题目
将一个给定字符串 s 根据给定的行数 numRows ,以从上往下、从左到右进行 Z 字形排列。
比如输入字符串为 "PAYPALISHIRING" 行数为 3 时,排列如下:
P A H N
A P L S I I G
Y I R
之后,你的输出需要从左往右逐行读取,产生出一个新的字符串,比如:"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"。
请你实现这个将字符串进行指定行数变换的函数:
string convert(string s, int numRows);
示例 1:
输入:s = “PAYPALISHIRING”, numRows = 3
输出:“PAHNAPLSIIGYIR”
示例 2:
输入:s = “PAYPALISHIRING”, numRows = 4
输出:“PINALSIGYAHRPI”
解释:
P I N
A L S I G
Y A H R
P I
示例 3:
输入:s = “A”, numRows = 1
输出:“A”
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000s由英文字母(小写和大写)、','和'.'组成1 <= numRows <= 1000
解题思路
1、按行排序
通过从左向右迭代字符串,我们可以轻松地确定字符位于 Z 字形图案中的哪一行。
从左到右迭代 s,将每个字符添加到合适的行。可以使用当前行和当前方向这两个变量对合适的行进行跟踪。
只有当我们向上移动到最上面的行或向下移动到最下面的行时,当前方向才会发生改变。
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n = len(s)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
2、按行访问
逐行读取 Z 字形图案的字符。
首先访问 行 0 中的所有字符,接着访问 行 1,然后 行 2,依此类推…
对于所有整数 k,
- 行 0 中的字符位于索引 k (2 · numRows - 2) 处;
- 行numRows−1 中的字符位于索引 k(2⋅numRows−2)+numRows−1 处;
- 内部的 行 i 中的字符位于索引 k(2⋅numRows−2)+i 以及 (k+1)(2⋅numRows−2)−i 处;
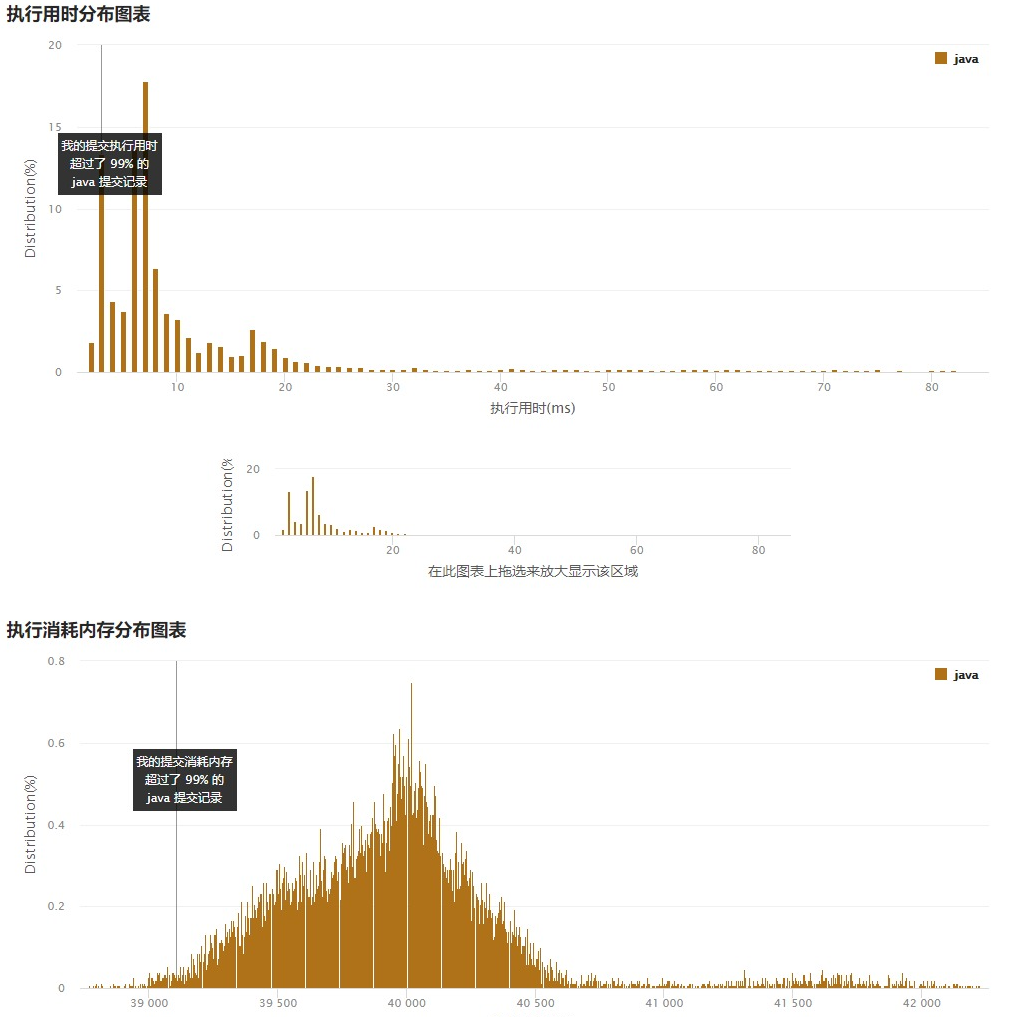
虽然执行效率较高,但发现其中规律并总结,编写出优雅的代码其实并不容易,在面试时不太推荐使用这种解法。
答案
1、按行排序
