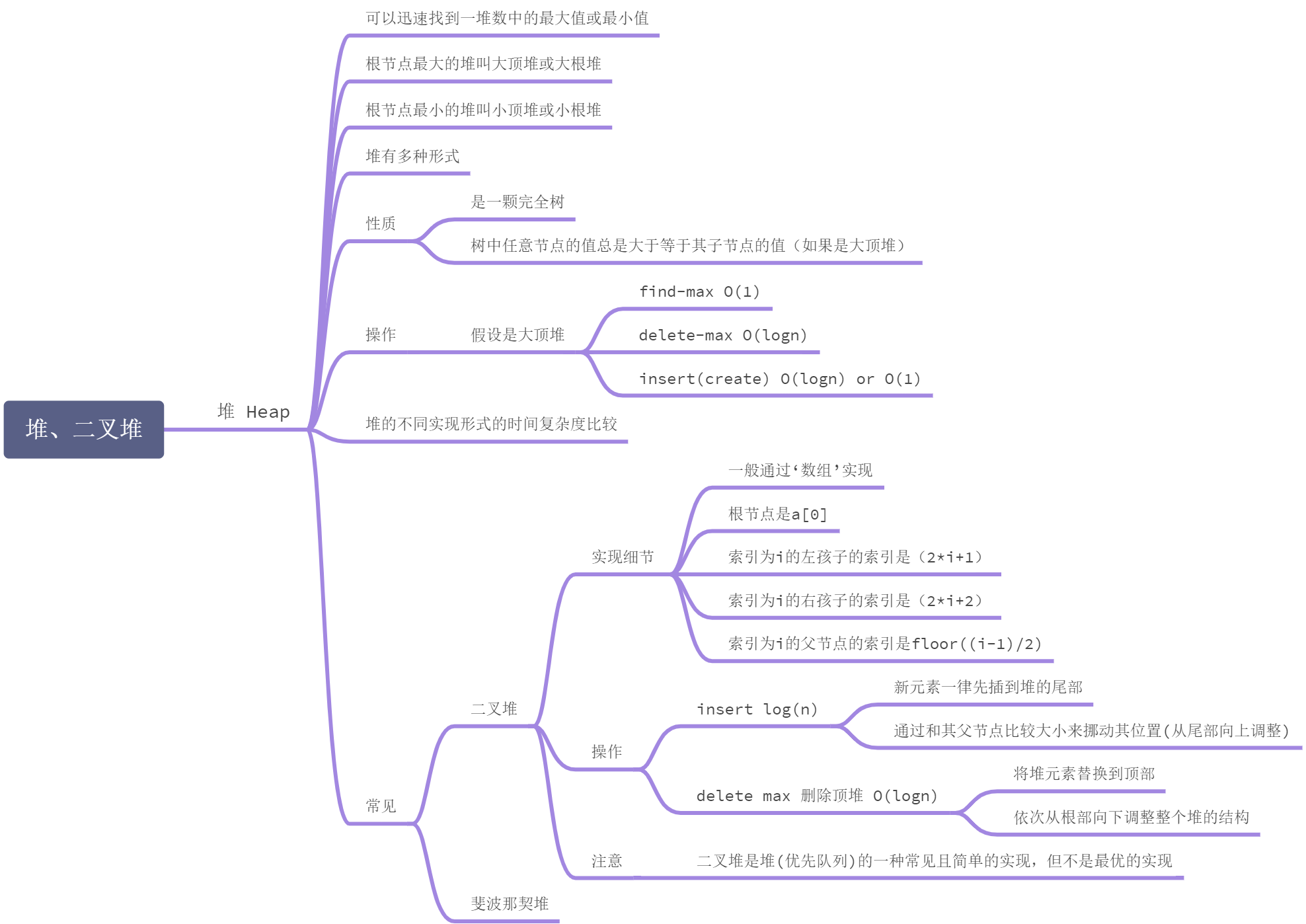
二叉堆
实现
二叉堆通过数组实现,假设第一个元素在数组中的索引为零的话:
- 索引为
i的左孩子的索引是(2*i+1) - 索引为
i的右孩子的索引是(2*i+2) - 索引为
i的父节点的索引是floor((i-1)/2)
将从根节点开始依次从左到右放入每一个节点的值:
可以看到满足堆的性质,是一颗完全树(除叶子节点外其他节点都是满的),而且根节点一定大于儿子节点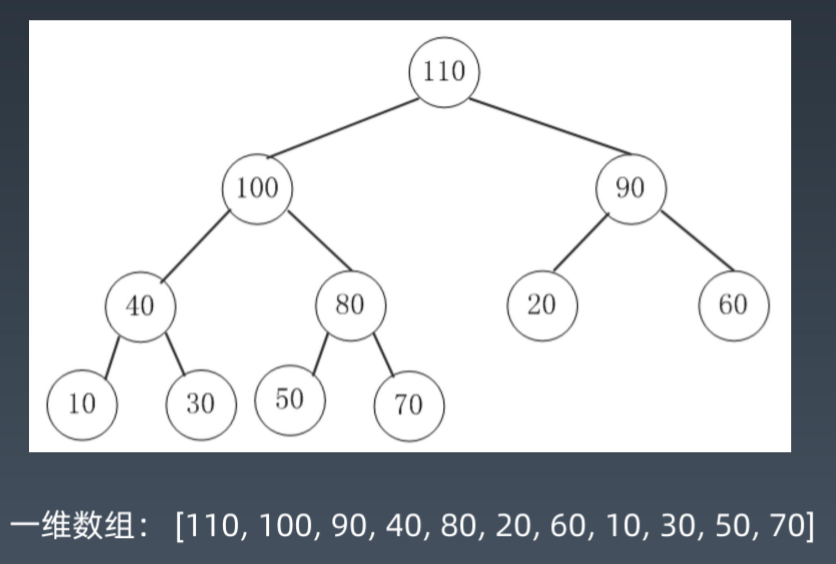
实现代码
// Javaimport java.util.Arrays;import java.util.NoSuchElementException;public class BinaryHeap {//这个d表示二叉树,如果想要三叉树、多叉树可以改变d的值private static final int d = 2;private int[] heap;private int heapSize;/*** This will initialize our heap with default size.*/public BinaryHeap(int capacity) {heapSize = 0;heap = new int[capacity + 1];Arrays.fill(heap, -1);}public boolean isEmpty() {return heapSize == 0;}public boolean isFull() {return heapSize == heap.length;}private int parent(int i) {return (i - 1) / d;}/*** 计算左右孩子的位置* i是父亲节点的位置* k=1就是左儿子,k=2就是右儿子*/private int kthChild(int i, int k) {return d * i + k;}/*** Inserts new element in to heap* Complexity: O(log N)* As worst case scenario, we need to traverse till the root*/public void insert(int x) {if (isFull()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is full, No space to insert new element");}heap[heapSize] = x;heapSize ++;heapifyUp(heapSize - 1);}/*** Deletes element at index x* Complexity: O(log N)*/public int delete(int x) {if (isEmpty()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is empty, No element to delete");}int maxElement = heap[x];heap[x] = heap[heapSize - 1];heapSize--;heapifyDown(x);return maxElement;}/*** Maintains the heap property while inserting an element.*/private void heapifyUp(int i) {int insertValue = heap[i];while (i > 0 && insertValue > heap[parent(i)]) {heap[i] = heap[parent(i)];i = parent(i);}heap[i] = insertValue;}/*** Maintains the heap property while deleting an element.*/private void heapifyDown(int i) {int child;int temp = heap[i];while (kthChild(i, 1) < heapSize) {child = maxChild(i);if (temp >= heap[child]) {break;}heap[i] = heap[child];i = child;}heap[i] = temp;}private int maxChild(int i) {int leftChild = kthChild(i, 1);int rightChild = kthChild(i, 2);return heap[leftChild] > heap[rightChild] ? leftChild : rightChild;}/*** Prints all elements of the heap*/public void printHeap() {System.out.print("nHeap = ");for (int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++)System.out.print(heap[i] + " ");System.out.println();}/*** This method returns the max element of the heap.* complexity: O(1)*/public int findMax() {if (isEmpty())throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is empty.");return heap[0];}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryHeap maxHeap = new BinaryHeap(10);maxHeap.insert(10);maxHeap.insert(4);maxHeap.insert(9);maxHeap.insert(1);maxHeap.insert(7);maxHeap.insert(5);maxHeap.insert(3);maxHeap.printHeap();maxHeap.delete(5);maxHeap.printHeap();maxHeap.delete(2);maxHeap.printHeap();}}
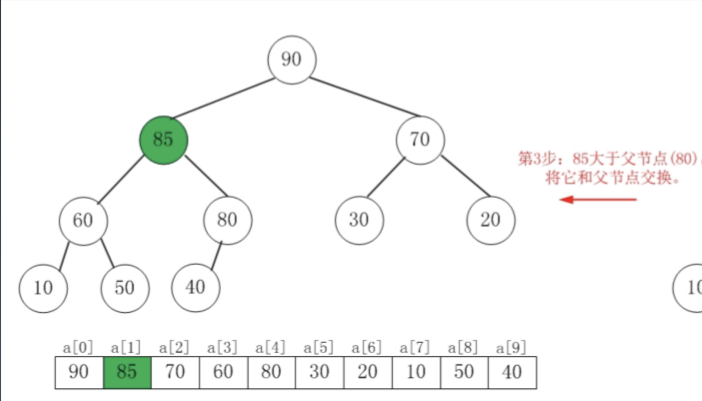
Insert 的实现细节
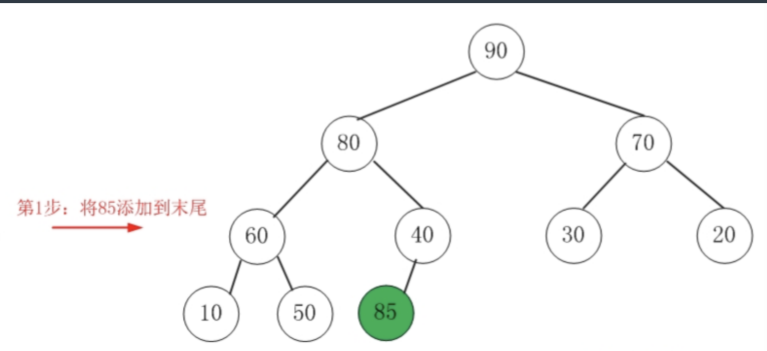
- 新元素一律先插到堆的尾部
- 依次向上调整整个堆的结构(一直到根即可)
如果要把85插到二叉堆中: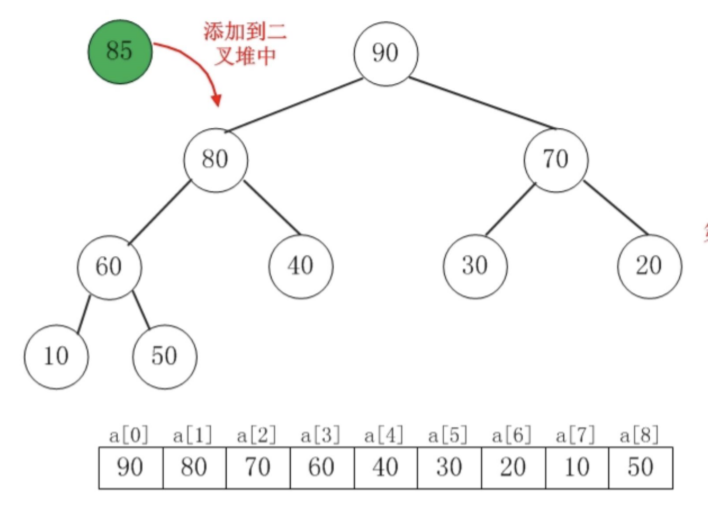
核心代码
