- 字符串匹配
- 📌 第一周 1ST
- 剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字">剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
- 剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树">剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
- 剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列">剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
- 剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列">剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列
- 剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字">剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
- 剑指 Offer 12. 搜索单词">剑指 Offer 12. 搜索单词
- 剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中1的个数">剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中1的个数
- 剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方">剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方
- 剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面">剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
- 剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵">剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
- 剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈">剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
- 剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列">剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- 剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径">剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
- 剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制">剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
- 剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表">剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
- 剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字">剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
- 剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数">剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数
- 剑指 Offer 43. 1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数">剑指 Offer 43. 1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数
- 剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字">剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字
- 剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数">剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数
- 剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串">剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串
- 剑指 Offer 49. 丑数">剑指 Offer 49. 丑数
- 剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对">剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对
- 剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字">剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
- 41. 缺失的第一个正数">41. 缺失的第一个正数
- 剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数">剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
- 剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列">剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
- 剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序">剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
- 剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值">剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值
- 60. 十进制转换八进制
- 📌 第二周 Leetcode
- 621. 任务调度器">621. 任务调度器
- 560. 和为K的子数组">560. 和为K的子数组
- 128. 最长连续序列">128. 最长连续序列
- 581. 最短无序连续子数组">581. 最短无序连续子数组
- 494. 目标和">494. 目标和
- 406. 根据身高重建队列">406. 根据身高重建队列
- 394. 字符串解码">394. 字符串解码
- 347. 前 K 个高频元素">347. 前 K 个高频元素
- 287. 寻找重复数">287. 寻找重复数
- 279. 完全平方数">279. 完全平方数
- 238. 除自身以外数组的乘积">238. 除自身以外数组的乘积
- 221. 最大正方形">221. 最大正方形
- 208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)">208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
- 152. 乘积最大子数组">152. 乘积最大子数组
- 148. 排序链表">148. 排序链表
- 📌 第二周 Leetcode
字符串匹配
public int search(String txt, String pat) {int i, N = txt.length();int j, M = pat.length();for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < N && j < M; i++) {if (txt.charAt(i) == pat.charAt(j)) {j++;} else {i -= j;j = 0;}}if (j == M) return i - M;else return N;}
📌 第一周 1ST
剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
在一个长度为 n 的数组 nums 里的所有数字都在 0~n-1 的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。
