- 1. 两数之和">1. 两数之和
- 2. 两数相加">2. 两数相加
- 3. 无重复字符的最长子串">3. 无重复字符的最长子串
- 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素">215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
- 25. K 个一组翻转链表">25. K 个一组翻转链表
- 146. LRU 缓存机制">146. LRU 缓存机制
- 15. 三数之和">15. 三数之和
- 103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历">103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
- 160. 相交链表">160. 相交链表
- 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先">236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 42. 接雨水">42. 接雨水
- 415. 字符串相加">415. 字符串相加
- 54. 螺旋矩阵">54. 螺旋矩阵
- 88. 合并两个有序数组">88. 合并两个有序数组
- 33. 搜索旋转排序数组">33. 搜索旋转排序数组
- 200. 岛屿数量">200. 岛屿数量
- 199. 二叉树的右视图">199. 二叉树的右视图
- 31. 下一个排列">31. 下一个排列
- 102. 二叉树的层序遍历">102. 二叉树的层序遍历
- 300. 最长递增子序列">300. 最长递增子序列
- 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树">105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 20. 有效的括号">20. 有效的括号
- 46. 全排列">46. 全排列
- 56. 合并区间">56. 合并区间
- 143. 重排链表">143. 重排链表
- 112. 路径总和">112. 路径总和
- 129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和">129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
- 69. x 的平方根">69. x 的平方根
- 23. 合并K个升序链表">23. 合并K个升序链表
- 5. 最长回文子串">5. 最长回文子串
- 113. 路径总和 II">113. 路径总和 II
- 124. 二叉树中的最大路径和">124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历">94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- 76. 最小覆盖子串">76. 最小覆盖子串
- 958. 二叉树的完全性检验">958. 二叉树的完全性检验
- 39. 组合总和">39. 组合总和
- 98. 验证二叉搜索树">98. 验证二叉搜索树
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点">19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 32. 最长有效括号">32. 最长有效括号
- 209. 长度最小的子数组">209. 长度最小的子数组
- 221. 最大正方形">221. 最大正方形
- 165. 比较版本号">165. 比较版本号
- 169. 多数元素">169. 多数元素
- 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素">83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
- 82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II">82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
- 48. 旋转图像">48. 旋转图像
- 718. 最长重复子数组">718. 最长重复子数组
- 162. 寻找峰值">162. 寻找峰值
- 0.36进制加法
- 148. 排序链表">148. 排序链表
- 394. 字符串解码">394. 字符串解码
- 114. 二叉树展开为链表">114. 二叉树展开为链表
动态规划
- 基本思想:问题的最优解如果可以由子问题的最优解推导得到,则可以先求解子问题的最优解,在构造原问题的最优解;若子问题有较多的重复出现,则可以自底向上从最终子问题向原问题逐步求解。
1.具有相同的子问题:我们必须保证我们分割成的子问题也能按照相同的方法分割成更小的自问题, 并这些自问题的最终分割情况是可以解决的。
2.满足最优子结构:就是一个决策的子决策也是最优的
3.无后效性:这是DP中最重要的一点, 他要求每个子问题的决策不能对后面其他未解决的问题产影响, 如果产生就无法保证决策的最优性, 这就是无后效性。往往需要我们找到一个合适的状态。
自己设计HashMap
class MyHashMap {private class Pair {private int key;private int value;public Pair(int key, int value) {this.key = key;this.value = value;}public int getKey() {return key;}public int getValue() {return value;}public void setValue(int value) {this.value = value;}}private static final int BASE = 769;private LinkedList[] data;public MyHashMap() {data = new LinkedList[BASE];for (int i = 0; i < BASE; ++i) {data[i] = new LinkedList<Pair>();}}public void put(int key, int value) {int h = hash(key);Iterator<Pair> iterator = data[h].iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Pair pair = iterator.next();if (pair.getKey() == key) {pair.setValue(value);return;}}data[h].offerLast(new Pair(key, value));}public int get(int key) {int h = hash(key);Iterator<Pair> iterator = data[h].iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Pair pair = iterator.next();if (pair.getKey() == key) {return pair.value;}}return -1;}public void remove(int key) {int h = hash(key);Iterator<Pair> iterator = data[h].iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Pair pair = iterator.next();if (pair.key == key) {data[h].remove(pair);return;}}}private static int hash(int key) {return key % BASE;}}
1. 两数之和
class Solution {public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {return new int[]{i, map.get(target - nums[i])};}map.put(nums[i], i);}return new int[]{-1, -1};}}
2. 两数相加
