前言
感谢黑马程序员
Spring概述
首先我们来看一张图片
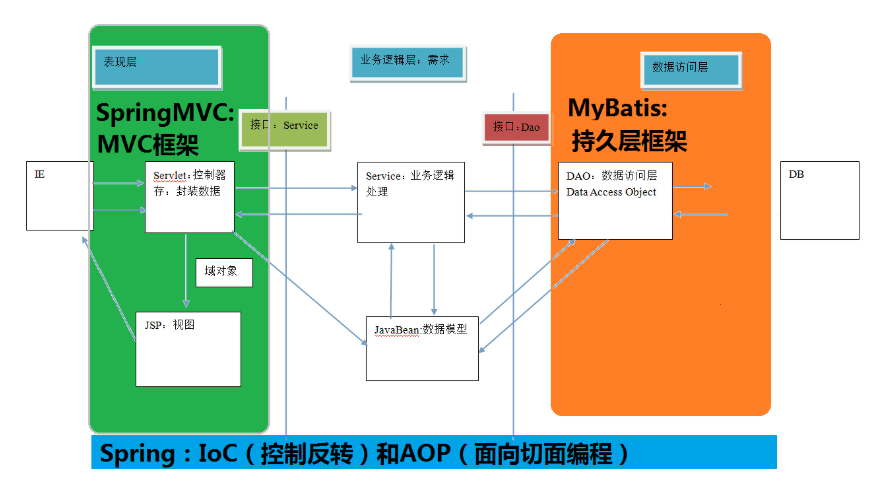
这就是我们将要学习的SSM框架的基本架子,我们可以看到,由SpringMVC去处理视图层,Mybatis去处理持久化层,而Spring干什么呢?其实什么也不做,它不属于我们熟知的三层架构的任何一层,但其实是SSM中的核心。
Spring是什么
Spring,是Java全栈轻量级开发框架,现如今成为了最多的JavaEE企业应用开源框架
Spring官网:https://spring.io
Spring的核心
Spring的核心就两件事:IOC控制反转和AOP面向切面编程,基于这两个特性,可以大大简化我们编写JavaEE应用,实现快速开发
IOC控制反转是什么
- 控制反转,就是将创建对象的活交给工厂区创建
打个比方,我现在要买个房子
以前的做法是:到处打听谁要买房,然后和具体的人去沟通协商,然后两家签订合同
现在的做法是:让中介去干这个活,我到最后只管签合同
AOP面向切面编程是什么
- 面向切面编程,就是通过预编译和运行期动态代理的方式实现功能的维护
打个比方,比如现在我的程序从上到下已经全部开发完成了,现在有个需求说我要在哪个过程上加上一个新功能 这个时候我只需要在那个过程范围内添加一个新的功能即可 形象化来说,我们开发过程是从上到下竖向进行的,面向切面编程就是在这基础上横向添加
Spring的优势
- 解耦
- AOP
- 声明式事务支持
- 方便测试
- 可以集成各种框架
- 降低API使用难度
- Spring源码是学习的范例
Spring的体系结构
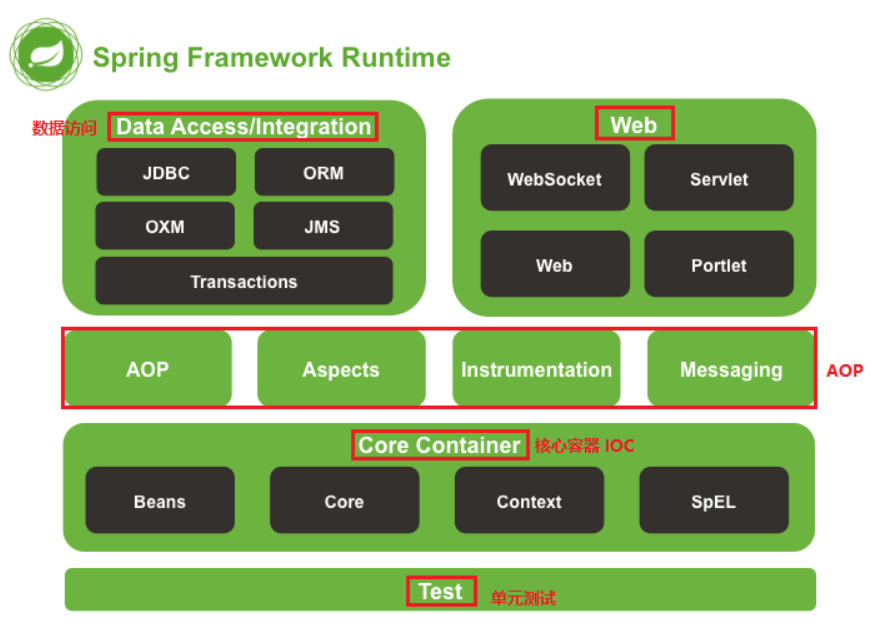
问题分析:如何将程序简化
以前的使用案例
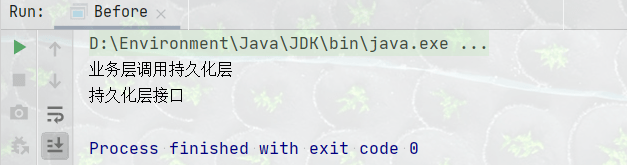
package com.howling.Before.Dao;/*** 持久层接口*/public interface AccountDao {void saveAccount();}
package com.howling.Before.Dao;/*** 持久层*/public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {public void saveAccount() {System.out.println("持久化层接口");}}
package com.howling.Before.Service;/*** 业务层接口*/public interface AccountService {void saveAccount();}
package com.howling.Before.Service;import com.howling.Before.Dao.AccountDao;import com.howling.Before.Dao.AccountDaoImpl;/*** 业务层*/public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService{private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl();public void saveAccount() {System.out.println("业务层调用持久化层");accountDao.saveAccount();}}
package com.howling.Before;import com.howling.Before.Service.AccountService;import com.howling.Before.Service.AccountServiceImpl;public class Before {public static void main(String[] args) {AccountService accountService = new AccountServiceImpl();accountService.saveAccount();}}
以前做法的缺点分析
以前的做法耦合太严重,既然说到耦合,就说一下程序的耦合
耦合:程序之间的依赖关系,其中包括类和类之间的依赖关系,程序和程序之间的依赖关系
我们要做到解耦合,应该做到的程度是:编译器中看不到依赖,但是在运行中能够依赖。
使用工厂和配置文件来简化
工厂模式概述
工厂模式,属于23种设计模式中的一种,属于比较常使用的设计模式之一
工厂模式,顾名思义。
假如我们之前都是手工制品,现在我们要上流水线了。
说到工厂模式在提一嘴JavaBean,Bean这个词在英语单词中有豆子的意思,也有着可重用组件的含义。
之前我们一直说创建一个实体类,一个标准的实体类可以叫做JavaBean,其实JavaBean的含义是包含实体类的。
JavaBean>实体类,JavaBean是可重用组件的一部分
准备工作
1、编写持久化层和业务层
package com.howling.FactoryDecoupl.Dao;/*** 持久层接口*/public interface AccountDao {void saveAccount();}
package com.howling.FactoryDecoupl.Dao;/*** 持久化层*/public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {public void saveAccount() {System.out.println("持久化层");}}
package com.howling.FactoryDecoupl.service;
/**
* 业务层接口
*/
public interface AccountService {
void saveAccount();
}
package com.howling.FactoryDecoupl.service;
/**
* 业务层
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService{
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("业务层");
}
}
因为要使用工厂来创建,所以业务层没有调用持久化层,表现层根本没写
2、通过反射来创建对象,从而避免使用new关键字
- bean.properties
# 在resources下面创建bean.prpperties
accountDao=com.howling.FactoryDecoupl.Dao.AccountDaoImpl
accountService=com.howling.FactoryDecoupl.service.AccountServiceImpl
使用工厂
创建Bean工厂
package com.howling.factory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* 静态工厂
*/
public class BeanFactory {
private static Properties properties;
static {
try {
properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 工厂模式创建bean工厂
*
* @param beanName bean的名称
* @return bean
*/
public static Object getBean(String beanName) {
Object bean = null;
try {
String property = properties.getProperty(beanName);
bean = Class.forName(property).newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bean;
}
/**
* 创建一个对应类型T的对象
*
* @param beanName bean的名称
* @param tClass 类型参数
* @param <T> 类型
* @return 对象
*/
public static <T> T getBean(String beanName, Class<T> tClass) {
T bean = null;
try {
String property = properties.getProperty(beanName);
bean = (T) Class.forName(property).newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bean;
}
}
package com.howling;
public class People {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
}
people=com.howling.People
现在我们可以来进行配置文件和工厂的测试了
工厂模式的问题
现在的工厂模式是不完美的
- 多例:工厂每次启动都会产生不同的实例,每次调用的实例均不相同,这样会导致内存大幅消耗
思路:
为了解决这个问题,我们引入单例模式,单例模式也是设计模式中的一种
1、我们使用单例模式对工厂进行改造,这样工厂每次返回的实例都是一个
2、之前我们每次创建一个新的对象都是使用Class.forName(beanName).newInstance();来进行创建的,假如我们要返回一个实例,那么这个语句只能执行一次
3、语句执行一次创建对象之后,我们将初始化的值存储起来以作备用,以后就不用创建,直接返回即可
单例工厂
package com.howling.factory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
public class SingleBeanFactory {
private static Properties properties;
private static Map<String, Object> factories = new HashMap<>();
static {
try {
properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = SingleBeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
// 获得所有的Key
Enumeration<Object> enumeration = properties.keys();
// 根据key进行遍历,将所有的东西装载进工厂中
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = enumeration.nextElement().toString();
String property = properties.getProperty(key);
Object o = Class.forName(property).newInstance();
factories.put(key, o);
}
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获得bean对象
*
* @param name bean对象的名称
* @return bean对象
*/
public static Object getBean(String name) {
Object o = null;
try {
o = factories.get(name);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return o;
}
/**
* 获得bean对象
*
* @param name bean对象的名称
* @param tClass bean对象类型
* @param <T>
* @return bean对象
*/
public static <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> tClass) {
T o = null;
try {
o = (T) factories.get(name);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return o;
}
}
懒加载静态单例工厂
我们可以看到,在上面的过程中,单例工厂是没有办法进行按需加载的,也就是说它必须要一次性加载完成,即使配置文件中存放有很多的类,所以我们必须要对他进行简化,让它懒加载
package com.howling.factory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
public class LazySingleBeanFactory {
private static Properties properties;
private static final Map<String, Object> factories = new HashMap<>();
static {
try {
properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = LazySingleBeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Object getBean(String name) {
Object o;
if ((o = factories.get(name)) != null) {
return o;
}
try {
String value = properties.getProperty(name);
o = Class.forName(value).newInstance();
factories.put(name, o);
return o;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> tClass) {
T o;
if ((o = (T) factories.get(name)) != null) {
return o;
}
try {
String value = properties.getProperty(name);
o = (T) Class.forName(value).newInstance();
factories.put(name, o);
return o;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
Spring快速开始
IOC
接下来我们要用Spring去实现上面我们解决的耦合问题,快速入门来体会一下Spring的感觉
1、准备持久层和业务层
package com.howling.SpringDemo1.Dao;
/**
* 持久层接口
*/
public interface AccountDao {
void saveAccount();
}
package com.howling.SpringDemo1.Dao;
/**
* 持久层
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("持久化层接口");
}
}
package com.howling.SpringDemo1.Service;
/**
* 业务层接口
*/
public interface AccountService {
void saveAccount();
}
package com.howling.SpringDemo1.Service;
import com.howling.SpringDemo1.Dao.AccountDao;
import com.howling.SpringDemo1.Dao.AccountDaoImpl;
/**
* 业务层
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl();
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("业务层调用持久化层");
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
2、导入Spring的依赖
<!--设置Spring-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
3、准备bean对象的xml文件
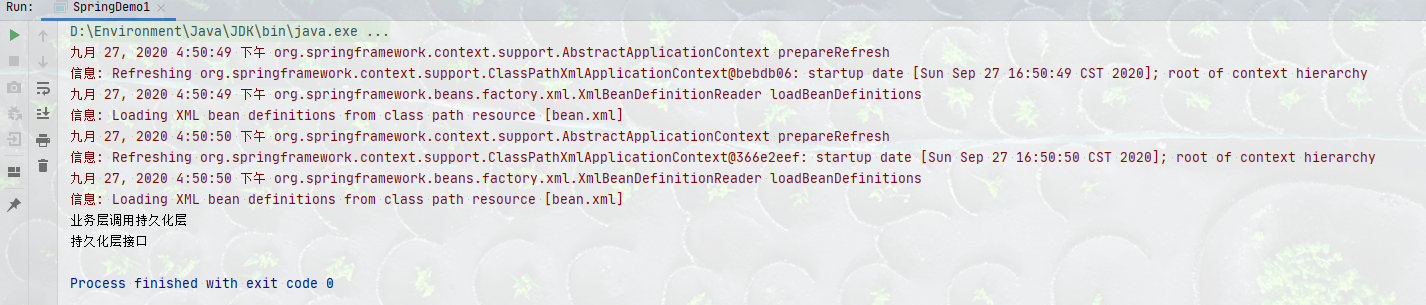
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--把对象的创建交给spring来管理
id:配置文件中的key值,与在讲工厂模式的时候的key值相同
class:配置文件中的value值,是全限定类名,与在讲工厂模式的时候的value值相同
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.howling.SpringDemo1.Service.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.howling.SpringDemo1.Dao.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
4、使用Spring获取bean对象
- 改造Service
package com.howling.SpringDemo1.Service;
import com.howling.SpringDemo1.Dao.AccountDao;
import com.howling.SpringDemo1.Dao.AccountDaoImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 业务层
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private static AccountDao accountDao = null;
static {
//获取bean.xml
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//根据key获取对象
accountDao = applicationContext.getBean("accountDao", AccountDao.class);
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("业务层调用持久化层");
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
- 改造Controller
package com.howling.SpringDemo1;
import com.howling.SpringDemo1.Service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 控制层
*/