class Solution {public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {if (nums[i] == i) {continue;} else if (nums[nums[i]] == nums[i]) {return nums[i];} else {swap(nums,nums[i], i);}}return -1;}private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {int t = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[j];nums[j] = t;}}
剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请构建该二叉树并返回其根节点。
class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {return traverse(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1,inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);}private TreeNode traverse(int[] preorder, int preS, int preE,int[] inorder, int inS, int inE) {if (preS > preE) return null;//一开始边界条件没有加,注意int rootVal = preorder[preS];int index = 0;for (int i = inS; i <= inE; i++) {if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {index = i;break;}}TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);int leftval = index - inS;root.left = traverse(preorder, preS + 1, preS + leftval,inorder, inS, index - 1);root.right = traverse(preorder,preS + leftval + 1, preE,inorder, index + 1, inE);return root;}}
剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
class CQueue {Stack<Integer> in;Stack<Integer> out;public CQueue() {in = new Stack<>();out = new Stack<>();}public void appendTail(int value) {in.push(value);}public int deleteHead() {if (out.isEmpty()) {//while保证in里面的全部元素都压进out里面while (!in.isEmpty()) {out.push(in.pop());}}if (out.isEmpty())return -1;return out.pop();}}
剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列
class Solution {public int fib(int n) {if(n == 0) return 0;int[] dp = new int[n + 1];dp[0] = 0;dp[1] = 1;for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];dp[i] %= 1000000007;}return dp[n];}}
剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
输入:[3,4,5,1,2]输出:1
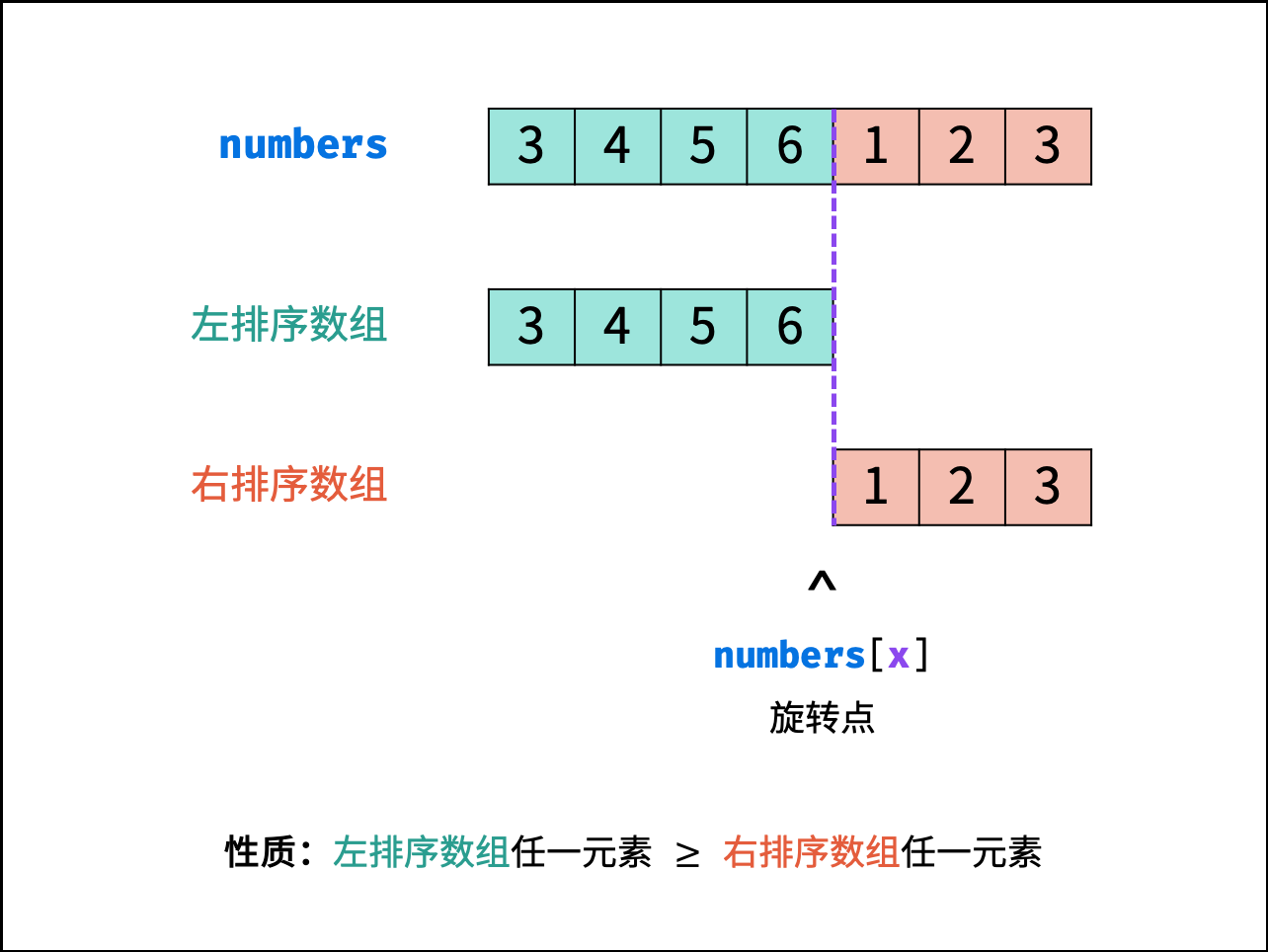
class Solution {public int minArray(int[] numbers) {int i = 0, j = numbers.length - 1;while (i < j) {int m = (i + j) / 2;if (numbers[m] < numbers[j]) j = m;else if (numbers[m] > numbers[j]) i = m + 1;else j--;//无法确定左区间还是右区间,缩小j}return numbers[j];}}
剑指 Offer 12. 搜索单词
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
class Solution {private int[][] direction = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};private int m;private int n;public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {if (word == null || word.length() == 0) return true;if (board == null || board.length == 0) return false;m = board.length;n = board[0].length;boolean[][] hasVisited = new boolean[m][n];for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (backtrack(board, word, hasVisited,i, j, 0)) return true;}}return false;}private boolean backtrack(char[][] board, String word, boolean[][] visited, int r, int c, int k) {if (k == word.length()) {return true;}if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n|| board[r][c] != word.charAt(k) || visited[r][c]) {return false;}visited[r][c] = true;for (int[] d : direction) {int dr = r + d[0];int dc = c + d[1];if (backtrack(board, word, visited, dr, dc, k + 1)) return true;}visited[r][c] = false;return false;}}
剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中1的个数
//把一个整数减去1,再和原整数做与运算,会把该整数最右边一个1变成0.//那么一个整数的二进制有多少个1,就可以进行多少次这样的操作。public class Solution {// you need to treat n as an unsigned valuepublic int hammingWeight(int n) {int count=0;while(n!=0){count++;n=n&(n-1);}return count;}}
剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方
输入:x = 2.00000, n = 10输出:1024.00000
class Solution {public double myPow(double x, int n) {double res = 1.0;for(int i = n; i != 0; i /= 2) {if(i % 2 != 0){res *= x;}x *= x;}return n < 0 ? 1 / res : res;}}
剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4]输出:[1,3,2,4]
class Solution {//while循环里面三个判断都没有加i < jpublic int[] exchange(int[] nums) {int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;while (i < j) {while (i < j && nums[i] % 2 != 0)i++;while (i < j && nums[j] % 2 == 0)j--;if (i < j) {int t = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[j];nums[j] = t;}}return nums;}}
剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
class Solution {public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {if (matrix.length == 0) return new int[0];int l = 0;int r = matrix[0].length - 1;int t = 0;int b = matrix.length - 1;int x = 0;int[] res = new int[(r + 1) * (b + 1)];while (true) {//从左往右//列在变,列为循环值//从左往右的下一步是往下走,上边界内缩,故++t//每做完一次循环收缩边界for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) res[x++] = matrix[t][i];if (++t > b) break;for (int i = t; i <= b; i++) res[x++] = matrix[i][r];if (--r < l) break;for (int i = r; i >= l; i--) res[x++] = matrix[b][i];if (--b < t) break;for (int i = b; i >= t; i--) res[x++] = matrix[i][l];if (++l > r) break;}return res;}}
剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
class MinStack {/** initialize your data structure here. */Stack<Integer> A, B;public MinStack() {A = new Stack<>();B = new Stack<>();}public void push(int x) {A.push(x);if (B.isEmpty() || B.peek() >= x) {B.push(x);}}public void pop() {if (A.pop().equals(B.peek()))B.pop();}public int top() {return A.peek();}public int min() {return B.peek();}}
剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果。如果是则返回 true,否则返回 false。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同
class Solution {public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {return recur(postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);}private boolean recur(int[] nums, int s, int e) {if (s >= e) return true;int rootVal = nums[e];int m = s;while(m < e && nums[m] < rootVal) {m++;}int k = m;while (k < e && nums[k] > rootVal) {k++;}return k == e && recur(nums, s, m - 1) && recur(nums, m, e - 1);}}
剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
5/ \4 8/ / \11 13 4/ \ / \7 2 5 1输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {if (root == null) return ret;List<Integer> track = new ArrayList<>();backtrack(track, root, target);return ret;}private void backtrack(List<Integer> track, TreeNode root, int target) {if (root == null) return;track.add(root.val);if (root.left == null && root.right == null && target == root.val) {ret.add(new ArrayList<>(track));//return;//不能加return,返回上一层状态没有重置}backtrack(track, root.left, target - root.val);backtrack(track, root.right, target - root.val);track.remove(track.size() - 1);}}
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
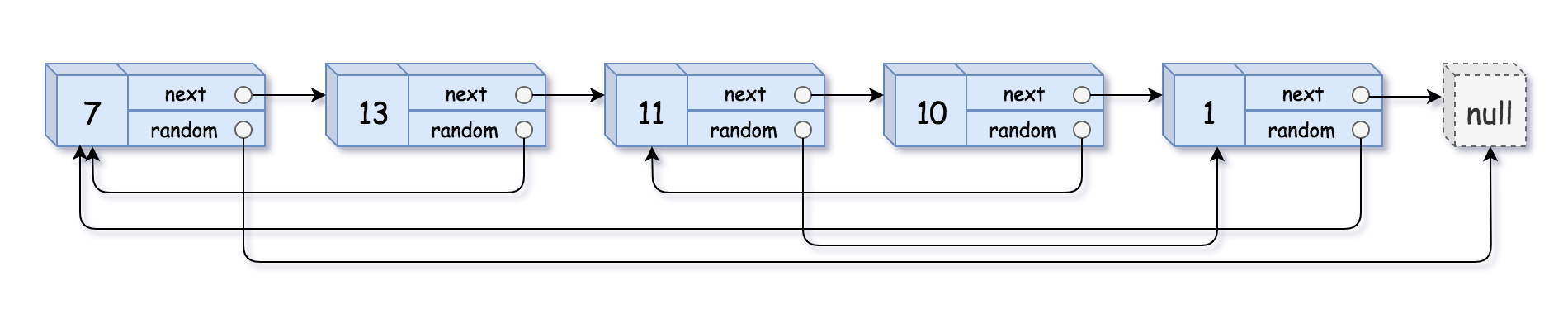
class Solution {public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {if (head == null) return null;// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表Node cur = head;while (cur != null) {Node next = cur.next;Node temp = new Node(cur.val);cur.next = temp;temp.next = next;cur = next;}//2.复制randomcur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.random != null)cur.next.random = cur.random.next;cur = cur.next.next;}// 3. 拆分两链表cur = head.next;Node pre = head, res = head.next;while(cur.next != null) {pre.next = pre.next.next;cur.next = cur.next.next;pre = pre.next;cur = cur.next;}pre.next = null; // 单独处理原链表尾节点return res; // 返回新链表头节点}}/**1.链表问题有时需要cur = head;2.在第二步复制random的时候没有判断cur.random是否为空3.拆分的时候要注意有一个pre节点,把最后指向复制链表的地方断开!*/
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
class Solution {Node head, pre;public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {if (root == null) return null;dfs(root);//首尾节点互指pre.right = head;head.left = pre;return head;}private void dfs(Node cur) {if (cur == null) return;dfs(cur.left);if (head == null)head = cur;if (pre != null)pre.right = cur;cur.left = pre;pre = cur;dfs(cur.right);}}
剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
//时间O(n),空间O(1)class Solution {public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {int x = 0, vote = 0;//x为众数,vote为票数for (int num : nums) {if (vote == 0) x = num;vote += num == x ? 1 : -1;}return x;}}
需要的数字出现次数多于一半 那么排序后必定在中间
//时间O(nlogn),空间O(1)class Solution {public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {Arrays.sort(nums);return nums[nums.length/2];}}
剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数
核心思想:大顶堆存放较小的元素,小顶堆存放较大的元素!!!