class Solution {public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode cur = dummy;int carry = 0;while (l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0) {int x = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;int y = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;int sum = x + y + carry;ListNode newHead = new ListNode(sum % 10);cur.next = newHead;cur = newHead;carry = sum / 10;if (l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;if (l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;}return dummy.next;}}
3. 无重复字符的最长子串
class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {Map<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();int left = 0, right = 0;int maxLen = 0;while (right < s.length()) {char c = s.charAt(right);window.put(c, window.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);right++;while (window.get(c) > 1) {char rc = s.charAt(left);window.put(rc, window.get(rc) - 1);left++;}maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, right - left);}return maxLen;}}
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
class Solution {public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();for (int val : nums) {if (pq.size() < k) {pq.offer(val);} else if (val > pq.peek()) {pq.poll();pq.offer(val);}}return pq.peek();}}
25. K 个一组翻转链表
class Solution {public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();for (int val : nums) {if (pq.size() < k) {pq.offer(val);} else if (val > pq.peek()) {pq.poll();pq.offer(val);}}return pq.peek();}}
146. LRU 缓存机制
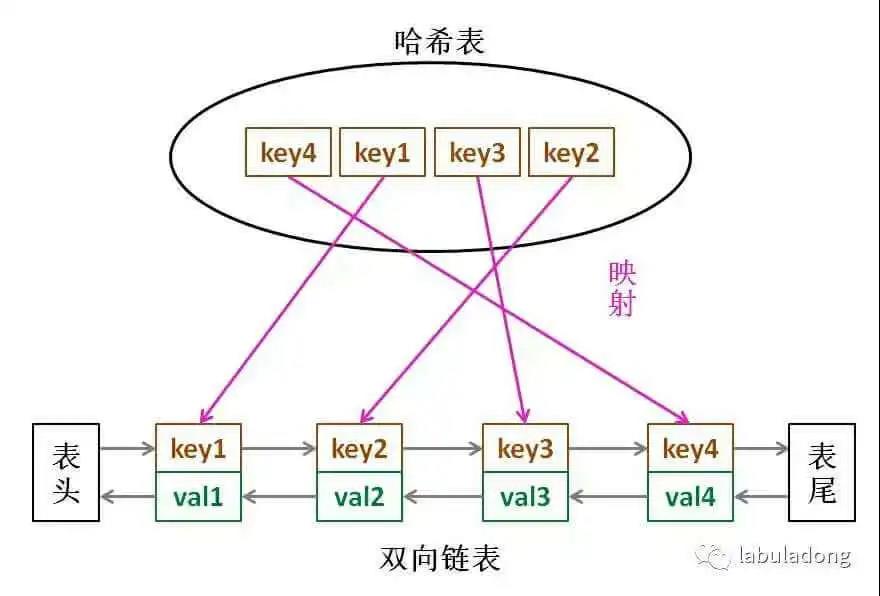
重点在makeRecently——remove之后再put
class LRUCache {int cap;//有序的双向链表LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> cache = new LinkedHashMap<>();public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.cap = capacity;}//get操作会有一次makeRecentlypublic int get(int key) {if (!cache.containsKey(key)) {return -1;}makeRecently(key);return cache.get(key);}//put操作如果key存在的话会更新值再做makerecently//如果不存在且大于容量会通过迭代器remove掉OldKeypublic void put(int key, int val) {if (cache.containsKey(key)) {cache.put(key, val);makeRecently(key);return;}if (cache.size() >= this.cap) {// 链表头部就是最久未使用的 keyint oldKey = cache.keySet().iterator().next();cache.remove(oldKey);}// 将新的 key 添加链表尾部cache.put(key, val);}private void makeRecently(int key) {int val = cache.get(key);// 删除 key,重新插入到队尾cache.remove(key);cache.put(key, val);}}
class LRUCache {private HashMap<Integer, Node> map;private DoubleList cache;private int cap;public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.cap = capacity;map = new HashMap<>();cache = new DoubleList();}public int get(int key) {if (!map.containsKey(key))return -1;int val = map.get(key).val;//Node.val// 利用 put 方法把该数据提前put(key, val);return val;}public void put(int key, int val) {// 先把新节点 x 做出来Node x = new Node(key, val);if (map.containsKey(key)) {// 删除旧的节点,新的插到头部cache.remove(map.get(key));cache.addFirst(x);// 更新 map 中对应的数据map.put(key, x);} else {if (cap == cache.size()) {// 删除链表最后一个数据Node last = cache.removeLast();map.remove(last.key);}// 直接添加到头部cache.addFirst(x);map.put(key, x);}}}class Node {public int key, val;public Node next, prev;public Node(int k, int v) {this.key = k;this.val = v;}}class DoubleList {// 头尾虚节点private Node head, tail;private int size;public DoubleList() {// 初始化双向链表的数据head = new Node(0, 0);tail = new Node(0, 0);head.next = tail;tail.prev = head;size = 0;}// 在链表尾部添加节点 x,时间 O(1)public void addLast(Node x) {x.prev = tail.prev;x.next = tail;tail.prev.next = x;tail.prev = x;size++;}// 删除链表中的 x 节点(x 一定存在)public void remove(Node x) {x.prev.next = x.next;x.next.prev = x.prev;size--;}// 删除链表中第一个节点,并返回该节点,时间 O(1)public Node removeFirst() {if (head.next == tail)return null;Node first = head.next;remove(first);return first;}// 返回链表长度,时间 O(1)public int size() { return size; }}
15. 三数之和
