1. http不同版本的差异
http是基于TCP链接实现的,一次完整的http请求包括三次握手、请求和响应、四次挥手三个部分。根据http版本的不同,一个完整的http链接可以实现不同数量的http请求。
| http版本 | 连接数 |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | 一个TCP链接只能完成一次请求,不支持长连接 |
| 1.1 | 一个TCP链接可以顺序的完成多个请求,一个链接不支持并发式访问。需要多个链接才能并发。 |
| 2.0 | 一个TCP链接可以异步完成多个请求。 |
Nginx是对链接和请求都可以进行限制,不同版本的http协议中,限制后的效果可能不同。
2. limit_conn_module
2.1. 指令
2.1.1. limit_conn_zone
Syntax: limit_conn_zone key zone=name:size ;Default: CloseContext: http
2.1.2. limit_conn
Syntax: limit_conn zone number ;Default: CloseContext: http,server,location
2.1.3. limit_conn_log_level
Syntax: limit_conn_log_level info|notice|warn|error ;Default: ErrorContext: http,sever,location
2.2. 说明
- limit_conn_zone
一般服务器做链接限制的时候,一般使用 $binary_remote_addr 而不是 $remote_addr 作为key , 后者是不定长(7-15个字节),前者固定4个字节。
针对size的设置: 在32位系统中,使用$binary_remote_addr或$remote_addr占用32或64字节,在64位系统中占用64个字节。因此1M空间在32位平台中最多存储:1 1024 1024 / 32 = 32768 个活动链接;在64位平台最多存储: 1 1024 1024 / 64 = 16384 个活动链接。
如果size被耗尽,服务器对所有后续请求均返回503错误码。
如果需要针对虚拟主机的总连接数进行设置,可以使用 limit_conn_zone $server_name zone=server_limit:10m; 并在server模块中引用。而且limit_conn_zone针对remote_addr和server_name可以同时使用。
- limit_conn
如果请求超过限制,则返回给客户端503。
该指令限制的并不是单个remote_addr与服务器创建的总连接数,而是限制了阻塞状态的TCP连接数量。
2.3. 案例
2.3.1. 使用ab命令压测
机器配置 | centos 7.4 | server | 192.168.1.81 | | —- | —- | —- | | centos 6.10 | client | 192.168.1.50 |
Nginx配置
[root@centos-81 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user nginx;worker_processes 1;error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;pid /var/run/nginx.pid;events {worker_connections 1024;}http {include /etc/nginx/mime.types;limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:1m;default_type application/octet-stream;log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;sendfile on;#tcp_nopush on;keepalive_timeout 5;#gzip on;include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;}
[root@centos-81 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/localhost.conf