class MedianFinder {PriorityQueue<Integer> small;PriorityQueue<Integer> large;public MedianFinder() {small = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v2 - v1);//大堆顶large = new PriorityQueue<>();//小堆顶}//维持两个顶堆的元素不超过1public void addNum(int num) {if (small.size() < large.size()) {large.offer(num);small.offer(large.poll());} else {small.offer(num);large.offer(small.poll());}}public double findMedian() {if (large.size() > small.size()) {return large.peek();} else if (large.size() < small.size()) {return small.peek();}return (large.peek() + small.peek()) / 2.0;}}
剑指 Offer 43. 1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数
class Solution {public int countDigitOne(int n) {return f(n);}//下面我们都用 1234 和 2345 来举例private int f(int n){// 上一级递归 n = 20、10之类的整十整百之类的情况;以及n=0的情况if(n== 0) return 0;// n < 10 即为个位,这样子只有一个1if(n < 10) return 1;String s = String.valueOf(n);//长度:按例子来说是4位int length = s.length();//这个base是解题速度100%的关键,本例中的是999中1的个数:300// 99的话就是20 ; 9的话就是1 ;9999就是4000 这里大家应该发现规律了吧。int base = (length-1)*(int)Math.pow(10,length-2);//high就是最高位的数字int high = s.charAt(0) - '0';//cur就是当前所数量级,即1000int cur = (int)Math.pow(10,length -1);if(high == 1){//最高位为1,1+n-cur就是1000~1234中由千位数提供的1的个数,剩下的f函数就是求1000~1234中由234产生的1的个数return base + 1 + n - cur + f(n - high * cur);}else{//这个自己思考return base * high + cur + f(n- high * cur);}}}
剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字
class Solution {public int findNthDigit(int n) {int digit = 1;// 记录位数,初始为一位数long start = 1; // 记录某一位数起始的第一个数,初始为一位数起点1long count = 9;// 记录某一位数所有包含的数字个数,初始为一位数个数9while (n > count) {n -= count;digit += 1;start *= 10;count = digit * start * 9;}long num = start + (n - 1) / digit; // 2.判断第n位数字属于哪一个数return Long.toString(num).charAt((n - 1) % digit) - '0'; // 3.对位数取余得到哪一位}}
剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数
输入: [3,30,34,5,9]输出: "3033459"
class Solution {public String minNumber(int[] nums) {if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return "";int n = nums.length;String[] arr = new String[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)arr[i] = nums[i] + "";Arrays.sort(arr, (s1, s2) -> (s1 + s2).compareTo(s2 + s1));String ret = "";for (String str : arr)ret += str;return ret;}}
剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串
输入: 12258输出: 5解释: 12258有5种不同的翻译,分别是"bccfi", "bwfi", "bczi", "mcfi"和"mzi"
class Solution {public int translateNum(int num) {String s = String.valueOf(num);int[] dp = new int[s.length() + 1];dp[0] = dp[1] = 1;for (int i = 2; i <= s.length(); i++) {String tmpStr = s.substring(i - 2, i);if (tmpStr.compareTo("10") >= 0 && tmpStr.compareTo("25") <= 0) {dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];} else {dp[i] = dp[i - 1];}}return dp[s.length()];}}//理解dp数组的含义//dp[i]就是第i个字符有多少种翻译的方法//[i-1..i]如果可以组成一种方法,该情况就为dp[i-2]的大小//[i]组成一种翻译方法,该情况就为dp[i-1]的大小
剑指 Offer 49. 丑数
我们把只包含质因子 2、3 和 5 的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。求按从小到大的顺序的第 n 个丑数。
class Solution {//dp[i]表示第i+1个丑数//这个题用三指针,第一个丑数是1,以后的丑数都是基于前面的小丑数分别乘2,3,5构成的。//我们每次添加进去一个当前计算出来个三个丑数的最小的一个,并且是谁计算的,谁指针就后移一位。public int nthUglyNumber(int n) {if (n <= 0)return -1;int[] dp = new int[n];dp[0] = 1;int id2 = 0, id3 = 0, id5 = 0;for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {dp[i] = Math.min(dp[id2] * 2, Math.min(dp[id3] *3, dp[id5] * 5));// 这里不用else if的原因是有可能id2(3) * 2 == id3(2) * 3// 这种情况两个指针都要后移if (dp[id2] * 2 == dp[i])id2 += 1;if (dp[id3] * 3 == dp[i])id3 += 1;if (dp[id5] * 5 == dp[i])id5 += 1;}return dp[n - 1];}}
剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对
在数组中的两个数字,如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数。
归并排序
输入: [7,5,6,4]输出: 5
class Solution {//用来统计逆序对的个数int count = 0;public int reversePairs(int[] nums) {merge(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);return count;}public void merge(int[] nums, int left, int right) {int mid = (left + right) / 2;if (left < right) {merge(nums, left, mid);merge(nums, mid + 1, right);mergeSort(nums, left, mid, right);}}public void mergeSort(int[] nums, int left, int mid, int right) {int[] temparr = new int[right - left + 1];int index = 0;int temp1 = left, temp2 = mid + 1;//左右两部分的起始索引while (temp1 <= mid && temp2 <= right) {if (nums[temp1] <= nums[temp2]) {temparr[index++] = nums[temp1++];} else {count += (mid - temp1 + 1);//左边和右边是有序的,当temp1>temp2时//说明temp1到mid的值都比temp2大,一共有这么多逆序对temparr[index++] = nums[temp2++];}}//把左边剩余的数移入数组while (temp1 <= mid) {temparr[index++] = nums[temp1++];}//把右边剩余的数移入数组while (temp2 <= right) {temparr[index++] = nums[temp2++];}//把新数组中的数覆盖nums数组//没有理解for (int k = 0; k < temparr.length; k++) {nums[k + left] = temparr[k];}}}
剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
一个长度为n-1的递增排序数组中的所有数字都是唯一的,并且每个数字都在范围0~n-1之内。在范围0~n-1内的n个数字中有且只有一个数字不在该数组中,请找出这个数字。
输入: [0,1,3]输出: 2
class Solution {//缺失的数字等于 “右子数组的首位元素” 对应的索引;因此考虑使用二分法查找 “右子数组的首位元素”public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;while (i <= j) {int m = (i + j) / 2;if (nums[m] == m) i = m + 1;else j = m - 1;}return i;}}
41. 缺失的第一个正数