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();int len = nums.length;if (nums == null || len < 3) {return ret;}Arrays.sort(nums);for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {int L = i + 1;int R = len - 1;if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;while (L < R) {int sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];if (sum == 0) {ret.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));while (L < R && nums[L] == nums[L + 1]) L++;while (L < R && nums[R] == nums[R - 1]) R--;L++;R--;} else if (sum < 0){L++;} else {R--;}}}return ret;}}
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) return ret;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.add(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int cnt = queue.size();List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();while (cnt-- > 0) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();temp.add(node.val);if (node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);if (node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);}if (ret.size() % 2 == 0) {ret.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));} else {Collections.reverse(temp);ret.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));}}return ret;}}
160. 相交链表
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;while (pA != pB) {pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;}return pA;}}
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
想象一个最简单场景——p, q为root的左右子树,则left和right都不为null
都为null则返回null
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);if (left == null && right == null) return null;else if (left != null && right != null) return root;else return left == null ? right : left;}}
42. 接雨水
class Solution {public int trap(int[] height) {int len = height.length;int[] max_r = new int[len];int[] max_l = new int[len];int res = 0;for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {max_l[i] = Math.max(max_l[i - 1], height[i - 1]);}for (int j = len - 2; j >= 0; j--) {max_r[j] = Math.max(max_r[j + 1], height[j + 1]);}for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {int min = Math.min(max_l[i], max_r[i]);if (min <= height[i]) continue;else {res += min - height[i];}}return res;}}
优化:空间复杂度降为O(1)——双指针
public int trap(int[] height) {if (height.length == 0) return 0;int sum = 0;int n = height.length;int left = 0, right = n - 1;int l_max = height[0];int r_max = height[n - 1];while (left <= right) {l_max = Math.max(l_max, height[left]);r_max = Math.max(r_max, height[right]);if (l_max < r_max) {sum += l_max - height[left];left++;} else {sum += r_max - height[right];right--;}}return sum;}
415. 字符串相加
class Solution {public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();int carry = 0, i = num1.length() - 1, j = num2.length - 1;while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || carry != 0) {if(i>=0) carry += num1.charAt(i)-'0';if(j>=0) carry += num2.charAt(j)-'0';sb.append(carry%10);carry /= 10;i--;j--;}return sb.reverse().toString();}}
54. 螺旋矩阵
class Solution {public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) return res;int t = 0;int l = 0;int b = matrix.length - 1;int r = matrix[0].length - 1;while (true) {for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) res.add(matrix[t][i]);if (++t > b) break;for (int i = t; i <= b; i++) res.add(matrix[i][r]);if (--r < l) break;for (int i = r; i >= l; i--) res.add(matrix[b][i]);if (--b < t) break;for (int i = b; i >= t; i--) res.add(matrix[i][l]);if (++l > r) break;}return res;}}
88. 合并两个有序数组
class Solution {public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {int len1 = m - 1;int len2 = n - 1;int len = m + n - 1;while (len1 >= 0 && len2 >= 0) {nums1[len--] = nums1[len1] > nums2[len2] ? nums1[len1--] : nums2[len2--];}//如果走完nums1 nums2里面的元素还没有转移完,一定是比之前比较和和转移小的元素//直接拷贝到nums1的前面while (len2 >= 0) {nums1[len--] = nums2[len2--];}}}
33. 搜索旋转排序数组