public class SpringDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取bean.xml文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//根据key获取value,如果不指定Class则需要强制转换
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) applicationContext.getBean("accountService");
accountService.saveAccount();
}
}
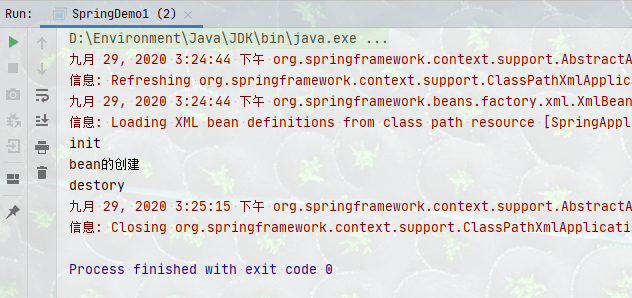
5、查看结果
上面的快速开始就是Spring的IOC,控制反转,其实在作用上感觉非常像我们刚才写的单例工厂,不用怀疑,它就是。 学习Spring一定要把单例工厂弄个门清,至少要会手写单例工厂,让别人看看你的Spring学会了。
Application和三种构造方法
下面我们来分析一下ApplicationContext
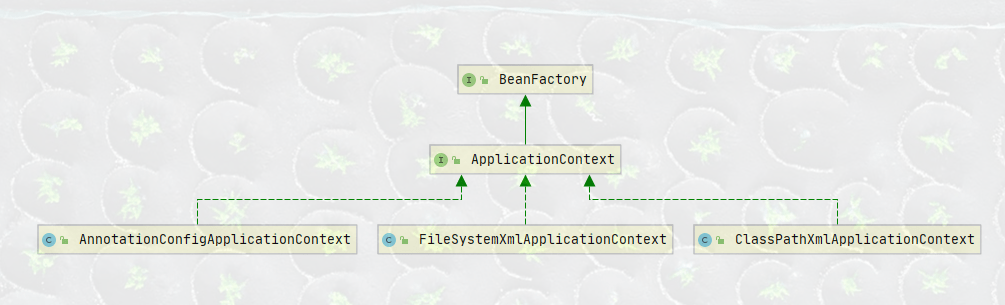
上面是ApplicationContext的体系结构,ApplicationContext是一个接口
1、我们可以看到他继承了BeanFactory
BeanFactory是Spring容器的顶层接口,他下面的实现接口有很多,其中我们常常使用的是ApplicationContext
2、ApplicationContext有三个比较常用的实现类
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:基于Xml的配置,刚才已经演示过了
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:也是基于Xml的配置
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:基于注解的配置
好的类和方法的命名让人一看就大体知道这个是干嘛的,比如 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:根据ClassPath(类路径)的xml创建 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:根据文件的xml来创建,但是必须要有访问权限 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:基于注解配置来创建
BeanFactory和Application的两个加载策略
1、BeanFactory:是延迟加载,也就是说什么时候根据id加载了对象什么时候真正创建对象
这个其实想一下我们没有完成单例的工厂模式就很好理解了 所以这个模式下其实不是单例模式,每次调用工厂都会产出一个新的单例 BeanFactory主要是面向Spring本身
2、ApplicationContext:立即加载
这个就是我们改造完成之后的单例工厂了 每次调用工厂都是返回相同的实例 ApplicationContext主要是面向开发者
其实我推荐使用ApplicationContext,因为这个继承了BeanFactory和其他的接口,功能相对于BeanFactory更加强大。
但是Spring是一个非常牛逼的框架,他会根据你的配置进行更改。
Spring的XML配置详解
Spring的Bean细节
Spring中bean.xml属性
- id:唯一标识
- name:名字,可以指定多个名字,使用逗号,分号,空格分隔
- class:映射的类,要用全类名
- scope:作用范围
- singleton:单例(默认值)
- prototype:多例(常用)
- request:作用于web应用的请求范围
- session:作用于web应用的会话范围
- global-session:作用于集群环境的会话范围(全局会话范围),当不是集群环境时他是session
- factory-method:可以让我们自己写bean的工厂,指定我们的方法来创建,有两种形式
- 静态方法
- 普通方法,需要借助factory-bean来使用
- factory-bean:指定工厂,说明这个类是工厂类
5、init-method:初始化要执行的方法
6、destory-method:销毁时要执行的方法
<bean id="" class="" factory-bean="" factory-method="" init-method="" destroy-method="" scope=""></bean>
这里只列出了部分,还有其他的后面都会一一讲到
三种创建Bean对象的方式
在上面的xml属性我们讲过了,其中可以看到,还有两种创建对象的属性:指定工厂和指定静态工厂
那么现在我们就有三种创建bean对象的方式了,在这里总结一下
1、根据默认的构造函数创建:默认使用。(这里简略写一下,反正前面都已经写过了)
- 编写类
/**
* 持久层
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("持久化层接口");
}
}
- 指定spring的配置文件:bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="com.howling.SpringDemo1.Service.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.howling.SpringDemo1.Dao.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
- Spring创建bean对象
/**
* 业务层
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private static AccountDao accountDao = null;
static {
//获取bean.xml
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//根据key获取对象
accountDao = applicationContext.getBean("accountDao", AccountDao.class);
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("业务层调用持久化层");
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
使用这种方式创建的bean对象会根据默认的构造函数进行创建,Spring直接通过反射给你创建一个
2、指定静态工厂创建
- 指定静态工厂
package com.howling.SpringDemo2.factory;
import com.howling.SpringDemo2.Dao.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.howling.SpringDemo2.Service.AccountServiceImpl;
public class BeanFactory {
public static AccountServiceImpl getAccountService() {
return new AccountServiceImpl();
}
public static AccountDaoImpl getAccountDao() {
return new AccountDaoImpl();
}
}
- 指定spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.howling.SpringDemo2.factory.BeanFactory"
factory-method="getAccountDao"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" class="com.howling.SpringDemo2.factory.BeanFactory"
factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
</beans>
除了这两个地方,其他都不用动
3、指定工厂方法创建
- 指定工厂
package com.howling.SpringDemo3.factory;
import com.howling.SpringDemo3.Dao.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.howling.SpringDemo3.Service.AccountServiceImpl;
public class BeanFactory {
public AccountServiceImpl getAccountService() {
return new AccountServiceImpl();
}
public AccountDaoImpl getAccountDao() {
return new AccountDaoImpl();
}
}
- 指定Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--定义工厂-->
<bean id="beanFactory" class="com.howling.SpringDemo3.factory.BeanFactory"></bean>
<!--指定工厂和工厂中的方法-->
<bean id="accountDao" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getAccountDao"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
</beans>
现在可能有人要问了:这不是还是new出了对象了么,不还是耦合了么
原因在于:第二种和第三种的方式是解决jar包的方法的。jar包中的代码是.class文件不能更改,所以只能new
也就是说,要是你想通过Spring来获得jar包中的某个方法就可以使用第二种和第三种方式。
我们自己写的话直接使用第一种方式即可
作用范围
作用范围在bean.xml属性中也已经讲过了,简单来说就是配置一个scope属性即可
之前我们讲过BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别,说这两个一个是多例一个是单例,但是可以根据配置具体更改
这就是我们说过的那个配置
scope:作用范围
- singleton:单例(默认值)
- prototype:多例(常用)
- request:作用于web应用的请求范围
- session:作用于web应用的会话范围
- global-session:作用于集群环境的会话范围(全局会话范围),当不是集群环境时他是session
生命周期
友情提示,在看生命周期的时候,多想想我们之前写过的两个工厂,然后结合理解
多例对象的生命周期
出生:当使用对象时,对象创建
活着:当使用的时候活着
死亡:GC垃圾回收,Spring不管
单例对象的生命周期
出生:容器创建时立刻出生
活着:只要容器还在就一直活着
死亡:容器销毁,对象死亡
也就是说,单例对象的生命周期和容器的生命周期是完全一致的,只不过我们一般发现不了,因为main函数执行完成之后内存直接就释放了,也就是说容器还没来得及调用销毁方法就已经被释放了内存
但是我们想要手动关闭也是可以的,Spring中提供了关闭的方法,但是有个注意点
我们一般使用的接口是ApplicationContext,但是Application中并没有关闭的方法,只有它的子类才有,所以假如想要调用关闭的方法,使用多态是不可以的,比如下面这种就不可以
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
在传统的Java中,我们对于Bean的管理也就是new一个出来,然后用完等待GC,但是Spring中要考虑的显然不止这些东西,它的加载顺序还是比较复杂的
1、Bean的实例化:Spring启动,扫描需要被Spring管理的Bean,进行Bean的实例化
2、依赖注入:Bean实例化之后,对Bean的引入和值注入到Bean的属性中
3、注入Aware:Spring会检测是否实现了xxxAware接口,并将对应的Aware接口注入给Bean
4、BeanPostProcessor:经过上面的几个步骤,bean对象已经构造,但是在这个情况下还没有被使用
接口BeanPostProcessor下面有两个函数
- postProcessBeforeInitialzation:bean对象传进来,早于Initialzation,所以叫做前置处理,所有的Aware接口在这一步注入
- postProcessAfterInitialzation:bean对象传进来,晚于Initialzation,所以叫后置处理
5、InitializingBean与init-method:前置处理之后会执行这个,可以在这一步添加一些代码的逻辑,但是它不会把bean对象传进来,所以不能处理对象本身
6、DisposableBean和destroy-method:可以在bean销毁前执行逻辑,但是bean不会传递进来
Spring依赖注入
依赖注入概述
什么叫做依赖注入
依赖注入:Dependency Injection
依赖注入的意思是:在当前类中需要用到其他类的对象,像这种依赖关系以后我们就都交给Spring去管理了,这种依赖关系的维护就叫做依赖注入
什么数据能够进行依赖注入
能够注入的数据分类三类
1、所有的基本类型和String
2、复杂类型(集合)
3、其他bean类型(在配置文件或者注解中配置过的bean)
注入的方式
依赖注入的方式有三种
1、构造函数
2、set方法
3、注解
经常要变化的数据是不适合注入的
构造函数注入
标签
构造函数的标签:<constructor-arg></constructor-arg>,其中有以下几个属性
- type:要注入的类型
- index:要注入数据的索引位置(构造函数上)
- name:要注入数据的名称呢过
- value:要注入数据的值
- ref:要注入数据的bean引用
构造函数注入的快速起步:基本类型的注入
1、写一个类,里面包含有参数的构造函数
package com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service;
public interface AccountService {
void saveAccount();
}
package com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private String name;
private Integer age;
/**
* 使用构造函数注入
*
* @param name name是String类型
* @param age age是Integer类型
*/
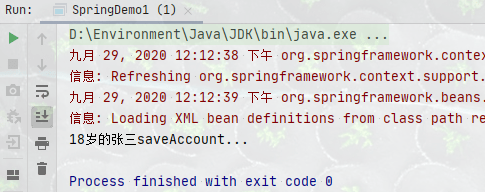
public AccountServiceImpl(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(this.age + "岁的" + this.name + "saveAccount...");
}
}
2、编写Spring的bean.xml
- ConstructorInjectionDemo1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 1、首先使用一个bean对象指定对应的类,这个类初始化的时候需要带有参数 -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 2、constructor-arg:构造函数注入方式
name:要注入的数据名称是什么
value:要制定基本类型和String类型的数据,可以自动转换,比如这个18会转为Integer
-->
<constructor-arg name="name" value="张三"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
3、进行测试
package com.howling.ConstructorInjection;
import com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ConstructorInjectionDemo1.xml");
AccountServiceImpl accountService = context.getBean("accountService", AccountServiceImpl.class);
accountService.saveAccount();
}
}
bean类型的注入
如果一个类A要依赖另一个类B,那么B首先要作为一个Spring管理的bean对象,然后才能被A引入,当然A也要成为一个bean对象
下面我们来做一个bean类型的注入
1、改造上面的类
package com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service;
import java.util.Date;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private String name;
private Integer age;
/**
* 一个Date类,作为bean对象来注入
*/
private Date birthday;
public AccountServiceImpl(String name, Integer age, Date birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(this.age + "岁的" + this.name + "saveAccount..." + "要过他" + birthday + "的生日");
}
}
2、做一个bean对象
- xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--我们做出了一个bean对象,Spring会使用反射初始化一个出来-->
<bean id="time" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" class="com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service.AccountServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="张三"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<!-- name还是指定类中的值,但是bean对象不能指定value,要使用引用的方式 -->
<constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="time"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
3、测试
可以看到,创建了一个Date对象
复杂类型的注入
复杂类型有这么几种
1、数组
2、集合
- List
- Map
3、Properties
所以我们根据数据的结构,分了两部分:
1、array和list
2、map和props
下面进行案例
1、改造类
package com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service;
import java.util.*;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private String[] strings;
private List<String> list;
private Map<String, Object> map;
private Properties properties;
public AccountServiceImpl(String[] strings, List<String> list, Map<String, Object> map, Properties properties) {
this.strings = strings;
this.list = list;
this.map = map;
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
Arrays.stream(strings).forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
list.forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
map.keySet().forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
properties.keySet().forEach(System.out::print);
}
}
2、xml改造
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
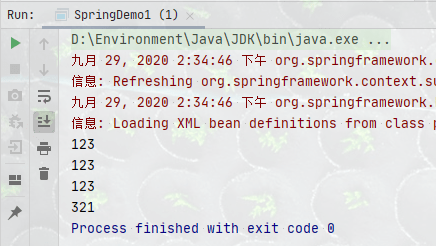
<bean id="accountService" class="com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service.AccountServiceImpl">
<!--参数1:数组:array-value-->
<constructor-arg index="0">
<array>
<value>a1</value>
<value>a2</value>
<value>a3</value>
</array>
</constructor-arg>
<!--参数2:列表:list-value-->
<constructor-arg index="1">
<list>
<value>l1</value>
<value>l2</value>
<value>l3</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
<!--参数3:map:map-entry(key-value)-->
<constructor-arg index="2">
<map>
<entry key="m1" value="m1"/>
<entry key="m2" value="m2"/>
<entry key="m3" value="m3"/>
</map>
</constructor-arg>
<!--参数4:properties-->
<constructor-arg index="3">
<props>
<prop key="p1">1</prop>
<prop key="p2">2</prop>
<prop key="p3">3</prop>
</props>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
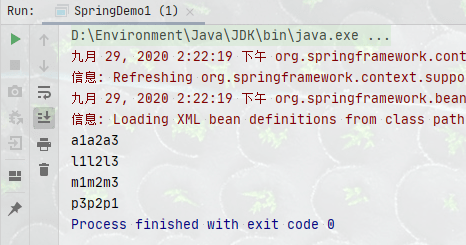
3、测试
package com.howling.ConstructorInjection;
import com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ConstructorInjectionDemo1.xml");
AccountServiceImpl accountService = context.getBean("accountService", AccountServiceImpl.class);
accountService.saveAccount();
}
}
set注入
Set注入概述
简单来说,就是将构造方法的注入转换为了set方法注入(不需要get方法)
标签
Set方法的标签是<property></property>,主要有这么几个属性
1、name:从set方法中得到的名字,比如:setName—>Name—>name
2、value:值
3、ref:注入数据的bean引用
没错,set注入直接就是property,而且set注入是最常用的一种注入方式
实例
1、代码改造
package com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service;
import java.util.*;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
private String[] strings;
private List<String> list;
private Map<String, Object> map;
private Properties properties;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public void setStrings(String[] strings) {
this.strings = strings;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, Object> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
Arrays.stream(strings).forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
list.forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
map.keySet().forEach(System.out::print);
System.out.println();
properties.keySet().forEach(System.out::print);
}
}
2、xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="time" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" class="com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 1、基础类型和字符串 -->
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
<!--bean类型-->
<property name="birthday" ref="time"></property>
<!--复杂类型-->
<property name="strings">
<array>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="1" value="1"></entry>
<entry key="2" value="2"></entry>
<entry key="3" value="3"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="1">1</prop>
<prop key="2">2</prop>
<prop key="3">3</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
3、测试
package com.howling.ConstructorInjection;
import com.howling.ConstructorInjection.service.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ConstructorInjectionDemo1.xml");
AccountServiceImpl accountService = context.getBean("accountService", AccountServiceImpl.class);
accountService.saveAccount();
}
}
Spring的注解详解
注解概述
首先明确一件事情:注解的方式和xml的方式本质上没有什么区别
注解按照作用分类
- 用于创建对象
- 改变作用范围
- 和生命周期相关
- 用于注入数据
环境准备
首先我们需要告诉Spring:我要用注解。
回想一下我们学习的JavaWeb,我们使用注解的使用是首先在web.xml上填写使用注解的命名空间,在Spring中也是这么干,那么我们的xml需要换成下面这个
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.howling"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
1、我们需要beans的命名空间 2、component-scan中的base-package告诉了Spring在创建容器要扫描com.howling下面的包 3、当扫描包的时候就会发现包中的类上的注解
创建对象的注解
注解说明
1、@Component:组件
2、@Controller:一般用于控制层(表现层)
3、@Service:一般用于业务层
4、@Repository:一般用于持久层
说明一下,其实上面这四个的作用都是一样的,但是分开命名就是让我们程序员开发的时候比较好理解,但是其实用啥都一样
属性说明
注解肯定要有属性,属性名就是value,属性值是唯一的,用于找到这个类
1、当不写value时,默认value是类的小驼峰形式
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("bean的创建");
}
}
这里的value就是accountServiceImpl
2、当自定义value时,就是你自己定义的值
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component(value = "accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("bean的创建");
}
}
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("bean的创建");
}
}
因为只有一个value赋值,所以value写不写都行
例子
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("bean的创建");
}
}
package com.howling.Annotation;
import com.howling.Annotation.service.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("SpringApplication.xml");
AccountServiceImpl accountServiceImpl = context.getBean("accountServiceImpl", AccountServiceImpl.class);
accountServiceImpl.saveAccount();
}
}
作用范围
注解
@Scope:指定bean的作用范围
属性
value:指定范围的取值
- singleton:单例,默认
- prototype:多例
例子
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("bean的创建");
}
}
生命周期
注解
- @PostConstruct:初始化要执行的方法
- @PreDestory:销毁前要执行的方法
1、这俩都用在方法上 2、不能用多态来测试销毁方法,因为ApplicationContext没有这个方法,子类才有 3、多例模式下GC回收,close也没用 4、详情查看Spring的生命周期
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("bean的创建");
}
@PostConstruct
void init(){
System.out.println("init");
}
@PreDestroy
void destory(){
System.out.println("destory");
}
}
package com.howling.Annotation;
import com.howling.Annotation.service.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("SpringApplication.xml");
AccountServiceImpl accountServiceImpl = context.getBean("accountServiceImpl", AccountServiceImpl.class);
accountServiceImpl.saveAccount();
context.close();
}
}
注入数据
注解分类
- @Autowried:先按照类型匹配,然后按照bean的id注入
- @Qualifier:给类成员注入和@Autowried一起使用,给方法参数注入可以单独使用
- @Resource:根据bean的id注入,不是Spring的注解
- @Value:注入基本类型和String
@Autowried
这个注解会首先按照类型匹配,假如只有一个匹配的类型就按照那个类型注入,假如有多个匹配的类型就按照名称注入
而且@Autowried会调用的是无参构造,所以是这样的:类型—>名称—>无参构造
而且假如只有有参构造没有无参构造,它也没法调用,因为没有值给它调用
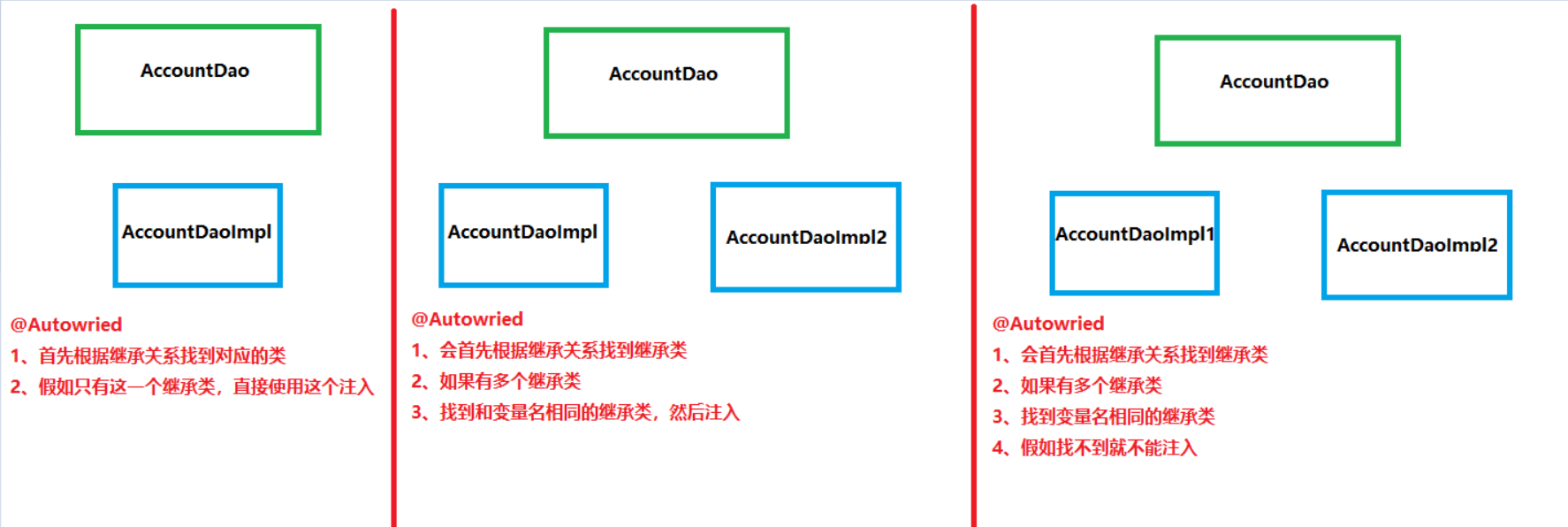
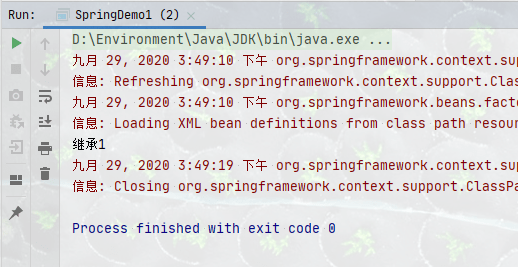
下面来进行情景一:只有一个继承类
package com.howling.Annotation.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao{
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("继承1");
}
}
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import com.howling.Annotation.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao = null;
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("bean的创建");
}
}
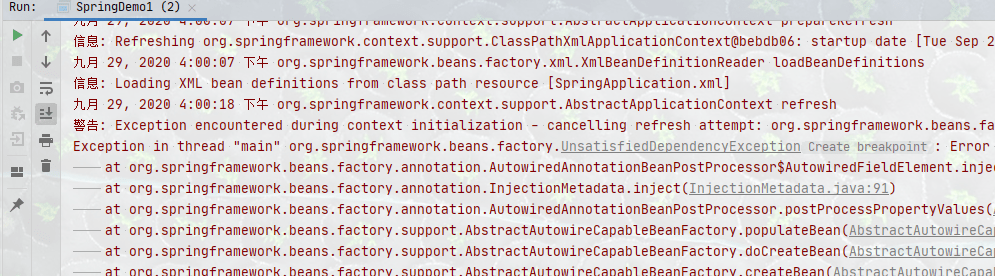
情景二:多个继承类
package com.howling.Annotation.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao{
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("继承1");
}
}
package com.howling.Annotation.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl2 implements AccountDao {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("继承2");
}
}
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import com.howling.Annotation.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao = null;
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("bean的创建");
}
}
accountDao是名字,@Autowried也会根据这个名字去找对应的类,但是很遗憾找不到,所以注入不进去 在这里要注意一件事情,两个类都要去交给Spring管理,也就是说都要加上注解,要不然白写
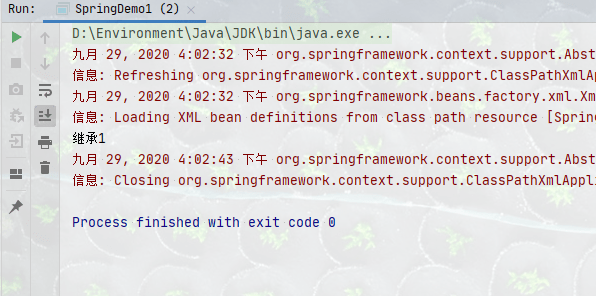
情景三:有相同的bean名字
package com.howling.Annotation.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao{
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("继承1");
}
}
package com.howling.Annotation.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl2 implements AccountDao {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("继承2");
}
}
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import com.howling.Annotation.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDaoImpl = null;
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("bean的创建");
}
}
@Qualifier
