性质:
- 左子树<根节点
- 右子树>根节点
用途:解决与排名有关的检索需求
结构操作
- 插入
- 例 : 插入10
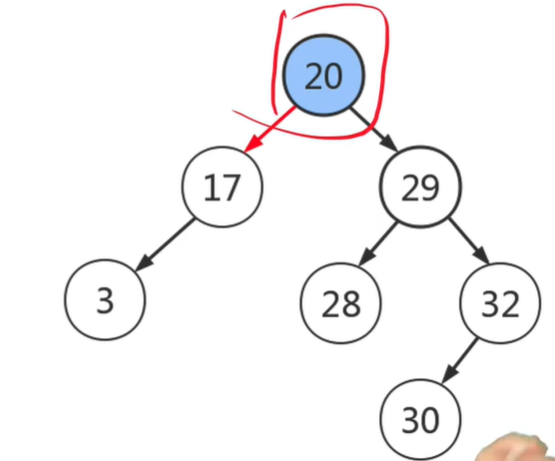
由性质,10插入到左子树,10 < 17, 10应该是17的左孩子,10 > 3, 10作为3的右孩子
- 删除
- 删除叶子节点 直接删除
- 删除度为1的节点 删除后,其唯一孩子替换其原来的位置
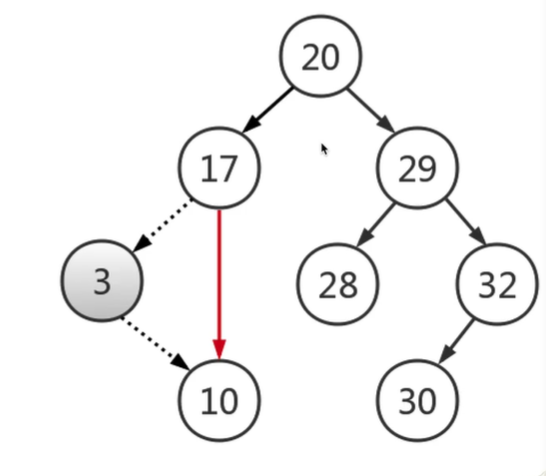
- 删除度为2的节点
找到前驱或后继,替换后转换为度为1或叶子节点问题 

- 课后练习:Leetcode 110 Leetcode 669
小结
性质
- 左子树 < 根节点
- 右子树 > 根节点
- 中序遍历的结果,是一个有序序列,所以称为二叉排序树
数据结构,就是定义一种性质,并维护这种性质的结构
插入操作
- 插入的新节点一定会作为叶子节点存在;
删除操作
- 删除度为0的节点,直接删除
- 删除度为1的节点,把其子树挂到其父节点上面
- 删除度为2的节点,可以转化为删除度为1或度为0的节点
对于度为2的节点:
- 前驱:左子树的最大值
- 后继:右子树的最小值
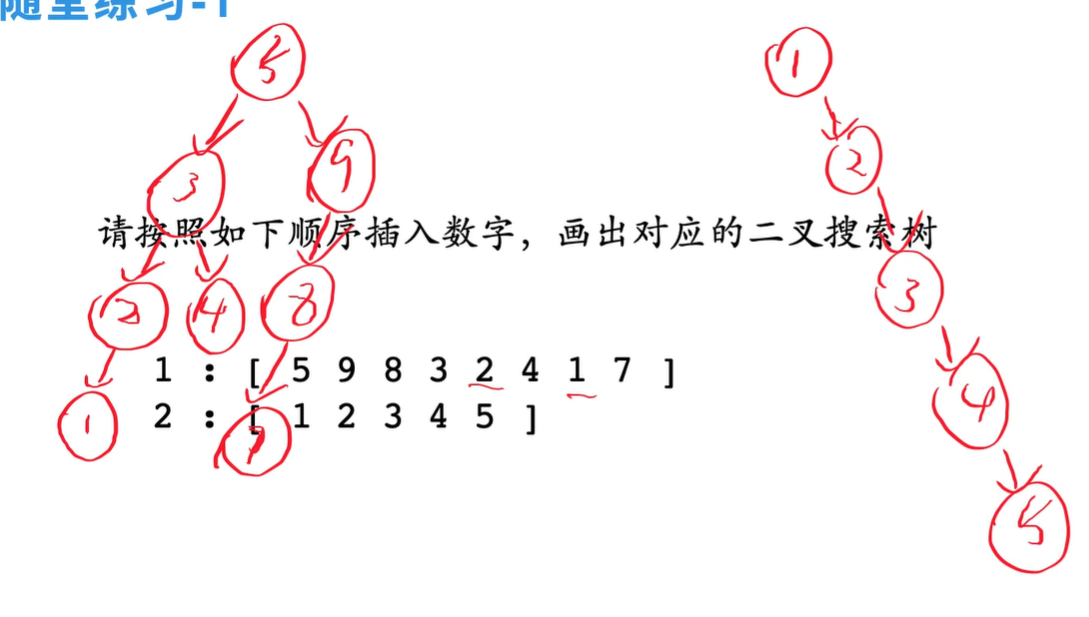
练习
- 插入顺序会影响树形结构;
- 不同的树形结构,查找效率不同;
平均查找效率:假设每个节点等概率被查找,节点查找次数的期望值,
总次数/总结点数;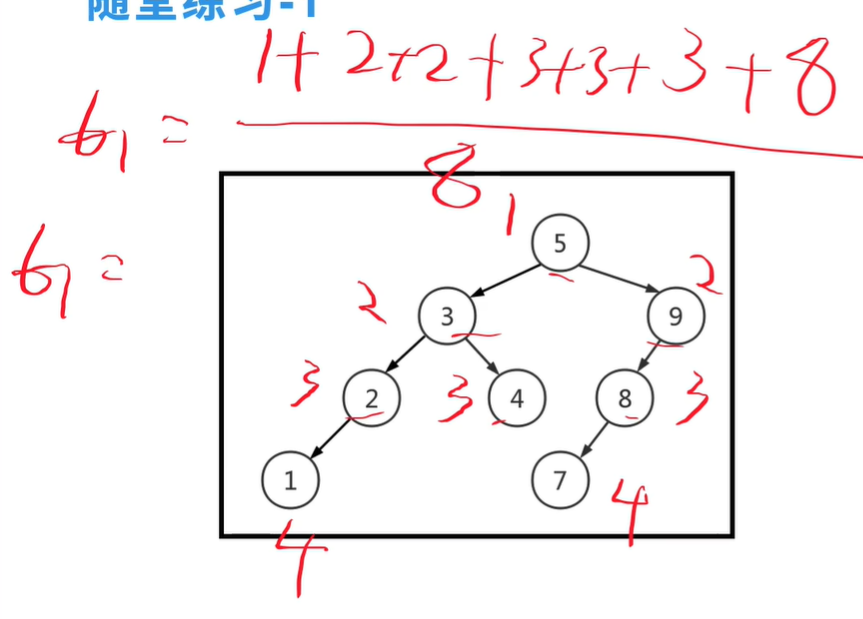
//file name:#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#define KEY(root) (root ? root->key : 0)typedef struct Node {int key;struct Node *lchild, *rchild;} Node;//新建节点Node *getNewNode(int val) {Node *p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));p->key = val;p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;return p;}//查找某节点int search(Node *root, int val) {if (root == NULL) return 0;if (root->key == val) return 1;if (val < root->key) return search(root->lchild, val); //遍历左子树return search(root->rchild, val); //左子树没有,则转向右子树}Node *insert(Node *root, int val) {if (root == NULL) return getNewNode(val); //不存在就新建if (root->key == val) return root; //结点已存在if (val < root->key) root->lchild = insert(root->lchild, val); //值小于根节点的值,插入左子树else root->rchild = insert(root->rchild, val); //值大于根结点的值,插入右子树return root;}//找到结点的前驱Node *predecessor(Node *root) {Node *temp = root->lchild;while (temp->rchild) temp = temp->rchild;return temp;}//删除值为val的结点Node *erase(Node *root, int val) {if (root == NULL) return NULL; //根结点不存在if (val < root->key) { //根节点的值大于要删除的值,走向左子树root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, val);} else if (val > root->key) { //根节点的值小于要删除的值,走向右子树root->rchild = erase(root->rchild, val);} else { //要删除的值是根结点的值,即删除度为1的结点,需要找前驱和后继if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL) { //如果无前驱和后继,直接删除free(root);return