Object类介绍
所有**类**都直接或间接的继承Object类,Object类是所有类的**根基类**,它里面定义的都是一个非常基础的方法,这些方法,通常都不适用,往往要**重写**。
这个类是java.lang包下的一个类,直接使用无需导包。
所有java对象都拥有Object类的属性方法作为参数,可以接受任何对象作为返回值,可返回任何对象
常用方法
toString() : String
作用:打印对象的信息
**重写前**:打印的是**全类名+@+16进制的hashcode()**```java public class Student { private String name; private int age;public Student() { }
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
```javapublic class Test02 {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "abc";System.out.println(str.toString());Student s = new Student("哈哈",34);System.out.println(s.toString());//Student@1b6d3586}}
**重写后**:打印的是**对象中的属性值**public class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}}
public class Test02 {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "abc";System.out.println(str.toString());Student s = new Student("哈哈",34);System.out.println(s.toString());}}
equals( Object other) : boolean
作用:比较两个对象是否相等,**默认比较的是地址**,如果对象需要比较**属性值**,则需**重写**
**重写前**:**比较的是对象中的地址值**public class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}}
public class Test05 {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "abc";String s2 = "abc";System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//trueStudent stu1 = new Student("哈哈",35);Student stu2 = new Student("哈哈",35);System.out.println(stu1.equals(stu2));//false}}
**重写后**:**比较的是对象中的属性值**```java public class Student { private String name; private int age;public Student() { }
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
}
```javapublic class Test05 {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "abc";String s2 = "abc";System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//trueStudent stu1 = new Student("哈哈",35);Student stu2 = new Student("哈哈",35);System.out.println(stu1.equals(stu2));//true}}
hashCode() : int
作用:获得该对象的哈希码,hashcode折射出的是该对象的**地址信息**(并不是直接地址)**用比较地址来判断是不是属于同一个对象**
public class TestPerson {public static void main(String[] args) {Person p1 = new Person();System.out.println(p1.hashCode());//内存地址:1872034366Person p2 = new Person();System.out.println(p2.hashCode());//内存地址:1581781576}}
不同对象的 hashcode 是不同的。两个对象不相等 那么 hashcode也应该不同。
getClass() :Class
作用:获得**对象类型信息**,比如获得类名,属性信息,方法信息等。
public class TestPerson {public static void main(String[] args) {Person person = new Person();Class<? extends Person> aClass = person.getClass();System.out.println(aClass);//class com.xixi.Person//这个类型有那些属性Field[] arr = aClass.getDeclaredFields();for(Field xx :arr){System.out.println(xx.getName());//name age}}}
finalize():void
- 当对象被判断为垃圾对象时,由
**jvm**自动调用此方法,用以标记垃圾对象,进入回收队列 - 垃圾对象:没有有效引用指向改对象时,为垃圾对象
- 垃圾回收:有GC销毁垃圾对象,次方数据存储空间
- 自动回收机制:jvm的内存耗尽,一次性回收所有垃圾对象
- 手动回收机制:使用System.gc();通过jvm执行垃圾回收
```java
class Student extends Person{
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable{
}System.out.println("GG");
}
```javapublic class TestStudent {public static void main(String[] args) {Student student = new Student();student = null;System.gc();//调用gc,触发jvm垃圾对象回收}}