- 给类成员注入的使用要和@Autowried配合使用,目的是为了消除歧义
- 给方法参数注入可以单独使用,这里不讲,不好举例子
给类成员注入
我们之前看过@Autowried在多个继承类下要去找和属性名一致的bean的id,但是加入找不到就会报错
这个时候我们可以和@Qualifier配合,@Qualifier用于指定你要指定的bean的id
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import com.howling.Annotation.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountDaoImpl")
private AccountDao accountDao = null;
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
这个时候假如有多个值,直接会找accountDaoImpl,即使有一个叫做accountDao的也会找accountDaoImpl
@Resource
@Resource其实就是@Autowried和@Qualifier的结合体,他直接根据bean的id注入,所以bean的id是必须写的
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import com.howling.Annotation.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl")
private AccountDao accountDaoImpl2 = null;
public void saveAccount() {
accountDaoImpl2.saveAccount();
}
}
@Value
@Value注解可以给属性赋值,有几种方式:
1、直接赋值
2、使用SpEL表达式赋值
3、读取配置文件赋值
下面依次来讲解(下面以基本类型来演示,但其实你完全可以使用复杂类型)
直接赋值
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Value("18")
private Integer age;
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(age);
}
}
注意,这种方式可以直接写在属性上,有set方法也可以卸载set方法上
使用SpEL表达式赋值
package com.howling.Annotation.domain;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
private String username;
@Value("张三")
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
}
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Value("#{user.username}")
private String username;
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(username);
}
}
通过SpEL表达式来进行其他类的读取,但是注意要有get方法,它是这样的user.username—>user.getUserName() 通过get方法来读取
读取配置文件赋值
1、首先需要在Spring的配置文件上加上一句话
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 表示读取classpath下面的application.properties文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:application.properties">
</context:property-placeholder>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.howling"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
关于classpath在编译前后的对应关系我有一篇闲谈
2、application.properties文件
address=Asia/Shanghai
3、编写bean
package com.howling.Annotation.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Value("${address}")
private String address;
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(address);
}
}
下面来看一下效果
其他注解
注解概述
1、@Configuration:指定配置类,主要作用是完全摆脱xml
2、@ComponentScan:指定创建容器时要扫描的包,在前面已经讲过了
3、@Bean:放在方法上,作用是将方法的返回值作为bean对象存到IOC容器里
4、@Import:在一个配置类中引入其他的配置类
5、@PropertySource:用于指定properties文件的路径,路径是编译后的classpath下的
6、@PropertySources:下面有多个@PropertySource
@Configuration
我们之前使用注解都是首先在配置文件上声明:我要用注解了,然后采用的注解。但是这种方式始终离不开xml注解。
我们在一开始讲过的创建IOC容器的时候说过,ApplicationContext由三个实现方法,我们之前一直用的是xml的方法,现在我们要换为注解的方法:new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(配置类.class),使用这个方法就可以完全脱离xml了。
但是使用这个方法的配置就需要一个配置类,我们的配置类声明的注解为:@Configuration
下面来测试一下
1、编写配置类
package com.howling.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Configuration:加到类上,说明这个类是配置类
* @ComponentScan("com.howling"):指定注解要扫描的包,和xml中指定的是一个道理
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.howling")
public class SpringConfiguration {
}
2、编写Service
package com.howling.servlet;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("saveAccount");
}
}
3、测试
package com.howling;
import com.howling.config.SpringConfiguration;
import com.howling.servlet.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
AccountServiceImpl accountServiceImpl =
context.getBean("accountServiceImpl", AccountServiceImpl.class);
accountServiceImpl.saveAccount();
}
}
4、其他说明
我们在controller中
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);这一步已经将SpringConfiguration这个类的class字节码加载进去了,所以其实在这个类上不写@Configuration也是可以的 但是其他的情况是需要写的,比如配置类A中引用了配置类B,然后在创建的时候引入了配置类A。这个时候虽然引用的是配置类A,但是和上面不同,这里必须写上注解。 顺便说明一下,A调用B是有可能的,只需要在A中的注解改动一下:@Configuration(“要扫描的包”,”配置类2”) 为了我们的规范使用,建议不管怎么样都要加上@Configuration这个注解,但是看到没有加上注解也不要奇怪
@Import
在刚才,我们在最后说了配置类A调用配置类B是可以的,但是@Configuration(“要扫描的包”,”配置类2”),像这种方式是非常不好用的,我们有一种更好的方式,就是使用注解@Import(字节码)
使用这种方式,我们就可以在配置类A中引入配置类B,将其整合到一个配置中
package com.howling.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ConfigurationB {
}
package com.howling.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
/**
* @Configuration:加到类上,说明这个类是配置类
* @ComponentScan("com.howling"):指定注解要扫描的包,和xml中指定的是一个道理
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.howling")
@Import(ConfigurationB.class)
public class SpringConfiguration {
}
@PropertySource
关于这个注解,其实前面我们已经提了一嘴,就是可以指定properties文件的路径,只需要指定classpath下面的properties文件即可
关于classpath虽然说了很多遍但是还要再说一遍,在项目编译后java和resources目录下的文件都会到classes下面,这个classes就是我们说的classpath
举个例子
1、application.properties
address=Asia/Shanghai
2、配置类
package com.howling.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class ConfigurationB {
}
package com.howling.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.howling")
@Import(ConfigurationB.class)
public class SpringConfiguration {
}
3、service
package com.howling.servlet;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Value("${address}")
private String address;
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println(address);
}
}
4、演示
package com.howling;
import com.howling.config.SpringConfiguration;
import com.howling.servlet.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class SpringDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
AccountServiceImpl accountServiceImpl = context.getBean("accountServiceImpl", AccountServiceImpl.class);
accountServiceImpl.saveAccount();
}
}
Spring整合Junit
Junit这么厉害是因为Junit集成了main方法,Junit不管我们是否采用了什么框架,他只会执行@Test注解上的内容
所以问题来了,Junit不知道我们使用了Spring,没法注入,所以我们需要想个办法,能让Junit在单元测试的时候能够注入
我们使用的方式是替换掉Junit中内置的main方法,这样就可以实现注入了
1、导入环境
<!--替换Junit的main方法让Spring能够在单元测试中注入-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Junit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
</dependency>
当使用Spring5.x的时候,Junit必须在4.12及以上,否则会报错
2、使用注解@RunWith(SpringJunit4ClassRunner.class)替换掉main方法
3、告知Spring运行器,Spring的IOC是基于xml还是基于注解,并且说明位置
- locations:指定xml所在目录,加上classpath关键字表示在类路径下
- classes:指定注解类所在的位置
4、测试
package howling;
import com.howling.servlet.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = com.howling.config.SpringConfiguration.class)
//@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:SpringConfiguration.xml"):使用xml时
public class TestJunit {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void account(){
accountService.saveAccount();
}
}
AOP
动态代理
动态代理概述
代理:在生活中,我们遇到了很多代理,比如买电脑买手机,找售后都是找代理。代理去代理厂家的产品,厂家卖的多,代理也抽成。
在Java中也有类似的概念,回想一下反射的内容,我们就很容易理解
动态代理:和代理差不多,不过更加高级一些
1、字节码随用随创建,随用随加载
2、不修改源码的基础上对方法继承增强
3、可以分类为:基于接口的动态代理,基于子类的动态代理
基于接口的动态代理
基于接口的动态代理,由JDK提供,需要Proxy类,这里是回顾前面讲过的反射的内容,更加具体的去看反射
1、首先我们来写厂家
package com.howling.proxy;
/**
* 这里是厂家的接口,有一个方法是销售的方法
*/
public interface Producer {
public void saleProducer(float money);
}
package com.howling.proxy;
/**
* 厂家的实现
*/
public class ProducerImpl implements Producer {
/**
* 厂家进行销售
*
* @param money
*/
public void saleProducer(float money) {
System.out.println("厂家赚得:" + money + "元");
}
}
2、我们来写代理和测试
package com.howling.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* 模拟消费者进行消费
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//必须是final修饰才可以被代理
final ProducerImpl producerImpl = new ProducerImpl();
//动态代理,也就是我们模拟的代理商
Producer producer = (Producer) Proxy.newProxyInstance(producerImpl.getClass().getClassLoader(), producerImpl.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//假如当前执行的方法是saleProducer
if ("saleProducer".equals(method.getName())) {
float money = (Float) args[0];//读取参数值
//代理商进行抽成
money *= 0.8;
System.out.println("代理商抽两成的利润");
//返回代理商的方法
return method.invoke(producerImpl, money);
}
return method.invoke(method,args);
}
});
//消费者去代理商那里进行购买,花了一万块
producer.saleProducer(10000f);
}
}
3、下面来讲一下几个参数
Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader,Class[],InvocationHandler)
1、类加载器,被代理的类的类加载器 2、字节码数组,这个的作用是让代理对象和被代理的对象有相同的方法,所以需要被代理对象的父级接口 3、提供增强代码,使用InvocationHandler(proxy,method,args) 1、proxy:当前被代理对象的引用,也就是InvocationHandler本身 2、method:当前方法的名称 3、args:当前执行的方法中的参数数组
基于子类的动态代理
基于子类的动态代理,我们需要一个外部的包CGLIB,他是一个功能强,性能高的代码生成包。
主要是为没有实现接口的类实现代理,算是对JDK代理的一个很好的补充。
1、依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>2.1_3</version>
</dependency>
2、编写生产者,这里就不需要写接口了
package com.howling.cglib;
/**
* 生产者
*/
public class Producer {
/**
* 实现销售方法
* @param money
*/
public void saleProducer(float money){
System.out.println("销售"+money+"...");
}
}
3、编写消费者
package com.howling.cglib;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* 模拟消费者
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Producer producer = new Producer();
