一、启动类
Tomcat的启动涉及到两个类:BootStrap和Catalina类。Catalina类用于启动和关闭Server对象,并通过Digester来解析conf目录下的Server.xml文件。BootStrap类则是一个入口类,入口是main方法。下面来看看源码中Tomcat的启动过程。
二、如何调试源码
这里介绍一种比较简单的方法:导入jar包调试法。
找一个自己配过tomcat的web项目,在pom中引入Tomcat的嵌入jar包,如下图所示。其中版本设置为你自己下载的tomcat版本即可。
1. <dependency>2. <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>3. <artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId>4. <version>7.0.84</version>5. </dependency>
三、启动过程
BootStrap类
首先在BootStrap类的main方法中打一个断点,启动项目就会停在如下断点: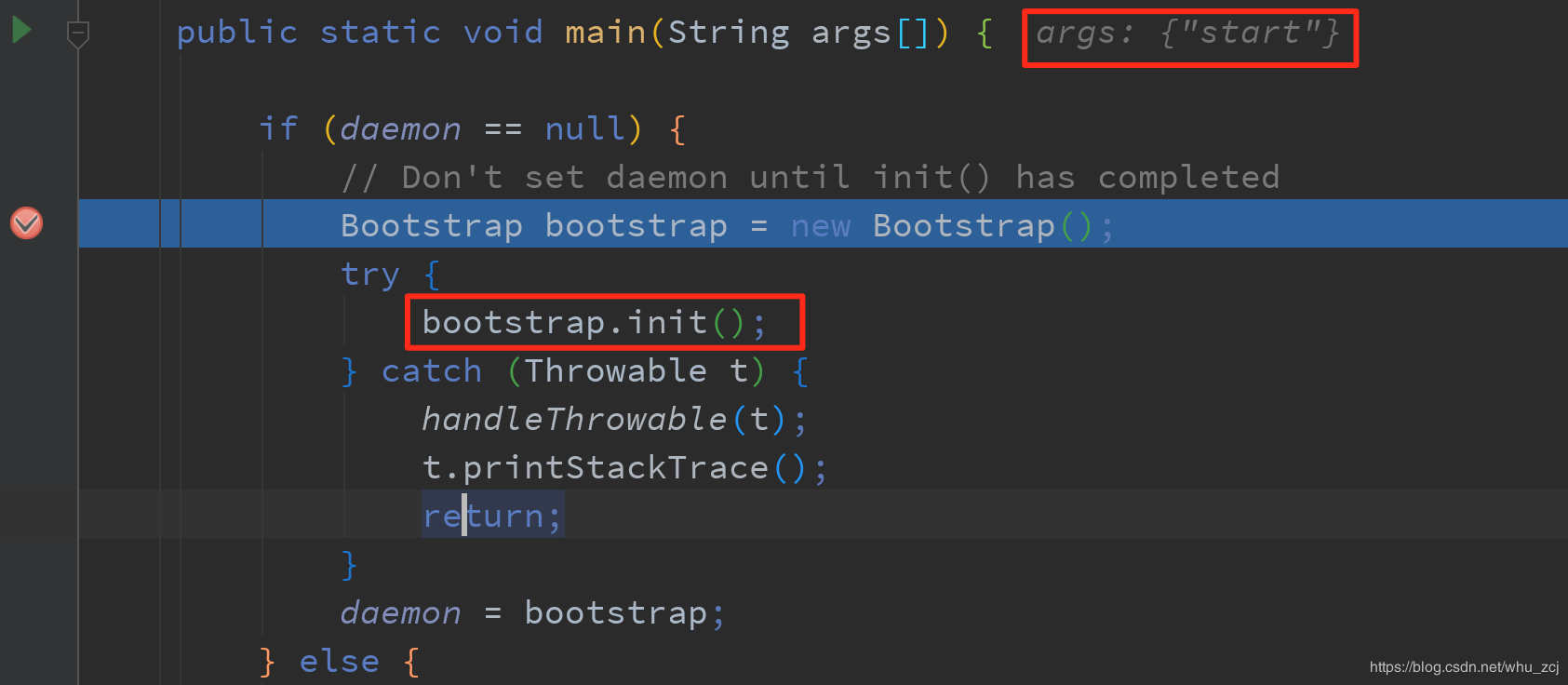
1.调用init方法
BootStrap的init方法会做以下的事情
(1)设置Catalina的一些目录信息。setCatalinaHome、setCatalinaBase
(2)初始化类加载器。initClassLoaders会初始化Tomcat的三个类加载器:CommonClassLoader、CatalinaClassLoader、SharedClassLoader
(3)用CatalinaClassLoader加载Catalina类,并通过反射得到Catalina的实例,再通过反射设置父加载器,最后将catalina实例赋值给Daemon