server {listen 80;server_name localhost;limit_conn addr 10;location / {root /usr/share/nginx/html;index index.html index.htm;}location ~ /gt[a-z]+ {proxy_pass http://www.jsmlr.gov.cn ;}error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;location = /50x.html {root /usr/share/nginx/html;}}
- 压测
[root@centos-50 ~]# ab -n 100 -c 10 http://192.168.1.81/index.htm
Concurrency Level: 10Time taken for tests: 0.038 secondsComplete requests: 100Failed requests: 0Write errors: 0Total transferred: 2424636 bytesHTML transferred: 2400800 bytesRequests per second: 2631.79 [#/sec] (mean)Time per request: 3.800 [ms] (mean)Time per request: 0.380 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)Transfer rate: 62315.67 [Kbytes/sec] received
[root@centos-81 ~]# netstat -anput | grep 192.168.1.50 | wc -l
100
- 实验结果
在实验前的预期中,客户端与服务端之间建立的连接数量被限制在10个(limit_conn addr 10),因此应该测试结束后,建立的总连接数是10个。但是实际结果确实不多不少的100个连接。因此可以判断Nginx限制的并不是客户端与服务端建立的总连接数。
需要设计更慢的请求来测试当前的流控参数。
2.3.2. 使用较慢的网页进行测试
- Nginx配置
[root@centos-81 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user nginx;worker_processes 1;error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;pid /var/run/nginx.pid;events {worker_connections 1024;}http {include /etc/nginx/mime.types;limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:1m;default_type application/octet-stream;log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;sendfile on;#tcp_nopush on;keepalive_timeout 5;#gzip on;include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;}
[root@centos-81 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/localhost.conf ## 主页中存在部分反向代理的内容,需要请求外部网站,速度较慢。
server {listen 80;server_name localhost;limit_conn addr 5;limit_conn vhost 10000;location / {root /usr/share/nginx/html;index index.html index.htm;}location ~ /gt[a-z]+ {proxy_pass http://www.jsmlr.gov.cn ;}error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;location = /50x.html {root /usr/share/nginx/html;}}
