异常
异常
- 异常的概述
异常就是程序出现了不正常的情况 - 异常的体系结构
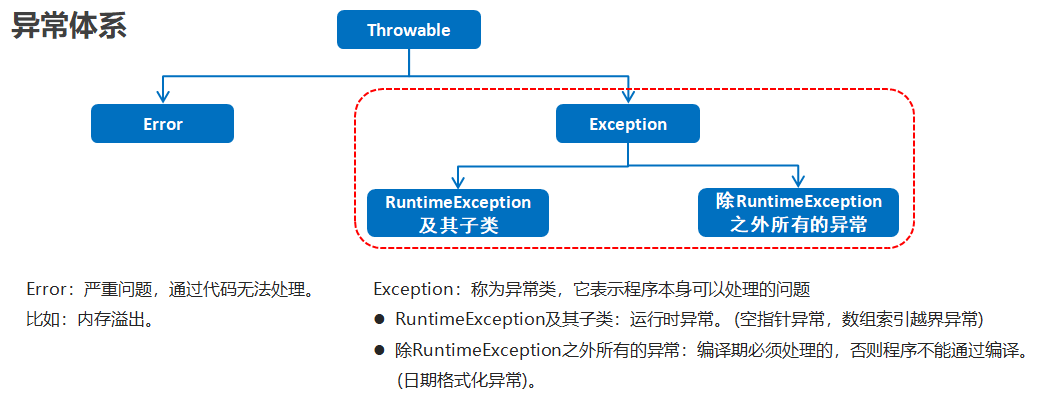
编译时异常和运行时异常的区别
- 编译时异常
- 都是Exception类及其子类
- 必须显示处理,否则程序就会发生错误,无法通过编译
- 运行时异常
- 都是RuntimeException类及其子类
- 无需显示处理,也可以和编译时异常一样处理
- 图示

JVM默认处理异常的方式
- 如果程序出现了问题,我们没有做任何处理,最终JVM 会做默认的处理,处理方式有如下两个步骤:
- 把异常的名称,错误原因及异常出现的位置等信息输出在了控制台
- 程序停止执行
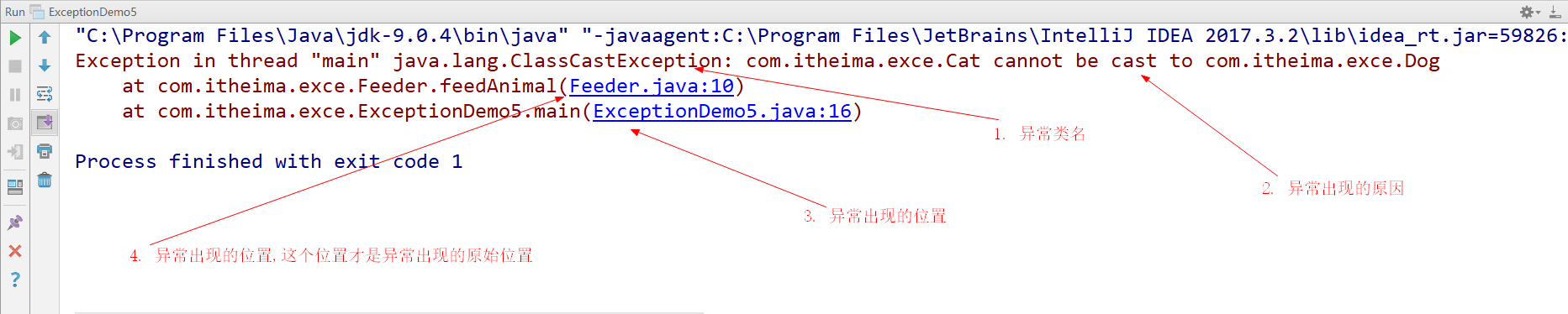
查看异常信息
控制台在打印异常信息时,会打印异常类名,异常出现的原因,异常出现的位置
我们调bug时,可以根据提示,找到异常出现的位置,分析原因,修改异常代码
throws方式处理异常
- 定义格式
```java public void 方法() throws 异常类名 {
}
- 示例代码```javapublic class ExceptionDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException{System.out.println("开始");// method();method2();System.out.println("结束");}//编译时异常public static void method2() throws ParseException {String s = "2048-08-09";SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");Date d = sdf.parse(s);System.out.println(d);}//运行时异常public static void method() throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};System.out.println(arr[3]);}}
- 注意事项
- 这个throws格式是跟在方法的括号后面的
- 编译时异常必须要进行处理,两种处理方案:try…catch …或者 throws,如果采用 throws 这种方案,在方法上进行显示声明,将来谁调用这个方法谁处理
- 运行时异常因为在运行时才会发生,所以在方法后面可以不写,运行时出现异常默认交给jvm处理
throw抛出异常
- 格式
throw new 异常(); - 注意
这个格式是在方法内的,表示当前代码手动抛出一个异常,下面的代码不用再执行了 throws和throw的区别
| throws | throw | | —- | —- | | 用在方法声明后面,跟的是异常类名 | 用在方法体内,跟的是异常对象名 | | 表示声明异常,调用该方法有可能会出现这样的异常 | 表示手动抛出异常对象,由方法体内的语句处理 |示例代码
```java public class ExceptionDemo8 { public static void main(String[] args) {//int [] arr = {1,2,3,4,5}; int [] arr = null; printArr(arr);//就会 接收到一个异常. //我们还需要自己处理一下异常.}
private static void printArr(int[] arr) {
if(arr == null){ //调用者知道成功打印了吗? //System.out.println("参数不能为null"); throw new NullPointerException(); //当参数为null的时候 //手动创建了一个异常对象,抛给了调用者,产生了一个异常 }else{ for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); } }}
}
<a name="7ffc6a56"></a>
### try-catch方式处理异常
- 定义格式
```java
try {
可能出现异常的代码;
} catch(异常类名 变量名) {
异常的处理代码;
}
- 执行流程
- 程序从 try 里面的代码开始执行
- 出现异常,就会跳转到对应的 catch 里面去执行
- 执行完毕之后,程序还可以继续往下执行
示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("开始"); method(); System.out.println("结束"); } public static void method() { try { int[] arr = {1, 2, 3}; System.out.println(arr[3]); System.out.println("这里能够访问到吗"); } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println("你访问的数组索引不存在,请回去修改为正确的索引"); } } }注意
- 如果 try 中没有遇到问题,怎么执行?