调用垃圾回收,需先重写
clone( ) : Object
复制一个对象的方法。通常一个对象要支持克隆需要实现一个 Cloneable 接口,否则引发 CloneNotSupportedException 。如果不实现这个接口,需要手动创建对象填充属性值。
Cloneable 是一个标志接口,用于标识一个类是否支持克隆。
class Foo implements Cloneable {String name;int age;public Foo(){}public Foo(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overrideprotected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {return super.clone();}}
Objectst类介绍
equals()方法
作用:比较两个**对象是否相同**,但是加了一些**健壮性的判断**
public class Test04 {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = null;String s2 = "abc";//System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//NullPointerExceptionboolean result = Objects.equals(s1, s2);System.out.println(result);}}
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2))打印输出结构会报
**空指针异常**,但是**Objects.equals**可打印输出结果
String类:
不可变字符串
概述
**java.lang.String**类代表字符串
程序当中所有的**双引号**字符串,都是String类的对象。(就算没有new,也照样是)
字符串的特点
- 字符串的
**内容永不可变** - 正是因为字符串不可改变,所以字符串是可以
**共享使用**的 - 字符串效果上相当于是
**char[]**字符数组,但是底层原理是**byte[]**字节数组
字符串的构造方法和直接创建
三种构造方法
public String()创建一个空白的字符串,不含任何内容 ```java public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) {
}//使用空参构造String s = new String();//小括号留空,表示啥字符都没有System.out.println("第一个字符串:"+s);
- `public String(char[] array)` 根据字符数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串```javapublic class Demo02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//根据自发数组创建字符串char[] charArray = {'A','B'};String s = new String(charArray);System.out.println(s);}}
public String(byte[] array)根据字节数组的内容,来创建对应的字符串public class Demo03 {public static void main(String[] args) {//根据字节数组创建字符串byte[] byteArray = {97,98,99};String s = new String(byteArray);System.out.println(s);}}
直接创建:String str = "heihei";
public class Demo04 {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "heihei";System.out.println(str);}}
注意:直接写上双引号,就是字符串对象
字符串常量池
字符串常量池:程序当中直接写上的双引号字符串,就在字符串常量池中
基本数据类型:**==**是进行【数值】的比较
引用数据类型:**==**是进行【地址值】的比较
public class Demo05 {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "abc";String str2 = "abc";char[] charArray = {'a','b','c'};String str3 = new String(charArray);System.out.println(str1==str2);//trueSystem.out.println(str1==str3);//falseSystem.out.println(str2==str3);//false}}
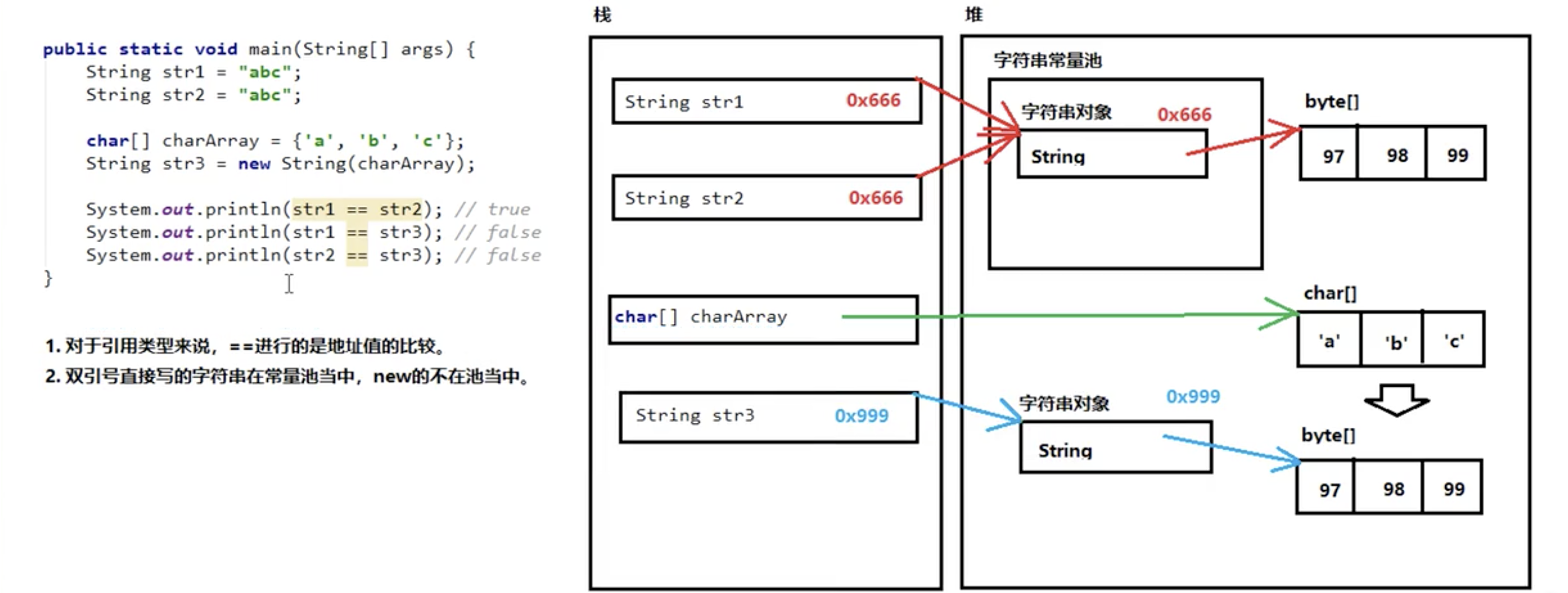
字符串比较方法
==是进行对象的【地址值】比较,如果确实需要字符串的【内容】比较,可以使用2个方法
public bollean equals(Object obj); 参数可以是任何对象,只有参数是一个字符并且内容相同,才是true,否则false
注意事项:
- 任何对象都能用Object进行接收
equals方法具有对称性,也就是a.equals(b)和b.equals(a)效果一样如果比较双方一个常量一个变量,推荐把常量字符串写在前面 。
推荐:`"abc".equals(str)`<br /> 不推荐:`str.equals("abc")`<br /> 原因:<br /> String str5 = null;<br /> System._out_.println_(_"abc.equals(str5)"_)_;//false<br /> System._out_.println_(_str5.equals_(_"abc"_))_;//NullPointerException 空指针异常
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase_(_String str_)_忽略大小写,进行内容比较,只有英文字母区分大小写,其他都不区分String strA = "Java";String strB = "java";System.out.println(strA.equals(strB));//false 严格区分大小写System.out.println(strA.equalsIgnoreCase(strB))//true