给你一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,请你找出其中没有出现的最小的正整数。请你实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 并且只使用常数级别额外空间的解决方案。
输入:nums = [3,4,-1,1]输出:2
class Solution {public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= len && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i]) {swap(nums, nums[i] - 1, i);}}for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {if (nums[i] != i + 1)return i + 1;}return len + 1;}private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {int t = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[j];nums[j] = t;}}
剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
由于数组中存在着两个数字不重复的情况,我们将所有的数字异或操作起来,最终得到的结果是这两个数字的异或结果
class Solution {public int[] singleNumbers(int[] nums) {//用于将所有的数异或起来int k = 0;// e.g. [2,4,2,3,3,6] 异或和:(2^2)^(3^3)^(4^6)=2=010for(int num: nums) {k ^= num;}//获得k中最低位的1int mask = 1;& operator只有1&1时等于1 其余等于0// 用上面的e.g. 4和6的二进制是不同的 我们从右到左找到第一个不同的位就可以分组 4=0100 6=0110// 根据e.g. 010 & 001 = 000 = 0则 mask=010// 010 & 010 != 0 所以mask=010// 之后就可以用mask来将数组里的两个数分区分开while((k & mask) == 0) {mask <<= 1;}int a = 0;int b = 0;for(int num: nums) {//根据&是否为0区分将两个数字分区,并分别求异或和if((num & mask) == 0) {a ^= num;} else {b ^= num;}}return new int[]{a, b};}}
剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
输入一个正整数 target ,输出所有和为 target 的连续正整数序列(至少含有两个数)。
输入:target = 9输出:[[2,3,4],[4,5]]
class Solution {public int[][] findContinuousSequence(int target) {List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();//套滑动窗口模板,l是窗口左边界,r是窗口右边界,窗口中的值一定是连续值。//当窗口中数字和小于target时,r右移; 大于target时,l右移; 等于target时就获得了一个解for (int l = 1, r = 1, sum = 0; r < target; r++) {sum += r;while (sum > target) {sum -= l;l++;}if (sum == target) {int[] temp = new int[r - l + 1];for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {temp[i] = l + i;}list.add(temp);}}int[][] res = new int[list.size()][];for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {res[i] = list.get(i);}return res;}}
剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
Input:"I am a student."Output:"student. a am I"
public String ReverseSentence(String str) {int n = str.length();char[] chars = str.toCharArray();int i = 0, j = 0;while (j <= n) {if (j == n || chars[j] == ' ') {reverse(chars, i, j - 1);i = j + 1;}j++;}reverse(chars, 0, n - 1);return new String(chars);}private void reverse(char[] c, int i, int j) {while (i < j)swap(c, i++, j--);}private void swap(char[] c, int i, int j) {char t = c[i];c[i] = c[j];c[j] = t;}
剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值
给定一个数组 nums 和滑动窗口的大小 k,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值。
输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3输出: [3,3,5,5,6,7]解释:滑动窗口的位置 最大值--------------- -----[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 31 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 31 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 51 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 51 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 61 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
class Solution {public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {if (nums.length == 0 || k == 0) return new int[0];int n = nums.length;// 双向队列 保存当前窗口最大值的数组位置 保证队列中数组位置的数按从大到小排序Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();int[] res = new int[n - k + 1];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 保证从大到小 如果前面数小 弹出while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[i] >= nums[deque.peekLast()]) {deque.pollLast();}deque.offerLast(i);//等到窗口长度为k时 下次移动在删除过期数值if (deque.peekFirst() <= i - k) {deque.pollFirst();}if (i - k + 1 >= 0) {res[i - k + 1] = nums[deque.peekFirst()];}}return res;}}
60. 十进制转换八进制
public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner number=new Scanner(System.in);int n=number.nextInt();String result="";while (n>8) {result = n%8+result;n=n/8;}result = n+result;System.out.println(result);}
📌 第二周 Leetcode
621. 任务调度器
你需要计算完成所有任务所需要的 最短时间 。
输入:tasks = ["A","A","A","B","B","B"], n = 2输出:8解释:A -> B -> (待命) -> A -> B -> (待命) -> A -> B在本示例中,两个相同类型任务之间必须间隔长度为 n = 2 的冷却时间,而执行一个任务只需要一个单位时间,所以中间出现了(待命)状态。
class Solution {//填桶public int leastInterval(char[] tasks, int n) {int[] temp = new int[26];int countMaxTask = 0;int maxTask=0;for(char c:tasks){temp[c-'A']++;maxTask = Math.max(temp[c-'A'],maxTask);}for(int i=0;i<26;i++){if(temp[i]==maxTask){countMaxTask++;}}return Math.max(tasks.length,(maxTask-1)*(n+1)+countMaxTask);//总排队时间 = (桶个数 - 1) * (n + 1) + 最后一桶的任务数}}
560. 和为K的子数组
给定一个整数数组和一个整数 k,你需要找到该数组中和为 k 的连续的子数组的个数。
输入:nums = [1,1,1], k = 2输出: 2 , [1,1] 与 [1,1] 为两种不同的情况。
class Solution {//题意:有几种 i、j 的组合,使得从第 i 到 j 项的子数组和等于 k。//有几种 i、j 的组合,满足 prefixSum[j] - prefixSum[i - 1] == k//前缀和public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {// key:前缀和,value:key 对应的前缀和的个数Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();// 对于下标为 0 的元素,前缀和为 0,个数为 1map.put(0, 1);//例子:nums = [3,...], k = 3int sum = 0, ret = 0;for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {sum += nums[i];if (map.containsKey(sum - k))ret += map.get(sum - k);map.put(sum, map.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1);}return ret;}}
