数据源
- 数据源即data source,提供数据的原始媒介。常见数据源有:数据库、文件、其他程序、内存、网络连接、IO设备。
数据源分为:源设备、目标设备。源设备为程序提供数据,一般对应输入流;目标设备是程序数据的目的地,一般对应输出流。
流
流是抽象、动态的概念,是一连串连续动态的数据集合。
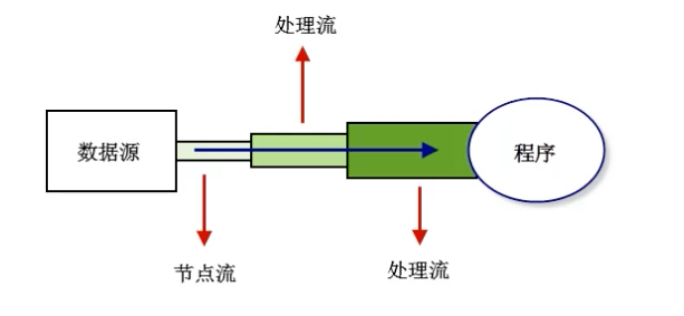
- 对于输入流。数据源就像水箱,流像水管中流动的水流,程序是最终的用户。通过流stream将数据源source中的数据information输送到程序program中。
- 对于输出流,目标数据源就是目的地dest,我们通过流将程序中的数据输送到目的数据源中。
-
流概念细分
流的方向
输入流:数据流向是数据源到程序(InputStream、Reader结尾的流)
输出流:数据流向是程序到目的地(OutputStream、Writer结尾的流)
处理的数据单元
字节流:以字节为单位获取数据,命名上以Stream结尾的流一般是字节流,如FileInputStream、FileOutputStream。
字符流:以字符为单位获取数据,命名上以Reader/Writer结尾的流一般是字符流,如FileReader、FileWriter,一般用于处理txt文本文件
处理对象
节点流:可以直接从数据源或目的地读写数据,如FileInputStream、FileReader、DataInputStream等
- 处理流:不直接连接到数据或目的地,是“处理其他流的流”。通过对其他流的处理提高程序的性能,如BufferedInputStream、BufferedReader等
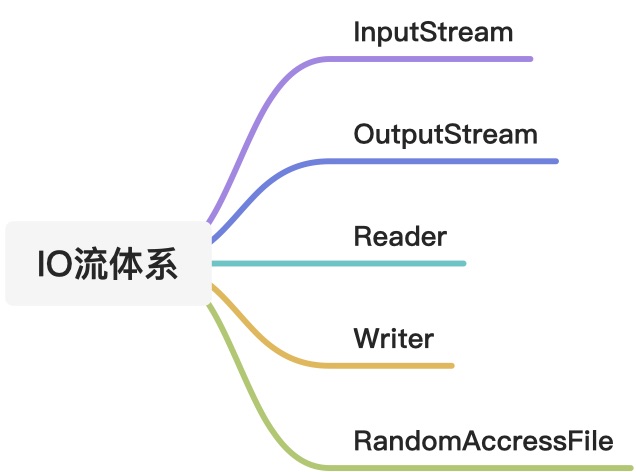
IO流的体系
文件字符流
文件字节流可以处理所有的文件,但是字节流不能很好的处理Unicode字符,经常出现乱码情况。所以处理文本文件,一般可以使用文件字符流,它以字符为单位进行操作。
FileReader fr = new FileReader("/d.txt");FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("/d_copy.txt")
缓冲字节流
Java缓冲流本身不具备IO流的读取与写入功能,只是在别的流(节点流或其他处理流)上加上缓冲功能以提高效率,就像是把别的流包装起来一样,因此缓冲流是一种处理流(包装流)。
- 当对文件或者其他数据源进行频繁的读写操作时,效率比较低,这时如果使用缓冲流就能够更高效的读写信息。因为缓冲流是先将数据缓存起来,然后当缓存区存满后或者手动刷新时再一次性的读取到程序或写入目的地,在IO操作时加上缓冲流可以提高性能。
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream这两个流是缓冲字节流,通过内部缓存数组来提高操作流的效率。
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/img.png");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/img_copy.png");BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);BufferedOutStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
缓冲字符流
BufferedReader/BufferedWriter增加了缓存机制,大大提高了读写文本文件的效率,同时提供了更方便的按行读取的方法:readLine();处理文本时,我们一般可以使用缓冲字符流。 ```java try( BufferReader br = new BufferReader(new FileReader(“/d.txt”));
BufferWriter bw = new BufferWriter(new FileWriter("/d2.txt"));
){
String tempString = “”; while((tempString = br.readLine) != null){
bw.write(tempString);bw.newLine();
} }
<a name="hDORV"></a>### 字节数组流- ByteArrayInputSream和ByteArrayOutputStream经常用在需要流和数组之间转化的情况,与FileInputStream把文件当作数据源不同,ByteArrayInputStream把内存中的某个字节数组对象当作数据源```javaByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream("abcdef".getBytes[])
数据流
- 将基本数据类型与字符串类型作为数据源,从而允许程序以与机器无关的方式从底层输入输出流中操作java基本数据类型与字符串类型。
- DataInputStream和DataOutputStream提供了可以存取与机器无关的所有java基础类型数据(如int、double、String等)
- DataInputStream和DataOutputStream时处理流,可以对其他节点流和处理流进行包装,使得更灵活、高效 ```java try(DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(“/data.txt”))){ dos.writeChar(‘a’); dos.writeInt(10); dos.writeDouble(Math.random()); dos.writeBoolean(true); dos.writeUTF(“程序员”); dos.flush(); // 手动刷新缓冲区,流中数据写入文件中 }catch…
