结构型设计模式就快要讲完了,还剩下两个不那么常用的:组合模式和享元模式。今天,我们来讲一下组合模式(Composite Design Pattern)。
1、什么是组合模式?
组合模式跟我们之前讲的面向对象设计中的“组合关系(通过组合来组装两个类)”,完全是两码事。这里讲的“组合模式”,主要是用来处理树形结构数据。这里的“数据”,你可以简单理解为一组对象集合,待会我们会详细讲解。
正因为其应用场景的特殊性,数据必须能表示成树形结构,这也导致了这种模式在实际的项目开发中并不那么常用。但是,一旦数据满足树形结构,应用这种模式就能发挥很大的作用,能让代码变得非常简洁。
在 GoF 的《设计模式》一书中,组合模式是这样定义的:
Compose objects into tree structure to represent part-whole hierarchies.Composite lets client treat individual objects and compositions of objects uniformly.
翻译成中文就是:将一组对象组织(Compose)成树形结构,以表示一种“部分 - 整体”的层次结构。组合让客户端(在很多设计模式书籍中,“客户端”代指代码的使用者。)可以统一单个对象和组合对象的处理逻辑。
组合模式的设计思路,与其说是一种设计模式,倒不如说是对业务场景的一种数据结构和算法的抽象。其中,数据可以表示成树这种数据结构,业务需求可以通过在树上的递归遍历算法来实现。
组合模式,将一组对象组织成树形结构,将单个对象和组合对象都看做树中的节点,以统一处理逻辑,并且它利用树形结构的特点,递归地处理每个子树,依次简化代码实现。使用组合模式的前提在于,你的业务场景必须能够表示成树形结构。所以,组合模式的应用场景也比较局限,它并不是一种很常用的设计模式。
2、为什么要使用组合模式?
3、例子
3.1、GoF(简单)
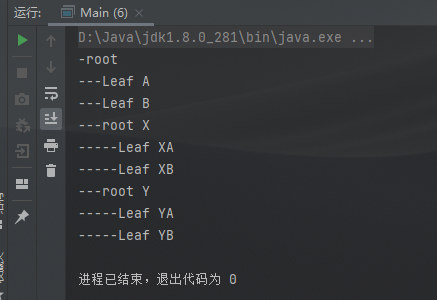
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Composite root = new Composite("root");root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf A"));root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf B"));Composite rootX = new Composite("root X");rootX.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XA"));rootX.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XB"));root.Add(rootX);Composite rootY = new Composite("root Y");rootY.Add(new Leaf("Leaf YA"));rootY.Add(new Leaf("Leaf YB"));root.Add(rootY);root.Display(1);}}abstract class Component {protected String name;public Component(String name) {this.name = name;}// 通常都使用 Add 和 Remove 方法来提供增加或移除树叶或树枝的功能public abstract void Add(Component c);public abstract void Remove(Component c);public abstract void Display(int depth);}class Leaf extends Component {public Leaf(String name) {super(name);}@Overridepublic void Add(Component c) {System.out.println("cannot add to a leaf");}@Overridepublic void Remove(Component c) {System.out.println("cannot remove from a leaf");}@Overridepublic void Display(int depth) {// 叶节点的具体方法,此处是显示其名称和级别StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {buffer.append("-");}System.out.println(buffer + name);}}class Composite extends Component {private List<Component> children = new ArrayList<>();public Composite(String name) {super(name);}@Overridepublic void Add(Component c) {children.add(c);}@Overridepublic void Remove(Component c) {children.remove(c);}@Overridepublic void Display(int depth) {StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {buffer.append("-");}System.out.println(buffer + name);for (Component component : children) {component.Display(depth + 2);}}}
4、总结
4.1、优缺点
1)优点
高层模块调用简单;
节点自由增加;
2)缺点
在使用组合模式时,其叶子和树枝的声明都是实现类,而不是接口,违反了依赖倒置原则。
4.2、扩展知识
tomcat的多层容器也是使用了组合模式。只需要调用最外层容器Server的init方法,整个程序就起来了。客户端只需要处理最外层的容器,就把整个系统拎起来了。
组合模式使用了树形的数据结构以及递归算法,这里也可以看出知识的相通性(算法和设计模式)。想到这方面的另外一个例子就是责任链模式,责任链模式就是使用了数据结构中的链表和递归算法。

