一、File类
概念
- 代表物理盘符中的一个文件或者文件夹
常见方法
**exists()** |
文件是否存在 |
|---|---|
| isDirectory() | 是否是目录 |
| isFile() | 是否是文件 |
| length() | 返回文件长度 |
**getName()** |
文件的名字 |
| getAbsolutePath() | 获取文件绝对路径 |
**createNewFile()** |
创建一个新的文件 |
**delete()** |
删除文件 |
| getParent() | 上级目录 |
| mkdir() | 创建一个新目录 |
| listFiles() | 列出目录中的所有内容 |
跟文件相关的
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建文件对象File f = new File("d:/test");File f1 = new File("d:\\test");/*File.separator获取当前操作系统的路径拼接符号File file2 = new File("d:"+File.separator+ "test");*/System.out.println("文件是否可读:" + f.canRead());System.out.println("文件是否可写:" + f.canWrite());System.out.println("文件的名字:" + f.getName());System.out.println("上级目录:" + f.getParent());System.out.println("是否是一个目录:" + f.isDirectory());System.out.println("是否是一个文件:" + f.isFile());System.out.println("是否隐藏:" + f.isHidden());System.out.println("文件的大小:" + f.length());System.out.println("是否存在:" + f.exists());System.out.println("比较两个对象对应的文件路径:" + f.equals(f1));System.out.println("绝对路径路径:" + f.getAbsolutePath());System.out.println("相对路径:" + f.getPath());System.out.println("toString:" + f.toString());//相当于相对路径if (f.exists()) {//如果文件存在,将文件删除操作f.delete();} else { //如果文件不存在,就创建这个文件f.createNewFile();}}}
跟目录相关的
public class File01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建文件对象File f = new File("d:/test");f.mkdir();//创建单层目录f.mkdirs();//创建多层目录f.delete();//只会删除一层,并且这层目录是空的,如果有内容就不会删除//查看文件下的目录File[] files = f.listFiles();for(File file:files){System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());}}}
二、io流
iO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输,io流形象地理解一个“管子”,程序和数据源直接**沟通**的桥梁
IO流分类
- 方向:输入流 和 输出流
- 内容:字节流 和 字符流
IO流体系
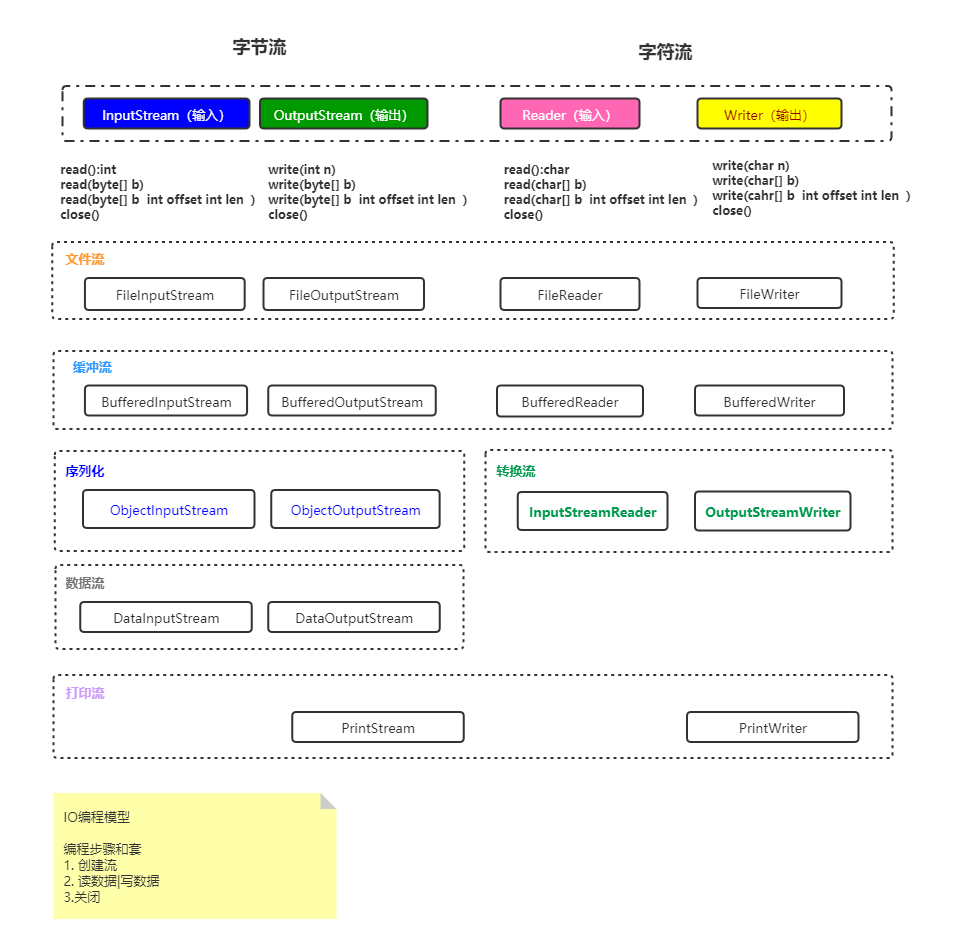
经验 , Stream结尾的为字节流 Reader Writer为字符流
三、字节流
文件流
以字节形式读取文件数据,通常适用于读二进制文件 如图片 视频 音频文件等。
输入流 FileInputStream
方式1
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1. 创建流对象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("G:\\LOL.jpg");// 2. 读数据int count = 0;//定义一个计数器,用来计读入的字节个数int n = frs.read();while(n! = -1){count++;System.out.print(n);n= frs.read();}System.out.print(count);// 3.关闭流fis.close();}
方式2
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1. 创建流对象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("G:\\LOL.jpg");// 2. 读数据byte[] buff = new byte[6];// 准备临时存放容器,用于每次存储读取的数据int len = 0;//本次读取的实际字节数//循环读取字节while ((len = fis.read(buff)) != -1) {String s = new String(buff, 0, len);System.out.println(s);}// 3.关闭fis.close();}
注意事项
- 文件是
**utf-8**进行存储的,**英文字符**:底层占用**1个字节**。**中文字符**,底层占用**3个字节** - 如果文件是文本文件,不要使用字节流读取,建议使用字符流
**read()**读取一个字节,返回值是int类型,而不是byte类型,这是因为read方法底层做了处理,让繁华的数据都是**正数**,就是为了避免如果字节繁华的是-1,那么到底是读入的字节,还是文件结尾呢
输出流 FileOutStream
public class FileOutputStreamCase {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1. 创建流FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("G:\\LOL.jpg",true);//2. 写数据String massage = "我喜欢景甜";fos.write( massage.getBytes() );//3 . 关闭流fos.close();}}
功能:完成图片复制
