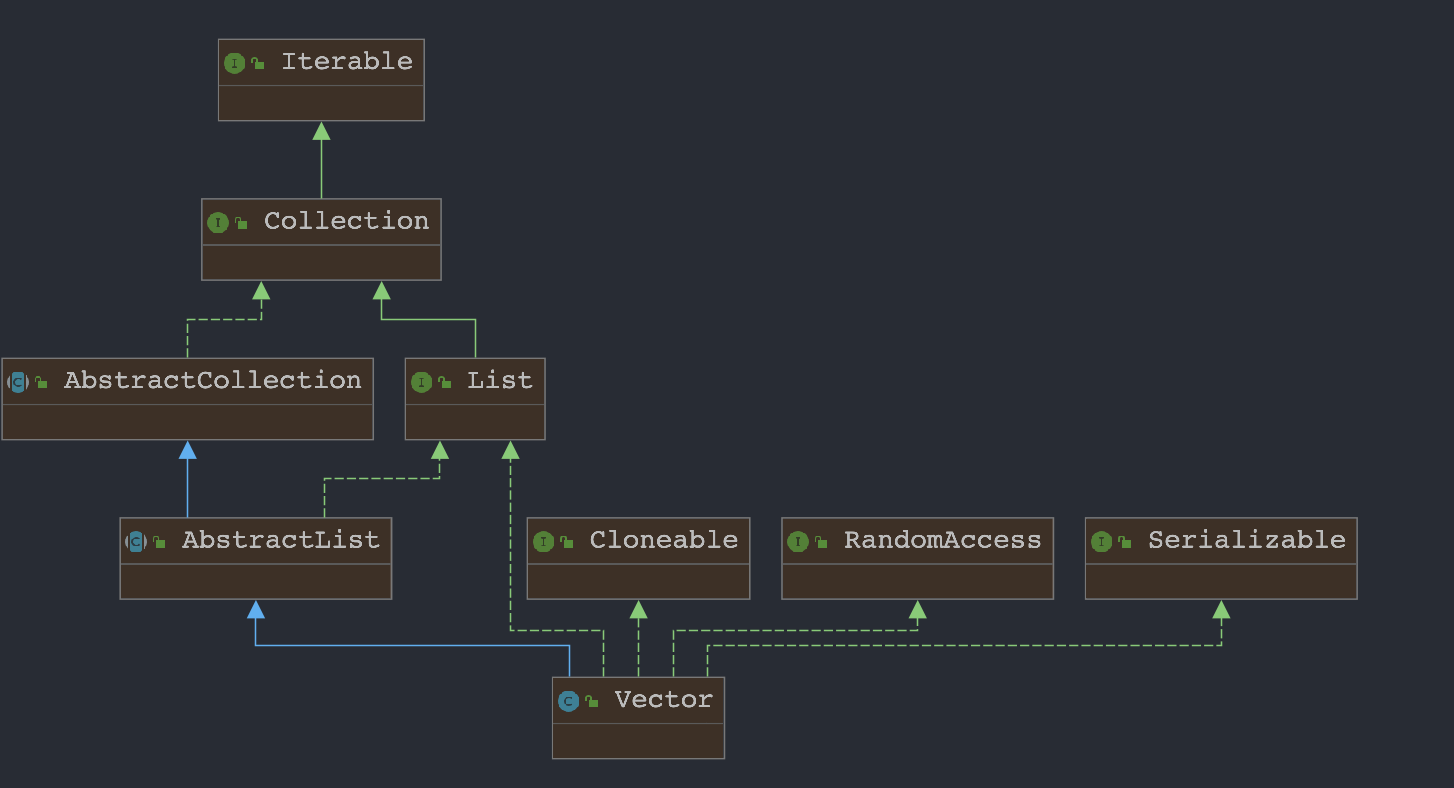
public class Vector<E>extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{ }
1. 成员变量
// 空对象 ,同ArrayListprotected Object[] elementData;// 数组容量, 同ArrayListprotected int elementCount;// Vector的增长系数,默认为0,即扩容2倍protected int capacityIncrement;
- 与ArrayList 中的成员变量相比,Vector 少了两个空数组对象: EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 和 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
因此,Vector 与 ArrayList 中的第一个不同点就是,成员变量不一致。
2. 构造方法
```java //默认构造函数 public Vector() {
this(10);
}
//带初始容量构造函数 public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
//带初始容量和增长系数的构造函数 public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); elementCount = elementData.length; // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class); }
JDK 1.2 之后提出了将Collection 转换成 Vector 的构造函数,实际操作就是通过Arrays.copyOf() 拷贝一份Collection 数组中的内容到Vector 对象中。这里会有可能抛出 **NullPointerException**。<a name="Ak3n8"></a>## 3. add方法Vector 在添加元素的方法上面,比ArrayList 中多了一个方法。Vector 支持的add 方法有:- add(E e)- addElement(E obj)[多出来的方法]- add(int i , E element)- addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)- addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)<a name="vxH4g"></a>## 3.1 addElement(E)```javapublic synchronized void addElement(E obj) {modCount++;ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);elementData[elementCount++] = obj;}
从注释上面来看,这个方法就是 跟 add(E)(List接口重写的方法) 方法是有着一样的功能的。该方法没有返回值。
3.2 add(E e)方法过程的变化
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {modCount++;ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);elementData[elementCount++] = e;return true;}// 确认容器大小private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {// 需要的容量比实际的容量大,需要扩容if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}// 扩容private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;// 变化int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (minCapacity < 0) // overflowthrow new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?Integer.MAX_VALUE :MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}
- Vector 对整个add 方法都上锁了(添加了 synchronized 修饰),其实我们可以理解,在添加元素的过程主要包括以下几个操作:
- ensureCapacityHelper():确认容器大小
- grow():如果有需要,进行容器扩展
- elementData[elementCount++] = obj:设值
- 为了避免多线程情况下,在 ensureCapacityHelper 容量不需要拓展的情况下,其他线程刚好将数组填满了,这时候就会出现 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ,因此对整个方法上锁,就可以避免这种情况出现。
- 在确认容器大小这一步,少了 ArrayList#ensureCapacityInternal 这一步骤,主要也是源于 Vector 在构造时创建好默认数组大小,不会出现ArrayList中默认空数组的情况。
