export function render(element: React$Element<any>,container: Container,callback: ?Function,) {return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(null,element,container,false,callback,);}
render函数中调用了legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer
function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>, //nullchildren: ReactNodeList,container: Container, //rootforceHydrate: boolean, //falsecallback: ?Function,) {// 初次调用, root还未初始化, 会进入此分支//1. 创建ReactDOMRoot对象, 初始化react应用环境let root = container._reactRootContainer;let fiberRoot: FiberRoot;if (!root) {// Initial mountconsole.log('render no root');root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(container,forceHydrate,);fiberRoot = root;if (typeof callback === 'function') {const originalCallback = callback;callback = function() {const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);originalCallback.call(instance);};}// Initial mount should not be batched.// 2. 更新容器// 初次渲染是非批量更新,可以保证 ( 更新效率与用户体验 )// 比如初次渲染希望更快的速速让用户看到 ui// - 函数签名:flushSyncWithoutWarningIfAlreadyRendering(fn) => fn()flushSyncWithoutWarningIfAlreadyRendering(() => {updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);});} else {console.log('render have root')// root已经初始化, 二次调用render会进入// 1. 获取ReactDOMRoot对象fiberRoot = root;if (typeof callback === 'function') {const originalCallback = callback;callback = function() {const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);originalCallback.call(instance);};}// Update// 2. 调用更新updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);}return getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);}
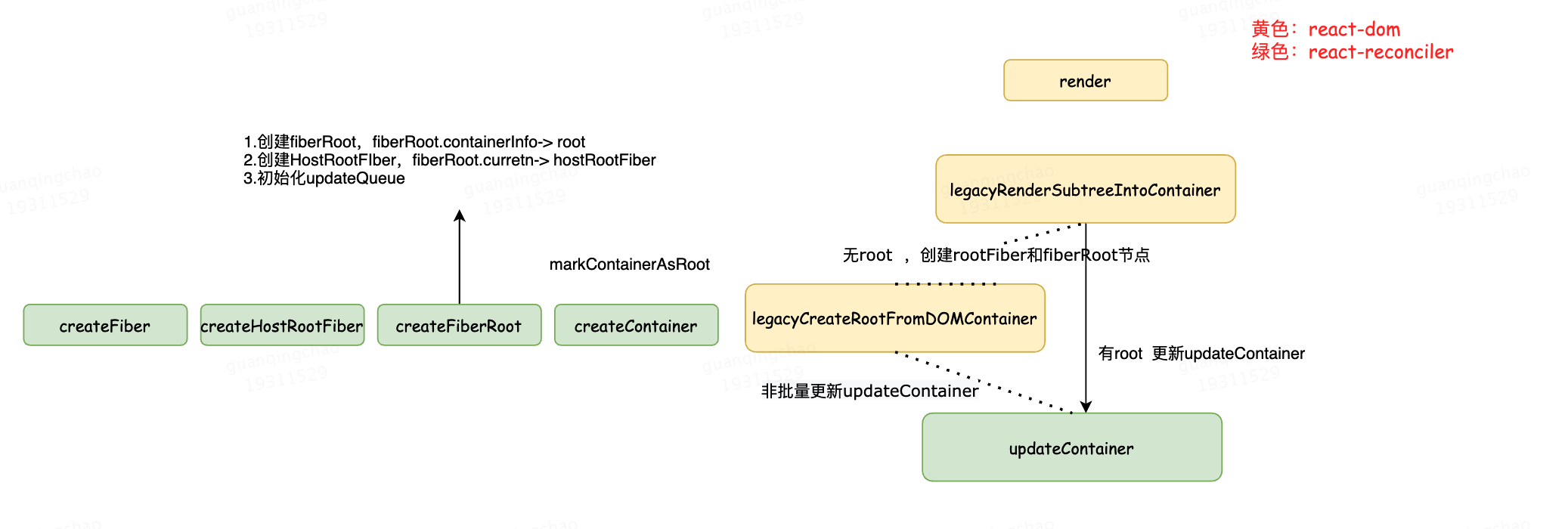
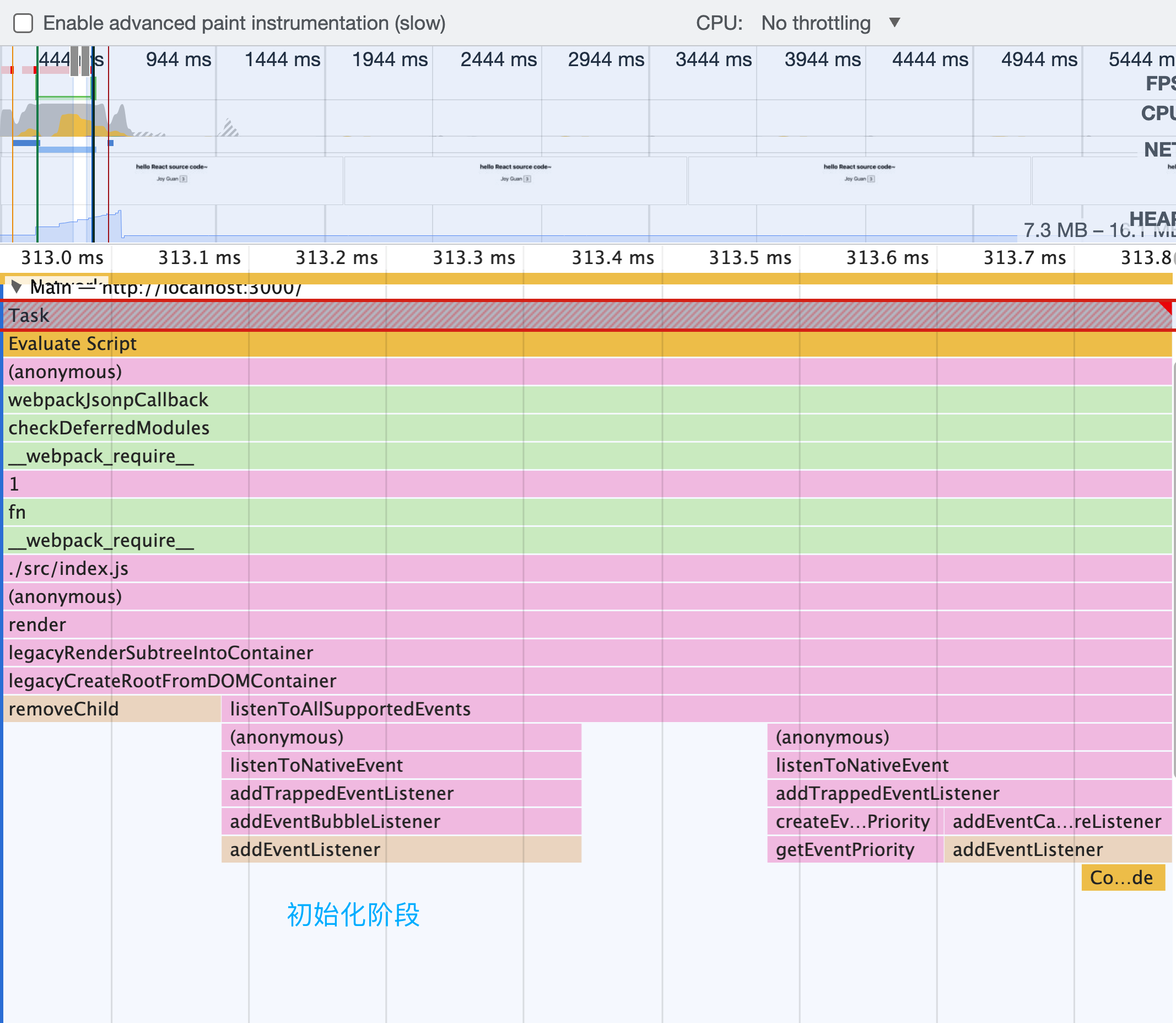
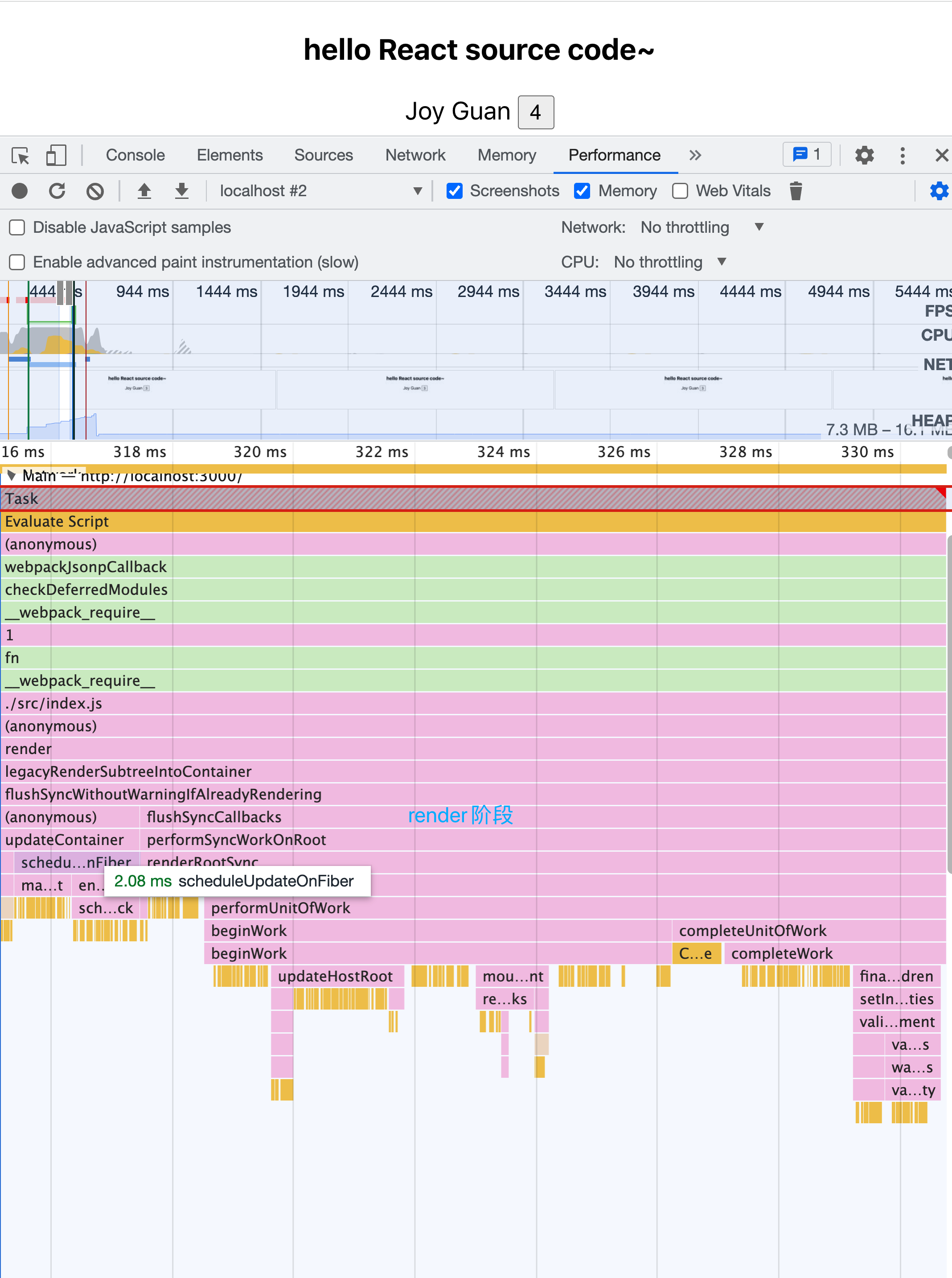