public class test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {String a = new String("ab"); // a 为一个引用String b = new String("ab"); // b为另一个引用,对象的内容一样String aa = "ab"; // 放在常量池中String bb = "ab"; // 从常量池中查找if (aa == bb) // trueSystem.out.println("aa==bb");if (a == b) // false,非同一对象System.out.println("a==b");if (a.equals(b)) // trueSystem.out.println("aEQb");if (42 == 42.0) { // trueSystem.out.println("true");}}}
字符串获取方法
public int length获取字符串长度public class Demo07 {public static void main(String[] args) {//获取字符串长度int length = "agsiwnemekke".length();System.out.println("字符串的长度:"+length);}}
public String concat(String str)将当前字符串和参数字符串拼接成为新的字符串public class Demo07 {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "hello";String str2 = "world";String str3 = str1.concat(str2);//拼接字符串System.out.println(str1);//helloSystem.out.println(str2);//worldSystem.out.println(str3);//helloworld}}
�public char charAt(int index)获取指定索引位置的单个字符public class Demo07 {public static void main(String[] args) {char c = "hello".charAt(2);System.out.println("在2号索引位置的字符是:"+c);}}
public int indexOf(String str)查找参数字符串在本字符串当中首次出现的索引位置,如果没有返回-1值public class Demo07 {public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "hehhhleowond";int index = s.indexOf("le");System.out.println("第一次索引值"+index);//5System.out.println("helloworld".indexOf("abc"));//-1 因为不存在abc}}
字符串截取方法
public String Substring(int index) 截取从参赛位置一直到字符串末尾,繁华新的字符串public String substring(int begin,int end) 截取从begin到end中间的字符串
备注:
[begin,end)包含左边,不包含右边
public class Demo08SubString {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "HelloWorld";String str2 = str1.substring(6);System.out.println(str1);//HelloWorldSystem.out.println(str2);//orldString str3 = str1.substring(3,7);System.out.println(str3);//loWo}}
public class Demo09SubString {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "Hello";System.out.println(str1);//Hellostr1 = "Java";System.out.println(str1);//Java}}
上面Demo09SubString这种写法,字符串内容仍然是没有改变的
str1保存的是地址值,相当于str1地址值Hello的0x99,后来地址值变成了Java的0x77�
字符串转换方法
public char[] toCharArray() 将当前字符串拆分成为字符数组作为返回值
public class DemoStringConvert {public static void main(String[] args) {char[] chars = "Hello".toCharArray();System.out.println(chars[0]);//HSystem.out.println(chars.length);//5}}
public byte[] getBytes() 获取当前字符串底层的字节数组
public class DemoStringConvert {public static void main(String[] args) {byte[] bytes = "abc".getBytes();for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {System.out.println(bytes[i]);}}}
public String replace(CharSequence oldString,CharSequence newString) 所有老字符串替换成新的字符串
public class DemoStringConvert {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "How do you do";String str2 = str1.replace("o","*");System.out.println(str1);//How do you doSystem.out.println(str2);//H*w d* y*u d*}}
分割字符串方法
public String split(String regex)按照参数的规则,将字符串切分若干部分
注意事项:
split方法的参数其实是一个正则表达式
如果按照英文句点.进行分割,必须写成\\.