扩容grow的机制改变:Vector支持自定义增长系数。如果为空,则默认的基础上增加一倍,变为原来的两倍(ArrayList是1.5倍)
3.3 add在指定位置上添加元素
add(int index, E element)
public void add(int index, E element) {insertElementAt(element, index);}public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {modCount++;if (index > elementCount) {throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index+ " > " + elementCount);}ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);elementData[index] = obj;elementCount++;}
与ArrayList无太大差异,抛出的异常不同:
ArrayList:IndexOutOfBoundsException
Vector:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
4. remove
与ArrayList类似
remove(int location) 重写List方法
- remove(Object object)
- removeAll(Collection<?> collection)
- removeAllElements()
- removeElement(Object object)
- removeElementAt(int location) 自定义方法
- removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
- clear()
4.1 remove(int location) & removeElementAt(int location)
```java public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
}modCount++;if (index >= elementCount) {throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +elementCount);}else if (index < 0) {throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);}int j = elementCount - index - 1;if (j > 0) {System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);}elementCount--;elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
public synchronized E remove(int index) { modCount++; if (index >= elementCount) throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index); E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its workreturn oldValue;}
remove 是重写了父类的操作,而removeElement 则是Vector 中自定义的方法,没有返回值。ArrayList 中提供了 fastRemove() 方法,与其有着同样的效果,不过removeElement 作用范围为public。<a name="OvX8f"></a>## 4.2 remove(Object object) & removeElement(Object object)```javapublic boolean remove(Object o) {return removeElement(o);}public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {modCount++;int i = indexOf(obj);if (i >= 0) {removeElementAt(i);return true;}return false;}
remove(Object object) 实际内部调用的就是 removeElement(Object object) 。删除操作首先找到 对象的索引(与ArrayList 中的remmove(E)一样),然后调用removeElementAt(i)(ArrayList 中调用 fastRemove()方法)进行删除。
5. 线程安全
Vector 中的每一个独立方法都是线程安全的,因为它有着 synchronized 进行修饰。但是如果遇到一些比较复杂组合的操作,并且多个线程需要依靠 vector 进行相关的判断,那么这种时候就不是线程安全的了。
if (vector.size() > 0) {System.out.println(vector.get(0));}
Vector 判断完 size()>0 之后,另一线程如果同时清空vector 对象,那么这时候就会出现异常。因此,在复合操作的情况下,Vector 并不是线程安全的。

