1、模板文件的自动更新
from flask import Flaskapp = Flask(__name__)app.config["TEMPLATES_AUTO_RELOAD"] = True # 实现模板文件修改后,python文件中能够自动更新# app.config.updata("TEMPLATES_AUTO_RELOAD"=True)
2、模板过滤器
定义:过滤器是通过管道符号shift+\(|)进行使用的,例如:{{ name(参数) | length(函数) }},将返回name的长度。过滤器相当于是一个函数,把当前的变量传入到过滤器中,然后过滤器根据自己的功能,再返回相应的值,之后再将结果渲染到页面中。Jinja2中内置了许多过滤器:(过滤器只能在模板中使用,而不能在python文件中使用)
• abs(value):返回一个数值的绝对值。
• default(value,default_value,boolean=false):如果当前变量没有值,则会使用参数中的值来代替。name|default(‘juran’)——如果name不存在,则会使用juran来替代。boolean=False默认是在只有这个变量为undefined的时候才会使用default中的值,如果想使用python的形式判断是否为false,则可以传递boolean=true。也可以使用or来替换。
• escape(value)或e:转义字符,会将<、>等符号转义成HTML中的符号。例如:content|escape或content|e。
• first(value):返回一个序列的第一个元素。names|first。
• format(value,*arags,kwargs):格式化字符串。例如以下代码:
{{ “%s” - “%s”|format(‘Hello?’,”Foo!”) }}将输出:Helloo? - Foo!
注意是横线(-)进行连接**
• last(value):返回一个序列的最后一个元素。示例:names|last。
• length(value):返回一个序列或者字典的长度。示例:names|length。
• join(value,d=u’’):将一个序列用d这个参数的值拼接成字符串。
• safe(value):如果开启了全局转义,那么safe过滤器会将变量关掉转义。示例:content_html|safe。
• int(value):将值转换为int类型。
• float(value):将值转换为float类型。
• lower(value):将字符串转换为小写。
• upper(value):将字符串转换为小写。
• replace(value,old,new): 替换将old替换为new的字符串。
• truncate(value,length=255,killwords=False):截取length长度的字符串。
• striptags(value):删除字符串中所有的HTML标签,如果出现多个空格,将替换成一个空格。
• trim:截取字符串前面和后面的空白字符。
• string(value):将变量转换成字符串。
• wordcount(s):计算一个长字符串中单词的个数。
1、示例:default过滤器
代码部分:(tel参数没有被定义)
from flask import Flask, render_templateapp = Flask(__name__)@app.route("/")def home():return "首页"# 改字典中不添加tel参数dic = {"name":"流浪者、j","home":"兰溪","age":18}@app.route("/index/")def index():return render_template("index.html", **dic)if __name__ == "__main__":# app.config.from_pyfile('settings.py',silent=True)app.run(debug=True)
模板部分:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><input type="text" class="query" id="upquery" name="query" maxlength="100" len="80" onfocus="focusInput(this)" ov="汇拼" value="汇拼" autocomplete="off"><h1>{{ name }}</h1><h1>{{ home }}</h1><h2>{{ age }}</h2><!-- 传入并不存在的参数tel --><h2>{{ tel|default('这个人的性别是一个秘密') }}</h2></body></html>
网页显示:(显示在default函数中添加的部分)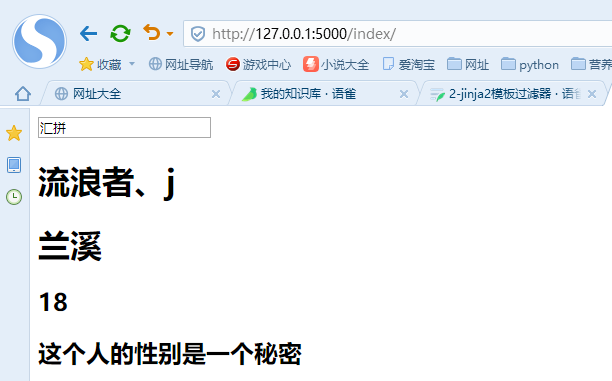