public class Demo05StringSplit {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "aaa,bbb,ccc";String[] array1 = str1.split(",");for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) {System.out.println(array1[i]);}System.out.println("===============");String str2 = "aaa bbb ccc";String[] array2 = str2.split(" ");for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) {System.out.println(array2[i]);}System.out.println("===============");String str3 = "XXX.YYY.ZZZ";String[] array3 = str3.split("\\.");System.out.println(array3.length); // 0for (int i = 0; i < array3.length; i++) {System.out.println(array3[i]);}}}
常用API练习
public class StringApiDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "爸爸,的快乐你不懂,爸爸hehe嗒";String s2 = "卢俊义,40,男,cosplay";String s3 = "PHP是世上最好的语音java不服";String s4 = "苍老师经典集合.mp4";String s5 = " hellojava ";System.out.println("-------1.获得字符串长度 length():int -------------------");System.out.println(s1.length());System.out.println("-------2.根据下标获取字符 charAt(int index):char -------------------");System.out.println(s1.charAt(3));System.out.println("-------3.获得子串首次出现的下标,存在返回该下标,不存在返回-1 indexOf(String son [,int fromIndex] ):int -------------------");System.out.println(s1.indexOf("快乐"));System.out.println("-------4.反向查找 lastIndexOf(String son [,int fromIndex] ):String -------------------");System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf("爸爸",6));System.out.println("-------5.截取字符串 substring(int star [, int end] ):String -------------------");System.out.println(s1.substring(3, 8));System.out.println("-------6.将旧的字符串替换成新的字符串 replace( String old,String new ):String -------------------");System.out.println(s1.replace("爸爸", "爷爷"));System.out.println("-------7.拆分 split( String flg ):String[] -------------------");String[] arr = s2.split(",");System.out.println(arr[0]);System.out.println(arr[1]);System.out.println(arr[2]);System.out.println(arr[3]);System.out.println("-------8.大小写转换 toUpperCase():String toLowerCase():String -------------------");System.out.println(s3.toLowerCase());System.out.println(s3.toUpperCase());System.out.println("-------9.起始和结尾 startWidth(String prefix ):boolean endsWith(String sufix ):boolean -------------------");System.out.println(s4.startsWith("王老师"));System.out.println(s4.endsWith("mp4"));System.out.println("-------10.字符串转数组 toCharArray():char[]-------------------");char[] chars = s4.toCharArray();System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars));System.out.println("-------11.去空格 trim():String 前后空格 -------------------");System.out.println(s5.trim());System.out.println("-------12.字符串连接 concat(String other):String ---------------");String s6 = "hello";String s7 = "hello";System.out.println(s6.concat(s7));System.out.println("--------13.包含 contains(String str):boolean ");System.out.println( s3.contains("java2") );System.out.println("---------14 比较值相等 equals(String other):boolean -------");String s8="2TsQ";String s9="2tsq";System.out.println(s8.equals(s9));System.out.println(s8.equalsIgnoreCase(s9));System.out.println("---------15 比较字符大小 compareTo(String other):int ----- ");String s10 = "z";String s11 = "a";int n = s10.compareTo(s11);System.out.println(n);System.out.println("----------16 静态方法 String.valueOf(Object obj):String -----------");int age = 10;String xx = String.valueOf(age);System.out.println(xx+10);}}
习题
题目:定义一个方法,把数组{1,2,3}按照指定格式拼接成一个字符串。格式参照如下:[word1#word2#word3]。
分析:
1. 首先准备一个int[]数组,内容是:1、2、3
2. 定义一个方法,用来将数组变成字符串
三要素
返回值类型:String
方法名称:fromArrayToString
参数列表:int[]
3. 格式:[word1#word2#word3]