class Solution {public int search(int[] nums, int target) {int lo = 0, hi = nums.length - 1;while (lo <= hi) {int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;if (nums[mid] == target) {return mid;}// 先根据 nums[mid] 与 nums[lo] 的关系判断 mid 是在左段还是右段if (nums[mid] >= nums[lo]) {// 再判断 target 是在 mid 的左边还是右边,从而调整左右边界 lo 和 hiif (target >= nums[lo] && target < nums[mid]) {hi = mid - 1;} else {lo = mid + 1;}} else {if (target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[hi]) {lo = mid + 1;} else {hi = mid - 1;}}}return -1;}}
200. 岛屿数量
class Solution {private int m, n;private int[][] direction = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {m = grid.length;n = grid[0].length;int count = 0;for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (grid[i][j] == '1') {dfs(grid, i, j);count++;}}}return count;}private void dfs(char[][] grid, int r, int c) {if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n || grid[r][c] != '1') {return;}grid[r][c] = '2';for (int[] d : direction) {dfs(grid, r + d[0], c + d[1]);}}}
199. 二叉树的右视图
class Solution {public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) {return res;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.add(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int cnt = queue.size();while (cnt-- > 0) {TreeNode temp = queue.poll();if (cnt == 0) {res.add(temp.val);}if (temp.left != null) queue.add(temp.left);if (temp.right != null) queue.add(temp.right);}}return res;}}
31. 下一个排列
class Solution {public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;int firstIndex = -1;//1.需要将后面大数的与前面小数的交换for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--) {if (nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {firstIndex = i;break;}}//2.如果不存在逆序整个数组if (firstIndex == -1) {reverse(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);return;}int secondIndex = -1;//3.从后往前找尽可能的大数,因为firstindex后面的是降序for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (nums[i] > nums[firstIndex]) {secondIndex = i;break;}}//4.交换大数与小数swap(nums, firstIndex, secondIndex);//5.firstindex后面是降序,reverse使其升序reverse(nums, firstIndex + 1, nums.length - 1);}private void reverse(int[] nums, int i, int j) {while (i < j) {swap(nums, i++, j--);}}private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int i1) {int tmp = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[i1];nums[i1] = tmp;}}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) return ret;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.add(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int cnt = queue.size();List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();while (cnt-- > 0) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();temp.add(node.val);if (node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);if (node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);}ret.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));}return ret;}}
300. 最长递增子序列
class Solution {public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {int n = nums.length;if (n < 2) {return n;}int[] dp = new int[n];Arrays.fill(dp, 1);int res = 0;for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);}}res = Math.max(res, dp[i]);}return res;}}
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {return traverse(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1,inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);}private TreeNode traverse(int[] preorder, int pS, int pE,int[] inorder, int iS, int iE) {if (pS > pE) return null;int rootVal = preorder[pS];int index = -1;for (int i = iS; i <= iE; i++) {if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {index = i;break;}}TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);int leftL = index - iS;root.left = traverse(preorder, pS + 1, pS +leftL,inorder, iS, index - 1);root.right = traverse(preorder, pS +leftL + 1, pE,inorder, index + 1, iE);return root;}}
20. 有效的括号