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//源图片File f1 = new File("G:\\LOL.jpg");//目标图片File f2 = new File("G:\\LOL.jpg");//创建输入流对象FileReader fr = new FileInputStream(f1);//创建输出流对象FileWriter fw = new FileOutputStream(f2);//【方式1 读数据 写数据】int n = fis.read();while(n! = -1){fw.write(n)n= fis.read();}//【方式2 利用缓冲字符数组】byte[] b = new byte[5];int len = fis.read(b);while(len != -1){fw.write(b,o,len)//将缓冲数组中有效长度写出len = fis.read(b);}//关闭流(关闭流的时候,倒着关闭,后用先关)fos.close();fis.close();}}
缓存流
没有特别功能,指定提供了缓冲,优先从缓存中读写,降低和IO设备访问次数提高效率。
输入流 BufferedInputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1. 创建流BufferedInputStream bis =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("G:\\LOL.jpg"));//2. 读文件byte[] buff = new byte[1024];int len = 0;while( (len=bis.read(buff)) !=-1 ){String xx = new String( buff, 0 , len );System.out.println(xx);}//3.关闭bis.close();}
输出流 BufferedOutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1. 创建流BufferedOutputStream bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("G:\\LOL.jpg) );//2. 写数据String massage = "q床前明月光,疑是地上霜q";bos.write( massage.getBytes() );bos.flush(); //缓冲流的方法//3. 关闭流bos.close();}
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//1. 源图片BufferedInputStream bis =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("G:\\LOL.jpg"));//1. 目标图片BufferedOutputStream bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("G:\\LOL1.jpg) );//利用缓冲字符数组byte[] b = new byte[1024*5];int len = bis.read(b);while(len != -1){bos.write(b,o,len)//将缓冲数组中有效长度写出len = bis.read(b);}//关闭流(bos.close();bis.close();}}
对象流
对象流作用是,可以把一个对象写到文件中,或者把一个文件中的对象,读取到内存。它就是序列化和反序列化的流:
序列化: 把对象二进制信息 写入流。
反序列化: 从流中读取对象的二进制信息,还原到内存。
序列化流ObjectOutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1 创建流ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("obj.dat") );//2. 写数据:将内存中的字符串写到文件中oos.writeInt("你好");//3.关闭oos.close();}
反序列化流ObjectInputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {//1. 创建流ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("obj.dat"));//2. 读,必须按照序列化顺序读取且不可多读,否则引发EOFException异常。String s = (String)(ois.readObject();System.out.println(s);//3.关闭ois.close();}
细节: 1. 反序列化必须提供需要的字节码 2. 本地字节码版本号和流中的版本号要一致。
四、字符流
文件流[重点]
以子符形式读取文件数据,通常适用于读取纯文本文件 存文本信息。
FileReader 输入流
/** 需求:往文件中读数据* 写数据--输出流--FileReader*/public class FileReaderDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建一个File类File f = new File("d:\\Test.txt");//创建输入流对象FileReader fr = new FileReader(f);//方式1:读数据int n = fr.read();while(n! = -1){System.out.print(n);n= fr.read();}//方式2:读数据int n;while((n=fr.read())!=-1) {System.out.print((char)n);}//关闭流fr.close();}}
FileWriter 输出流
/** 需求:往文件中写数据* 写数据--输出流--FileWriter*/public class FileWriter {public static void main(String[] args) {//目标文件File f = new File("d:\\demo.txt");//创建输出流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter();//写数据String str = "你好中国";char[] chars = str.toCharArray();fw.write(chars);//关闭流fw.close();}}
利用:FileReader、FileWriter文件复制
public class FileWriter {public static void main(String[] args) {//源文件File f1 = new File("d:\\demo.txt");//目标文件File f2 = new File("d:\\demo1.txt");//创建输入流对象FileReader fr = new FileReader(f1);//创建输出流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(f2);//【方式1 读数据 写数据】int n = fr.read();while(n! = -1){fw.write(n)n= fr.read();}//【方式2 利用缓冲字符数组】char[] ch = new char[5];int len = fr.read(ch);while(len != -1){fw.write(ch,o,len)//将缓冲数组中有效长度写出len = fr.read(ch);}//关闭流(关闭流的时候,倒着关闭,后用先关)fw.close();fr.close();}}