NULL;} else if (root->lchild == NULL || root->rchild == NULL) { //前驱和后继有一个不存在Node *temp = root->lchild ? root->lchild : root->rchild; //free(root);return temp;} else {Node *temp = predecessor(root); //找到前驱root->key = temp->key; //将度为2的结点的值替换为其前驱的值root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, temp->key); //删除前驱}}return root;}//输出二叉排序树void output(Node *root) {if (root == NULL) return ;output(root->lchild);printf("%d(%d, %d)\n", KEY(root), KEY(root->lchild), KEY(root->rchild));output(root->rchild);return ;}void post_output(Node *root) {if (root == NULL) return ;printf("%d(%d, %d)\n", KEY(root), KEY(root->lchild), KEY(root->rchild));output(root->lchild);output(root->rchild);return ;}//清除结点void clear(Node *root) {if (root == NULL) return ;clear(root->lchild);clear(root->rchild);free(root);return ;}int main() {int op, val;Node *root = NULL;while (~scanf("%d%d", &op, &val)) {switch(op) {case 0: printf("search %d, result = %d\n", val, search(root, val)); break;case 1: root = insert(root, val); break;case 2: root = erase(root, val); break;}if (op){output(root);printf("--------------------\n");}}printf("-----------------");post_output(root);printf("===================");clear(root);return 0;}
扩展内容
- 二叉排序树的删除的优化
define KEY(root) (root ? root->key : 0)
typedef struct Node { int key; struct Node lchild, rchild; } Node;
//新建节点 Node getNewNode(int val) { Node p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); p->key = val; p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL; return p; }
//查找某节点 int search(Node *root, int val) { if (root == NULL) return 0; if (root->key == val) return 1; if (val < root->key) return search(root->lchild, val); //遍历左子树
return search(root->rchild, val); //左子树没有,则转向右子树
}
Node insert(Node root, int val) {
if (root == NULL) return getNewNode(val); //不存在就新建
if (root->key == val) return root; //结点已存在
if (val < root->key) root->lchild = insert(root->lchild, val); //值小于根节点的值,插入左子树