- 使用浏览器测试

部分页面内容异常,使用开发者模式能看到返回预期状态码 503。错误日志中也反映了异常: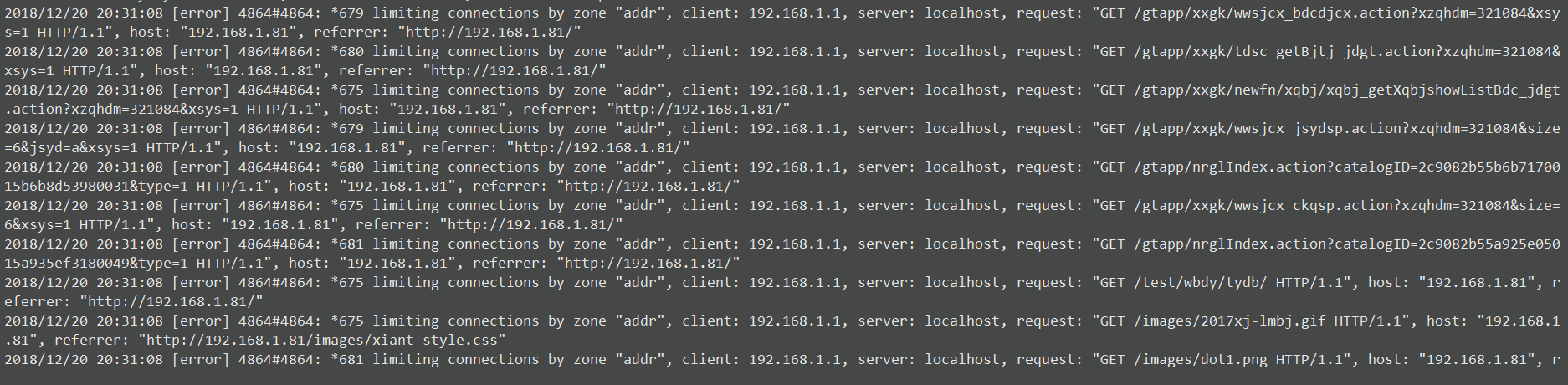
- 修改日志格式,并抓包验证
[root@centos-81 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
log_format main '$remote_addr|$remote_port|$status|$time_local|$request ''$body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
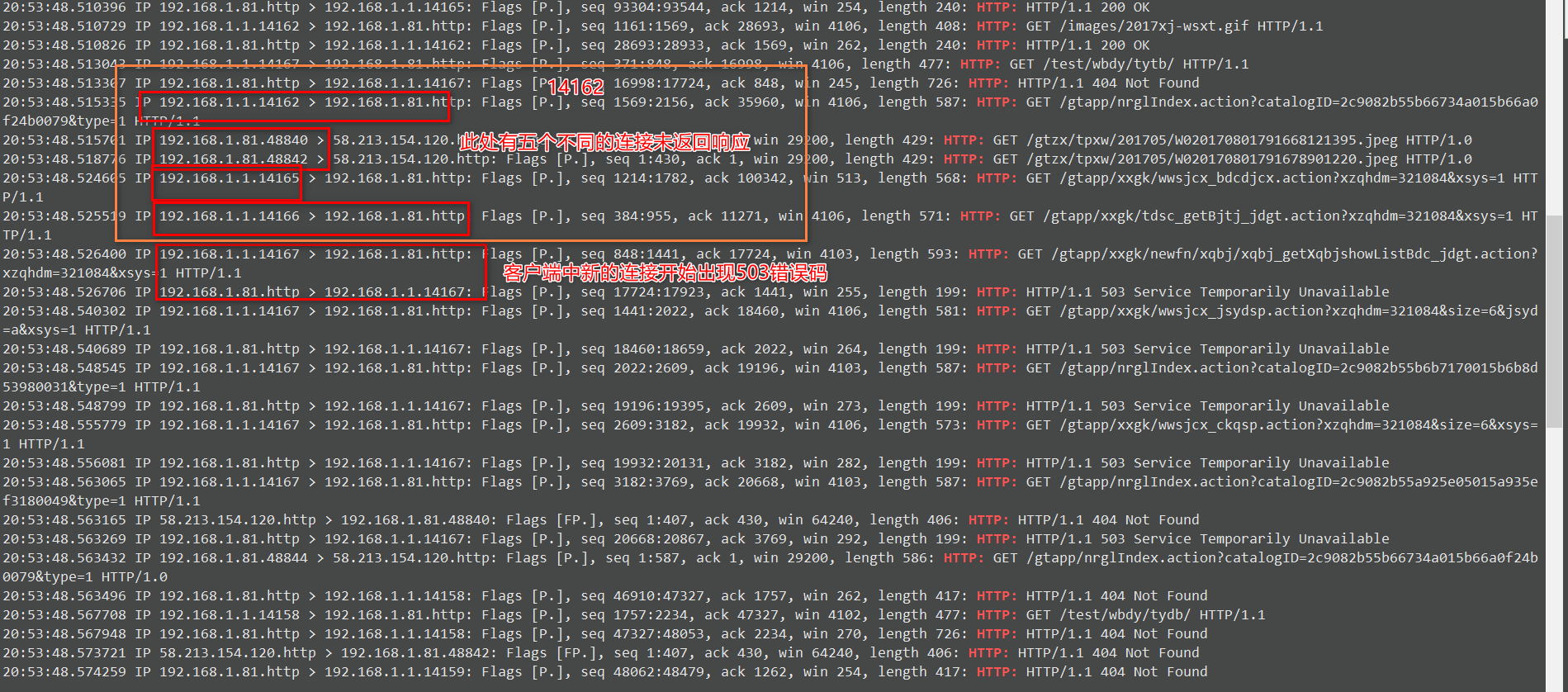
查看access.log日志,发现与抓包结果一致:
- 对ab测试结果再次分析:
[root@centos-50 ~]# ab -n 100 -c 10 http://192.168.1.81/index.htm
Concurrency Level: 10Time taken for tests: 0.035 secondsComplete requests: 100Failed requests: 0Write errors: 0Total transferred: 2424400 bytesHTML transferred: 2400800 bytesRequests per second: 2846.08 [#/sec] (mean)Time per request: 3.514 [ms] (mean)Time per request: 0.351 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)Transfer rate: 67383.26 [Kbytes/sec] received
仍然没有发现失败的请求,此时查看access.log:
[root@centos-81 ~]# tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log
……192.168.1.50|46462|200|21/Dec/2018:09:20:04 +0800|GET /index.htm HTTP/1.0 24008 "-" "ApacheBench/2.3" "-"192.168.1.50|46464|200|21/Dec/2018:09:20:04 +0800|GET /index.htm HTTP/1.0 24008 "-" "ApacheBench/2.3" "-"192.168.1.50|46466|200|21/Dec/2018:09:20:04 +0800|GET /index.htm HTTP/1.0 24008 "-" "ApacheBench/2.3" "-"192.168.1.50|46468|200|21/Dec/2018:09:20:04 +0800|GET /index.htm HTTP/1.0 24008 "-" "ApacheBench/2.3" "-"192.168.1.50|46470|200|21/Dec/2018:09:20:04 +0800|GET /index.htm HTTP/1.0 24008 "-" "ApacheBench/2.3" "-"192.168.1.50|46472|200|21/Dec/2018:09:20:04 +0800|GET /index.htm HTTP/1.0 24008 "-" "ApacheBench/2.3" "-"
ab命令在压测时,仅请求页面本身,不对页面中嵌套资源进行加载,类似于curl命令,同时由于时局域网环境,完成一次请求的时间非常短。
2.3.3. 测试结论与limit_conn总结
此次浏览器测试过程与结果总结:
- 采用响应元素多,且响应慢的页面作为测试主页;同时采用浏览器测试而不是ab,原因是浏览器会对网页中的css,js,jpg等各种资源进行请求,而ab命令仅请求首页本身
- 测试中发现,客户端与服务端产生多个TCP连接(而localhost.conf设置为5个),因此Nginx限制的不是建立TCP连接的数量
- 测试中发现,客户端请求响应慢的资源时,当前连接处于阻塞状态(http 1.1),阻塞的连接数达到5后,超过的连接将直接返回503.