会把try中所有的代码全部执行完毕,不会执行catch里面的代码 - 如果 try 中遇到了问题,那么 try 下面的代码还会执行吗?
那么直接跳转到对应的catch语句中,try下面的代码就不会再执行了
当catch里面的语句全部执行完毕,表示整个体系全部执行完全,继续执行下面的代码 - 如果出现的问题没有被捕获,那么程序如何运行?
那么try…catch就相当于没有写.那么也就是自己没有处理.
默认交给虚拟机处理. - 同时有可能出现多个异常怎么处理?
出现多个异常,那么就写多个catch就可以了.
注意点:如果多个异常之间存在子父类关系.那么父类一定要写在下面
- 如果 try 中没有遇到问题,怎么执行?
Throwable成员方法
常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public String getMessage() | 返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串 | | public String toString() | 返回此可抛出的简短描述 | | public void printStackTrace() | 把异常的错误信息输出在控制台 |示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("开始"); method(); System.out.println("结束"); } public static void method() { try { int[] arr = {1, 2, 3}; System.out.println(arr[3]); //new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); System.out.println("这里能够访问到吗"); } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { //new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); // e.printStackTrace(); //public String getMessage():返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串 // System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //Index 3 out of bounds for length 3 //public String toString():返回此可抛出的简短描述 // System.out.println(e.toString()); //java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 3 out of bounds for length 3 //public void printStackTrace():把异常的错误信息输出在控制台 e.printStackTrace(); // java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 3 out of bounds for length 3 // at com.itheima_02.ExceptionDemo02.method(ExceptionDemo02.java:18) // at com.itheima_02.ExceptionDemo02.main(ExceptionDemo02.java:11) } } }
异常的练习
- 需求
键盘录入学生的姓名和年龄,其中年龄为18 - 25岁,超出这个范围是异常数据不能赋值.需要重新录入,一直录到正确为止 - 实现步骤
- 创建学生对象
- 键盘录入姓名和年龄,并赋值给学生对象
- 如果是非法数据就再次录入
代码实现
学生类public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { if(age >= 18 && age <= 25){ this.age = age; }else{ //当年龄不合法时,产生一个异常 throw new RuntimeException("年龄超出了范围"); } } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }测试类
public class ExceptionDemo12 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 键盘录入学生的姓名和年龄,其中年龄为 18 - 25岁, // 超出这个范围是异常数据不能赋值.需要重新录入,一直录到正确为止。 Student s = new Student(); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入姓名"); String name = sc.nextLine(); s.setName(name); while(true){ System.out.println("请输入年龄"); String ageStr = sc.nextLine(); try { int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr); s.setAge(age); break; } catch (NumberFormatException e) { System.out.println("请输入一个整数"); continue; } catch (AgeOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println(e.toString()); System.out.println("请输入一个符合范围的年龄"); continue; } /*if(age >= 18 && age <=25){ s.setAge(age); break; }else{ System.out.println("请输入符合要求的年龄"); continue; }*/ } System.out.println(s); } }
自定义异常
- 自定义异常概述
当Java中提供的异常不能满足我们的需求时,我们可以自定义异常 - 实现步骤
- 定义异常类
- 写继承关系
- 提供空参构造
- 提供带参构造
- 代码实现
异常类
public class AgeOutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException {
public AgeOutOfBoundsException() {
}
public AgeOutOfBoundsException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if(age >= 18 && age <= 25){
this.age = age;
}else{
//如果Java中提供的异常不能满足我们的需求,我们可以使用自定义的异常
throw new AgeOutOfBoundsException("年龄超出了范围");
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类
public class ExceptionDemo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 键盘录入学生的姓名和年龄,其中年龄为 18 - 25岁,
// 超出这个范围是异常数据不能赋值.需要重新录入,一直录到正确为止。
Student s = new Student();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入姓名");
String name = sc.nextLine();
s.setName(name);
while(true){
System.out.println("请输入年龄");
String ageStr = sc.nextLine();
try {
int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr);
s.setAge(age);
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("请输入一个整数");
continue;
} catch (AgeOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
System.out.println("请输入一个符合范围的年龄");
continue;
}
/*if(age >= 18 && age <=25){
s.setAge(age);
break;
}else{
System.out.println("请输入符合要求的年龄");
continue;
}*/
}
System.out.println(s);
}
}