else root->rchild = insert(root->rchild, val); //值大于根结点的值,插入右子树
return root;
}
//找到结点的前驱 Node predecessor(Node root) { Node *temp = root->lchild; while (temp->rchild) temp = temp->rchild; return temp; }
//删除值为val的结点 Node erase(Node root, int val) { if (root == NULL) return NULL; //根结点不存在 if (val < root->key) { //根节点的值大于要删除的值,走向左子树 root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, val); } else if (val > root->key) { //根节点的值小于要删除的值,走向右子树 root->rchild = erase(root->rchild, val); } else { //要删除的值是根结点的值,即删除度为1的结点,需要找前驱和后继 // if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL) { //如果无前驱和后继,直接删除 // free(root); // return NULL; // } if (root->lchild == NULL || root->rchild == NULL) { //前驱和后继有一个不存在 Node temp = root->lchild ? root->lchild : root->rchild; // free(root); return temp; } else { Node temp = predecessor(root); //找到前驱 root->key = temp->key; //将度为2的结点的值替换为其前驱的值 root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, temp->key); //删除前驱 } } return root; }
//输出二叉排序树 void output(Node *root) { if (root == NULL) return ; output(root->lchild); printf(“%d(%d, %d)\n”, KEY(root), KEY(root->lchild), KEY(root->rchild)); output(root->rchild); return ; }
void post_output(Node *root) { if (root == NULL) return ; printf(“%d(%d, %d)\n”, KEY(root), KEY(root->lchild), KEY(root->rchild)); output(root->lchild); output(root->rchild); return ; }
//清除结点 void clear(Node *root) { if (root == NULL) return ; clear(root->lchild); clear(root->rchild); free(root); return ; }
int main() { int op, val; Node *root = NULL; while (~scanf(“%d%d”, &op, &val)) { switch(op) { case 0: printf(“search %d, result = %d\n”, val, search(root, val)); break; case 1: root = insert(root, val); break; case 2: root = erase(root, val); break; } if (op){ output(root); printf(“——————————\n”); } } printf(“————————-“); post_output(root); printf(“===================”); clear(root); return 0; } ```
- 如何解决排名相关的检索需求
- 修改二叉排序树的结构定义,增加一个size字段,记录每棵树的节点数量;
,左子树的结点数量等于k-1,则根节点就是排名第k位的元素;
, 排名第k位的元素在左子树中去找
- 如何解决Top-K问题