用到:for循环、字符串拼接、每个数组元素之前都有一个word字样、分隔使用的是#、区分一下是不是最后一个
4. 调用方法,得到返回值,并打印结果字符串
public class Demo06StringPractise {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4};String result = fromArrayToString(array);System.out.println(result);}public static String fromArrayToString(int[] array) {String str = "[";for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {if (i == array.length - 1) {str += "word" + array[i] + "]";} else {str += "word" + array[i] + "#";}}return str;}}
题目:键盘输入一个字符串,并且统计其中各种字符出现的次数。
种类有:大写字母、小写字母、数字、其他
思路:1. 既然用到键盘输入,肯定是Scanner
2. 键盘输入的是字符串,那么:String str = sc.next();
3. 定义四个变量,分别代表四种字符各自的出现次数。
4. 需要对字符串一个字、一个字检查,String—>char[],方法就是toCharArray()
5. 遍历char[]字符数组,对当前字符的种类进行判断,并且用四个变量进行++动作。
6. 打印输出四个变量,分别代表四种字符出现次数。
可变字符串
StringBuilder 可变字符串
为了解决 StringBuffer 效率问题,java 1.5 再推出这个StringBuilder,StringBuilder这个类是线程不安全的。
public class StringBuilderDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {StringBuilder ss = new StringBuilder("静夜诗");ss.append("床前明月光,疑是地上霜,");ss.append("举头望明月,低头思故乡。");ss.insert(3,"李白");ss.insert(5,"\n");System.out.println(ss);}}
核心方法是 追加新内容的方法 append(Object xx )
StringBuffer 可变字符串
这类是JDK1.0推出的可变字符串,这个类被设计为线程安全的,这个类的效率低。
public class StringBufferDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {StringBuffer ss = new StringBuffer("静夜诗");ss.append("床前明月光,疑是地上霜,");ss.append("举头望明月,低头思故乡。");ss.insert(3,"李白");ss.insert(5,"\n");System.out.println(ss);}}
String StringBuilder StringBuffer 区别
- 可变性 String 是不可变 ,其他两个是可变的
- 安全性 StringBuffer 线程安全的。StringBulder不安全。 String视为安全的,他的方法都是建立副本,不再原有的基础上做修改。
包装类
java中有**基本数据类型**和**引用类型**,如果要把基本数据类型变成引用类型,那么需要**一次包装**,java中就给出了基本数据类型对应的包装。
基本数据类型包装类
| byte | short | int | long | float | double | char | boolean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Byte | Short | Integer | Long | Float | Double | Character | Boolean |
| Number |
Number 核心方法
Number 类是6个数值包装类的父类,它提供了6个拆箱方法
byte |
[**byteValue**](../../java/lang/Number.html#byteValue())()以 byte形式返回指定的数值。 |
|---|---|
abstract double |
[**doubleValue**](../../java/lang/Number.html#doubleValue())()以 double形式返回指定的数值。 |
abstract float |
[**floatValue**](../../java/lang/Number.html#floatValue())()以 float形式返回指定的数值。 |
abstract int |
[**intValue**](../../java/lang/Number.html#intValue())()以 int形式返回指定的数值。 |
abstract long |
[**longValue**](../../java/lang/Number.html#longValue())()以 long形式返回指定的数值。 |
short |
[**shortValue**](../../java/lang/Number.html#shortValue())()以 short形式返回指定的数值。 |
装箱拆箱
**装箱**: 把一个基本数类型 变成引用数据类型**拆箱**: 把一个引用数据类型变成 基本数据类型
public class WarpperDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// JDK.1.5以前 手动完成 装箱 和 拆箱// 装箱: 把一个基本数类型变成 引用 数据类型int num = 100; // 基本数据类型Integer numPlus = new Integer( num ); // 引用数据类型// 拆箱: 把引用数据类型变成 基本 数据类型Integer nPlus = new Integer(100); //引用类型int n = nPlus.intValue(); // 基本数据类型}}
自动装箱与拆箱[jdk5+]
public class WarpperDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//JDK 1.5+ 自动 装箱拆箱 , 使转换更容易。int x = 10;Integer xPlus = x; //自动装箱Integer yPlus = 100;int y = yPlus; //自动拆箱}}
包装类提供的方法
使用包装类,提供的静态方法完成一些简单功能。
public class WarpperApi {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 查看类型的 取值区间System.out.println( Integer.MIN_VALUE+ "-"+ Integer.MAX_VALUE );// 2. 转进制System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(10));System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(10));// 3. 比较大小System.out.println(Integer.max(10, 50));System.out.println(Integer.min(10, 50));System.out.println(Integer.compare(10, 3));}}
数值类型与字符串转换[掌握]
开发中很多时候,需要把**字符串类型 转成 数值类型**,比如需要把 String “99.8” 变成 double 99.8 。