代码部分:如果在代码部分存在参数那么就显示该参数对应的值,无论该参数对应的是什么(空、None)都会在网页中体现**
from flask import Flask, render_templateapp = Flask(__name__)@app.route("/")def home():return "首页"dic = {"name":"流浪者、j","home":"兰溪","age":18"tel":None}@app.route("/index/")def index():return render_template("index.html", **dic)if __name__ == "__main__":# app.config.from_pyfile('settings.py',silent=True)app.run(debug=True)
模板部分不变
网页显示:(显示自己定义的参数值)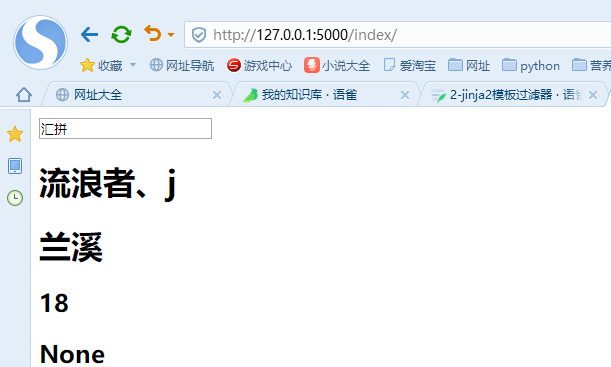
2、模板转义机制的说明与解决
代码部分:定义一个代码**
from flask import Flask, render_templateapp = Flask(__name__)@app.route("/")def home():return "首页"dic = {"es":"<script>alert('hello');</script>"}@app.route("/index/")def index():return render_template("index.html", **dic)if __name__ == "__main__":# app.config.from_pyfile('settings.py',silent=True)app.run(debug=True)
模板部分:(为了防止外来代码注入带来的影响,所以会自动将其转义)
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><input type="text" class="query" id="upquery" name="query" maxlength="100" len="80" onfocus="focusInput(this)" ov="汇拼" value="汇拼" autocomplete="off"><!-- 自动转义 --><h1>{{ es }}</h1></body></html>
网页显示: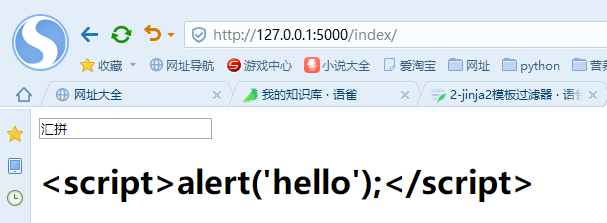
解决方案:
第一种方式:局部不转义{% autoescape off %} {% endautoescape %} 适用于代码块
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><input type="text" class="query" id="upquery" name="query" maxlength="100" len="80" onfocus="focusInput(this)" ov="汇拼" value="汇拼" autocomplete="off"><!-- 自动转义 -->{% autoescape off %}<h1>{{ es }}</h1>{% endautoescape %}</body></html>
第二种方式:safe过滤器定义安全,适用于少量,离散代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><input type="text" class="query" id="upquery" name="query" maxlength="100" len="80" onfocus="focusInput(this)" ov="汇拼" value="汇拼" autocomplete="off"><!-- 自动转义 --><!-- 标记它是安全的 --><h1>{{ es|safe }}</h1></body></html>
网页显示,代码生效: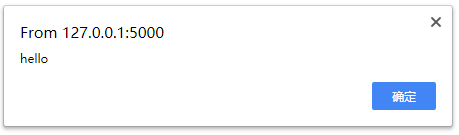
3、 truncate过滤器( truncate(value,length=255,killwords=False):截取length长度的字符串)
代码部分:
from flask import Flask, render_templateapp = Flask(__name__)app.config["TEMPLATES_AUTO_RELOAD"] = True@app.route("/")def home():return "首页"dic = {"bookname":"早安世界,如果天上有一抹色彩" # 在这里}@app.route("/index/")def index():return render_template("index.html", **dic)if __name__ == "__main__":# app.config.from_pyfile('settings.py',silent=True)app.run(debug=True)
