内容概述
插值操作
绑定属性
计算属性
事件监听
条件判断
循环遍历
阶段案例
v-model
插值操作
如何将data中的文本数据,插入到HTML中呢?
我们已经学习过了,可以通过Mustache语法(也就是双大括号)。
Mustache:胡子/胡须
我们可以像下面这样来使用,并且数据是响应式的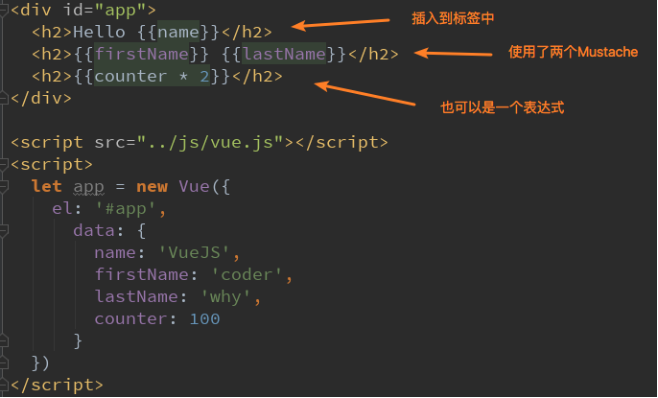
基础指令-内容
指令: v-noce 只渲染一次,加载完之后,你再控制台修改内容,修改的则无效
<div v-once id="app">
指令:v-html=’url’ 作用于带有标签的数据 (url)是定义的值
<h2 v-html='url'></h2>
指令:v-text=’url’ 作用等于字符串类型的
<h2 v-text='mingzi'></h2>
指令:v-pre 作用原封不动的显示出来
<h2 v-pre>{{mingzi}}</h2>
指令:v-cloak 斗篷的意思(挡住)配合css使用,当网页加载完成后,浏览器会把这个命令解析掉,v-cloak会消失掉
<div id="app" v-cloak>
动态指令-绑定属性
指令:v-bind
前面我们学习的指令主要作用是将值插入到我们模板的内容当中。
但是,除了内容需要动态来决定外,某些属性我们也希望动态来绑定。
比如动态绑定a元素的href属性
比如动态绑定img元素的src属性
这个时候,我们可以使用v-bind指令:
作用:动态绑定属性 可以绑定任何的属性
缩写: :
预期:any (with argument) | Object (without argument)
参数:attrOrProp (optional)
下面,我们就具体来学习v-bind的使用。
<body><div id="app"><!-- 错误的做法: 这里不可以使用mustache语法 --><!-- <img src="{{imgUrl}}" alt=""> --><!-- 正确的做法: 使用v-bind指令 --><h2><a v-bind:href="aHerf">212</a> 111</h2><img v-bind:src="imgUrl" alt="">//语法糖写法<a :href="aHerf">你好世界</a><img :src="imgUrl" alt=""></div><script>const app = new Vue({el:'#app',data:{mingzi:'小明',url:'<a href="https://184383.vip">编程记录</a>',imgUrl:'https://cn.vuejs.org/images/imooc-sponsor2.png',aHerf:'https://184383.vip'}})</script></body>
动态绑定class对象语法
{} 一个大括号表示对象语法
{{}} 2个大括号表示Mustache语法
通过布尔值,决定是否显示这个类型,这个作用在于显示不同的样式
Class对象语法(1)
<style>.huoyue{color: red;font-weight: bold;font-size: 50px;}.line{color: green;font-weight: bold;font-size: 50px;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><!-- <div :class="huoyue">class绑定(普通绑定的方式)</div><div :class="{{}}">{{mingzi}}</div> --><!-- 对象的意义里面可以放键值对 --><!-- <h2 class="{key1: value1, key2: value2,key3: value3}">{{mingzi}}</h2> --><!-- <h2 v-bind:class="{类名1: boolean, 类名2: boolean}">{{mingzi}}</h2> --><!-- 通过类名的布尔值类型 来决定 是否添加这个类型 -->标题的class=”title”这个class是默认的,会和bind的class合并,不覆盖<h2 class="title" v-bind:class="{huoyue: isHuoyue, line: isLine}">{{mingzi}}</h2></div><script>const app = new Vue({el:'#app',data:{mingzi:'小明',url:'<a href="https://184383.vip">编程记录</a>',imgUrl:'https://cn.vuejs.org/images/imooc-sponsor2.png',aHerf:'https://184383.vip',isHuoyue:true,//true 决定显示isLine:false //false 决定不显示}})</script></body>
Class对象语法(2)
直接调用函数
<style>.huoyue {color: red;font-weight: bold;font-size: 50px;}.line {color: green;font-weight: bold;font-size: 50px;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><!-- <div :class="huoyue">class绑定(普通绑定的方式)</div><div :class="{{}}">{{mingzi}}</div> --><!-- 对象的意义里面可以放键值对 --><!-- <h2 class="{key1: value1, key2: value2,key3: value3}">{{mingzi}}</h2> --><!-- <h2 v-bind:class="{类名1: boolean, 类名2: boolean}">{{mingzi}}</h2> --><!-- 通过类名的布尔值类型 来决定 是否添加这个类型 --><h2 class="title" v-bind:class="{huoyue: isHuoyue, line: isLine}">{{mingzi}}</h2><h2 class="title" v-bind:class="getClass()">{{mingzi2}}</h2>调用函数<button v-on:click='btnClick'>按钮</button></div><script>const app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {mingzi: '小明',mingzi2: 'leochen',isHuoyue: true,//true 决定显示isLine: true, //false 决定不显示},methods: {btnClick: function () {this.isLine = !this.isLine},getClass:function () {return { huoyue: this.isHuoyue, line: this.isLine }}}})</script></body>