字符串转数值类型,需要找到对应的包装类型,比如要转**int 找Integer** 转d**ouble就找Double**。 包装类提供 parseByte() parseShort() parseInt() parseLong() parseFloat() parseDouble 。
public class WarpperApi {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("------------------ 数值 ==> String ----------------------");int a = 10;String b = a + "";System.out.println(b);//10System.out.println("------------------ String ==> 数值 ----------------------");int i = Integer.parseInt(b);System.out.println(i);//10}}
BigDecimal
由于java中浮点数计算不精确,可以使用BigDecimal解决问题,需要注意的是必须以字符串方式构造BigDecimal。
BigDecimal 提供了API来计算:
- add( BigDecimal other ):BigDecimal
- subtract( BigDecimal other ):BigDecimal
- multiply( BigDecimal other ):BigDecimal
- divide( BigDecimal other ,int scale , int rondModel ):BigDecimal
重点说明:
对于除法,因为存在无限循环小数,所以可能会引发异常,通过 参数 scale 控制小数点位数, rondModel控制取舍策略。
常用取舍策略:
ROUND_UP = 0
ROUND_DOWN =1
ROUND_CEILING =2
ROUND_FLOOR = 3
ROUND_HALF_UP = 4 四舍五入
public class BigDecimalDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {double a = 1.0;double b = 0.9;System.out.println(a-b);//0.99999999998 不精确//包装BigDecimal n1 = new BigDecimal( String.valueOf(a) );BigDecimal n2 = new BigDecimal( String.valueOf(b) );System.out.println("-------加法------");BigDecimal result1 = n1.add(n2);System.out.println(result1.doubleValue());System.out.println("-------减法------");BigDecimal result2 = n1.subtract(n2);System.out.println(result2.doubleValue());System.out.println("-------乘法--------");BigDecimal result3 = n1.multiply(n2);System.out.println(result3.doubleValue());System.out.println("-------除法--------");BigDecimal result4 = n1.divide(n2,2,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);System.out.println(result4.doubleValue());}}
BigInteger
当运算数据非常大的情况下,基本数据类型无法完成运算,比如两个long的最大值相加,没有办法直接运算,这时可以借助 BigInter包装类使用API运算,API与BigDecimal完全一致
// 大数运算public class BigInteDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {long x1 = 9223372036854775807L;long x2 = 9223372036854775807L;BigInteger n1 = new BigInteger( String.valueOf(x1) );BigInteger n2 = new BigInteger( String.valueOf(x2) );BigInteger result = n1.add(n2);System.out.println(ru); //18446744073709551614}}
大数运算 不可拆箱,因为可能超过 类型的范围。但是可以转字符串,保存这个字符串,日后可以继续运算。
日期相关类
Date类
Date类是用来描述时间的。一个时刻,一个瞬间都是 **Date**的实例。在java.util包中。
创建对象
**系统时间对象****毫秒数指定时间对象**~~ 年月日直接对象(过期)~~
public class TestDate {public static void main(String[] args) {//获得当前系统时间对应Date 对象Date date = new Date();System.out.println(date.toLocaleString);//2021-8-1 10:42:50 当前时间//构造一个指定时间的对象Date date2 = new Date(3000L);System.out.println(date2.toLocaleString);//1970-1-1 8:00:03//过期了Date date3 = new Date(2021-1900,11,10);System.out.println(date3.toLocaleString);}}
常用方法
getTime():long获得时间毫秒值after(Date when ): 判断是否在指定日期前before( Date when ):判断是否在指定日期后getXXX():int 获得年、月、日 过期了,不推荐使用public class TestDateApi {public static void main(String[] args) {Date date = new Date();//1. 获得时间的毫秒数long time = date.getTime();System.out.println(time);//2. 日期比较 after beforeDate date2= new Date(1618191582373L);boolean after = date.before(date2);System.out.println(after);//3. 过期的方法System.out.println(date.getYear()+1900);System.out.println(date.getMonth()+1);System.out.println(date.getDate());}}
SimpleDateFormat 类[掌握]
是一个简单的日期格式化工具类,可以把**日期对象通过 日期的格式符号 转换成一个字符串**。
创建对象
//SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("包含格式符号的模板字符串");SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
格式符号: y: 年 M: 月 d: 日 h: 时 m: 分 s: 秒
核心方法 format(Date date)
根据指定格式转换成日期对象