执行完初始化之后,会回到main执行后续的逻辑
1. public void init()2. throws Exception3. {4.5. // Set Catalina path6. setCatalinaHome();7. setCatalinaBase();8.9. initClassLoaders();10.11. Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);12.13. SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);14.15. // Load our startup class and call its process() method16. if (log.isDebugEnabled())17. log.debug("Loading startup class");18. Class<?> startupClass =19. catalinaLoader.loadClass20. ("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");21. Object startupInstance = startupClass.newInstance();22.23. // Set the shared extensions class loader24. if (log.isDebugEnabled())25. log.debug("Setting startup class properties");26. String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";27. Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];28. paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");29. Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];30. paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;31. Method method =32. startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);33. method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);34.35. catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;36.37. }
2.依据传入的args类型,分别执行不同的动作方法
前面截图中已经看到参数是“start”,因此会走到如下逻辑: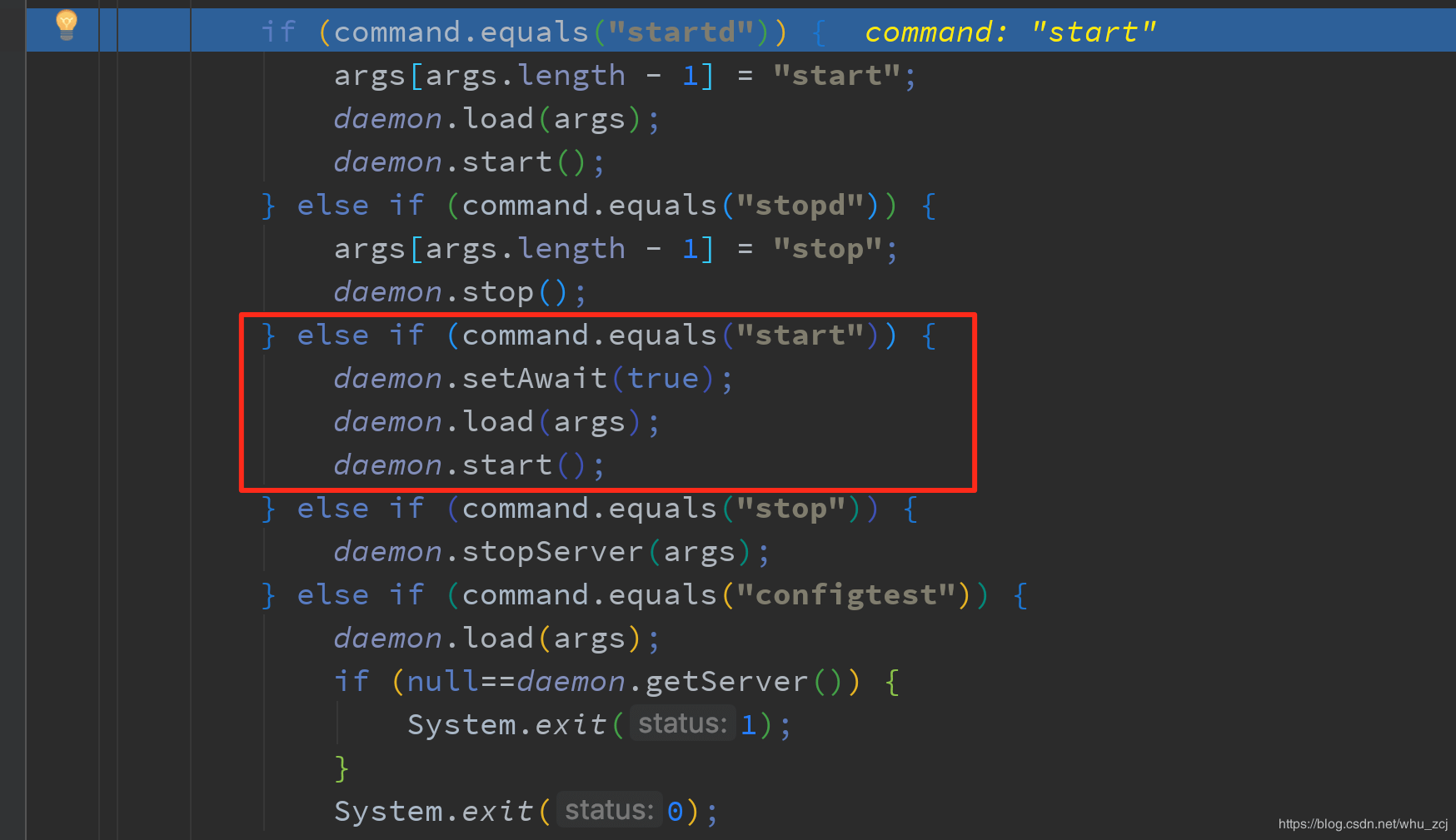 3.接下来看看load和start中做了些什么
3.接下来看看load和start中做了些什么
load方法中通过反射调用了daemon的load方法,也就是Catalina的load方法
start方法和load方法类似,这里不再赘述
总体看来,BootStrap做的工作也不多,初始化了几个类加载器,然后将所有的load、start等动作通过反射反映到Catalina上面
Catalina类
1.首先看下被Bootstrap调用的load方法
(1)创建一个Digester对象。createStartDigester方法里面点进去看看就是按照xml中配置的结构
