什么是AQS
AQS是AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的简称,即抽象队列同步器,从字面意思上理解:
- 抽象:抽象类,只实现一些主要逻辑,有些方法由子类实现;
- 队列:使用先进先出(FIFO)队列存储数据;
- 同步:实现了同步的功能。
用于自定义锁和同步,JUC包下的工具大多基于AQS设计
AQS的数据结构

类结构如下
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer{int stat;head Node;tail Node;Node class{Thread = thread}}
AQS解析
AQS的设计是基于模板方法模式
而资源有两种共享模式,或者说两种同步方式:
- 独占模式(Exclusive):资源是独占的,一次只能一个线程获取。如ReentrantLock。
- 共享模式(Share):同时可以被多个线程获取,具体的资源个数可以通过参数指定。如Semaphore/CountDownLatch。
AQS常用方法
- isHeldExclusively():判断该线程是否正则独占资源;
- tryAcquire():独占方式尝试获取资源;
- tryRelease():独占方式尝试释放资源;
- tryAcquireShared():共享方式尝试获取资源;
- tryReleaseShared():共享方式尝试释放资源;
获取资源
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
tryAcquire方法由子类实现,尝试失败后调用addWaiter方法
CLH队列通过CAS添加当前的Node线程,这是因为AQS本身会存在多个线程争夺资源,避免同时插入节点的问题
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 生成该线程对应的Node节点
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// 将Node插入队列中
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
// 使用CAS尝试,如果成功就返回
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 如果等待队列为空或者上述CAS失败,再自旋CAS插入
enq(node);
return node;
}
// 自旋CAS插入等待队列
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
CLH队列的每个结点会执行acquireQueued方法,判断自己是否为head的第二个节点,否则调用park()是使自己阻塞,直到被unpark()
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
// 自旋
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 如果node的前驱结点p是head,表示node是第二个结点,就可以尝试去获取资源了
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 拿到资源后,将head指向该结点。
// 所以head所指的结点,就是当前获取到资源的那个结点或null。
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 如果自己可以休息了,就进入waiting状态,直到被unpark()
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
获取资源流程图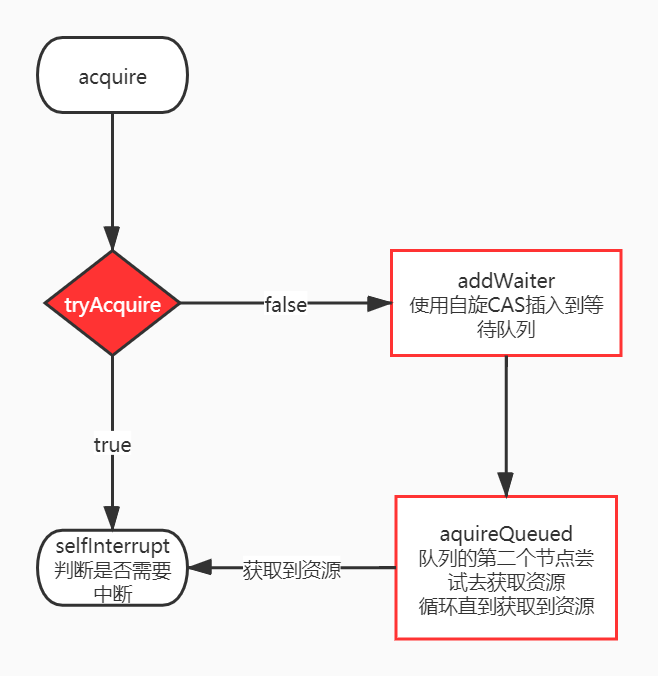
释放资源
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
// 如果状态是负数,尝试把它设置为0
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
// 得到头结点的后继结点head.next
Node s = node.next;
// 如果这个后继结点为空或者状态大于0
// 通过前面的定义我们知道,大于0只有一种可能,就是这个结点已被取消
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
// 等待队列中所有还有用的结点,都向前移动
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
// 如果后继结点不为空,
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}