class Solution {public boolean isValid(String s) {Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {if (c == '(') stack.push(')');else if (c == '[') stack.push(']');else if (c == '{') stack.push('}');//没有考虑stack.isEmpty(),当只有右括号的时候不会入栈,此时栈是空的,不用后面的判断语句就可返回falseelse if (stack.isEmpty() || c != stack.pop()) return false;}//只有左括号的情况return stack.isEmpty();}}
46. 全排列
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {if (nums.length == 0) return ret;List<Integer> track = new ArrayList<>();boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[nums.length];backtrack(nums, track, hasVisited);return ret;}private void backtrack(int[] nums, List<Integer> track, boolean[] visited) {if (track.size() == nums.length) {ret.add(new ArrayList<>(track));return;}for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {if (visited[i]) continue;visited[i] = true;track.add(nums[i]);backtrack(nums, track, visited);track.remove(track.size() - 1);visited[i] = false;}return;}}
56. 合并区间
class Solution {public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {int len = intervals.length;Arrays.sort(intervals, (v1, v2) -> v1[0] - v2[0]);int[][] res = new int[len][2];int idx = -1;//索引for (int[] interval : intervals) {//判断遍历元素和结果数组if (idx == -1 || interval[0] > res[idx][1]) {res[++idx] = interval;} else {res[idx][1] = Math.max(res[idx][1], interval[1]);}}//因为合并区间之后会小于len,所以要截取要不然会有[0, 0]return Arrays.copyOf(res, idx + 1);}}
143. 重排链表
class Solution {public void reorderList(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return;ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;while (fast.next != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}ListNode needReverse = reverse(slow.next);slow.next = null;while (needReverse != null) {ListNode next = head.next;ListNode needNext = needReverse.next;needReverse.next = head.next;head.next = needReverse;head = next;needReverse = needNext;}}private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);while (head != null) {ListNode next = head.next;head.next = dummy.next;dummy.next = head;head = next;}return dummy.next;}}
112. 路径总和
//错误写法class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) return false;if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == root.val) {return true;}hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val);hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);return false;}}//函数返回类型是boolean类型的,所以递归的时候直接返回就可以了//对递归理解还是不够return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
字节实习面试算法题
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {return helper(root, 0);}public int helper(TreeNode root, int i){if (root == null) return 0;int temp = i * 10 + root.val;if (root.left == null && root.right == null)return temp;return helper(root.left, temp) + helper(root.right, temp);}
//思考每个节点需要做什么//如果是叶子节点,把该节点的值加到sum中//如果不是叶子节点,把左子树节点和右子树的节点加上该节点的值*10;private int sum = 0;public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return sum;if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {sum += root.val;}if (root.left != null) root.left.val += root.val*10;if (root.right != null) root.right.val += root.val*10;sumNumbers(root.left);sumNumbers(root.right);return sum;}
69. x 的平方根
class Solution {public int mySqrt(int x) {if (x <= 1) return x;int l = 1, h = x;while (l <= h) {int mid = l + (h - l) / 2;int sqrt = x / mid;if (sqrt == mid) {return mid;} else if (mid < sqrt){l = mid + 1;} else {h = mid - 1;}}return h;}}
23. 合并K个升序链表
class Solution {public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {if (lists.length == 0) return null;ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode cur = dummyHead;PriorityQueue<ListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v1.val - v2.val);for (ListNode list : lists) {if (list != null) {pq.add(list);}}while (!pq.isEmpty()) {ListNode nextnode = pq.poll();cur.next = nextnode;cur = cur.next;if (nextnode.next != null) {pq.add(nextnode.next);}}return dummyHead.next;}}
5. 最长回文子串