128. 最长连续序列
给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。
请你设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
输入:nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2] 输出:4 解释:最长数字连续序列是 [1, 2, 3, 4]。它的长度为 4。
class Solution {public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {Set<Integer> num_set = new HashSet<Integer>();for (int num : nums) {num_set.add(num);}int longestLen = 0;for (int num : num_set) {//使用set去重if (!num_set.contains(num - 1)) {int currentNum = num;int currentLen = 1;while (num_set.contains(currentNum + 1)) {currentNum += 1;currentLen += 1;}longestLen = Math.max(longestLen, currentLen);}}return longestLen;}}
581. 最短无序连续子数组
给你一个整数数组 nums ,你需要找出一个 连续子数组 ,如果对这个子数组进行升序排序,那么整个数组都会变为升序排序。
请你找出符合题意的 最短 子数组,并输出它的长度。
输入:nums = [2,6,4,8,10,9,15]输出:5解释:你只需要对 [6, 4, 8, 10, 9] 进行升序排序,那么整个表都会变为升序排序。
//1.简单的方法就是可以copy一个数组,和原始数组比较//2.双指针+双向遍历class Solution {public int findUnsortedSubarray(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;if(len <= 1) return 0;int high = 0, low = len-1;int max = nums[0], min = nums[len-1];for(int i = 1; i < len; i++){max = Math.max(max, nums[i]);min = Math.min(min, nums[len-1-i]);if(nums[i] < max) high = i;if(nums[len-1-i] > min) low = len-1-i;}return high > low ? high - low + 1 : 0;}}//子数组右边的所有元素, 值都要比子数组的最大元素要大.//子数组左边的所有元素, 值都要比子数组的最小元素要小.//左到右,记录最大值为 max,若 nums[i] < max, 表明位置 i 需要调整,记录需要调整的最大位置 i 为 high.//右到左,记录最小值为 min, 若 nums[i] > min, 表明位置 i 需要调整,记录需要调整的最小位置 i 为 low.
494. 目标和
输入:nums = [1,1,1,1,1], target = 3输出:5解释:一共有 5 种方法让最终目标和为 3 。-1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3+1 - 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3+1 + 1 - 1 + 1 + 1 = 3+1 + 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 3+1 + 1 + 1 + 1 - 1 = 3
class Solution {/**target = 正数和 - 负数和 = x - ysum = x + yx = (target + sum) /2从nums中选择几个数,令其和为(target + sum) /2变成0-1背包问题*/public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {int sum = 0;for (int n : nums){sum += n;}if (sum < target || (sum + target) % 2 == 1) {return 0;}int V = (sum + target) / 2;int[] dp = new int[W + 1];dp[0] = 1;for (int num : nums) {for (int j = V; j >= num; j--) {dp[j] += dp[j - num];}}return dp[V];}}
406. 根据身高重建队列
people[i] = [hi, ki] 表示第 i 个人的身高为 hi ,前面 正好 有 ki 个身高大于或等于 hi 的人。
输入:people = [[6,0],[5,0],[4,0],[3,2],[2,2],[1,4]]输出:[[4,0],[5,0],[2,2],[3,2],[1,4],[6,0]]
//好好理解class Solution {public int[][] reconstructQueue(int[][] people) {//按照身高降序 K升序排序Arrays.sort(people, new Comparator<int[]>() {@Overridepublic int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {return o1[0] == o2[0] ? o1[1] - o2[1] : o2[0] - o1[0];}});List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int[] p : people) {list.add(p[1], p);//List插入的时候会挪动之前的元素,使其在合适的位置}return list.toArray(new int[list.size()][2]);}}
394. 字符串解码
编码规则为: k[encodedstring],表示其中方括号内部的 _encoded_string 正好重复 k 次。注意 k 保证为正整数。
输入:s = “3[a2[c]]” 输出:“accaccacc”
class Solution {public String decodeString(String s) {StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();int multi = 0;Stack<Integer> stack_multi = new Stack<>();Stack<String> stack_res = new Stack<>();for(char c : s.toCharArray()) {if(c == '[') {stack_multi.push(multi);stack_res.push(res.toString());multi = 0;res = new StringBuilder();}else if(c == ']') {StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();int cur_multi = stack_multi.pop();for(int i = 0; i < cur_multi; i++) tmp.append(res);res = new StringBuilder(stack_res.pop() + tmp);}else if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') multi = multi * 10 + c - '0';//如果k不是个位数而是n位整数的话就要通过不停的乘10来更新值else res.append(c);}return res.toString();}}
347. 前 K 个高频元素
输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 输出: [1,2]
class Solution {public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList();HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap();for(int num : nums){map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);}//桶排序//将频率作为数组下标,对于出现频率不同的数字集合,存入对应的数组下标List<Integer>[] list = new List[nums.length+1];for(int key : map.keySet()){// 获取出现的次数作为下标int i = map.get(key);if(list[i] == null){list[i] = new ArrayList();}list[i].add(key);}// 倒序遍历数组获取出现顺序从大到小的排列for(int i = list.length - 1;i >= 0 && res.size() < k;i--){if(list[i] == null) continue;res.addAll(list[i]);}int[] arr = new int[k];for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {arr[i] = res.get(i);}return arr;}}
287. 寻找重复数
给定一个包含 n + 1 个整数的数组 nums ,其数字都在 1 到 n 之间(包括 1 和 n),可知至少存在一个重复的整数。
假设 nums 只有 一个重复的整数 ,找出 这个重复的数 。
你设计的解决方案必须不修改数组 nums 且只用常量级 O(1) 的额外空间。
class Solution {public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {/**快慢指针思想, fast 和 slow 是指针, nums[slow] 表示取指针对应的元素注意 nums 数组中的数字都是在 1 到 n 之间的(在数组中进行游走不会越界),因为有重复数字的出现, 所以这个游走必然是成环的, 环的入口就是重复的元素,即按照寻找链表环入口的思路来做**/int fast = 0, slow = 0;while(true) {fast = nums[nums[fast]];//走两步slow = nums[slow];//走一步if(slow == fast) break;}fast = 0;while(slow != fast) {fast = nums[fast];slow = nums[slow];}return slow;}}