注意事项
相对路径:相对当前项目而言的,在项目的根目录下(Test.txt)
绝对路径:以盘符开始的路径(d:\Test.txt)
* 不要用字符流操作非文本文件
close()和flush()方法的区别:
flush(): 刷新缓冲区。流对象还可以继续使用。close(): 先刷新缓冲区,然后通知系统释放资源。流对象不可以再被使用了。public class FileWriterDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建输出流对象//FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:\\word.txt");FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("word.txt");//调用输出流对象的写数据方法,并刷新缓冲区fw.write("helloworld");fw.flush();fw.write("java");fw.flush();//释放资源fw.close();//Stream closed//fw.write("javaee");//fw.flush();}}
构造方法
void write(String str):写一个字符串数据void write(String str,int index,int len):写一个字符串中的一部分数据void write(int ch):写一个字符数据,这里写int类型的好处是既可以写char类型的数据,也可以写char对应的int类型的值。’a’,97void write(char[] chs):写一个字符数组数据void write(char[] chs,int index,int len):写一个字符数组的一部分数据public class FileWriterDemo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建输出流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.txt");//void write(String str):写一个字符串数据//fw.write("abcde");//void write(String str,int index,int len):写一个字符串中的一部分数据//fw.write("abcde",0,5);//fw.write("abcde",1,3);//void write(int ch):写一个字符数据,这里写int类型的好处是既可以写char类型的数据,也可以写char对应的int类型的值。'a',97//fw.write('a');//fw.write(97);//void write(char[] chs):写一个字符数组数据char[] chs = {'a','b','c','d','e'};//fw.write(chs);//void write(char[] chs,int index,int len):写一个字符数组的一部分数据//fw.write(chs,0,5);fw.write(chs,2,3);//释放资源fw.close();}}
缓冲流
BufferedReader 输入流
BufferedWriter 输出流
特别方法 **readLine() **可以一次读取一行,如果未读到返回null
特别方法 **newLine() **相当于写一个**换行**符
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1 创建流BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("g:/book.txt"));//1 创建流BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter( new FileWriter("node.txt",true));//2 读数据String str = br.readLine()//每次读取文本中一行,返回字符串while( str !=null ){br.write(str)bw.newLine();//换行str = br.readLine()}//3.关闭流bw.close();br.close();}
转换流
有些时候,如果读取的文件是文本文件,但是提供的却是字节流,字符流明显读取文本字符更加方便,这时可以把字节流转换成字符流操作。
只有字节流转 字符流没有字符流转字节流,转换流本身就是一种字符流。
InputStreamReader 输入流
/*** 字节输入流 转 字符输入流*/public class InputStreamReaderCase {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//字符流BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader( new FileInputStream("d:/text.txt") ) );String buff = null;while ( (buff=br.readLine()) !=null ){System.out.println(buff);}br.close();}}
OutputStreamWriter 输出流
** 字节输出流 转 字符输出流*/public class OutputStreamWriterCase {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter( new OutputStreamWriter( new FileOutputStream("d:/text.txt") ) );bw.newLine();bw.write("王麻子,20,男,C#");bw.flush();bw.close();}}
利用:InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter文件复制
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//源文件输入方向BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader( new FileInputStream("d:/text.txt") ) );//目标文件输出方向BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter( new OutputStreamWriter( new FileOutputStream("d:/text1.txt") ) );//开始动作char[] ch = new char[20];int len = br.read(ch);while(len!=-1){bw.write(ch,0,len)en = br.read(ch);}//关闭流bw.close();br.close();}}
编码与字符集