Producer proxyProducer = (Producer) Enhancer.create(producer.getClass(), new MethodInterceptor() {
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
if ("saleProducer".equals(method.getName())){
float money = (Float) objects[0];
return method.invoke(producer,money*0.8f);
}
return null;
}
});
proxyProducer.saleProducer(10000f);
}
}
4、结果
AOP概述
1、AOP:面向切面编程,通过预编译和运行期动态代理实现程序功能统一维护的技术
2、AOP是OOP(面向对象)的延伸,是软件开发的一个热点
3、AOP是Spring中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生模型
4、利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使业务逻辑的各个部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性
优势:减少重复代码,提高开发效率,维护方便
AOP有以下术语
1、连接点:JoinPoint:所谓连接点是那些被拦截到的点,在Spring中是方法,因为Spring只支持方法类型的连接点
也就是我们所说的要增强的方法
2、切入点:Pointcut:所为切入点是指我们要对哪些连接点进行拦截的定义
在事务中被增强的方法就叫做切入点 注意连接点和切入点的区别,连接点指的就是原来定义的方法,切入点指的是我们已经明确进行拦截的方法
3、通知:Active:拦截到连接点之后要做的事情
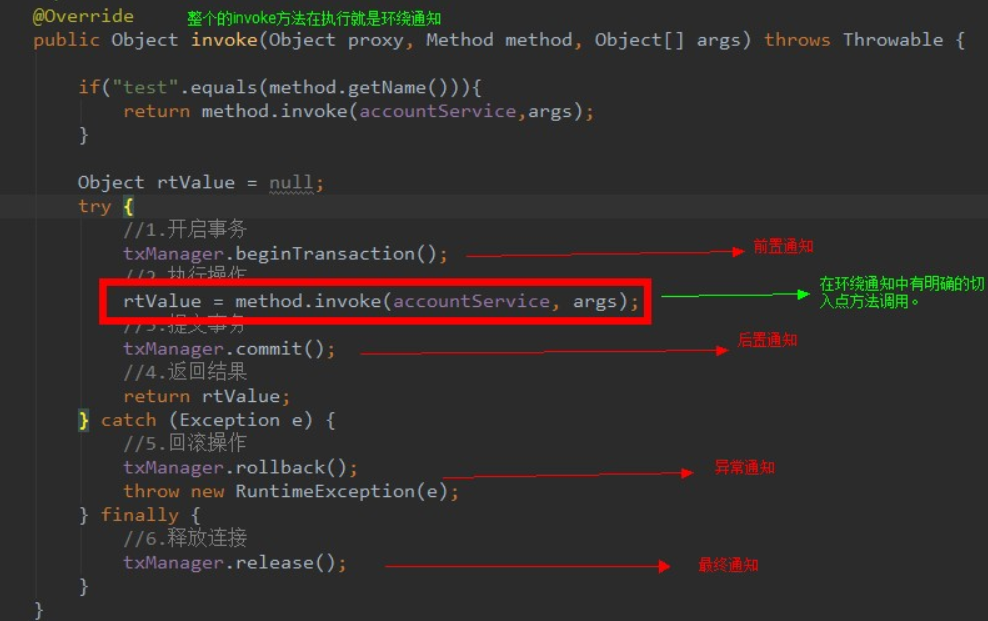
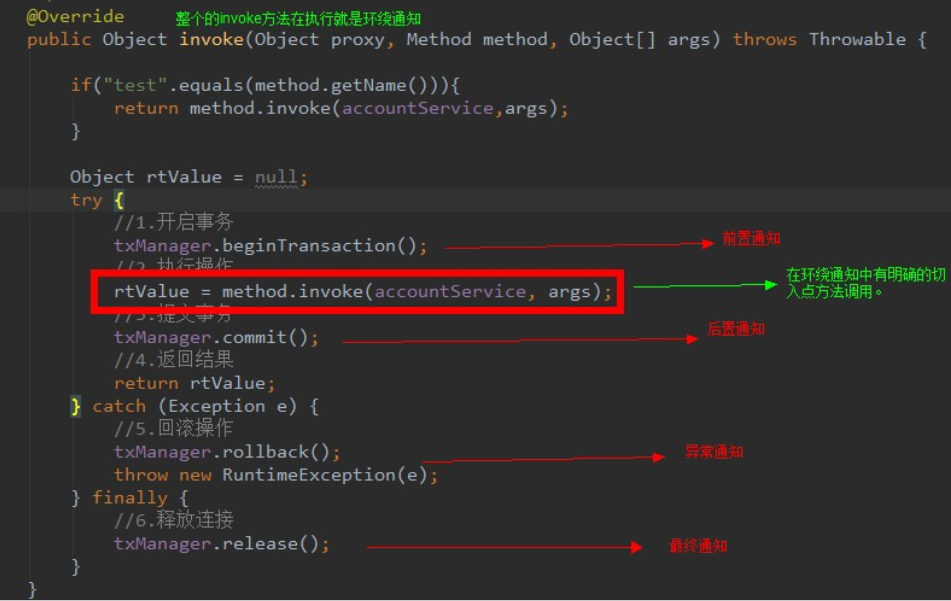
通知也就是指的增强,通知分为:前置通知,后置通知,异常通知,最终通知 现在想一下我们在JDK动态代理中的的invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//假如当前执行的方法是saleProducer
if ("saleProducer".equals(method.getName())) {
float money = (Float) args[0];//读取参数值
//代理商进行抽成
money *= 0.8;
System.out.println("代理商抽两成的利润");
//返回代理商的方法
return method.invoke(producerImpl, money);
}
return method.invoke(method,args);
}
method.invoke(producerImpl, money)这段代码也就是我们最终要执行的方法,也就是我们的切入点,看好这个切入点 1、在切入点之前的代码的都是前置通知 2、在切入点之后的都是后置通知 3、出现异常,被捕获的都叫做异常通知 4、不论如何都要执行的就是最终通知 5、整个invoke方法就是环绕通知
如图:
4、引介:Introduction:引介是一种特殊的通知,在不改变类代码的前提下,引介可以在运行期为类动态地添加一些方法或者成员变量
5、目标对象:Target:代理的目标对象
6、织入:Weaving:指把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程,Spring使用动态代理,而AspectJ使用编译器和类装载器
7、代理:Proxy:一个类被织入之后,就会产生一个结果代理类
8、切面:Aspect:切入点+通知=切面
AOP其实非常简单,我们只需要
1、编写核心业务代码
2、抽取公共代码,制作为通知
3、在配置文件中声明切入点和通知的关系(切面)
基于XML的AOP配置
快速起步
1、pom.xml
<!--Spring-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--用于解析切入点表达式-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.7</version>
</dependency>
2、service
package com.howling.aop.service;
/**
* 对账户的操作
*/
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 模拟保存操作
*/
void saveAccount();
/**
* 模拟更新操作
*
* @param i
*/
void updateAccount(int i);
/**
* 模拟删除操作
*
* @return
*/
int deleteAccount();
}
package com.howling.aop.service;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("用户已保存");
}
public void updateAccount(int i) {
System.out.println("用户已更新" + i);
}
public int deleteAccount() {
System.out.println("用户已删除");
return 0;
}
}
3、通知
package com.howling.aop.utils;
/**
* 模拟日志记录的工具类,一会就会将此方法进行织入
*/
public class Logger {
public void printLogger() {
System.out.println("日志已经开始记录...");
}
}
4、xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注意,上面是新的规范-->
<!-- 首先将我们的Target交给Spring管理 -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.howling.aop.service.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--将Logger也交给Spring管理-->
<bean id="logger" class="com.howling.aop.utils.Logger"></bean>
<!--配置AOP-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切面,引用通知方法-->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger">
<!--配置通知的方式,指定被增强的方法-->
<aop:before method="printLogger" pointcut="execution(public void com.howling.aop.service.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount())">
</aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<!--我们需要使用AspectJ来解析切入点表达式,所以我们需要AspectJ的支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
</beans>
5、测试
package com.howling.aop;
import com.howling.aop.service.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AOPTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
AccountServiceImpl accountServiceImpl = context.getBean("accountService", AccountServiceImpl.class);
accountServiceImpl.saveAccount();
}
}
切入点表达式
之前我们在快速起步的时候曾经见过切入点表达式
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger">
<aop:before method="printLogger" pointcut="execution(public void com.howling.aop.service.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount())">
</aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
pointcut="execution(public void com.howling.aop.service.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount())"
准确的说这并不是切入点表达式,只是指定了这个方法的访问修饰符,返回值,全类名,参数等等
这样的写法在开发中肯定是不可以的,接下来就是切入点表达式
1、访问修饰符可以省略
void com.howling.aop.service.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount()
2、所有的返回值可以使用星号来表示
* com.howling.aop.service.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount()
3、包名可以使用*来代替,但是有几级包就要写几个*
* *.*.*.*.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount()
4、如果有多个子包,可以使用..代替当前包和子包
* *..AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount()
5、类名可以使用*来代替
* *..*.saveAccount()
6、方法名可以使用*来代替
* *..*.*
7、基本类型的参数可以直接写名称,引用类型需要全类名
* *..*.*(int,java.lang.String)
8、参数可以使用*来代替,但是必须要有参数才能够使用*
* *..*.*(*)
9、参数可以使用..来代替有参数或者无参数,参数可以为任意类型
* *..*.*(..)
所以最终可以简化为
* *..*.*(..)
注意:我们在开发过程中不建议使用全通配的表示方式,建议是切换到业务层底下再使用通配
* com.howling.aop.service.*.*(..)
四种常用的通知类型
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 异常通知
- 最终通知
- Logger
package com.bean.utils;
/**
* 模拟用于记录日志的工具类,里面提供了公共代码
*/
public class Logger {
/**
* 前置通知
*/
public void beforePrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的前置通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
/**
* 后置通知通知
*/
public void afterReturningPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的后置通知开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
/**
* 异常通知
*/
public void afterThrowsPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的异常通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
public void afterPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的最终通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
}
- bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注意,上面是新的规范-->
<!--配置spring的IOC,把service对象配置进来
我们想要对service方法进行增强,使service中执行任意一个方法前都执行一个日志
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--我们有这个通知类,通知类就是记录日志,我们也交给spring-->
<bean id="logger" class="com.bean.utils.Logger"></bean>
<!--配置AOP-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切面,引用通知方法-->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger">
<!--配置前置通知-->
<aop:before method="beforePrintLog" pointcut="execution(* com.bean.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:before>
<!--配置后置通知-->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturningPrintLog" pointcut="execution(* com.bean.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:after-returning>
<!--<!–异常通知–>-->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowsPrintLog" pointcut="execution(* com.bean.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:after-throwing>
<!--<!–最终通知–>-->
<aop:after method="afterPrintLog" pointcut="execution(* com.bean.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- AOPTest
package com.bean.test;
import com.bean.service.IAccountService;
import com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AOPTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService accountService = (IAccountService) context.getBean("accountService");
accountService.saveAccount();
}
}
使用标签配置切入点表达式
<aop:pointcut></<aop:pointcut>
- id
- expression
此标签可以写在
<aop:aspect></aop:aspect>里面,那么只能在这里面使用,再来一个切面要重新配 所以我们把它挪到外面挪到外面之后可能发现会报错,所以注意这个东西必须在aop:aspect之前,因为这是约束。 不然就会报错,一定要注意
- bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注意,上面是新的规范-->
<!--配置spring的IOC,把service对象配置进来
我们想要对service方法进行增强,使service中执行任意一个方法前都执行一个日志
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--我们有这个通知类,通知类就是记录日志,我们也交给spring-->
<bean id="logger" class="com.bean.utils.Logger"></bean>
<!--配置AOP-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切面表达式-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* com.bean.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:pointcut>
<!--配置切面,引用通知方法-->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger">
<!--配置前置通知,引用切面表达式-->
<aop:before method="beforePrintLog" pointcut-ref="pointCut" ></aop:before>
<!--配置后置通知,引用切面表达式-->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturningPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:after-returning>
<!--异常通知,引用切面表达式;-->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowsPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:after-throwing>
<!--最终通知,引用切面表达式-->
<aop:after method="afterPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
Spring中的环绕通知
- 环绕通知
这个是我们前面讲的基于动态代理的通知
- 我们发现环绕通知就是这整个方法
- 里面包含着
- 前置通知
- 方法调用
- 后置通知
- 异常通知
- 最终通知
所以环绕通知在
Spring中的地位非同一般首先我们需要注意几件事:
- 既然环绕通知包含了这些东西,那么也就代表着在
spring中可以在环绕通知中配置其他的通知- 既然上面的动态代理图片中有明确的方法调用,所以在环绕通知中也应该进行方法调用,要不然就不会进行方法执行