public class TestSimpleDateFormat {public static void main(String[] args) {Date date = new Date();//格式化输出/*** 格式模板 yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss* y:年 M:月 d:日 h:时 m:分 s:秒*/SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");String strDate = sdf.format(date);System.out.println(strDate);}}
开发中,可以通过 常量接口 定义各种格式化模板 public interface Paten { //常规格式
_public static final String _DATE = “yyyy-MM-dd”; public static final String DATE_TIME = “yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss”; public static final String TIME = “hh:mm:ss”; //中文格式
_public static final String _DATE_CHINA = “yyyy年MM月dd日”; public static final String DATE_TIME_CHINA = “yyyy年MM月dd日 hh:mm:ss”; //自定义格式
_public static final String _DATE_STYLE = “dd/MM/yyyy”; }
核心方法 parse( String str )
根据指定格式解析字符串,把**一个字符串** **转换成 日期对象**,往往用户输入的都是字符串,即便是一个时间也是以一个字符串输入的比如 2008-10-10,而程序中需要的是一个对象。
public class Test02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {Date d = new Date();System.out.println(d.toLocaleString());//创建日期格式化对象SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");String format = sdf.format(d);System.out.println(format);//2021年08月01日 11:18:56String str = "2021年08月01日 11:18:56";Date parse = sdf.parse(str);System.out.println(parse);//Sun Aug 01 11:18:56 CST 2021}
Calander 类
日历类,Date 绝大部分api过期了,很多功能就需要借助 Calander 完成。日历除了当前时间以外,还存储了与此相关的其他信息(日历字段)和处理日期一些方法。位于java.util包
创建
public class TestCalendar {public static void main(String[] args) {//获得实例Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();}}
核心方法
get( int field):int;获取指定日历字段信息set( int field , int value );将指定日历字段设置为指定的值add( int field , int amount)getActualMaximum(int field)getActualMinimum(int field)```java package case1.calander;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class TestCalendar {
public static void main(String[] args) {//获得实例Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();// get(int x):int 获得日历字段int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);int month = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH);int day = calendar.get(Calendar.DATE);int h = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR);int m = calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE);int s = calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND);System.out.println( year );System.out.println( month+1);System.out.println( day );System.out.println("------------------------------");System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK));// set( int field , int value ): 修改日历字段值// calendar.set( Calendar.YEAR , 2099);// add( int filed, int amont ): 增加日历字段值calendar.add(Calendar.MONTH,1);// 获得当月最大实际日历信息// int maxDay = calendar.getActualMaximum(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);// int minDay = calendar.getActualMinimum(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);//System.out.println(maxDay+" "+minDay);}
}
<a name="hquO2"></a>#### 日历案例```javapackage case1.calander;import java.util.Calendar;import java.util.Map;//日历public class DisplayCalendar {public static void main(String[] args) {//获得日历Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();calendar.set(2021,5,1);//输出日历头部String[] days = {"一","二","三","四","五","六","日"};for ( String day : days){System.out.print(day+"\t");}System.out.println();//输出日历身体int min = calendar.getActualMinimum(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);int max = calendar.getActualMaximum(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);int xq = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);//输出首行空格for(int i=1; i<=xq-2;i++){System.out.print("\t");}// 输出全部号数for(int i=min; i<=max; i++){System.out.print(i+"\t");calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,i); //把日历指向这一天int x= calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK) ; //如果这一天是星期天 则换行if (x==1){System.out.println();}}}}