public void insert(int x) {if (isFull()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is full, No space to insert new element");}heap[heapSize] = x;heapSize ++;heapifyUp(heapSize - 1);}/*** Maintains the heap property while inserting an element.*/private void heapifyUp(int i) {int insertValue = heap[i];while (i > 0 && insertValue > heap[parent(i)]) {heap[i] = heap[parent(i)];i = parent(i);}heap[i] = insertValue;}
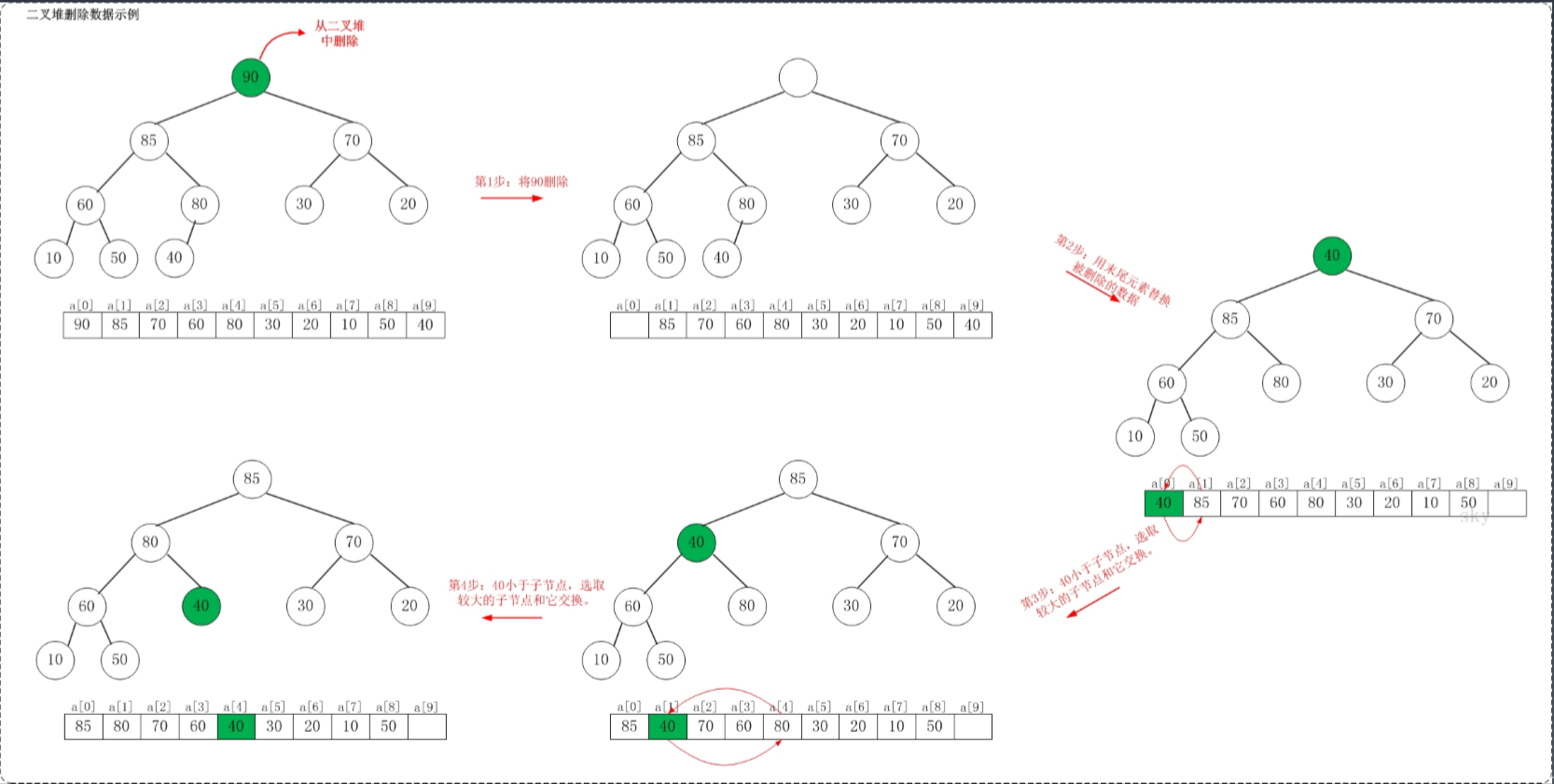
Delete Max 的实现细节
- 将堆尾元素替换到顶部
- 依次从根部向下调整整个堆的结构(一直到堆尾即可)
核心代码
/*** Deletes element at index x* Complexity: O(log N)*/public int delete(int x) {if (isEmpty()) {throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is empty, No element to delete");}int maxElement = heap[x];heap[x] = heap[heapSize - 1];heapSize--;heapifyDown(x);return maxElement;}/*** Maintains the heap property while deleting an element.*/private void heapifyDown(int i) {int child;int temp = heap[i];while (kthChild(i, 1) < heapSize) {child = maxChild(i);if (temp >= heap[child]) {break;}heap[i] = heap[child];i = child;}heap[i] = temp;}