try(DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileIntputStream(“/data.txt”))){ // 读取数据与写入数据顺序保持一致,否则无法正确读取 dis.readChar(‘a’); dis.readInt(10); dis.readDouble(Math.random()); dis.readBoolean(true); dis.readUTF(); }catch…
<a name="rBwtv"></a>### 对象流和序列化/反序列化- ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream是以“对象”为数据源,但是必须将传输的对象进行序列话与反序列化操作。- 需要序列化的对象,需要实现java.io.Serializable(标记接口)- 对象序列化的作用有- 持久化:把对象的字节序列永久的保存在硬盘上,通常存放在一个文件中,比如休眠的实现,以后服务器session管理,hibernate将对象持久化实现- 网络通信:在网络上传送对象的字节序列。比如服务器之间的数据通信、对象传递。<a name="L3vDt"></a>### - static属性不参与序列化,对象中的某些属性如果不想被序列化,不能使用static,用**transient**修饰```javapublic class User implements java.io.Serializable{private int id;private String uname;transient private String pwd;// constructor...// getter\setter...}class Test{public static void main(String[] agrs){writeObj();readObj();}public static void writeObj(){try(ObjectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("/obj.txt"))){ArrayList<User> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new User(1001,"bob","123"));list.add(new User(1002,"boo","231"));list.add(new User(1003,"bbo","321"));oos.writeObject(list);oos.flush();}catch...}public static void readObj(){try(ObjectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("/obj.txt"))){ArrayList<User> list = (ArrayList)ois.readObject;for(User u:list){System.out.println(u.getId()...)}// 但是密码时空的,不参与序列化}catch...}}
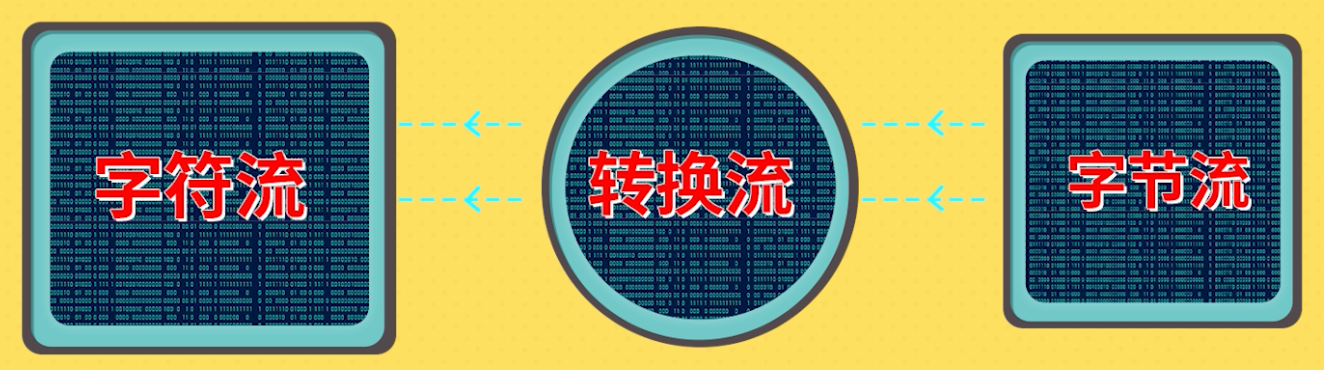
转换流
InputStreamReader/OutputStreamWriter用来实现将字节流转化成字符流
try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));){String str = br.readLine();while(!"exit".equals(str)){bw.write("键盘输入," + str);bw.newLine();bw.flush();str = br.readLine();}}
随意访问文件流
RandomAccessFile可以实现
分别使用try-catch-finally、try-with-resource两种结构写经典的io字节流程序 ```java package bosoftware;
import java.io.*;
public class test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { readFile(); writeFile(); copyFile(“/Users/bomb/LearningSpace/JavaBasic/Practise/files/sinopec.jpeg”,”/Users/bomb/LearningSpace/JavaBasic/Practise/files/sinopec_copy.jpeg”); }
public static void readFile() {FileInputStream fis = null;try {fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/bomb/LearningSpace/JavaBasic/Practise/files/a.txt");int temp = 0;StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();while ((temp = fis.read()) != -1) {sb.append((char)temp);}System.out.println(sb);} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if (fis != null) {fis.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public static void writeFile() {try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/bomb/LearningSpace/JavaBasic/Practise/files/b.txt")) {fos.write("fuck java".getBytes());} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void copyFile(String srcpath,String destpath) {try ( FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcpath);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destpath)) {
