1. 事务基本概念:
1. 原子性:一个事务的所有操作,要么全部执行,要么全部不执行。2. 一致性:执行事务时保持数据库从一个一致的状态变更到另一个一致的状态。3. 隔离性:即使每个事务都能确保一致性和原子性,如果并发执行时,由于它们的操作以人们不希望的方式交叉运行,就会导致不一致的情况发生。确保事务与事务并发执行时,每个事务都感觉不到有其它事务在并发的执行。
2. 四种隔离级别:
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 | 序列化异常 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| read uncommitted | 不可能 | 可能 | 可能 | 可能 |
| read committed | 不可能 | 可能 | 可能 | 可能 |
| repeatable read | 不可能 | 不可能 | 不可能 | 可能 |
| serializable | 不可能 | 不可能 | 不可能 | 不可能 |
2.1 查看和设置数据库的事务隔离级别:
# 查看全局事务隔离级别:select name,setting from pg_settings where name='default_transaction_isolation';# 修改全局事务隔离级别:方法一:修改postgresql.conf配置文件中的default_transaction_isolation。方法二:alter system set default_transaction_isolation to 'repeatable read';pg_ctl reload# 查看当前会话的事务隔离级别:show transaction_isolation;# 设置当前会话的事务隔离级别:set session characteristics as transaction isolation level read uncommitted;# 设置当前事务的隔离级别:begin isolation level read uncommitted read write;commit;
3. 并发问题模拟
3.1 脏读问题: 🤷♂️
PG中不存在未提交读隔离级别,显示使用未提交读隔离级别时,PG内部会使用为提交读隔离级别处理,脏读在PG中不会发生。
# 脏读演示:(PG数据无法演示脏读,请用其它数据库)create table tb1_mvcc (id serial not null primary key,ival int);insert into tb1_mvcc (ival) values (1);会话一:set session transaction isolation level read uncommitted;begin;会话二:set session transaction isolation level read uncommitted;begin;update tb1_mvcc set ival=10 where id=1;会话一:select * from tb1_mvcc where id=1;会话二:rollback;
3.2 不可重复读问题:
# 不可重复读:会话一:begin transaction isolation level read committed;会话二:begin;update tb1_mvcc set ival=10 where id=1;commit;会话一:select * from tb1_mvcc where id=1;end;
3.3 幻读问题:
# 幻读create table tb1_mvcc (id serial not null primary key,ival int);insert into tb1_mvcc (ival) select generate_series(1,5);会话一:begin transaction isolation level read committed;select id,ival from tb1_mvcc where id>3 and id<10;会话二:begin;insert into tb1_mvcc (ival) values (6);commit;会话一:select id,ival from tb1_mvcc where id>3 and id<10;end;
3.4 序列化一场问题:
# 序列化异常:create table tb1_mvcc (id serial not null primary key,ival int);insert into tb1_mvcc (ival) values (1);会话一:begin transaction isolation level repeatable read;select * from tb1_mvcc where id=1;会话二:update tb1_mvcc set ival=10 where id=1;会话一:update tb1_mvcc set ival= ival+1 where id=1;rollback;# 不可能出现幻读:create table tb1_mvcc (id serial not null primary key,ival int);insert into tb1_mvcc (ival) select generate_series(1,5);会话一:begin transaction isolation level repeatable read;select id,ival from tb1_mvcc where id>3 and id<10;会话二:begin;insert into tb1_mvcc (ival) values (6);commit;会话一:select id,ival from tb1_mvcc where id>3 and id<10;end;
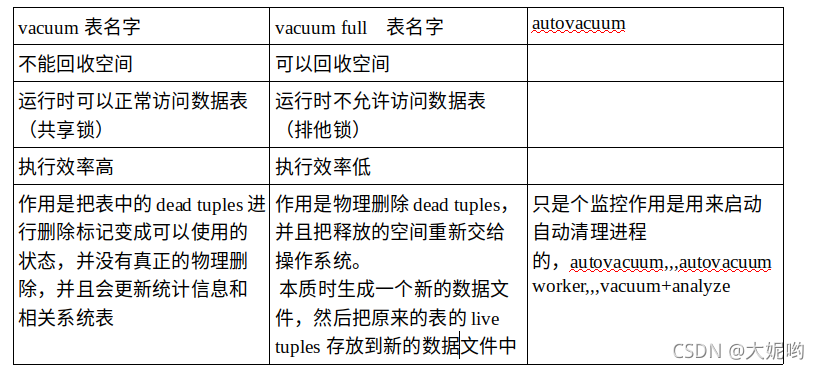
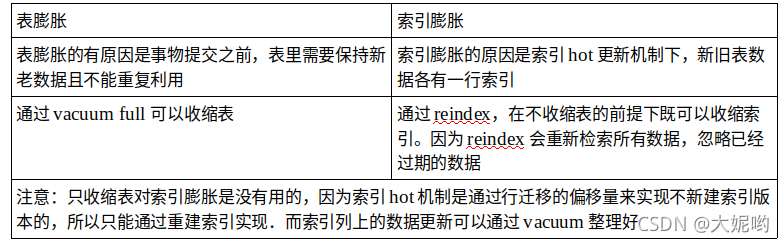
4. 使用pg_repack解决表膨胀:
# 安装pg_repack工具:## yum安装:(yum安装的repack只能针对yum安装的pg)yum install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpmyum install pg_repack13 -yvi /etc/profileexport PATH=/usr/pgsql-13/bin:$PATH## 源码安装:yum install gcc postgresql-devel postgresql-static zlib-devel readline-devel -yunzip pg_repack-master.zipcd pg_repack-mastermake && make installpg_repack --version# 创建pg_repack扩展:create extension pg_repack;# 进行对表进行重建:pg_repack -t t1 -j 2 -D -k -U postgres -d postgres
1. 表膨胀的直接触发因素是表上的大量更新,如全表的update操作、大量的insert+delete操作等2. 一个update操作执行后,被更改的数据的旧版本也被保留下来,直到对表做vacuum操作的时候,才考虑回收旧版本。3. 旧版本不及时回收就会造成表膨胀
特点:
1. 更新过数据的事务,长时间不提交会造成表膨胀,只读的事务也是同样的,也要及时提交,同时避免在存在大量更新操作的实例上,跑运行时间很长的查询语句。
避免表膨胀的方法:
1. 尽早的、及时的提交事务;2. 设计应用时,要使事务尽量短小;3. 注意配置与应用规模相适应的硬件资源(IO能力、CPU、内存等),并调教好数据库,使其性能最优,避免有些事务因为资源或性能问题长时间无法完成;4. 提交autovacuum,使其能按合理的周期运行。这方面的内容,我们今后专门介绍;5. 定期监控系统中是否有长事务,可以使用下面的SQL监控持续时间超过一定时间的事务