(2)读取并解析配置文件。configFile默认就是server.xml,首先将当前对象Catalina设置为根对象
(3)解析完之后就得到了Server对象,并设置Server对象的Catalina参数未当前对象
(4)调用Server的init方法进行初始化。
Server对象是StandardServer的实例,它内部的initInternal方法会遍历该Server下的Service实例的init方法。
Service的initInternal方法又会初始化Container、Executor和Connectors。
Connector会调用各个ProtocolHandler的init方法。Protocol是处理各种协议处理的父接口,里面又会调用各个处理协议的Endpoint的init方法,并绑定端口
这样依次各个组件都得到了初始化
1. /**2. * Start a new server instance.3. */4. public void load() {5.6. long t1 = System.nanoTime();7.8. initDirs();9.10. // Before digester - it may be needed11.12. initNaming();13.14. // Create and execute our Digester15. Digester digester = createStartDigester();16.17. InputSource inputSource = null;18. InputStream inputStream = null;19. File file = null;20. try {21. file = configFile();22. inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);23. inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString());24. } catch (Exception e) {25. if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {26. log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail", file), e);27. }28. }29. if (inputStream == null) {30. try {31. inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()32. .getResourceAsStream(getConfigFile());33. inputSource = new InputSource34. (getClass().getClassLoader()35. .getResource(getConfigFile()).toString());36. } catch (Exception e) {37. if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {38. log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",39. getConfigFile()), e);40. }41. }42. }43.44. // This should be included in catalina.jar45. // Alternative: don't bother with xml, just create it manually.46. if( inputStream==null ) {47. try {48. inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()49. .getResourceAsStream("server-embed.xml");50. inputSource = new InputSource51. (getClass().getClassLoader()52. .getResource("server-embed.xml").toString());53. } catch (Exception e) {54. if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {55. log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",56. "server-embed.xml"), e);57. }58. }59. }60.61.62. if (inputStream == null || inputSource == null) {63. if (file == null) {64. log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",65. getConfigFile() + "] or [server-embed.xml]"));66. } else {67. log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",68. file.getAbsolutePath()));69. if (file.exists() && !file.canRead()) {70. log.warn("Permissions incorrect, read permission is not allowed on the file.");71. }72. }73. return;74. }75.76. try {77. inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream);78. digester.push(this);79. digester.parse(inputSource);80. } catch (SAXParseException spe) {81. log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " +82. spe.getMessage());83. return;84. } catch (Exception e) {85. log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " , e);86. return;87. } finally {88. try {89. inputStream.close();90. } catch (IOException e) {91. // Ignore92. }93. }94.95. getServer().setCatalina(this);96.97. // Stream redirection98. initStreams();99.100. // Start the new server101. try {102. getServer().init();103. } catch (LifecycleException e) {104. if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE")) {105. throw new java.lang.Error(e);106. } else {107. log.error("Catalina.start", e);108. }109.110. }111.112. long t2 = System.nanoTime();113. if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {114. log.info("Initialization processed in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");115. }116.117. }
StandardServer中的initInternal方法: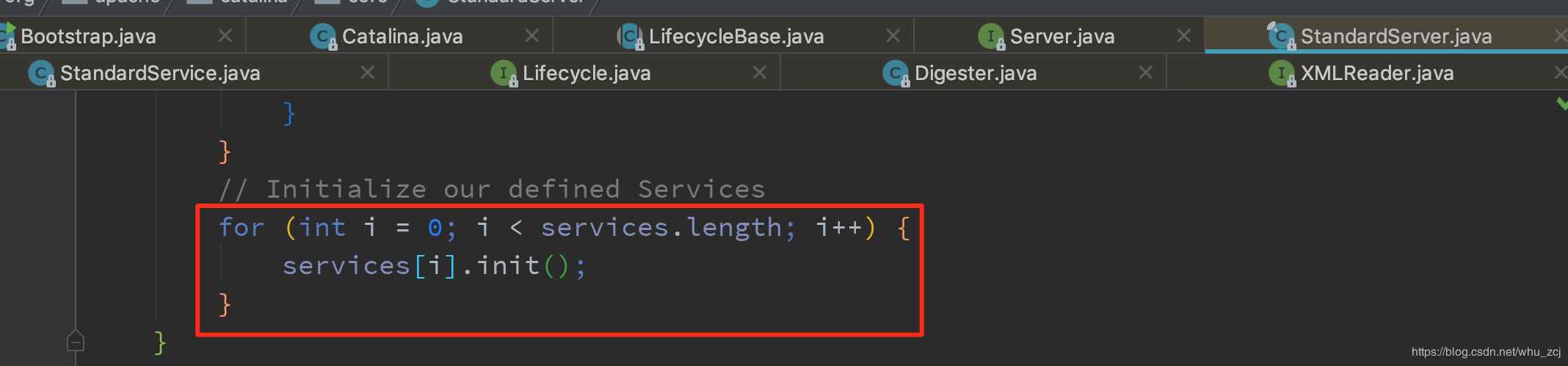
StandardService中的initInternal方法: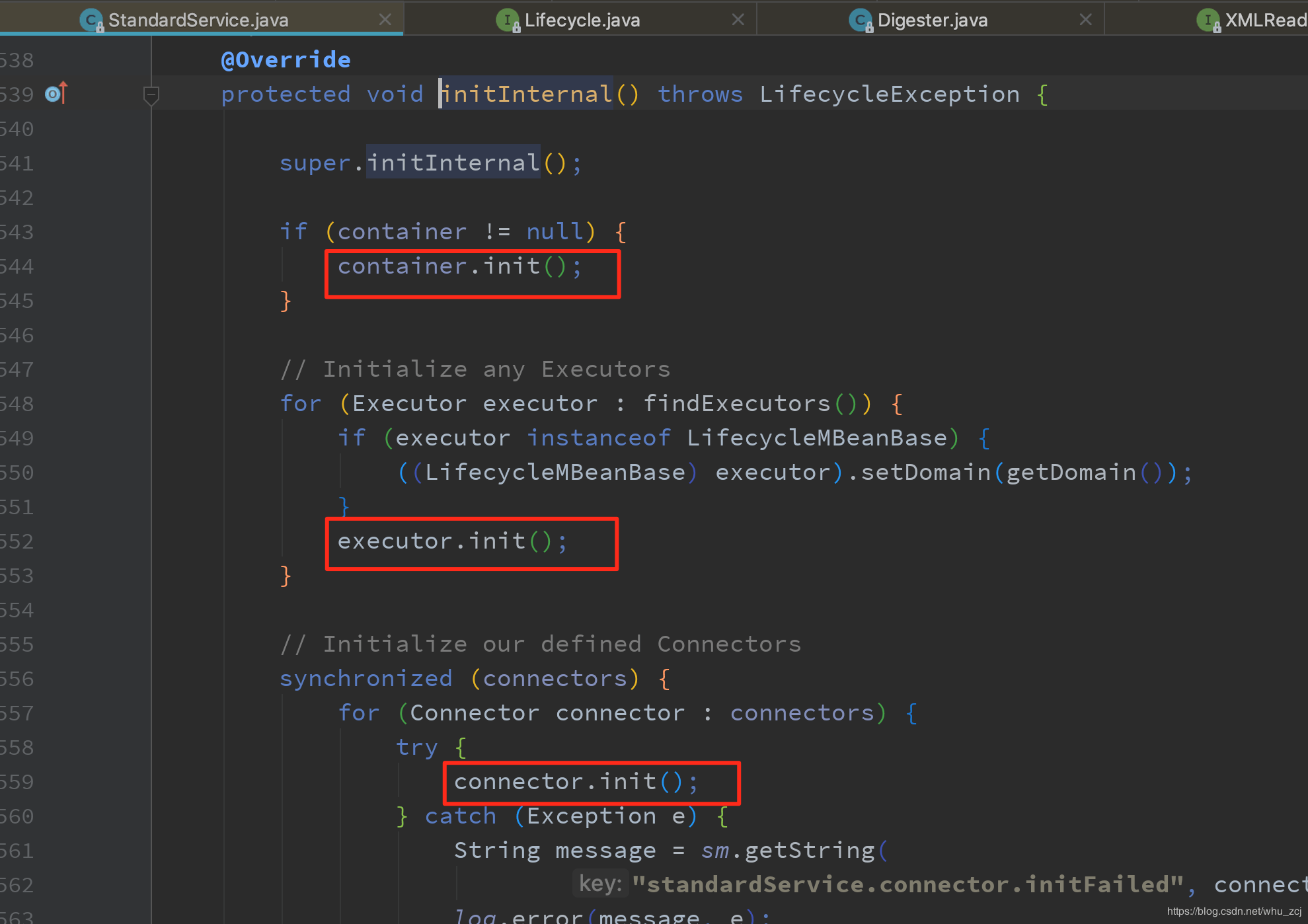
Connector中的init方法,这里protocolHandler取决于xml中的配置,如处理bio的Http11Protocol
Protocolhandler的init实现是在AbstractProtocol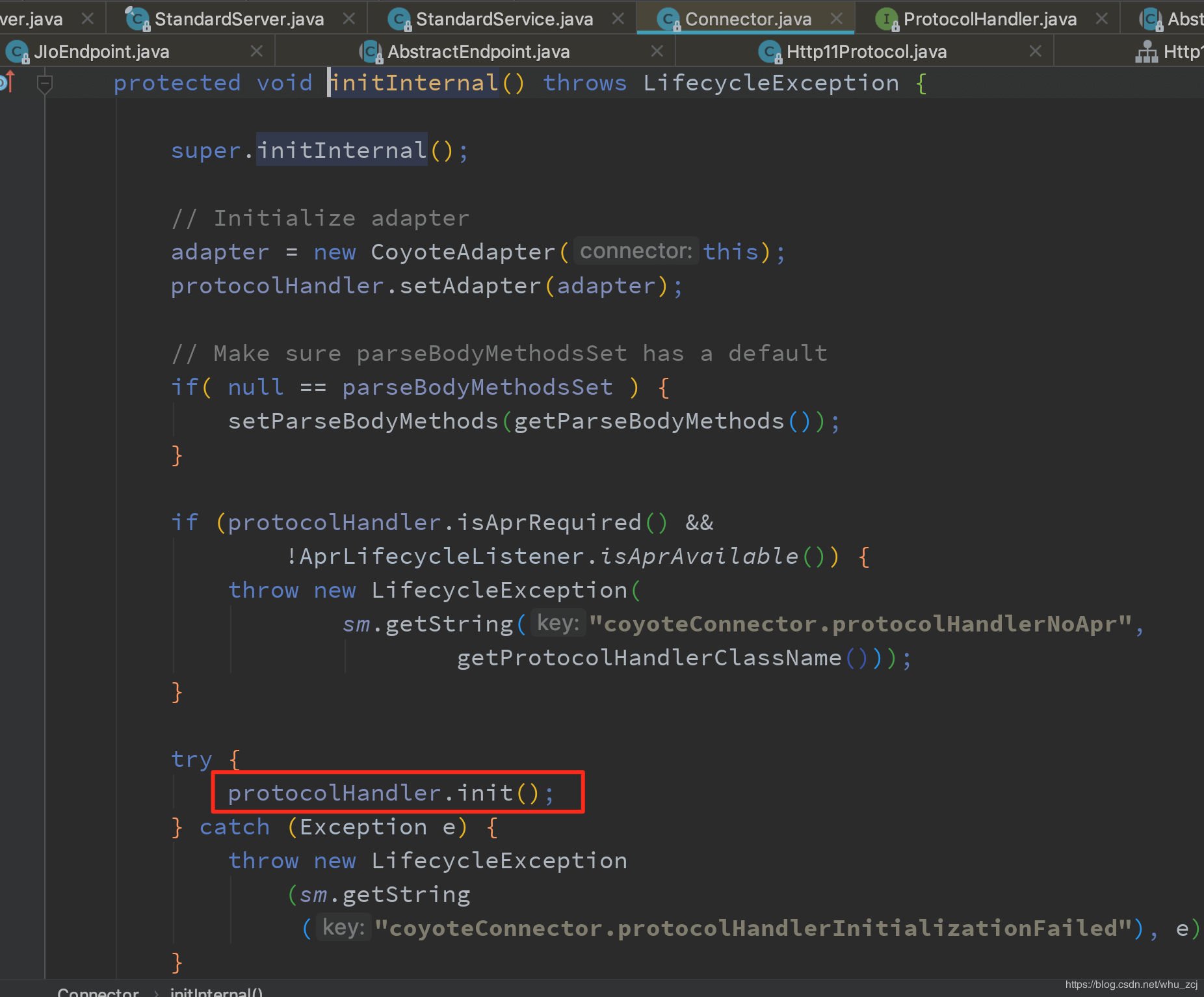
AbstractProtocol中的init实现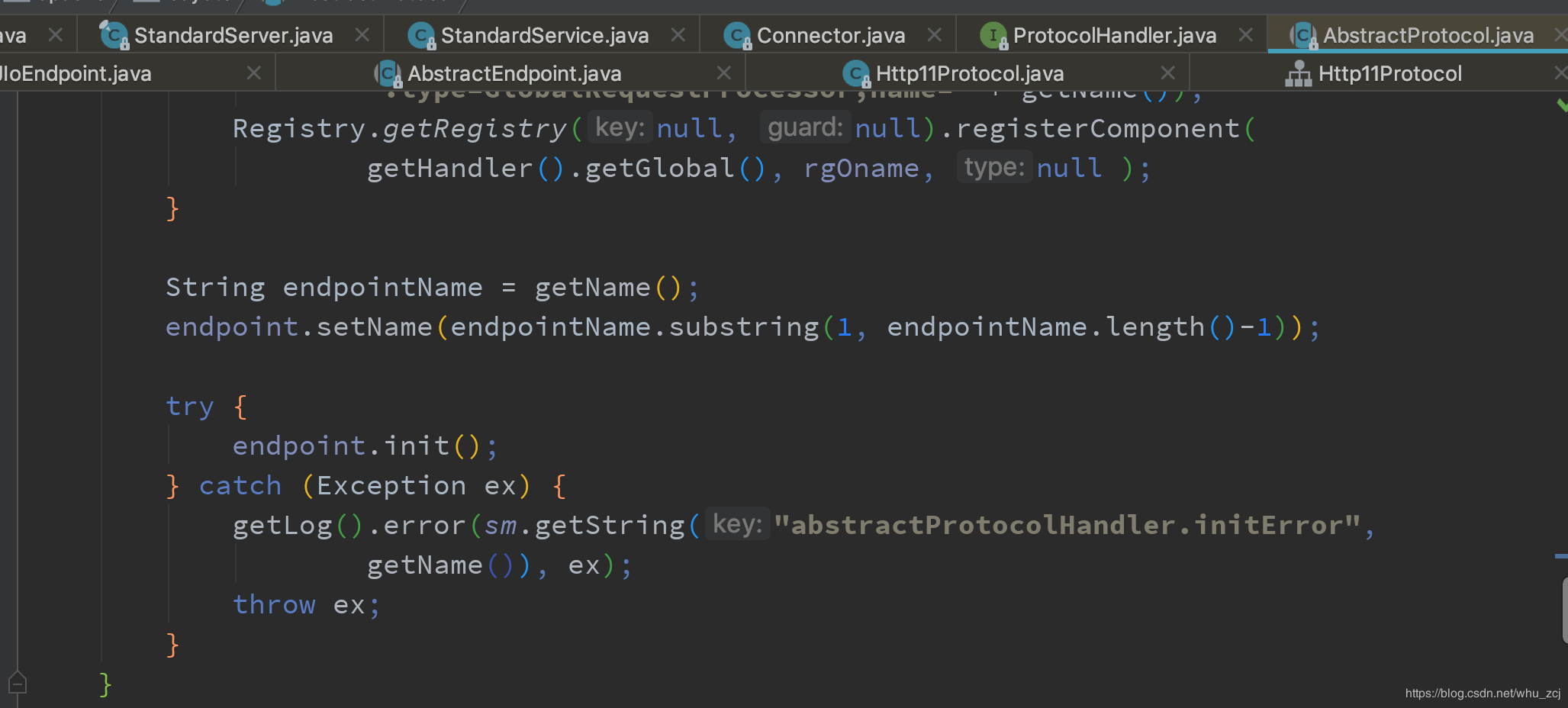
AbstractEndPoint中的init方法,调用bind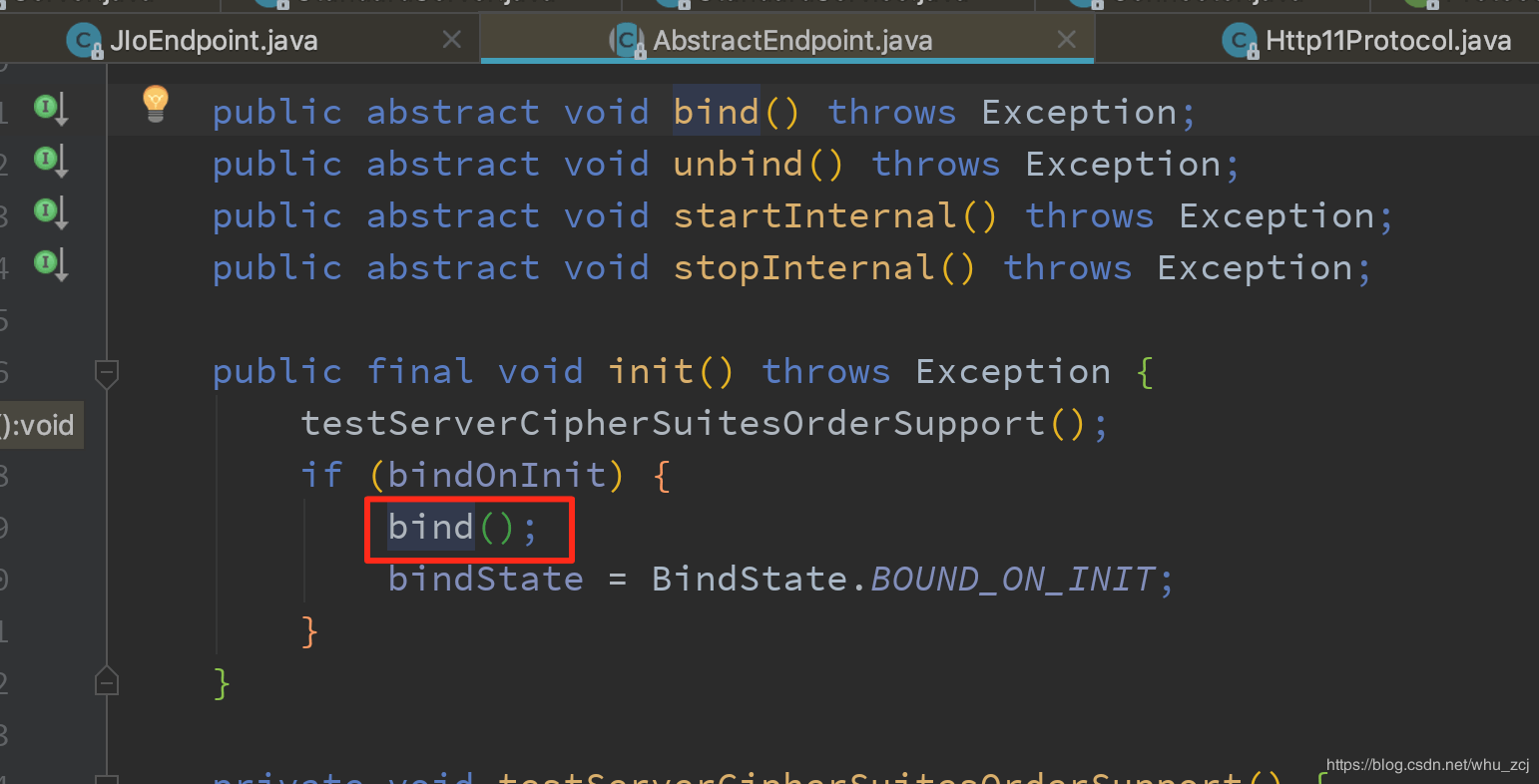
2.start方法和load中的init方法类似,不再赘述
对于Connector,各个EndPoint实现中会启动acceptor线程,每个Acceptor就会监听Sorket的连接