// int temp = 0; // while ((temp = fis.read()) != -1) { // fos.write(temp); // } byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; while ((fis.read(buffer)) != -1) { fos.write(buffer); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
}
<a name="XDjkO"></a># Apache IO包<a name="vuV3c"></a>## 装饰器模式构建IO流体系- 装饰器模式是GOF23种设计模式中较为常用的一种模式。它可以实现对原有类的包装和修饰,使新类具有更强的功能。- 处理流是用装饰器模式实现的<a name="REmUo"></a>## apche commons的IO类- [https://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/](https://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/)```javapackage com.de;import org.apache.commons.io.*;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileFilter;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.net.MalformedURLException;import java.net.URL;import java.util.List;public class TestApacheIOUtils {public static void main(String[] args) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){sb.append(Math.random()+"\n");}writeFile(sb.toString());readFile();readURL();copyFile();}public static void writeFile(String sb) {try {FileUtils.write(new File("/Users/bomb/LearningSpace/JavaBasic/Practise/files/c.txt"), sb, "gbk");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void readFile(){try {List<String> content= FileUtils.readLines(new File("/Users/bomb/LearningSpace/JavaBasic/Practise/files/c.txt"),"gbk");for (String temp:content) {System.out.println(temp);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void copyFile(){File srcFile = new File("/Users/bomb/LearningSpace/JavaBasic/Practise/files/c.txt");File destFile = new File("/Users/bomb/LearningSpace/JavaBasic/Practise/files/d.txt");try {FileUtils.copyFile(srcFile,destFile);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void copyDirectory() {File dir1 = new File("/文件夹1");File dir2 = new File("/文件夹2");try {FileUtils.copyDirectory(dir1, dir2, new FileFilter() {@Overridepublic boolean accept(File pathname) {if (pathname.isDirectory() || pathname.getName().endsWith("png")) {return true;} else {return false;}}});} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void readURL(){try {URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");InputStream is = url.openStream();String s = IOUtils.toString(is,"UTF-8");System.out.println(s);} catch (MalformedURLException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}