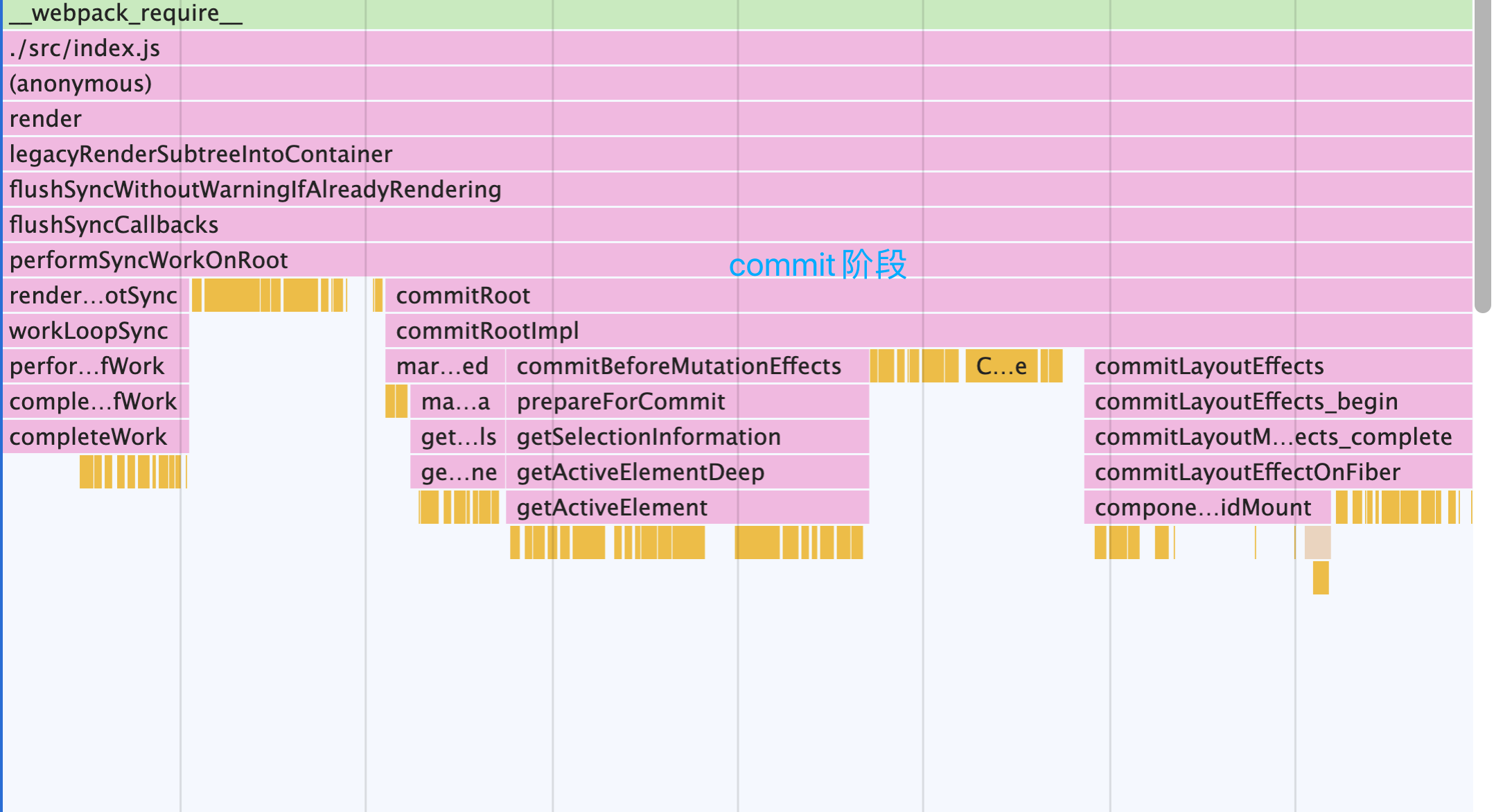
render之后的调用过程如上图所示,
判断是否有root节点,创建rootFiber,FiberRoot等,节点之间的关系如下图所示: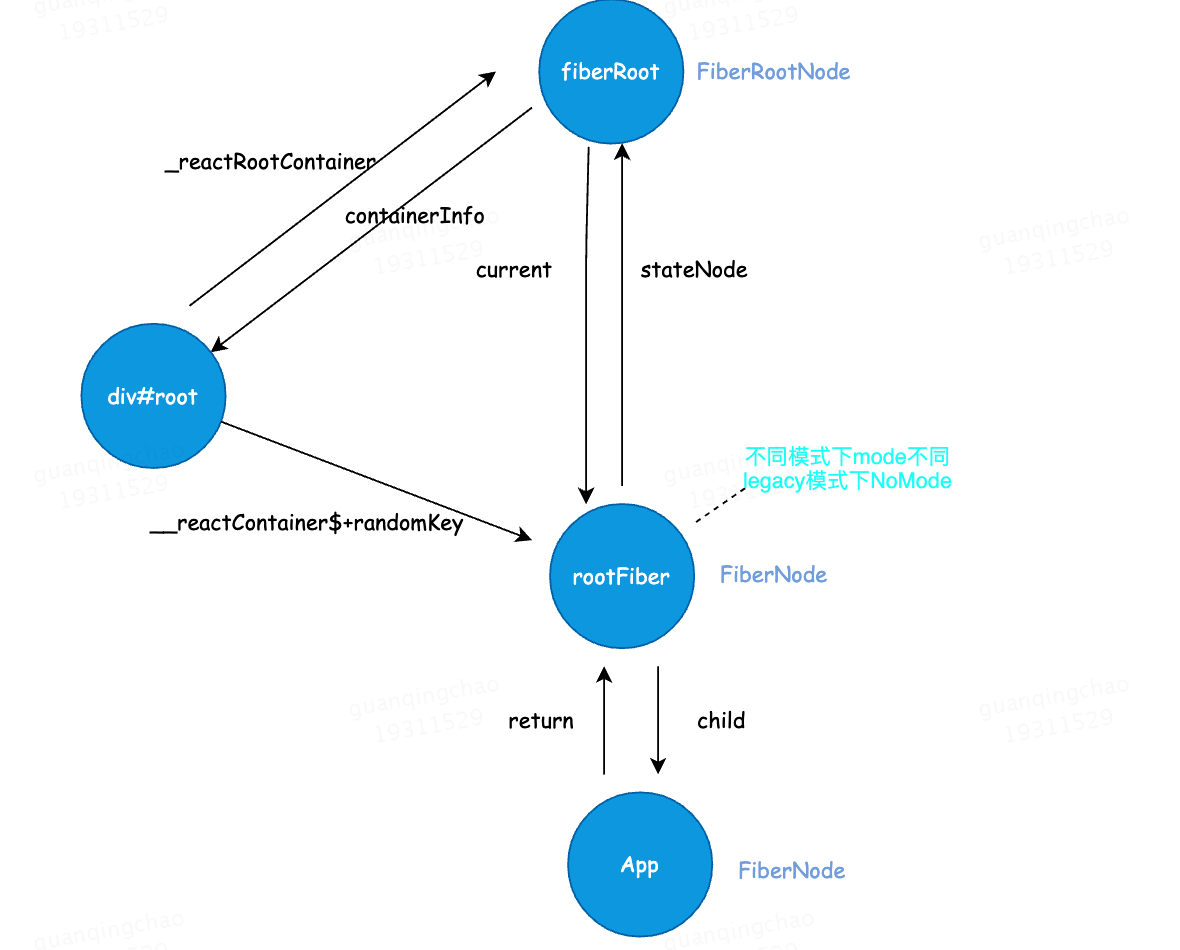
updateContainer函数位于react-reconciler包中, 它串联了react-dom与react-reconciler.
此处暂时不深入分析updateContainer函数的具体功能, 需要关注其最后调用了scheduleUpdateOnFiber.
在前文reconciler 运作流程中, 重点分析过scheduleUpdateOnFiber是输入阶段的入口函数.
所以到此为止, 通过调用react-dom包的api(如: ReactDOM.render), react内部经过一系列运转, 完成了初始化, 并且进入了reconciler 运作流程的第一个阶段.

