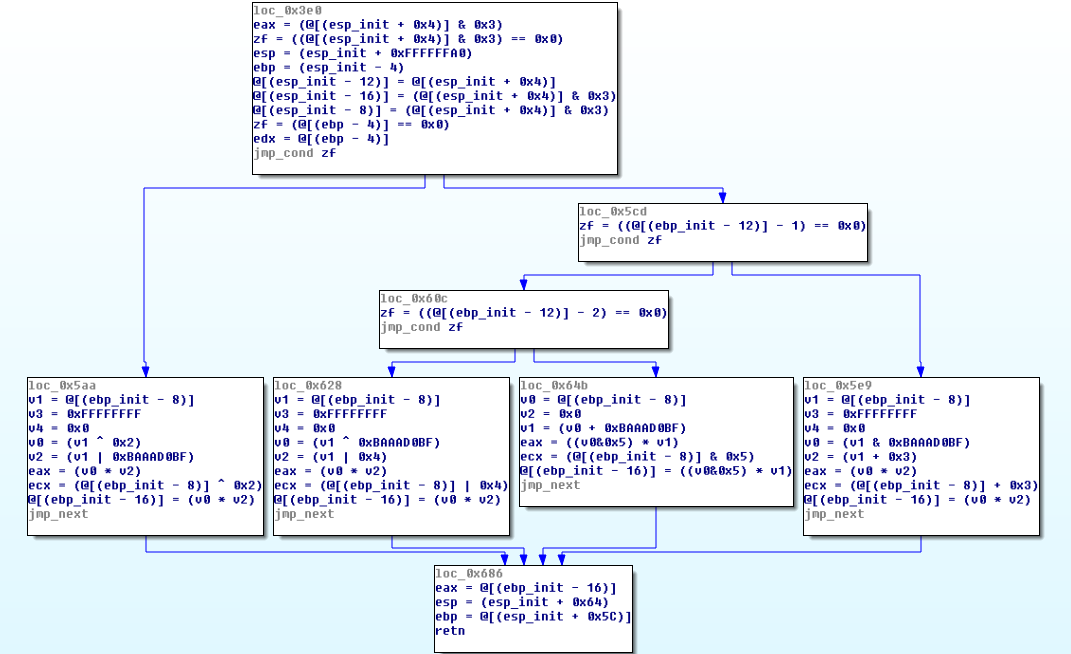
unsigned int target_function(unsigned int n){unsigned int mod = n % 4;unsigned int result = 0;if (mod == 0) result = (n | 0xBAAAD0BF) * (2 ^ n);else if (mod == 1) result = (n & 0xBAAAD0BF) * (3 + n);else if (mod == 2) result = (n ^ 0xBAAAD0BF) * (4 | n);else result = (n + 0xBAAAD0BF) * (5 & n);return result;}
https://github.com/obfuscator-llvm/obfuscator/wiki/Control-Flow-Flattening
../build/bin/clang -m32 target.c -o target_flat -mllvm -fla -mllvm -perFLA=100
控制流平坦化并不会施加指令上的混淆和保护,代码依然是可读的,但是控制流图被破坏了。想要恢复函数原有的CFG图需要理清楚各个基本块之间的关系。

由该图可以看出,真实块的后继块就是 预处理器 只需要 找到预处理器 就ok,ret 块是没有后继的块 序言是没有前继。
然后找各个块之间逻辑关系的方法就是根据cfg图先找没有前继块的序言块和没有后继块的ret块,然后根据主分发器的前继来寻找预处理器,找到预处理器之后直接找真实块,然而最大的问题在于如何确定真实块之间的逻辑关系
解决这个问题的其中一种方式就是通过符号执行,Miasm框架或者angr框架都能起到相应的效果。
angr对于这个问题的处理方法是通过修改临时变量,再执行就可以得到分支的地址。这一做法可以得到两个分支的逻辑,如果遇到call就直接返回,看看执行的块是否在真实块集合里面,如果在的话就把真实块地址返回最后就是根据调用块来直接patch。如果是有分支的话,针对产生分支的真实块把CMOV指令改成相应的条件跳转指令跳向符合条件的分支,例如CMOVZ 改成JZ,再在这条之后添加JMP 指令跳向另一分支。
# Imports from Miasm frameworkfrom miasm2.core.bin_stream import bin_stream_strfrom miasm2.arch.x86.disasm import dis_x86_32from miasm2.arch.x86.ira import ir_a_x86_32from miasm2.arch.x86.regs import all_regs_ids, all_regs_ids_initfrom miasm2.ir.symbexec import symbexecfrom miasm2.expression.simplifications import expr_simp# Binary path and offset of the target functionoffset = 0x3e0fname = "../src/target"# Get Miasm's binary streambin_file = open(fname).read()bin_stream = bin_stream_str(bin_file)# Disassemble blocks of the function at 'offset'mdis = dis_x86_32(bin_stream)disasm = mdis.dis_multibloc(offset)# Create target IR object and add all basic blocks to itir = ir_a_x86_32(mdis.symbol_pool)for bbl in disasm: ir.add_bloc(bbl)# Init our symbols with all architecture known registerssymbols_init = {}for i, r in enumerate(all_regs_ids):symbols_init[r] = all_regs_ids_init[i]# Create symbolic execution enginesymb = symbexec(ir, symbols_init)# Get the block we want and emulate it# We obtain the address of the next block to executeblock = ir.get_bloc(offset)nxt_addr = symb.emulbloc(block)# Run the Miasm's simplification engine on the next# address to be sure to have the simplest expressionsimp_addr = expr_simp(nxt_addr)# The simp_addr variable is an integer expression (next basic block offset)if isinstance(simp_addr, ExprInt):print("Jump on next basic block: %s" % simp_addr)# The simp_addr variable is a condition expressionelif isinstance(simp_addr, ExprCond):branch1 = simp_addr.src1branch2 = simp_addr.src2print("Condition: %s or %s" % (branch1,branch2))############################################################################# Here we disassemble target function and collect relevants blocks# Collapsed for clarity but nothing complicated here, and the algorithm is given aboverelevants = get_relevants_blocks()# Control flow dictionnary {parent: set(childs)}flow = {}# Init flow dictionnary with empty sets of childsfor r in relevants: flow[r] = set()# Start loop of symbolic executionwhile True:block_state = # Get next block state to emulate# Get current branch parameters# "parent_addr" is the parent block variable se seen earlier# "symb" is the context (symbols) of the current branchparent_addr, block_addr, symb = block_state# If it is a relevant blockif block_addr in flow:# We avoid the prologue's parent, as it doesn't existif parent_addr != ExprInt32(prologue_parent):# Do the link between the block and its relevant parentflow[parent_addr].add(block_addr)# Then we set the block as the new relevant parentparent_addr = block_addr# Finally, we can emulate the next block and so on.