279. 完全平方数
给定正整数 n,找到若干个完全平方数(比如 1, 4, 9, 16, …)使得它们的和等于 n。你需要让组成和的完全平方数的个数最少。
给你一个整数 n ,返回和为 n 的完全平方数的 最少数量 。
class Solution {public int numSquares(int n) {int[] dp = new int[n + 1];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {dp[i] = i;for (int j = 1; i - j * j >= 0; j++) {dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - j*j] + 1);}}return dp[n];}}
238. 除自身以外数组的乘积
给你一个长度为 n 的整数数组 nums,其中 n > 1,返回输出数组 output ,其中 output[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积。
/***原数组: [1 2 3 4]*左部分的乘积: 1 1 1*2 1*2*3*右部分的乘积: 2*3*4 3*4 4 1*结果: 1*2*3*4 1*3*4 1*2*4 1*2*3*1*/class Solution {public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {int[] res = new int[nums.length];int p = 1, q = 1;for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {res[i] = p;p *= nums[i];}for (int i = nums.length - 1; i > 0 ; i--) {q *= nums[i];res[i - 1] *= q;}return res;}}
221. 最大正方形
在一个由 ‘0’ 和 ‘1’ 组成的二维矩阵内,找到只包含 ‘1’ 的最大正方形,并返回其面积。
class Solution {public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) {/**dp[i][j]表示matrix[i - 1][j - 1]为右下角所能构成的最大正方形边长, 则递推式为:dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);**/int m = matrix.length;int n =matrix[0].length;int max = 0;int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {if (matrix[i - 1][j - 1] == '1') {dp[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(dp[i-1][j-1], Math.min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]));max = Math.max(max, dp[i][j]);}}}return max * max;}}
208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
class Trie {private boolean isEnd;private Trie[] children;public Trie() {isEnd = false;children = new Trie[26];}public void insert(String word) {Trie node = this;for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {int index = word.charAt(i) - 'a';if (node.children[index] == null) {node.children[index] = new Trie();}node = node.children[index];}node.isEnd = true;}public boolean search(String word) {Trie node = searchPrefix(word);return node != null && node.isEnd;}public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {return searchPrefix(prefix) != null;}public Trie searchPrefix(String prefix) {Trie node = this;for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {int index = prefix.charAt(i) - 'a';if (node.children[index] == null) {return null;}node = node.children[index];}return node;}}
152. 乘积最大子数组
输入: [2,3,-2,4] 输出: 6 解释: 子数组 [2,3] 有最大乘积 6。
class Solution {public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;int i_max = 1;int i_min = 1;for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {if (nums[i] < 0) {int t = i_max;i_max = i_min;i_min = t;}i_max = Math.max(i_max*nums[i], nums[i]);i_min = Math.min(i_min*nums[i], nums[i]);max = Math.max(i_max, max);}return max;}}
148. 排序链表
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
class Solution {public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;ListNode l, r;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}r = sortList(slow.next);slow.next = null;l = sortList(head);return merge(l, r);}private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode p = dummy;while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {if (l1.val < l2.val) {p.next = l1;l1 = l1.next;} else {p.next = l2;l2 = l2.next;}p = p.next;}p.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;return dummy.next;}}
📌 第二周 Leetcode
23. 合并K个升序链表
class Solution {public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {if (lists.length == 0) return null;ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode cur = dummyHead;PriorityQueue<ListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v1.val - v2.val);for (ListNode list : lists) {if (list != null) {pq.add(list);}}while (!pq.isEmpty()) {ListNode nextnode = pq.poll();cur.next = nextnode;cur = cur.next;if (nextnode.next != null) {pq.add(nextnode.next);}}return dummyHead.next;}}
31. 下一个排列
实现获取 下一个排列 的函数,算法需要将给定数字序列重新排列成字典序中下一个更大的排列(即,组合出下一个更大的整数)。
输入:nums = [1,2,3]输出:[1,3,2]
class Solution {public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;int firstIndex = -1;//1.需要将后面大数的与前面小数的交换for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--) {if (nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {firstIndex = i;break;}}//2.如果不存在逆序整个数组if (firstIndex == -1) {reverse(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);return;}int secondIndex = -1;//3.从后往前找尽可能的大数,因为firstindex后面的是降序for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (nums[i] > nums[firstIndex]) {secondIndex = i;break;}}//4.交换大数与小数swap(nums, firstIndex, secondIndex);//5.firstindex后面是降序,reverse使其升序reverse(nums, firstIndex + 1, nums.length - 1);}private void reverse(int[] nums, int i, int j) {while (i < j) {swap(nums, i++, j--);}}private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int i1) {int tmp = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[i1];nums[i1] = tmp;}}
32. 最长有效括号
给你一个只包含 ‘(‘ 和 ‘)’ 的字符串,找出最长有效(格式正确且连续)括号子串的长度。
