- 数据结构
- stack(栈)
- queue(队列)
- linkedList(链表)
- 206. Reverse Linked List(反转链表)">206. Reverse Linked List(反转链表)
- 203. 移除链表元素">203. 移除链表元素
- 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs">24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
- 237. Delete Node in a Linked List">237. Delete Node in a Linked List
- 19. Remove Nth Node From End of List">19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
- 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists">160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
- 234. Palindrome Linked List">234. Palindrome Linked List
- binaryTree(二叉树)
- collection(查找表)
- 算法思想
数据结构
stack(栈)
20. 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 ‘(‘,’)’,’{‘,’}’,’[‘,’]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
//用一个map去存储,右边的符号做对比,用栈结构去判断,每次有开有合public boolean isValid(String s) {int n = s.length();//奇数一定是没有闭合的if (n % 2 == 1) {return false;}HashMap<Character, Character> pairs = new HashMap<Character, Character>() {{put(')', '(');put('}', '{');put(']', '[');}};Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//取出字符串中的字符char ch = s.charAt(i);if (pairs.containsKey(ch)) {//如果有右边的符号,就去栈里面去取出来对比,没有就是falseif (stack.isEmpty() || !stack.peek().equals(pairs.get(ch))) {return false;}//出栈stack.pop();} else {//入栈stack.push(ch);}}return stack.isEmpty();}
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();//为空直接返回if (root == null) {return res;}Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();TreeNode node = root;//栈不为空或者二叉树不为空就开始循环while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {//二叉树不为空就开始循环while (node != null) {//结果集加上当前的res.add(node.val);//入栈stack.push(node);//取左节点node = node.left;}//出栈node = stack.pop();//取右节点node = node.right;}return res;}
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。 有效的算符包括 +、-、*、/ 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。 注意 两个整数之间的除法只保留整数部分。 可以保证给定的逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。
示例 1: 输入:tokens = [“2”,”1”,”+”,”3”,”“] 输出:9 解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:((2 + 1) 3) = 9 示例 2: 输入:tokens = [“4”,”13”,”5”,”/“,”+”] 输出:6 解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:(4 + (13 / 5)) = 6 示例 3: 输入:tokens = [“10”,”6”,”9”,”3”,”+”,”-11”,”“,”/“,”“,”17”,”+”,”5”,”+”] 输出:22 解释:该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为: ((10 (6 / ((9 + 3) -11))) + 17) + 5 = ((10 (6 / (12 -11))) + 17) + 5 = ((10 (6 / -132)) + 17) + 5 = ((10 0) + 17) + 5 = (0 + 17) + 5 = 17 + 5 = 22
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();for (String token : tokens) {if ("+".equals(token) || "-".equals(token) || "*".equals(token) || "/".equals(token)) {Integer pop1 = stack.pop();Integer pop2 = stack.pop();switch (token) {case "+":stack.push(pop2 + pop1);break;case "-":stack.push(pop2 - pop1);break;case "*":stack.push(pop2 * pop1);break;case "/":stack.push(pop2 / pop1);break;default:}} else {stack.push(Integer.valueOf(token));}}return stack.peek();}
42. 接雨水(Trapping Rain Water)
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。 示例 1: 输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 输出:6 解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。 示例 2: 输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5] 输出:9
public int trap(int[] height){int ans = 0;Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();int n = height.length;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()]){Integer pop = stack.pop();if (stack.isEmpty()){break;}int left = stack.peek();int currWidth = i - left -1;int currhight = Math.min(height[left],height[i]) - height[pop];ans += currhight * currWidth;}stack.push(i);}return ans;}
queue(队列)
347. Top K Frequent Elements(前 K 个高频元素)
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。 示例 1: 输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 输出: [1,2]
示例 2: 输入: nums = [1], k = 1 输出: [1]
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {Map<Integer, Integer> occurrences = new HashMap<>();for (int num : nums) {occurrences.put(num, occurrences.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);}//构建一个最小堆去最对比,由于堆的大小至多为 kPriorityQueue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[1]));for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : occurrences.entrySet()) {int num = entry.getKey();int count = entry.getValue();if (queue.size() == k) {if (queue.peek()[1] < count) {queue.poll();queue.offer(new int[]{num, count});}} else {queue.offer(new int[]{num, count});}}int[] ret = new int[k];for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {ret[i] = Objects.requireNonNull(queue.poll())[0];}return ret;}
102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal(二叉树的层序遍历)
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点) 示例 1: 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]] 示例 2: 输入:root = [1] 输出:[[1]] 示例 3: 输入:root = [] 输出:[]
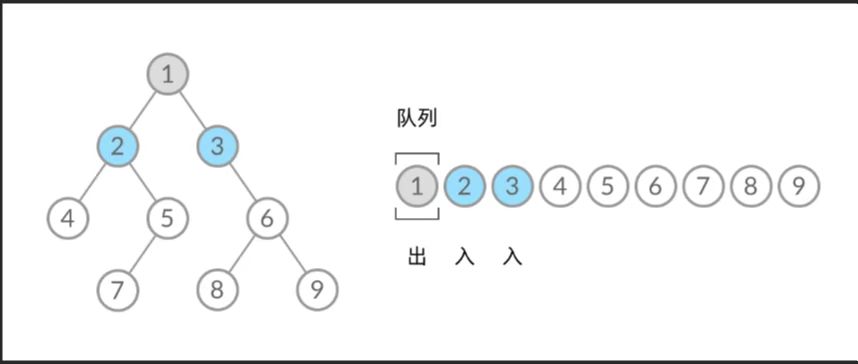
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();if (root != null) {queue.add(root);}while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int n = queue.size();List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();level.add(node.val);if (node.left != null) {queue.add(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.add(node.right);}}res.add(level);}return res;}