class Solution {public String longestPalindrome(String s) {String res = "";int n = s.length();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {String t1 = palindrome(s, i, i + 1);String t2 = palindrome(s, i, i);res = res.length() > t1.length() ? res : t1;res = res.length() > t2.length() ? res : t2;}return res;}public String palindrome(String s, int i, int j) {while (i >= 0 && j < s.length() && s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {i--;j++;}return s.substring(i + 1, j);}}
113. 路径总和 II
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) return ret;List<Integer> track = new ArrayList<>();backtrack(root, targetSum, track);return ret;}private void backtrack(TreeNode root, int targetSum, List<Integer> track) {if (root == null) return ;track.add(root.val);targetSum -= root.val;if (targetSum == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) {ret.add(new ArrayList<>(track));}backtrack(root.left, targetSum, track);backtrack(root.right, targetSum, track);track.remove(track.size() - 1);}}
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
class Solution {private int ret = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {/**对于任意一个节点, 如果最大和路径包含该节点, 那么只可能是两种情况:1. 其左右子树中所构成的和路径值较大的那个加上该节点的值后向父节点回溯构成最大路径,不能都在,都在就会重复2. 左右子树都在最大路径中, 加上该节点的值构成了最终的最大路径**/getMax(root);return ret;}private int getMax(TreeNode node) {if (node == null) return 0;int left = Math.max(0, getMax(node.left));//如果子树为负应该置0表示不包含子树int right = Math.max(0, getMax(node.right));ret = Math.max(ret, node.val + left + right);//判断在该节点包含左右子树的路径和是否大于当前最大路径和return Math.max(left, right) + node.val;// 返回经过root的单边最大分支给当前root的父节点计算使用}}
[
](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/)
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
好好理解迭代——不太好懂
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();while(stack.size()>0 || root!=null) {//不断往左子树方向走,每走一次就将当前节点保存到栈中//这是模拟递归的调用if(root!=null) {stack.add(root);root = root.left;//当前节点为空,说明左边走到头了,从栈中弹出节点并保存//然后转向右边节点,继续上面整个过程} else {TreeNode tmp = stack.pop();res.add(tmp.val);root = tmp.right;//这一句当时没理解}}return res;}
76. 最小覆盖子串
输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"输出:"BANC"
class Solution {public String minWindow(String s, String t) {Map<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap<>();Map<Character, Integer> need = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {char c = t.charAt(i);need.put(c, need.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);}int left = 0, right = 0, vaild = 0;int start = 0, len = Integer.MAX_VALUE;while (right < s.length()) {char addChar = s.charAt(right);window.put(addChar, window.getOrDefault(addChar, 0) + 1);right++;if (need.containsKey(addChar) && need.get(addChar).equals(window.get(addChar))) vaild++;while (vaild == need.size()) {if (right - left < len) {start = left;len = right - left;}char removeChar = s.charAt(left);left++;if (need.containsKey(removeChar) && window.get(removeChar).equals(need.get(removeChar))) vaild--;window.put(removeChar, window.get(removeChar) - 1);}}return len == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(start, start + len);}}
958. 二叉树的完全性检验
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return true;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.add(root);TreeNode temp;boolean flag = false;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {temp = queue.remove();if (temp == null) {flag = true;//如果遇到空,执行下一次continue;}if (flag) return false;//下一次不能有非空,否则不是完全树queue.add(temp.left);queue.add(temp.right);}return true;}
[
](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/)
[
](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/min-stack/)
39. 组合总和
输入: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7输出: [[7],[2,2,3]]