- 测试中发现,客户端请求反向代理资源时,服务端与后端资源服务器建立的连接数纳入到客户端TCP请求的连接总数中
- limit_conn 并不限制客户端与服务端之间的TCP连接数量,仅限制活跃状态(读取了请求,但未返回响应)的http请求产生的TCP连接数。
3. limit_req_module
3.1. 指令
3.1.1. limit_req_zone
Syntax: limit_req_zone key zone=name:size rate=Nr/s;Default: closeContext: http
3.1.2. limit_req
Syntax: limit_req zone=name [burst=number] [nodelay|delay=N] ;Default: closeContext: http,server,location
3.1.3. limit_req_log_level
Syntax: limit_req_log_level info|notice|warn|error ;Default: limit_req_log_level error ;Context: http,server,loaction
3.2. 说明
- limit_req_zone
大多数时候仅针对$remote_addr进行限制,使用变量名 $binary_remote_addr ,类似于 limit_conn_zone,1m的共享空间可以存储约 1024 * 1024 / 64 = 16384 个请求的key,一般设置10m足够了。此处直接指定每秒钟接收的请求数量。
- limit_req
- delay=N 仅在1.15.7 版本才有
- 未使用burst和delay时,将一秒钟的切割成N片,每个时间片中至多处理一个请求。
- 指定burst后,每秒钟超过限制的请求将被延迟到下一秒处理,且每秒钟能处理的最大请求数为rate中的限速,超过的请求会一直被延迟直到处理完毕或者客户端断开。
- 使用burst指定多个少请求延迟到下一次处理,即延迟响应,处理请求的速率不变,超过的请求将返回503。在不设置nodelay时,burst大小并无意义。
3.3. 案例
3.3.1. 主配置文件
| centos 7.4 | server | 192.168.1.81 | | —- | —- | —- | | centos 6.10 | client | 192.168.1.50 |
[root@centos-81 conf.d]# cat ../nginx.conf
user nginx;worker_processes 1;error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;pid /var/run/nginx.pid;events {worker_connections 1024;}http {include /etc/nginx/mime.types;limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=limit_addr:10m rate=5r/s ;default_type application/octet-stream;log_format main '$remote_addr|$remote_port|$status|$time_local|$request ''$body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;sendfile on;#tcp_nopush on;keepalive_timeout 5;#gzip on;include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;}
3.3.2. 测试1
虚拟主机配置
server {listen 80;server_name localhost;limit_req zone=limit_addr ;# limit_req zone=limit_addr burst=5;# limit_req zone=limit_addr burst=5 nodelay;......
预期效果: 单个客户端IP每秒接受的请求数量为5个,超过部分将以503状态码返回
测试
[root@centos-50 ~]# time (for i in {1..100};do curl http://192.168.1.81/index.htm &>/dev/null ; sleep 0.1 ;done)
[root@centos-81 ~]# tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log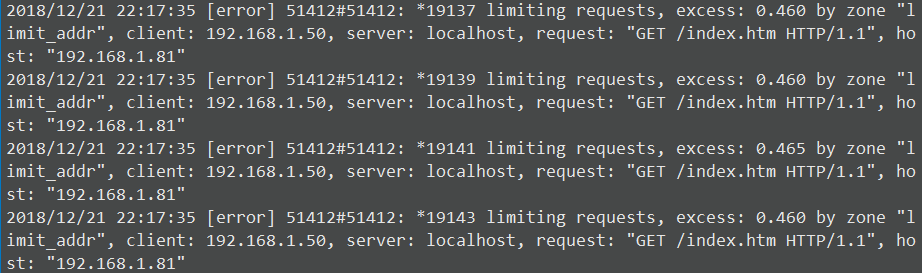
[root@centos-81 ~]# > /var/log/nginx/access.log ; tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log | awk-F’[|/]’ ‘$1==”192.168.1.50”{print $6”—->”$3}’
2018:22:17:25 +0800--->2002018:22:17:25 +0800--->5032018:22:17:25 +0800--->2002018:22:17:25 +0800--->5032018:22:17:25 +0800--->2002018:22:17:25 +0800--->503
对access.log日志进行分析:
[root@centos-81 ~]# awk -F’[|/]| +’ ‘$1==”192.168.1.50”{print $6”\t”$3}’ /var/log/nginx/access.log | sort |uniq -c
3 2018:22:17:25 2003 2018:22:17:25 5035 2018:22:17:26 2005 2018:22:17:26 5035 2018:22:17:27 2004 2018:22:17:27 5034 2018:22:17:28 2005 2018:22:17:28 503
- 测试结果:
未指定burst和nodelay时,每秒钟超过限制的请求直接返回503错误。此处200和503交替出现比较诡异,针对这种请求,再次抓包确认:
[root@centos-81 ~]# grep ‘HTTP/1.1’ tcp.pak | head -30 | awk ‘{print $1,$3,$5,$(NF-1),$NF}’