v-bind绑定class(一)
很多时候,我们希望动态的来切换class,比如:
当数据为某个状态时,字体显示红色。
当数据另一个状态时,字体显示黑色。
绑定class有两种方式:
对象语法
数组语法
v-bind绑定class(二)
用法一:直接通过{}绑定一个类
Hello World
用法二:也可以通过判断,传入多个值
Hello World
用法三:和普通的类同时存在,并不冲突
注:如果isActive和isLine都为true,那么会有title/active/line三个类
Hello World
用法四:如果过于复杂,可以放在一个methods或者computed中
注:classes是一个计算属性
Hello World
动态绑定class 数组语法
动态绑定style对象语法
1.对象的方式 2.函数的方式
<body><div id="app"><!-- <h2 class="title" :style="{key(属性名):value(属性值)}">{{mingzi}}</h2> --><h2 class="title" :style="{fontSize:daxiao,backgroundColor :backColor}">{{mingzi}}</h2><h2 class="title" :style="getStyle()">{{mingzi}}</h2></div><script>const app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {mingzi: '小明',daxiao:'100px',backColor:'red'},methods:{getStyle:function(){return {fontSize :this.daxiao , backgroundColor:this.backColor}}}})</script></body>
动态绑定style 数组语法
1.数组的方式 2. 函数的方式
<body><div id="app"><!-- <h2 class="title" :style="[变量]">{{mingzi}}</h2> --><h2 class="title" :style="[baseColor]">{{mingzi}}</h2><h2 class="title" :style="getStyle()">{{mingzi}}</h2></div><script>const app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {mingzi: '小明',daxiao:'100px',backColor:'blue',baseColor:{backgroundColor:'pink',fontSize:'100px'}},methods:{getStyle:function(){return {fontSize :this.daxiao , backgroundColor:this.backColor}}}})</script></body>
计算属性基本使用
<body><div id="app"><!-- <h2 class="title" :style="[变量]">{{mingzi}}</h2> --><h2>{{firstName +''+lastName}}</h2><h2>{{lastName}}{{firstName}}</h2><h2>{{getFunllName()}}</h2><!-- 计算属性的最常用法 --><h2>{{funllName}}</h2></div><script>const app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {firstName: '小明',lastName: '老陈'},computed:{//固定的计算属性命令funllName:function(){return this.firstName+''+this.lastName}},methods:{getFunllName:function(){return this.firstName + ''+this.lastName}}})</script></body>
计算属性的复杂操作
<body><div id="app"><!-- 计算属性的最常用法 --><h2>总价格:{{totalPrice}}</h2></div><script>const app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {firstName: '小明',lastName: '老陈',books: [{ id: 100, name: '编程艺术', price: 15 },{ id: 100, name: '代码大全', price: 25 },{ id: 100, name: '深入理解计算器原理', price: 23 },{ id: 100, name: '现代操作系统', price: 56 },]},computed: {//固定的计算属性命令//高级函数 filter / map / reducetotalPrice: function () {let result=0//方法1 (es5的语法)// for (let i = 0; i < this.books.length; i++) {// result+= this.books[i].price// }//方法2// for(let i in this.books){// result+=this.books[i].price// }//方法3 (ES6的语法)for(let book of this.books){result+=book.price}return result}}})</script></body>