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {List<Integer> track = new ArrayList<>();backtrack(0, candidates, target, track);return ret;}private void backtrack(int index, int[] candidates, int target, List<Integer> track) {if (target == 0) {ret.add(new ArrayList<>(track));return;}for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) {if (candidates[i] <= target) {track.add(candidates[i]);backtrack(i, candidates, target - candidates[i], track);track.remove(track.size() - 1);}}}}
98. 验证二叉搜索树
class Solution {long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE;public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return true;}// 访问左子树if (!isValidBST(root.left)) {return false;}// 访问当前节点:如果当前节点小于等于中序遍历的前一个节点,说明不满足BST,返回 false;否则继续遍历。if (root.val <= pre) {return false;}pre = root.val;// 访问右子树return isValidBST(root.right);}}
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode fast = head;while (n-- >0) {fast = fast.next;}if (fast == null) return head.next;ListNode slow = head;while (fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}slow.next = slow.next.next;return head;}}
32. 最长有效括号
class Solution {public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {int max=0;//存放最大的长度int len=s.length();//字符串长度Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();//暂存字符stack.push(-1);//初始化栈底for(int i=0;i<len;i++) {if(s.charAt(i)=='(')//字符串存在(stack.push(i);else {stack.pop();//下标出栈if(stack.isEmpty()) {//出栈以后,栈为空stack.push(i);}else {max=Math.max(max, i-stack.peek());//选出最长的长度}}}return max;}}
思想:栈——左括号入栈,右括号是让栈里的元素出栈计算长度,如果出栈后栈为空,则让当前元素入栈。
注意:栈中元素是下标
209. 长度最小的子数组
滑动窗口——当sum大于等于target时计算长度移动左指针
class Solution {//滑动窗口//使用 while 循环时对左侧窗口在哪里进行移动,在计算结果之前移动还是计算结果之后移动,里面有很大的差别,//这也就是和很多题解中使用 for 循环时最后计算结果有 right - left + 1 存在的原因 。public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {int left = 0, right = 0;int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int sum = 0;while (right < nums.length) {sum += nums[right];right++;while (sum >= target) {result = (result < right -left) ? result : right -left;sum -= nums[left];left++;}}return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : result;}}
221. 最大正方形
class Solution {public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) {/**dp[i][j]表示matrix[i - 1][j - 1]为右下角所能构成的最大正方形边长, 则递推式为:dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);**/int m = matrix.length;int n =matrix[0].length;int max = 0;int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {if (matrix[i - 1][j - 1] == '1') {dp[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(dp[i-1][j-1], Math.min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]));max = Math.max(max, dp[i][j]);}}}return max * max;}}
165. 比较版本号
输入:version1 = "1.01", version2 = "1.001"输出:0解释:忽略前导零,"01" 和 "001" 都表示相同的整数 "1"
class Solution {public int compareVersion(String version1, String version2) {int i = 0, j = 0;//每过一个段a和b重新计算char[] v1 = version1.toCharArray();char[] v2 = version2.toCharArray();while (i < version1.length() || j < version2.length()) {int a = 0, b= 0;while(i < version1.length() && v1[i] != '.') a = a * 10 + v1[i++] - '0';while(j < version2.length() && v2[j] != '.') b = b * 10 + v2[j++] - '0';if (a > b) return 1;else if (a < b) return -1;i++;j++;}return 0;}}
169. 多数元素
class Solution {public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {int vote = 0, x = 0;for (int val : nums) {if (vote == 0) x = val;vote += val == x ? 1 : -1;}return x;}}
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次
class Solution {public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;ListNode next = head.next;if (head.val == next.val) {while (next != null && head.val == next.val) {next = next.next;}head.next = deleteDuplicates(next);} else {head.next = deleteDuplicates(next);}return head;}}
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
重复元素需要删除
class Solution {public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;ListNode next = head.next;if (head.val == next.val) {while (next != null && head.val == next.val) {next = next.next;}head = deleteDuplicates(next);} else {head.next = deleteDuplicates(next);}return head;}}
