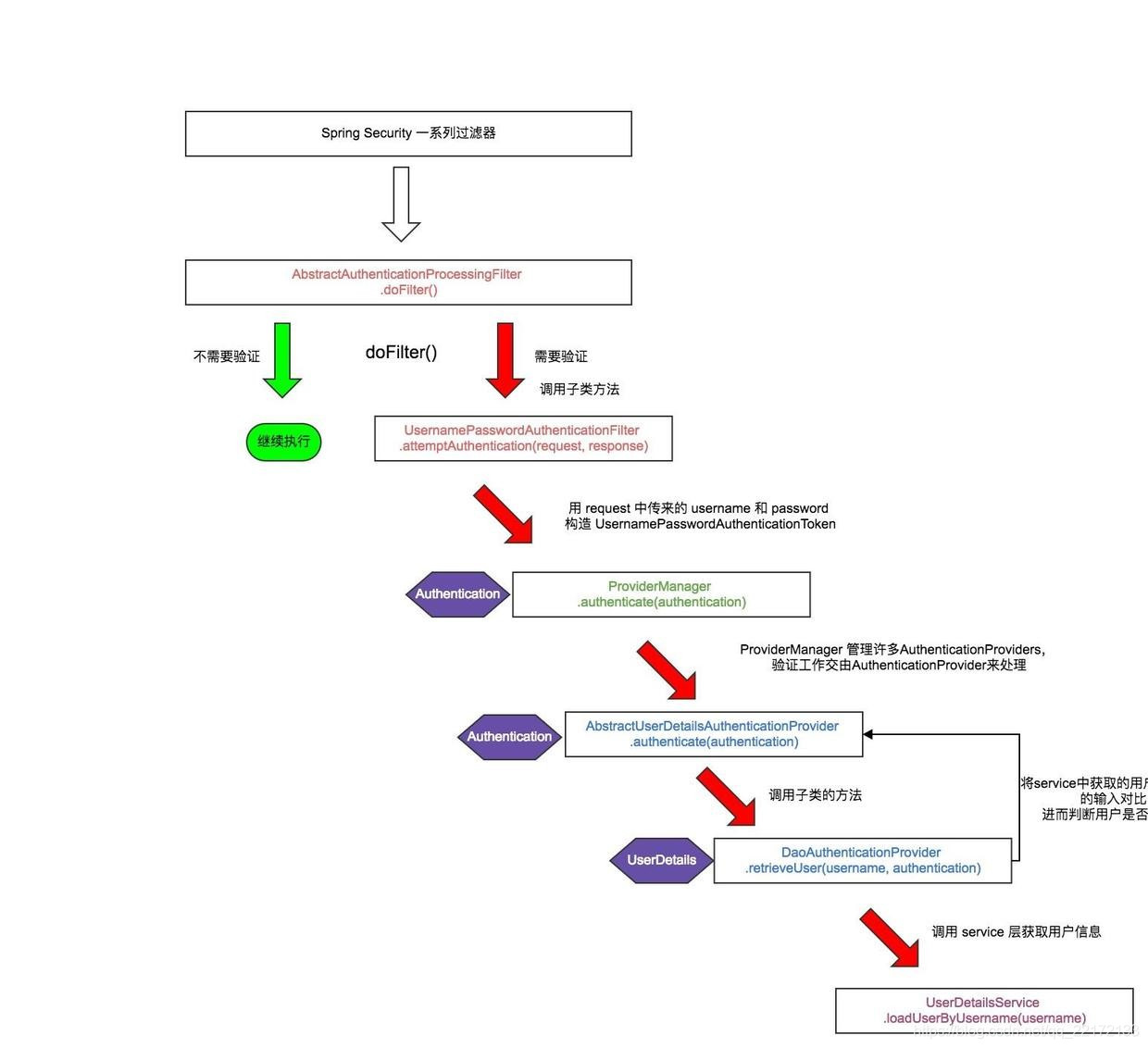
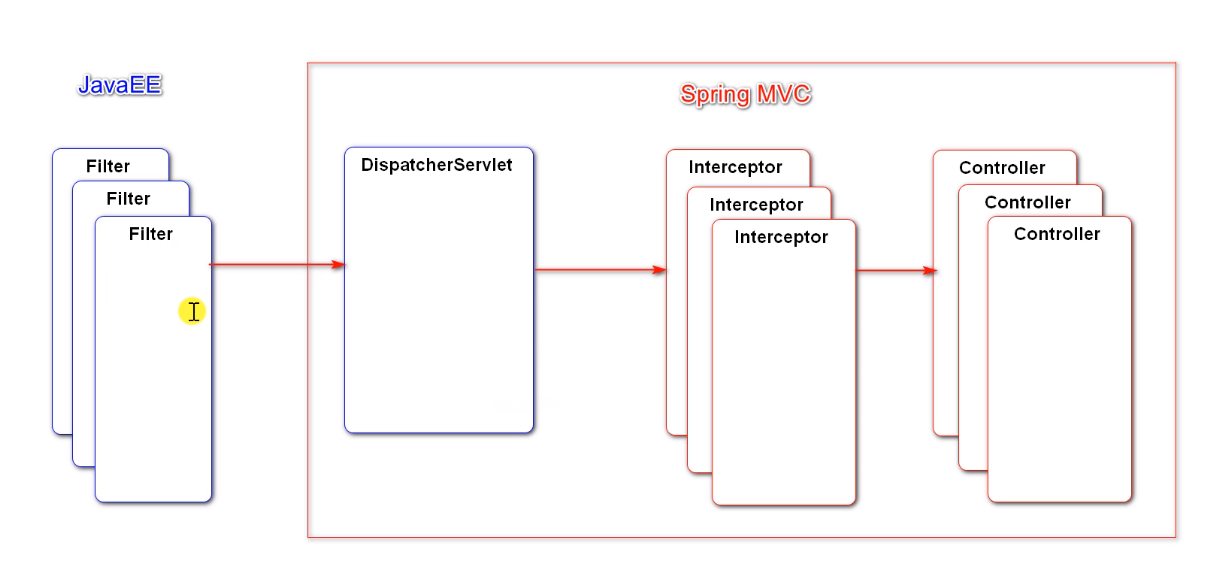
其核心就是一组过滤器链,项目启动后将会自动配置。最核心的就是 Basic Authentication Filter 用来认证用户的身份,一个在spring security中一种过滤器处理一种认证方式。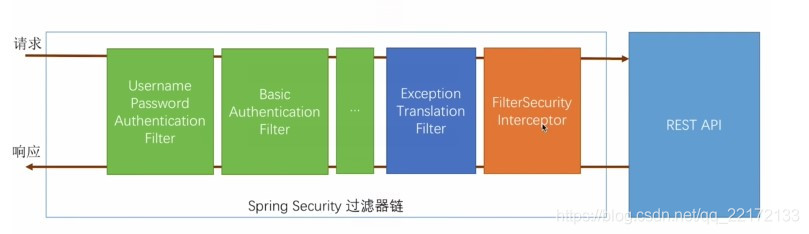
比如,对于username password认证过滤器来说,
会检查是否是一个登录请求;
是否包含username 和 password (也就是该过滤器需要的一些认证信息) ;
如果不满足则放行给下一个。
下一个按照自身职责判定是否是自身需要的信息,basic的特征就是在请求头中有 Authorization:Basic eHh4Onh4 的信息。中间可能还有更多的认证过滤器。最后一环是 FilterSecurityInterceptor,这里会判定该请求是否能进行访问rest服务,判断的依据是 BrowserSecurityConfig中的配置,如果被拒绝了就会抛出不同的异常(根据具体的原因)。Exception Translation Filter 会捕获抛出的错误,然后根据不同的认证方式进行信息的返回提示。
注意:绿色的过滤器可以配置是否生效,其他的都不能控制。
原理讲解
1、校验流程图