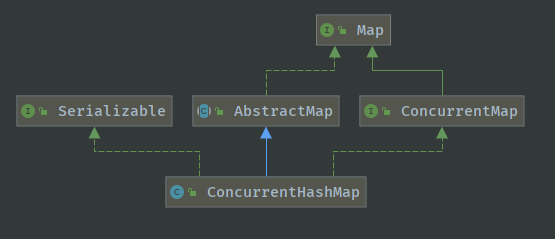
前有HashMap作为基于哈希表实现的用于映射(键值对)处理的容器,在介绍HashMap或者看HashMap源码的时候也知道HashMap不是线程安全的。因此引入了ConcurrentHashMap,它也是基于哈希表的,但是它是线程安全的并发容器,在java.util.concurrent包下。
属性
哈希表中真正存放数据的结点Node,和HashMap中的区别在于加了 volatile 关键字确定其可见性。
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {final int hash;final K key;volatile V val;volatile Node<K,V> next;Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {this.hash = hash;this.key = key;this.val = val;this.next = next;}}
ConcurrentHashMap中同样是使用的结点数组存储哈希表,区别在于加了 volatile 关键字确定其可见性。
private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
get方法
public V get(Object key) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;int h = spread(key.hashCode());if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))return e.val;}else if (eh < 0)return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;while ((e = e.next) != null) {if (e.hash == h &&((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))return e.val;}}return null;}
这个方法没什么特别的,根据计算出的hashcode寻址,如果就在桶上那么直接返回值,如果是红黑树就按照树的方式获取值,不是就按照链表的方式遍历获取值。该方法没有涉及到并发的设计。
put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {return putVal(key, value, false);}/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();//计算hashcodeint hash = spread(key.hashCode());int binCount = 0;for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;//2. 判断是否需要初始化if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)tab = initTable();//f为当前key定位出的Node,如果为空表示当前位置可以写入数据,利用CAS尝试写入else if ((f = tabAxt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))break; // no lock when adding to empty bin}//需要扩容 当前位置hashcode==MOVED==-1else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);else {V oldVal = null;//都不满足,在synchronized锁里写入数据,进行了并发优化的地方synchronized (f) {if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {if (fh >= 0) {binCount = 1;for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {K ek;if (e.hash == hash &&((ek = e.key) == key ||(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {oldVal = e.val;if (!onlyIfAbsent)e.val = value;break;}Node<K,V> pred = e;if ((e = e.next) == null) {pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,value, null);break;}}}else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {Node<K,V> p;binCount = 2;if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,value)) != null) {oldVal = p.val;if (!onlyIfAbsent)p.val = value;}}}}if (binCount != 0) {//和原hashmap一样,转为红黑树if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)treeifyBin(tab, i);if (oldVal != null)return oldVal;break;}}}addCount(1L, binCount);return null;}
- 根据 key 计算出 hashcode 。
- 判断是否需要进行初始化。
f即为当前 key 定位出的 Node,如果为空表示当前位置可以写入数据,利用 CAS 尝试写入,失败则自旋保证成功。- 如果当前位置的
hashcode == MOVED == -1,则需要进行扩容。 - 如果都不满足,则利用 synchronized 锁写入数据。
- 如果数量大于
TREEIFY_THRESHOLD则要转换为红黑树。
CAS,乐观锁,在这里使用了乐观锁的原理来实现数据写入
JDK1.7 与 1.8的区别
首先是结构不同
在1.7里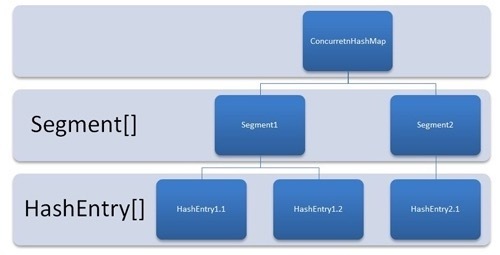
在1.8里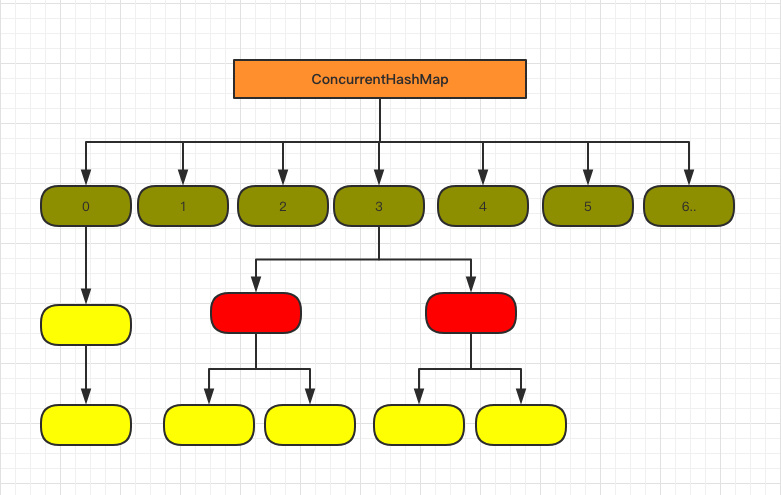
两种结构的调整主要解决了1.7版本中对于查询遍历链表效率太低的问题。在1.8引入了红黑树,当链表长度超过8时,即转换为红黑树存储信息,提高了遍历的速率。
其二
在JDK1.7里,ConcurrentHashMap的put方法里主要使用了ReentrantLock来实现并发阻塞,对HashEntry,即结点加锁,在做完put操作之后再释放该锁,做到并发同步。
//jdk1.7final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null :scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);V oldValue;try {HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index);for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) {if (e != null) {K k;if ((k = e.key) == key ||(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {oldValue = e.value;if (!onlyIfAbsent) {e.value = value;++modCount;}break;}e = e.next;}else {if (node != null)node.setNext(first);elsenode = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first);int c = count + 1;if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)rehash(node);elsesetEntryAt(tab, index, node);++modCount;count = c;oldValue = null;break;}}} finally {unlock();}return oldValue;}
步骤:
- 首先第一步的时候会尝试获取锁,如果获取失败肯定就有其他线程存在竞争,则利用 scanAndLockForPut() 自旋获取锁。
- 尝试自旋获取锁。
- 如果重试的次数达到了 MAX_SCAN_RETRIES 则改为阻塞锁获取,保证能获取成功
- 将当前 Segment 中的 table 通过 key 的 hashcode 定位到 HashEntry。
- 遍历该 HashEntry,如果不为空则判断传入的 key 和当前遍历的 key 是否相等,相等则覆盖旧的 value
- 不为空则需要新建一个 HashEntry 并加入到 Segment 中,同时会先判断是否需要扩容
- 最后会解除在 1 中所获取当前 Segment 的锁
get方法非常高效,整个过程都不需要加锁。
1.8 在 1.7 的数据结构上做了大的改动,采用红黑树之后可以保证查询效率(O(logn)),甚至取消了 ReentrantLock 改为了 synchronized,这样可以看出在新版的 JDK 中对 synchronized 优化是很到位的。