输入:s = ")()())"输出:4解释:最长有效括号子串是 "()()"
class Solution {public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {int len = s.length();int max = 0;Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(-1);//一开始压入-1使得栈底元素为最后一个没有匹配的右括号的下标for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {if (s.charAt(i) == '(') {stack.push(i);} else {stack.pop();if (stack.isEmpty()) {stack.push(i);} else {max = Math.max(max, i - stack.peek());}}}return max;}}
33. 搜索旋转排序数组
整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。
输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0输出:4
class Solution {public int search(int[] nums, int target) {int lo = 0, hi = nums.length - 1;while (lo <= hi) {int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;if (nums[mid] == target) {return mid;}// 先根据 nums[mid] 与 nums[lo] 的关系判断 mid 是在左段还是右段if (nums[mid] >= nums[lo]) {// 再判断 target 是在 mid 的左边还是右边,从而调整左右边界 lo 和 hiif (target >= nums[lo] && target < nums[mid]) {hi = mid - 1;} else {lo = mid + 1;}} else {if (target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[hi]) {lo = mid + 1;} else {hi = mid - 1;}}}return -1;}}
42. 接雨水
class Solution {public int trap(int[] height) {int len = height.length;int[] max_r = new int[len];int[] max_l = new int[len];int res = 0;for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {max_l[i] = Math.max(max_l[i - 1], height[i - 1]);}for (int j = len - 2; j >= 0; j--) {max_r[j] = Math.max(max_r[j + 1], height[j + 1]);}for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {int min = Math.min(max_l[i], max_r[i]);if (min <= height[i]) continue;else {res += min - height[i];}}return res;}}
55. 跳跃游戏
给定一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的 第一个下标 。数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。判断你是否能够到达最后一个下标。
class Solution {public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {if (nums.length == 0) return false;int k = 0;//要理解k是最大索引位置,nums[i]的值加上去也是索引值for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {if (i > k) return false;k = Math.max(k, i + nums[i]);}return true;}}
56. 合并区间
输入:intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]输出:[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]解释:区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
class Solution {public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {int len = intervals.length;Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);int[][] res = new int[len][2];int idx = -1;for (int[] num : intervals) {if (idx == -1 || num[0] > res[idx][1]) {res[++idx] = num;} else {res[idx][1] = Math.max(res[idx][1], num[1]);}}return Arrays.copyOf(res, idx + 1);}}
75. 颜色分类
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 n 个元素的数组,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。此题中,我们使用整数 0、 1 和 2 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
输入:nums = [2,0,2,1,1,0]输出:[0,0,1,1,2,2]
class Solution {public void sortColors(int[] nums) {int zero = -1, one = 0, two = nums.length;while (one < two) {if (nums[one] == 0) {swap(nums, ++zero, one++);} else if (nums[one] == 1) {one++;} else {swap(nums, --two, one);}}}private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {int t = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[j];nums[j] = t;}}
114. 二叉树展开为链表
class Solution {public void flatten(TreeNode root) {if(root == null){return ;}//将根节点的左子树变成链表flatten(root.left);//将根节点的右子树变成链表flatten(root.right);TreeNode temp = root.right;//把树的右边换成左边的链表root.right = root.left;//记得要将左边置空root.left = null;//找到树的最右边的节点while(root.right != null) root = root.right;//把右边的链表接到刚才树的最右边的节点root.right = temp;}}
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
class Solution {private int ret = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {/**对于任意一个节点, 如果最大和路径包含该节点, 那么只可能是两种情况:1. 其左右子树中所构成的和路径值较大的那个加上该节点的值后向父节点回溯构成最大路径,不能都在,都在就会重复2. 左右子树都在最大路径中, 加上该节点的值构成了最终的最大路径**/getMax(root);return ret;}private int getMax(TreeNode node) {if (node == null) return 0;int left = Math.max(0, getMax(node.left));//如果子树为负应该置0表示不包含子树int right = Math.max(0, getMax(node.right));ret = Math.max(ret, node.val + left + right);//判断在该节点包含左右子树的路径和是否大于当前最大路径和return Math.max(left, right) + node.val;// 返回经过root的单边最大分支给当前root的父节点计算使用}}
442. 数组中重复的数据
给定一个整数数组 a,其中1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n (n为数组长度), 其中有些元素出现两次而其他元素出现一次。
找到所有出现两次的元素。
输入:[4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]输出:[2,3]
class Solution {/*** 观察发现1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n 这个条件,正好和我们数组的下标差1,我们可以按照数值* 来遍历数组,那么在数组中具有相同值的元素,会被经过两次,那么我们只要想出一种方式* 在这个遍历结束后可以区分,哪些元素被经过了多次即可,由于数组元素具有1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n* 这样的范围,那其实我们当每次经过一个元素时,给他加上n,当遍历结束时,我们再次遍历数组* 那些数值超过2n的元素索引+1,对应的就是我们的出现了两次的元素。*/public List<Integer> findDuplicates(int[] nums) {List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();int n = nums.length;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {nums[(nums[i] - 1) % n] += n;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (nums[i] > 2 * n) ret.add(i + 1);}return ret;}}