class Solution {public String convert(String s, int numRows) {// 特殊情况if (numRows == 1) {return s;}// 字符串长度int len = s.length();// 结果StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer("");// numRows 个 StringBuffer 数组,按照顺序模拟放入,最后拼接到 resultStringBuffer[] strs = new StringBuffer[numRows];for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {// 初始化strs[i] = new StringBuffer("");}// 模式:true 为 index 递增 ,false 为 index 递减boolean isAdd = true;// 计数器int index = 0;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {strs[index].append(s.charAt(i));if (isAdd) {// index 递增index++;} else {// index 递减index--;}if (index == numRows - 1) {// 如果相等,说明该切换为递减模式了isAdd = false;} else if (index == 0) {// 如果等于 0,说明下次该切换为递增模式了isAdd = true;}}// 拼接结果for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {result.append(strs[i]);}return result.toString();}}
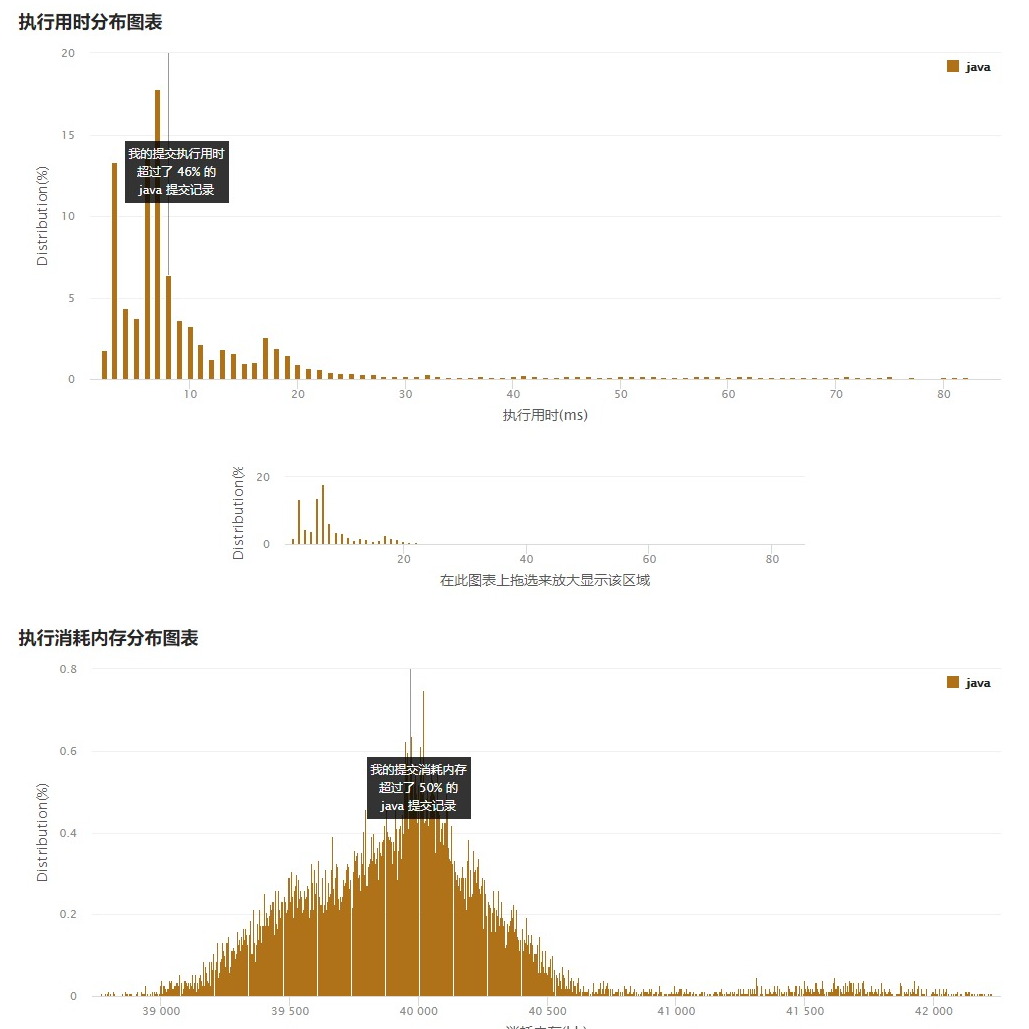
2、按行访问
class Solution {public String convert(String s, int numRows) {// 特殊情况if (numRows == 1) return s;// 结果StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();int n = s.length();int cycleLen = 2 * numRows - 2;for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {for (int j = 0; j + i < n; j += cycleLen) {result.append(s.charAt(j + i));if (i != 0 && i != numRows - 1 && j + cycleLen - i < n)result.append(s.charAt(j + cycleLen - i));}}return result.toString();}}