48. 旋转图像
//先上下,再对角线class Solution {public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;for (int i = 0; i < m / 2; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {int t = matrix[i][j];matrix[i][j] = matrix[m - i - 1][j];matrix[m - i - 1][j] = t;}}for (int i =0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {int t =matrix[i][j];matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];matrix[j][i] = t;}}}}
718. 最长重复子数组
输入:A: [1,2,3,2,1]B: [3,2,1,4,7]输出:3解释:长度最长的公共子数组是 [3, 2, 1] 。
class Solution {public int findLength(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {if (nums1.length == 0 || nums2.length == 0) return 0;int m = nums1.length, n = nums2.length;int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];//有索引偏移,dp[i][j]代表以A[i-1]与B[j-1]结尾的公共字串的长度,//数组中的m + 1和 n + 1是数组长度,而不是可以取到该索引处int result = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {if (nums1[i - 1] == nums2[j - 1]) {dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;result = Math.max(result, dp[i][j]);}}}return result;}}
162. 寻找峰值
二分查找——判断nums[i]和nums[i + 1]的关系
class Solution {public int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;while (left < right) {int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) {right = mid;} else {left = mid + 1;}}return left;}}
0.36进制加法
class Solution {public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();int carry = 0, i = num1.length() - 1, j = num2.length - 1;while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || carry != 0) {if(i>=0) carry += getInt(num1.charAt(i));if(j>=0) carry += getInt(num2.charAt(j));sb.append(getChar(carry%36));carry /= 36;i--, j--;}return sb.reverse().toString();}private char getChar(int n) {if (n <= 9) return n + '0';else return n - 10 + 'a';}private int getInt(char ch) {if ('0' <= ch && ch <= '9')return ch - '0';elsereturn ch - 'a' + 10;}}
148. 排序链表
使用归并排序,快慢指针找中点,拆分链表,再合并链表
class Solution {public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;ListNode l, r;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}r = sortList(slow.next);slow.next = null;l = sortList(head);return merge(l, r);}private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode p = dummy;while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {if (l1.val < l2.val) {p.next = l1;l1 = l1.next;} else {p.next = l2;l2 = l2.next;}p = p.next;}p.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;return dummy.next;}}
394. 字符串解码
输入:s = “3[a]2[bc]” 输出:“aaabcbc”
class Solution {public String decodeString(String s) {StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();int multi = 0;Stack<Integer> stack_multi = new Stack<>();Stack<String> stack_res = new Stack<>();for(char c : s.toCharArray()) {if(c == '[') {stack_multi.push(multi);stack_res.push(res.toString());multi = 0;res = new StringBuilder();}else if(c == ']') {StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();int cur_multi = stack_multi.pop();for(int i = 0; i < cur_multi; i++) tmp.append(res);res = new StringBuilder(stack_res.pop() + tmp);}else if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') multi = multi * 10 + c - '0';//如果k不是个位数而是n位整数的话就要通过不停的乘10来更新值else res.append(c);}return res.toString();}}
114. 二叉树展开为链表
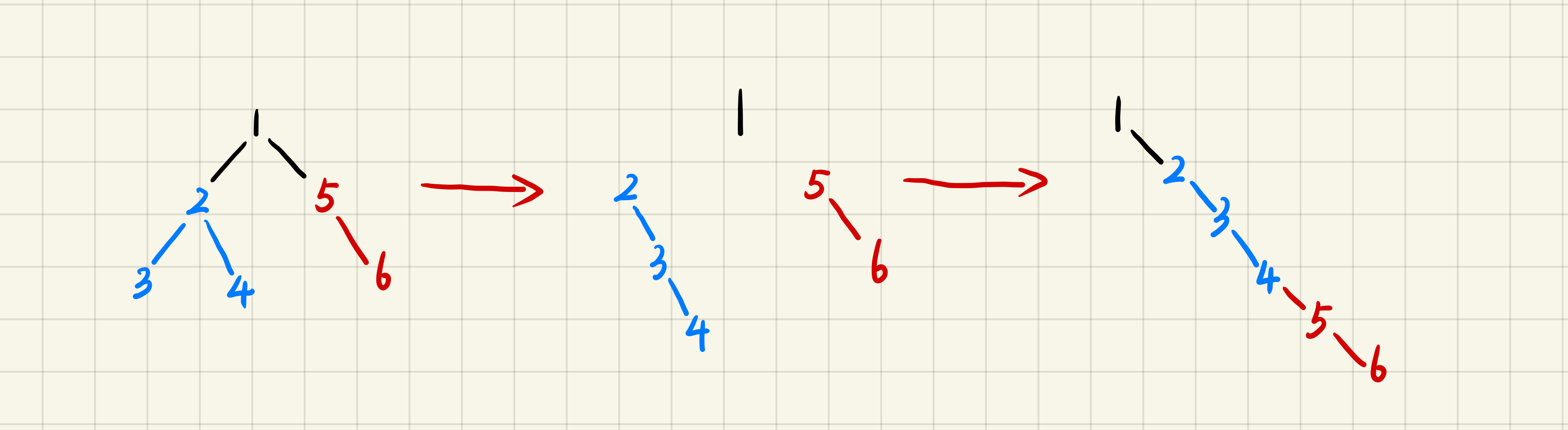
- 首先将根节点的左子树变成链表
- 其次将根节点的右子树变成链表
- 最后将变成链表的右子树放在变成链表的左子树的最右边
```java
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
} }if(root == null){return ;}//将根节点的左子树变成链表flatten(root.left);//将根节点的右子树变成链表flatten(root.right);TreeNode temp = root.right;//把树的右边换成左边的链表root.right = root.left;//记得要将左边置空root.left = null;//找到树的最右边的节点while(root.right != null) root = root.right;//把右边的链表接到刚才树的最右边的节点root.right = temp;
``` [
](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/diao-zheng-shu-zu-shun-xu-shi-qi-shu-wei-yu-ou-shu-qian-mian-lcof/)