编码指的是把字符与数字对应的过程。 字符集就是一张记录了对应关系的信息表。ASCII就是一种编码表。像这种还有很多。
- GBK 国标码
- ISO-8859-1 西欧语言
- Big5 台湾香港 繁体字
Unicode 联合编码( UTF-8 UTF-16 )
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String hello = "你好中国";byte[] bytes = hello.getBytes();// UTF-8 解码System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));byte[] buff = {-28, -67, -96, -27, -91, -67, -28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67};String newHello = new String( buff ,"UTF-8" ); // 使用 UTF-8 编码System.out.println(newHello);System.out.println("--------------------------------------");FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:/hello.txt");InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"GBK");char[] buff2= new char[1204];int len;while ( ( len = isr.read(buff2))!=-1 ){System.out.println(buff2);}isr.close();fis.close();}
编码解码不一致,就会出现乱码
打印流
字节打印流PrintStream
public class PrintDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 直接打印到文件PrintStream out = new PrintStream("d:/abc.txt");out.println("helloword");// 打印到 其他字节输出流FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("d:/abc.txt",true);PrintStream out2 = new PrintStream( os);out2.println("java");}}
字符打印流 PrintWriter
public class PrintDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//直接 打印到文件PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("D:/abc.txt");pw.println("css");pw.close();//打印 到其它字符输出流PrintWriter pw2 = new PrintWriter( new FileWriter("d:/abc.txt",true));pw2.println("java");pw2.close();//打印 到其他字节输出流PrintWriter pw2 = new PrintWriter( new FileOutputStream("d:/abc.txt",true) );pw2.println("java");pw2.close();}}
键盘录入的内容输出到文件中【重点】
public class Test03 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1、先准备输入方向//键盘录入InputStream in = System.in;//属于字节流//字节流转字符流InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in);//在isr外面套一个缓冲流BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);// 2、再准备输出方向//准备目标文件File f = new File("d:\\test.tex");FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(f);BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);// 3、开始动作String s = br.readLine();while (!s.equals("exit")){bw.write(s);bw.newLine();s = br.readLine();}// 4、关闭流bw.close();br.close();}}
随机文件访问类
RandomAccessFile 此类是一个文件读写操作工具类,它和其他流不同,它没有方向性,它既可以读文件,也可以写文件。
支持模式: r 只读 w只写 rw读写
通过seek(int pos) 方法移动指针
package print;import java.io.*;public class PrintDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//随机访问文件类RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("d:/abc.txt","rw");//移动光标到末尾 写数据raf.seek( raf.length() );raf.writeBytes("mysql");//移动光标到 开始 读操作raf.seek(0);String line = raf.readLine();System.out.println(line);raf.close();}}
System类对IO流的支持
**System.in**:输入流——>默认情况下,从键盘输入**Scanner**: 起扫描作用
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Scanner sc = new Scanner(new FileInputStream(new File("d\\Test.txt")));while (sc.hasNext()){System.out.println(sc.next());}}}
�**System.out**: 输出流——>默认情况下,输出到控制台
public class Test02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//写到控制台PrintStream out = System.out;//调用方法:不换行out.print("你好1");out.print("你好2");out.print("你好3");//换行out.println("你好1");out.println("你好2");out.println("你好3");System.out.println("你是");System.out.print("中国人");}}