模板部分:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><h1>{{ bookname|truncate(length=4) }}</h1></body></html>
网页返回:由于存在小小的问题所以我选择了自定义过滤器@app.template_filter(“模板调用时使用的过滤器名称”)详细见3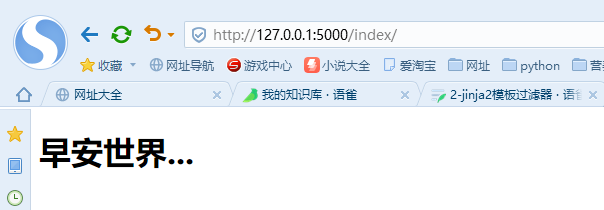
3、自定义过滤器(@app.template_filter(“模板调用时使用的过滤器名称”))
第一个小例子:完成对输入内容进行部分省略
from flask import Flask, render_templateapp = Flask(__name__)app.config["TEMPLATES_AUTO_RELOAD"] = True@app.route("/")def home():return "首页"dic = {"bookname":"早安世界,如果天上有一抹色彩"}@app.route("/index/")def index():return render_template("index.html", **dic)@app.template_filter("truncate") # 代码在这里# 传入需要显示的字符串长度def truncate(value,length):# 如果输入的length大于字符的长度则输出全字符加...if len(value)<length:return value + "..."# 如果输入在正常范围elif 0<length and length<len(value):return value[:length] + "..."if __name__ == "__main__":# app.config.from_pyfile('settings.py',silent=True)app.run(debug=True)
然后在模板中进行调用就可以了
第二个小例子:完成不同时间的显示
代码部分:**
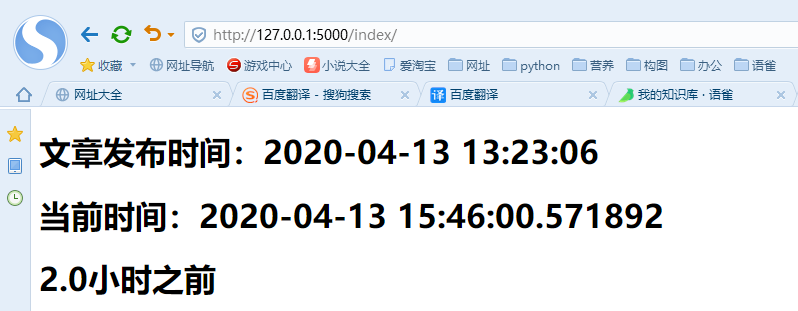
from datetime import datetimefrom flask import Flask, render_templateapp = Flask(__name__)app.config["TEMPLATES_AUTO_RELOAD"] = Truedic = {"bookname": "早安世界,如果天上有一抹色彩","time": datetime(2020, 4, 13, 13, 23, 6),"nowtime": datetime.now()}@app.route("/")def home():return "首页"@app.route("/index/")def index():return render_template("index.html", **dic)@app.template_filter("handle_time")def handle_time(time):if isinstance(time, datetime):now = datetime.now()# 转化为间隔为几秒timestamp = (now - time).total_seconds()if timestamp < 60:return "刚刚"elif 60 <= timestamp and timestamp < 60*60:return f"{timestamp//60}分钟之前"elif 60*60 <= timestamp and timestamp < 60*60*24:return f"{timestamp//(60*60)}小时之前"elif 60*60*24 <= timestamp:return f"{timestamp//(60*60*24)}天之前"else:return timeif __name__ == "__main__":# app.config.from_pyfile('settings.py',silent=True)app.run(debug=True)
模板部分:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><h1>文章发布时间:{{ time }}</h1><h1>当前时间:{{ nowtime }}</h1><!-- 调用handle_time过滤器 --><h1>{{ time|handle_time }}</h1></body></html>
4、过滤器的连用
在符合业务逻辑的前提下可以使用过滤器的连用
<h1>{{ es|safe|length }}</h1>