掌握了以上几件事,我们开始敲代码
- bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="logger" class="com.bean.utils.Logger"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* com.bean.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:pointcut>
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger">
<!--只配置了一个环绕通知,环绕通知的标签就是<aop:around></aop:around>-->
<aop:around method="aroudnPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- Logger
package com.bean.utils;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
/**
* 模拟用于记录日志的工具类,里面提供了公共代码
*/
public class Logger {
/*
* 我们刚才在事项里面说到
* 1. 环绕通知必须要进行方法调用,否则方法不会执行
* 2. 观看之前我们写的基于动态代理执行的方法,我们也可以进行其他四种通知的调用
* 3. 我们也要有返回值
*
* 既然要进行方法调用,就要有参数
* ProceedingJoinPoint就是参数,用于获取方法
* - proceed():参数下面有一个方法proceed(),这个就相当于明确调用切入点方法
* - getArgs():用于获取切入点点方法的参数
* */
public Object aroudnPrintLog(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object returnValue = null;
try {
System.out.println("这叫前置通知");
returnValue = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs()); //这叫切入点方法调用
System.out.println("这叫后置通知");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {//注意这里使用的是Throwable,因为Exception拦不住它
System.out.println("这叫异常通知");
throwable.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("这叫最终通知");
}
return returnValue;
}
}
基于注解的AOP配置
快速起步
1、需要更改一下约束条件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
</beans>
2、加入bean对象并且配置注解
- service
package com.bean.service.impl;
import com.bean.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存方法执行了");
}
public void updateAccount(int i) {
System.out.println("更新方法执行了"+i);
}
public int deleteAccount() {
System.out.println("删除方法执行了");
return 0;
}
}
- Logger
package com.bean.utils;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 模拟用于记录日志的工具类,里面提供了公共代码
*/
@Component//加入bean
@Aspect//注意,这里制定了这个Logger类是一个切面类
public class Logger {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.bean.service.impl.*.*(..))")//配置切面表达式,id就是方法名称
public void AspectPointCut(){};
/**
* 前置通知
*/
@Before("AspectPointCut()")//指定前置通知,注意看好包,配置了切面表达式,注意一定要加括号
public void beforePrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的前置通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
/**
* 后置通知通知
*/
@AfterReturning("AspectPointCut()")//指定后置通知,配置切面表达式,注意加括号
public void afterReturningPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的后置通知开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
/**
* 异常通知
*/
@AfterThrowing("AspectPointCut()")//指定异常通知,配置切面表达式,注意加括号
public void afterThrowsPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的异常通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@After("AspectPointCut()")//指定最终通知,配置切面表达式,注意加括号
public void afterPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的最终通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
//环绕通知
@Around("AspectPointCut()")//指定环绕通知,配置切面表达式,注意加括号
public Object aroudnPrintLog(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object returnValue = null;
try {
System.out.println("这叫前置通知");
returnValue = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs()); //这叫切入点方法调用
System.out.println("这叫后置通知");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {//注意这里使用的是Throwable,因为Exception拦不住它
System.out.println("这叫异常通知");
throwable.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("这叫最终通知");
}
return returnValue;
}
}
- AOPTest
package com.bean.test;
import com.bean.service.IAccountService;
import com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AOPTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService accountService = (IAccountService) context.getBean("accountServiceImpl");
accountService.saveAccount();
}
}
AOP注解中的问题,实际开发中应该怎么做
其实虽然注解好用,但是我不得不告诉你,Spring在完全使用注解方式执行AOP的时候会出现问题,就是顺序调用问题,比如下面的
Logger类中的前置通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。
保存方法执行了
Logger类中的最终通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。
Logger类中的后置通知开始记录日志了。。。。。。
- 这是不使用环绕通知的时候进行的测试,代码写的没有问题,但是调用顺序出错了,其实是
Spring有问题 - 调用顺序为:前置通知—>最终通知—>后置通知
- 所以假如使用注解,可能会出现问题
所以在这个方法下,采用半注解半代码的形式来配置(注解环绕通知)或者使用xml的形式,便可以避免调用顺序出错的问题
使用纯注解
1、首先看一下前面的不使用xml的时候使用的配置类
2、然后在配置类上加上一个@EnableAspectJAutoProxy来配置好切面类
3、下面是一个例子
- java.config.SpringConfiguration
package config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.bean")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SpringConfiguration {
}
- java.com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
package com.bean.service.impl;
import com.bean.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存方法执行了");
}
public void updateAccount(int i) {
System.out.println("更新方法执行了"+i);
}
public int deleteAccount() {
System.out.println("删除方法执行了");
return 0;
}
}
- java.com.bean.utils.Logger
package com.bean.utils;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 模拟用于记录日志的工具类,里面提供了公共代码
*/
@Component//加入bean
@Aspect//注意,这里制定了这个Logger类是一个切面类
public class Logger {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.bean.service.impl.*.*(..))")//配置切面表达式,id就是方法名称
public void AspectPointCut(){};
/**
* 前置通知
*/
@Before("AspectPointCut()")//指定前置通知,注意看好包,配置了切面表达式,注意一定要加括号
public void beforePrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的前置通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
/**
* 后置通知通知
*/
@AfterReturning("AspectPointCut()")//指定后置通知,配置切面表达式,注意加括号
public void afterReturningPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的后置通知开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
/**
* 异常通知
*/
@AfterThrowing("AspectPointCut()")//指定异常通知,配置切面表达式,注意加括号
public void afterThrowsPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的异常通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@After("AspectPointCut()")//指定最终通知,配置切面表达式,注意加括号
public void afterPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的最终通知方法开始记录日志了。。。。。。");
}
//环绕通知
@Around("AspectPointCut()")//指定环绕通知,配置切面表达式,注意加括号
public Object aroudnPrintLog(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object returnValue = null;
try {
System.out.println("这叫前置通知");
returnValue = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs()); //这叫切入点方法调用
System.out.println("这叫后置通知");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {//注意这里使用的是Throwable,因为Exception拦不住它
System.out.println("这叫异常通知");
throwable.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("这叫最终通知");
}
return returnValue;
}
}
- test.com.bean.test.AOPTest
package com.bean.test;
import com.bean.service.IAccountService;
import com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import config.SpringConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AOPTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
IAccountService accountService = (IAccountService) context.getBean("accountServiceImpl");
accountService.saveAccount();
}
}
Spring中的JDBCTemplate
基本概述
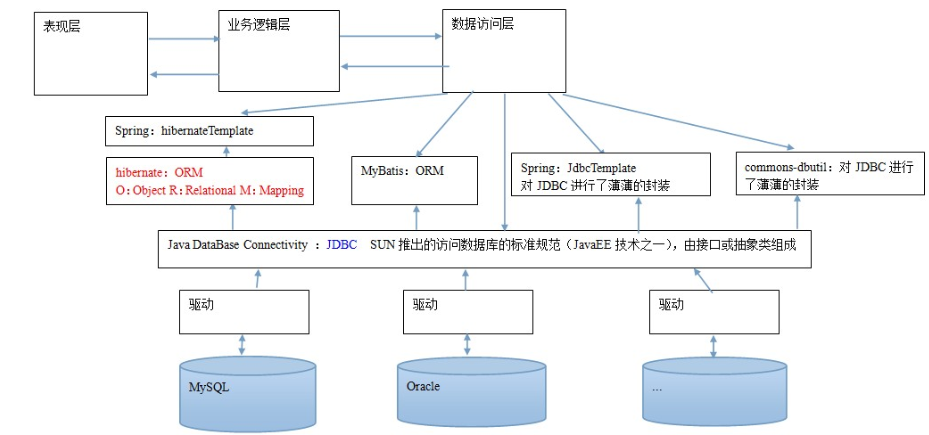
上面这张图是持久层总图,我们今天的主角是
JdbcTemplate,可以看到对JDBC进行了薄薄封装它是 spring 框架中提供的一个对象,是对原始 Jdbc API 对象的简单封装。spring 框架为我们提供了很多的操作模板类。
- 操作关系型数据的:
JdbcTemplateHibernateTemplate- 操作 nosql 数据库的:
RedisTemplate- 操作消息队列的:
JmsTemplate- 我们今天的主角在
spring-jdbc-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar中- 还需要导入一个
spring-tx-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar(它是和事务相关的)。- 不可避免地要导入数据库驱动
JDBCTemplate的作用
与数据库进行交互,实现对表的CRUD
如何创建该对象
原始方式
1、依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.bean</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringAOP</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2、表
create table account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40),
money float
)character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;
insert into account(name,money) values('aaa',1000);
insert into account(name,money) values('bbb',1000);
insert into account(name,money) values('ccc',1000);
3、实体类
package com.bean.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Float money;
public Account() {
}
public Account(Integer id, String name, Float money) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
4、使用JDBCTemplate
package com.bean.jdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
public class JdbcTemplateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//准备数据源:JdbcTemplate内置数据源
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
//JdbcTemplate
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
//设置数据源
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
jdbcTemplate.execute("select * from account");
}
}
使用Spring来创建
XML创建
1、bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置jdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