22:36:54.904636 192.168.1.50.51560 192.168.1.81.http: /index.htm HTTP/1.122:36:54.904935 192.168.1.81.http 192.168.1.50.51560: 200 OK22:36:55.012549 192.168.1.50.51562 192.168.1.81.http: /index.htm HTTP/1.122:36:55.012692 192.168.1.81.http 192.168.1.50.51562: Temporarily Unavailable22:36:55.119265 192.168.1.50.51564 192.168.1.81.http: /index.htm HTTP/1.122:36:55.119430 192.168.1.81.http 192.168.1.50.51564: 200 OK22:36:55.226971 192.168.1.50.51566 192.168.1.81.http: /index.htm HTTP/1.122:36:55.227185 192.168.1.81.http 192.168.1.50.51566: Temporarily Unavailable22:36:55.335680 192.168.1.50.51568 192.168.1.81.http: /index.htm HTTP/1.122:36:55.335803 192.168.1.81.http 192.168.1.50.51568: 200 OK
从结果中来看,数据包确实按照时间顺序依次出现200,503。因此推测,5r/s 其实是每0.2s限制一个请求。针对此推测,继续实验,模拟0.1秒钟多个请求:
[root@centos-50 ~]# for i in {1..10};do curl http://192.168.1.81/index.htm &>/dev/null ; sleep 0.01;done
[root@centos-81 ~]# > /var/log/nginx/access.log ; tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log | awk-F’[|/]’ ‘$1==”192.168.1.50”{print $6”—->”$3}’
2018:22:49:50 +0800--->2002018:22:49:50 +0800--->5032018:22:49:50 +0800--->5032018:22:49:50 +0800--->5032018:22:49:50 +0800--->5032018:22:49:50 +0800--->5032018:22:49:50 +0800--->5032018:22:49:50 +0800--->5032018:22:49:50 +0800--->5032018:22:49:50 +0800--->503
此实验证实了 5r/s 实际是将1秒切割成5等份(每0.2秒为一个时间片),每个时间片中至多同时处理一个请求。
3.3.2. 测试2
location.conf 配置
server {listen 80;server_name localhost;# limit_req zone=limit_addr ;limit_req zone=limit_addr burst=3;# limit_req zone=limit_addr burst=5 nodelay;......
预期效果: 单个客户端IP每秒接受的请求数量为5个,超过部分将持续被延期,burst的值大小并没有意义
测试
[root@centos-50 ~]# time (for i in {1..100};do curl http://192.168.1.81/index.htm &>/dev/null ; sleep 0.1 ;done)
real 0m19.908s
[root@centos-81 ~]# awk -F’[|/]’ ‘$1==”192.168.1.50”{print $3}’ /var/log/nginx/access.log|sort|uniq -c
100 200
此时:请求全部完成需要20s,且所有响应都是200。符合预期
修改burst的值
server {listen 80;server_name localhost;# limit_req zone=limit_addr ;limit_req zone=limit_addr burst=1;# limit_req zone=limit_addr burst=5 nodelay;
继续测试
[root@centos-50 ~]# time (for i in {1..100};do curl http://192.168.1.81/index.htm &>/dev/null ; sleep 0.1 ;done)
real 0m19.907s
[root@centos-81 ~]# awk -F’[|/]’ ‘$1==”192.168.1.50”{print $3}’ /var/log/nginx/access.log|sort|uniq -c
100 200
结论: 未设置nodelay值时,burst的值大小没有意义
3.3.3. 测试3
location.conf 配置
server {listen 80;server_name localhost;# limit_req zone=limit_addr ;# limit_req zone=limit_addr burst=3;limit_req zone=limit_addr burst=3 nodelay;......
预期效果: 每秒钟允许延期的请求是3个,超过的将被纳入下一秒处理。如果下一秒请求超过8个(包括上一秒延期的请求),超过的部分继续返回503,且有三个继续被延期。
测试
[root@centos-50 ~]# time (for i in {1..100};do curl http://192.168.1.81/index.htm &>/dev/null ; sleep 0.1 ;done)
real 0m10.712s
[root@centos-81 ~]# awk -F’[|/]’ ‘$1==”192.168.1.50”{print $3}’ /var/log/nginx/access.log|sort|uniq -c
56 20044 503
[root@centos-81 ~]# awk -F’[|/]| +’ ‘$1==”192.168.1.50”{print $6”\t”$3}’ /var/log/nginx/access.log | sort |uniq -c
5 2018:23:12:02 2001 2018:23:12:02 5035 2018:23:12:03 2004 2018:23:12:03 5035 2018:23:12:04 200
实验结果:虽然没有抓包验证,但是可靠性很高: 第一秒钟应该是9个请求,因为200的结果比503多很多,并不符合第一个实验的结论,因此推测有9个请求(5个成功,3个延期,1个失败)。后面每秒钟失败和成功的请求数量接近,符合第一次实验结果。