其他的类
Arrays
它是一个数组的工具类,提供很多数组操作的方法。
核心方法:
package case1.arrays;import java.util.Arrays;// 数组工具类public class TestArrays {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {45,29,16,5,20,23,22,9,4};// 1. toString(T[] arr) // 数组转字符串System.out.println( Arrays.toString(arr) );// 2. sort(T[] ) // 排序Arrays.sort(arr);System.out.println( Arrays.toString(arr));// 3. binarySearch(T[] T key) // 二分查找System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 20));// 4. copyOf(int[] arr , int len) // 数组拷贝int[] newArr = Arrays.copyOf(arr, 5);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newArr));// 5. copyOfRange(T[] arr, int from, int to) // 数组区间拷贝int[] newArr2 = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 3, 7);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newArr2));// 6. equals(T[] a1, T[] a2) // 两数组相等比较int[] xrr = {1,2,3};int[] yrr = {1,2,3,4};System.out.println(Arrays.equals(xrr, yrr));// 7 .fill(T[] arr , int value) // 数组元素填充int[] zrr = new int[10];Arrays.fill( zrr,2,5, -1 );System.out.println(Arrays.toString(zrr));}}
Random
这类是一个生成伪随机数类,底层原理使用 使用线性同余公式 ,生成的数字,如果种子相同,进行相同次数的调用得到的值是相同的。
nextInt( int n): int 生成一个0-N之间的整数
nextDouble() :double 生成一个浮点数
nextBoolean(): boolean 生成一个Boolean值
public class TestRandom {public static void main(String[] args) {Random rd = new Random(100);// 100为随机数种子for (int i= 0; i<4; i++){int num = rd.nextInt(100);System.out.println(num);}}}
UUID
这个类用于生成 唯一字符串序列
public class TestUUID {public static void main(String[] args) {//获得一个随机的UUIDUUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();//获得UUID字符串String uuidStr = uuid.toString();//替换 -uuidStr = uuidStr.replace("-","");System.out.println(uuidStr);}}
Math
它是一个数学工具类,提供了数学计算上的一些方法。全部是静态方法。
public class TestMath {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(Math.PI); // 获得 PISystem.out.println(Math.abs(-100)); // 计算绝对值System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 11));// 计算次方System.out.println( (int)(Math.random()*10) ); // 随机数0.0-1.0间System.out.println(Math.round(3.7)); // 四舍五入System.out.println(Math.floor(3.9)); // 向下取整System.out.println(Math.ceil(3.1)); // 向上取整System.out.println(Math.sqrt(81)); // 开平方根}}
Runtime
它的对象表示运行环境的对象,通过这个对象可以获得,运行平台的相关信息。
public class TestRuntime {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//获得实例Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();//获得运行环境信息int n = runtime.availableProcessors(); // 获得处理器个数的System.out.println(n);//runtime.exec("C:/Program Files (x86)/Tencent/QQLive/QQLive.exe"); //打开一些软件//runtime.exit(0); //立即退出long freeMemory = runtime.freeMemory();System.out.println(freeMemory/1024/1024); // 返回 Java 虚拟机中的空闲内存量。long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory(); // 返回 Java 虚拟机试图使用的最大内存量。System.out.println(maxMemory/1024/1024);long totalMemory = runtime.totalMemory(); // 返回 Java 虚拟机中的内存总量。System.out.println(totalMemory/1024/1024);System.out.println("over");}}
System
System 类包含一些有用的类字段和方法。它不能被实例化。
在 System 类提供的设施中,有标准输入、标准输出和错误输出流;对外部定义的属性和环境变量的访问;加载文件和库的方法;还有快速复制数组的一部分的实用方法。
public class TestSystem {public static void main(String[] args) {// 输入流Scanner sc = new Scanner( System.in );//输出流System.out.println( "hello");//错误,打印错误信息System.err.println("world");// 读取环境变量Map<String, String> info = System.getenv();System.out.println(info.get("KEY"));}}