2、JDBCTemplateDemo
package com.bean.jdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
public class JdbcTemplateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate)context.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into account (name,money) values ('dd',1000)");
}
}
注解创建
1、注解配置
- config.SpringConfiguration
package config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.bean")
public class SpringConfiguration {
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplateBean(){
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSourceBean());
}
@Bean
public DriverManagerDataSource dataSourceBean(){
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
}
- JDBCTemplateDemo
package com.bean.jdbcTemplate;
import config.SpringConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
public class JdbcTemplateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate)context.getBean("jdbcTemplateBean");
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into account (name,money) values ('dd',1000)");
}
}
注解不能和
xml一起,否则报错,前面已经讲过了
JDBCTemplate的CRUD
一个Demo
- JDBCTemplateDemo
package com.bean.jdbcTemplate;
import com.bean.domain.Account;
import config.SpringConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import java.util.List;
public class JdbcTemplateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate)context.getBean("jdbcTemplateBean");
// 增加:使用update,没啥好说的的,注意类型是float
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account (name,money) values(?,?)","new Account",1000f);
// 删除:使用update,没啥好说的的,注意类型是float
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from account where id=?",5);
// 更新:没啥好说的的,注意类型是float
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?","update test",100f,6);
// 查询
// 查询所有:查询所有,使用query方法,spring使用了这个BeanPropertyRowMapper封装进去了类型,然后直接封装进去
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class));
for (Account account : accounts) {
System.out.println(account);
}
// 查询一个:这里也可以使用查询出List的,不过输出第0位就可以了,注意这里使用的构造函数中的最后一个参数为可变参数,只有在jdk1.5之后才能使用
List<Account> account = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id=?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), 7);
System.out.println(account.isEmpty()?"无参数":account.get(0));
// 查询一行一列(聚合函数):这里需要的就是一个类型,当查到的时候会自动转变为这个类型,不过一般推荐Long,因为假如int范围不够了呢
//注意这里使用的是queryForObject
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(id) from account",Long.class);
//加参数:jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(id) from account where money>?",Long.class,1500);
}
}
下面是实际开发中的写法,结合
Spring使用
使用XML配置
1、bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--首先配置dao-->
<bean id="accountDaoImpl" class="com.bean.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplateBean"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置JdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplateBean" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
2、Account
package com.bean.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Float money;
public Account() {
}
public Account(Integer id, String name, Float money) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
- AccountDaoImpl
package com.bean.dao.impl;
import com.bean.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.bean.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.util.List;
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
public Account findById(Integer id) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id=?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), id);
return accounts.isEmpty()?null:accounts.get(0);
}
public Account findByName(String name) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * form account where name=?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), name);
//假如没有查到,返回null
if (accounts.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
//假如有多个,返回异常
if (accounts.size()>1)
{
throw new RuntimeException("结果不唯一");
}
//否则返回唯一一个
return accounts.get(0);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney());
}
}
- JDBCTemplateDemo
package com.bean.jdbcTemplate;
import com.bean.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.bean.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.bean.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class JdbcTemplateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountDao accountDao = (IAccountDao) context.getBean("accountDaoImpl");
System.out.println(accountDao.findById(7));
}
}
使用注解配置
- SpringConfiguration
package config;
import com.bean.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.bean")
public class SpringConfiguration {
// 声明dao
@Bean
public AccountDaoImpl accountDao(){
return new AccountDaoImpl();
}
// 声明JdbcTemplate
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(){
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource());
}
// 声明数据源
@Bean
public DriverManagerDataSource dataSource(){
DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
driverManagerDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring");
driverManagerDataSource.setUsername("root");
driverManagerDataSource.setPassword("root");
return driverManagerDataSource;
}
}
- Account
package com.bean.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Float money;
public Account() {
}
public Account(Integer id, String name, Float money) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
- AccountDaoImpl
package com.bean.dao.impl;
import com.bean.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.bean.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
@Component
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
// public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
//// this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
//// }
public Account findById(Integer id) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id=?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), id);
return accounts.isEmpty()?null:accounts.get(0);
}
public Account findByName(String name) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * form account where name=?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), name);
//假如没有查到,返回null
if (accounts.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
//假如有多个,返回异常
if (accounts.size()>1)
{
throw new RuntimeException("结果不唯一");
}
//否则返回唯一一个
return accounts.get(0);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney());
}
}
- JDBCTemplateDemo
package com.bean.jdbcTemplate;
import com.bean.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.bean.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.bean.domain.Account;
import config.SpringConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class JdbcTemplateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
IAccountDao accountDao = (IAccountDao) context.getBean("accountDaoImpl");
System.out.println(accountDao.findById(7));
}
}
Spring中的事务控制
Spring控制我们需要明确的
1、javaEE体系分层开发,事务处理位于业务层,Spring提供了分层设计业务层的事务处理解决方案
2、Spring框架为我们提供了一组事务控制的接口,具体后面介绍,这组接口是在spring-tx-5.0.2.RELEASSE.jar中
3、Spring中的事务控制都是基于AOP的,它既可以使用编程的方式进行实现,也可以使用配置的方式进行实现
Spring中事务控制的API介绍
1、依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2、事务管理器
PlatformTransacionManager管理器,这是个事务接口,包含三个具体操作
- 获取事务状态信息:
TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) - 提交事务:
void commit(TransactionStatus status) - 回滚事务:
void rollback(TransactionStatus status)
实现类
DataSourceTransactionManager- 包:
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager - 使用
Spring JDBC或者iBatis进行持久化数据时使用
- 包:
HibernateTransactionManager- 包:
org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager - 使用
Hibernate版本进行持久化数据时使用
- 包:
3、事务的定义信息
TransactionDefinition:事物的定义信息对象,里面有如下方法
String getName():获取事务对象名称int getIsolationLevel():获取事务隔离级别ISOLATION_DEFAULT:默认级别,归属下列某一种ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED:可以读取未提交数据ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED:只能读取已提交数据,解决脏读问题(Oracle默认级别)ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ:是否读取其他事务提交修改后的数据,解决不可重复度的问题(MYSQL默认)ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE:是否读取其他事务提交添加后的数据,解决幻影读问题
int getPropagetionBehavior():获取事务传播行为REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务,加入到这个事务(默认),增删改的事务SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,加入当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务),只有查询才能用的事务MANDATORY:使用当前事务,如果当前没有事务,抛出异常REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,就把当前事务挂起NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起NEVER:以非事务方式运行,加入当前存在事务,抛出异常NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行;如果当前没有事务,则执行REQUIRED类似的操作
int getTimeout():获取事务超时时间:默认值为-1(没有超时时间)。假如有,则以秒为单位进行设置boolean isReadOnly():获取事务是否只读:建议查询时设置为只读
4、事务的状态信息
TransactionStatus接口描述了某个时间点上事务的状态信息,包含有六个基本操作
- 刷新事务:
void flush() - 获取是否是存在存储点:
boolean hasSavepoint()
事务是以节点来提交的,每一个节点都是一个储存点,当事务回滚的时候,只会回滚到上个节点,而不是从头来
- 获取事务是否完成:
boolean isCompleted() - 获取事务是否为新的事务:
boolean isNewTransaction() - 获取事务是否回滚:
boolean isRollbackOnly() - 设置事务回滚:
void setRollbackOnly()
环境准备
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.bean</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringAOP</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
基于XML的事务控制
1、配置事务管理器:注入DataSource
2、配置事务通知
- 注入事务的约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
- 配置事务管理器的bean对象:包为:
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager - 使用标签
<tx:advice></tx:advice>标签配置事务通知id:配置唯一标识transaction-manager:事务管理器
- 在
<tx:advice></tx:advice>内部配置事务的属性<tx:attributes></tx:attributes><tx:method>name指定service中的方法isolation
用于指定事物的隔离级别,默认值为
DEFAULT,表示使用数据库的默认隔离级别propagetion- 用于指定事物的传播行为,默认值为
REQUIRED,表示一定会有事务,这是增删改的选择 - 查询可以选择为
SUPPORTS read-only
指定事物是否只读,只有查询方法才能设置为
true,默认值为false,表示读写timeout
用于指定事物的超时时间,默认值为-1,表示永不超时,如果指定数值则以秒为单位
rollback-for
用于指定一个异常,碰到这个异常则回滚,其他异常不会滚。 没有默认值,表示任何异常都回滚
no-rollback-for
用于指定一个异常,碰到这个异常不回滚,其他异常都回滚。 没有默认值,表示任何异常都回滚
3、配置AOP的通用切入点表达式
4、建立事务通知和切入点表达式的对应关系:使用<aop:advisor></aop:advicor>
- bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="accountService" class="com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.bean.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<!--上面是配的bean对象,下面开始编写事务-->
<!--首先要有一个事务管理器,包为:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
事务管理器内要配置dataSource
-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--现在配置事务的状态
id 为唯一标识
transaction-manager为配置事务管理器
-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!--配置事务属性-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--
<tx:method></tx:method>
name:要配置的方法名称,比如我们这里用AOP配置的全都是service.impl包下的,所以
* :匹配全部的方法(虽然也就那么一个transer方法)
find*:将来假如有方法为find开头的时候,匹配折现方法
优先级:find* 高于 *
isolation:指定事物的隔离级别,默认值为DEFAULT,表示数据库的默认隔离级别
read-only:是否只读
propagation:指定事物的传播行为,默认为REQUIRED,为增删改的,查询可以为SUPPORTS
timeout:指定超时时间
rollback-for:用于指定一个异常,发生了此异常则回滚,其他异常不回滚。默认值无,表示任何异常都回滚。
no-rollback-for:指定一个异常,发生此异常不回滚,其余异常全都回滚。默认值无,表示任何异常都回滚。
-->
<tx:method name="*" read-only="false" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true" propagation="SUPPORTS"></tx:method>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* com.bean.service.impl.*.*(..))"></aop:pointcut>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
</beans>
- AccountDaoImpl
package com.bean.dao.impl;
import com.bean.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.bean.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.util.List;
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
public Account findById(Integer id) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id=?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),id);
return accounts.isEmpty()?null:accounts.get(0);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
}
- AccountServiceImpl
package com.bean.service.impl;
import com.bean.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.bean.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.bean.domain.Account;
import com.bean.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void transfer(Integer Transferer, Integer Payee, Float money) {
System.out.println("transer");
Account accountMinus = accountDao.findById(1);
Account accountAdd = accountDao.findById(2);
accountMinus.setMoney(accountMinus.getMoney()-money);
accountAdd.setMoney(accountAdd.getMoney()+money);
accountDao.updateAccount(accountMinus);
// int i = 1/0;
accountDao.updateAccount(accountAdd);
}
}
- 测试
import com.bean.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.bean.service.IAccountService;
import com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
@SpringJUnitConfig
public class TransactionTest {
@Test
public void Test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IAccountService accountService = (IAccountService) context.getBean("accountService");
accountService.transfer(1,2,100F);
}
}
- 效果
效果就是:
- 当没有报错时:转账正常执行
- 当出现错误时:回滚
基于注解的事务控制
1、导入关于context的名称空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
2、配置事务管理器
3、开启Spring对注解的支持,使用<tx:annotation-drivern/>
4、在需要事务支持的时候使用@Transactional注解
- bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--首先配置一下spring创建容器时要扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.bean"></context:component-scan>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--
使用注解进行事务控制的配置
1. 配置事务管理器
2. 开启spring对注解事务的支持:使用<tx:annotation-driven/>,里面配置事务管理器
3. 在需要事务支持的时候使用@Transactional注解
-->
<!--事务管理器还得留下-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--开启spring对注解事务的支持-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
</beans>
- AccountDaoImpl
package com.bean.dao.impl;
import com.bean.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.bean.domain.Account;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Component
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public Account findById(Integer id) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id=?",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class),id);
return accounts.isEmpty()?null:accounts.get(0);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
}
- AccountServiceImpl
package com.bean.service.impl;
import com.bean.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.bean.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.bean.domain.Account;
import com.bean.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS,readOnly = true) //这里是配置事务控制的注解的,配置的全局为只读型的配置
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
//这里单独配置,配置可写型的配置
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly = false)
public void transfer(Integer Transferer, Integer Payee, Float money) {
System.out.println("transer");
Account accountMinus = accountDao.findById(1);
Account accountAdd = accountDao.findById(2);
accountMinus.setMoney(accountMinus.getMoney()-money);
accountAdd.setMoney(accountAdd.getMoney()+money);
accountDao.updateAccount(accountMinus);
// int i = 1/0;
accountDao.updateAccount(accountAdd);
}
}
- 测试
import com.bean.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.bean.service.IAccountService;
import com.bean.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:bean.xml")
public class TransactionTest {
@Autowired
private IAccountService accountService;
@Test
public void Test(){
accountService.transfer(1,2,100F);
}
}
事务回滚规则
默认只接受不受检查(Error和RuntimeException),但是可以利用rollbackFor的参数(类的class数组)指定遇到这个异常来回滚
可以通过noRollbackFor来定义参数(类的class数组)来指定遇到异常不回滚
Spring5新特性介绍
与JDK相关的升级
1、JDK版本要求
spring5.0在2017-9发布了GA(通用)版本,该版本基于jdk8编写的,所以jdk8之前的版本无法使用 同时tomcat要求8.5以上 我们使用jdk8构建工程,可以降低版本编译,但是不能使用jdk8以下版本构建工程IDE同时需要更新,eclipse 4.7.2之前的就甭想了
2、升级说明
1、基于JDK8的反射增强 2、@NonNu11注解和@Nullable注解的使用 用@Nullable和@NotNull注解来显示表明可为空的参数和以及返回值。 这样就够在编译的时候理空值而不是在运行时抛出NullPointerExceptions。 3、日志记录方面 Spring Framework 5.0带来了Commons Logging 桥接模块的封装,它被叫做spring-jcl 而不是标准的Commons Logging。 当然,无需任何额外的桥接,新版本也会对Log4j2.x,SLF4J,JUL( java.util. logging) 进行自动检测。
核心容器的升级
Spring Framework 5.0现在支持候选组件索引作为类路径扫描的替代方案。
该功能已经在类路径扫描器中添加,以简化添加候选组件标识的步骤。
应用程序构建任务可以定义当前项目自己的META-INE/spring.components文件。
在编译时,源模型是自包含的,JPA实体和Spring组件是已被标记的。
从索引读取实体而不是扫描类路径对于小于200 个类的小型项目是没有明显差异,但对大型项目影响较大。
加载组件索引开销更低。因此,随着类数的增加,索引读取的启动时间将保持不变。
加载组件索引的耗费是廉价的。因此当类的数量不断增长,加上构建索引的启动时间仍然可以维持一一个常数,
不过对于组件扫描而言,启动时间则会有明显的增长。
这个对于我们处于大型spring项目的开发者所意味着的,是应用程序的启动时间将被大大缩减。
虽然20或者30秒钟看似没什么,但如果每天要这样登上好几百次,加起来就够你受的了。使用了组件索引的话,就能帮
助你每天过的更加高效。
你可以在Spring的Jira上了解更多关于组件索引的相关信息。
JetBarins Kotlin语言支持
这个不多赘述
响应式编程风格
此次spring发行版本的一个激动人心的特性就是新的响应式堆栈WEB框架。
这个堆栈完全的响应阻塞,适合于事件循环风格的处理,可以进行少量线程的扩展。
Junit5支持
完全支持JUnit 5 Jupiter, 所以可以使用JUnit 5来编写测试以及扩展。
此外还提供了一个编程以及扩展模型,Jupiter子项目提供了一个测试引擎来在Spring上运行基于 Jupiter的测试。
另外,spring Framework 5还提供了在Spring TestContext Framework 中进行并行测试的扩展。
针对响应式编程模型,spring-test 现在还引入了支持spring webFlux的WebTestclient 集成测试的支持,类似于MockMvc,并不需要一一个运行着的服务端。
使用一个模拟的请求或者响应,WebTestClient就可以直接绑定到webFlux服务端设施。
你可以在这里找到这个激动人心的TestContext 框架所带来的增强功能的完整列表。
依赖库的更新
终止支持的类库:
- Portlet .
- Velocity .
- JasperReports .
- XMLBeans .
- JDO.
- Guava .
支持的类库:
- Jackson 2.6+
- EhCache 2.10+ 1 3.0 GA
- Hibernate 5.0+
- JDBC 4.0+
- XmlUnit 2 .x+
- OkHttp 3.X+
- Netty 4.1+