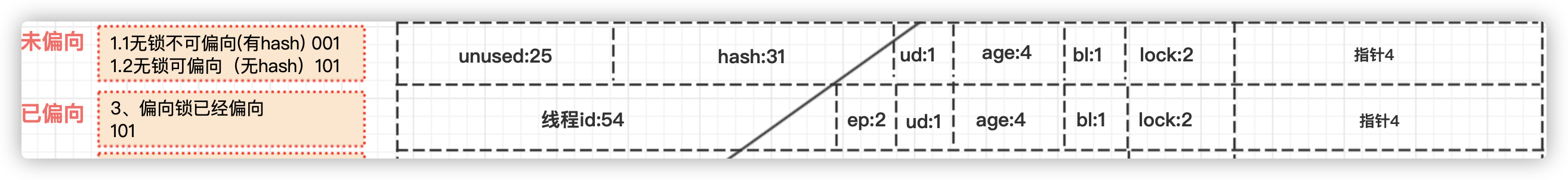
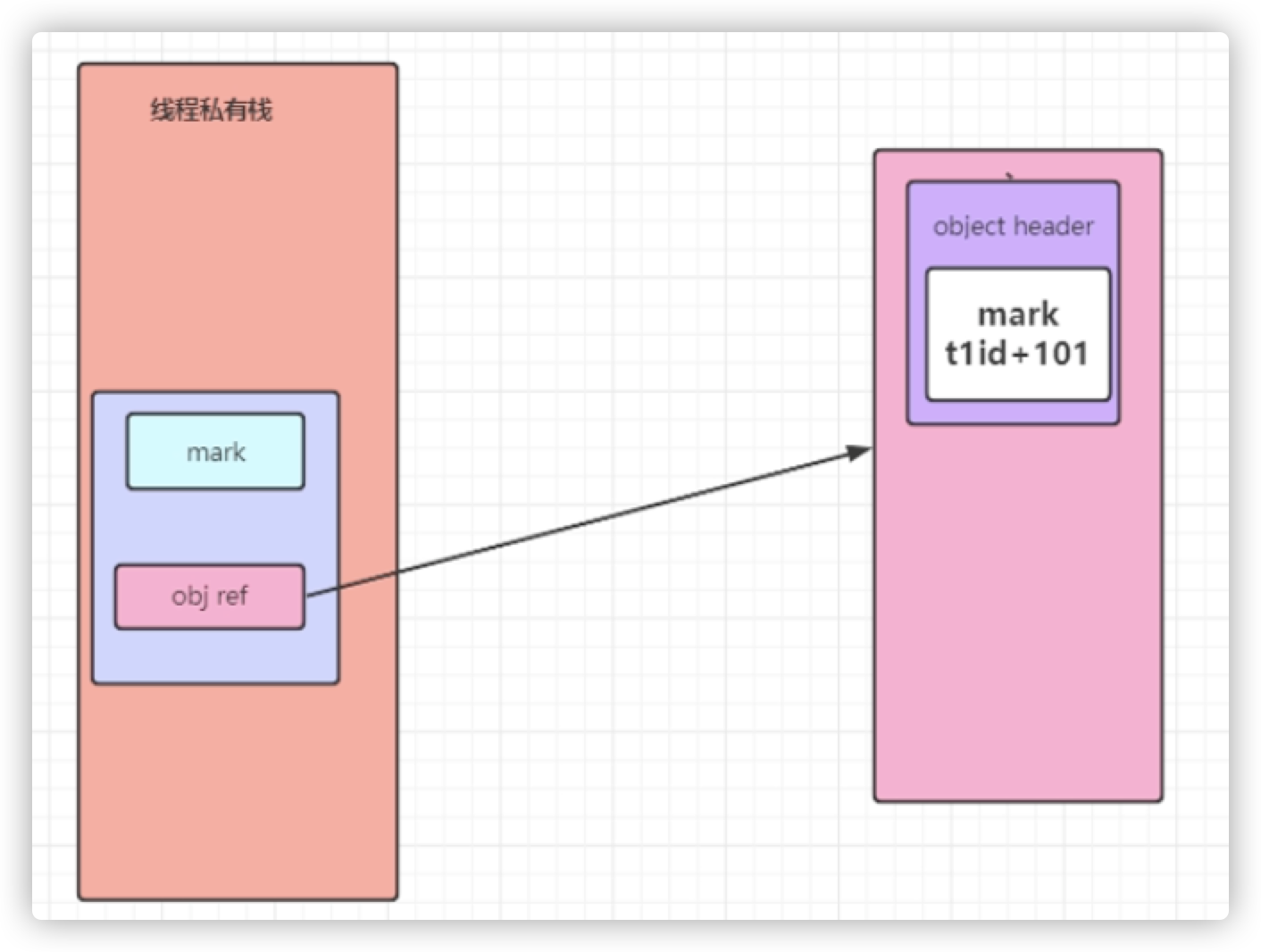
1.场景:匿名偏向
2.场景:重入
重入后的状态
3.场景:重新加锁
重新加锁(再次偏向)是指线程t1 释放偏向锁后,再次访问这个偏向锁。
第二次偏向的性能要比第一次高,因为第一次还需要有一个CAS设置线程id的过程。
bytecodeInterpreter.cpp
/* monitorenter and monitorexit for locking/unlocking an object */CASE(_monitorenter): {//为这个锁 创建一个空的Lock Recordoop lockee = STACK_OBJECT(-1);CHECK_NULL(lockee);BasicObjectLock* limit = istate->monitor_base();BasicObjectLock* most_recent = (BasicObjectLock*) istate->stack_base();BasicObjectLock* entry = NULL;while (most_recent != limit ) {if (most_recent->obj() == NULL) entry = most_recent;else if (most_recent->obj() == lockee) break;most_recent++;}if (entry != NULL) {//把当前锁对象的markword存储到1ock Record当中的displaced headerentry->set_obj(lockee);int success = false;uintptr_t epoch_mask_in_place = (uintptr_t)markOopDesc::epoch_mask_in_place;markOop mark = lockee->mark();intptr_t hash = (intptr_t) markOopDesc::no_hash;// 是否开启偏向锁if (mark->has_bias_pattern()) {uintptr_t thread_ident;uintptr_t anticipated_bias_locking_value;//获取线程idthread_ident = (uintptr_t)istate->thread();anticipated_bias_locking_value =(((uintptr_t)lockee->klass()->prototype_header() | thread_ident) ^ (uintptr_t)mark) &~((uintptr_t) markOopDesc::age_mask_in_place);if (anticipated_bias_locking_value == 0) {// 值为0 表示已经是偏向自己if (PrintBiasedLockingStatistics) {(* BiasedLocking::biased_lock_entry_count_addr())++;}success = true;}// 偏向禁用else if ((anticipated_bias_locking_value & markOopDesc::biased_lock_mask_in_place) != 0) {// try revoke bias 禁用:撤销偏向达到40次 从类当中拿到的对象头markOop header = lockee->klass()->prototype_header();if (hash != markOopDesc::no_hash) {header = header->copy_set_hash(hash);}if (lockee->cas_set_mark(header, mark) == mark) {if (PrintBiasedLockingStatistics)(*BiasedLocking::revoked_lock_entry_count_addr())++;}}//poch_mask_in_place 判断是否过期else if ((anticipated_bias_locking_value & epoch_mask_in_place) !=0) {// try rebias 重新偏向// 创建一个偏向当前线程的markwordmarkOop new_header = (markOop) ( (intptr_t) lockee->klass()->prototype_header() | thread_ident);if (hash != markOopDesc::no_hash) {new_header = new_header->copy_set_hash(hash);}//将该锁设置为偏向当前线程if (lockee->cas_set_mark(new_header, mark) == mark) {if (PrintBiasedLockingStatistics)(* BiasedLocking::rebiased_lock_entry_count_addr())++;}else {//CAS失败CALL_VM(InterpreterRuntime::monitorenter(THREAD, entry), handle_exception);}success = true;}else {// 匿名偏向 或者 偏向了别人 这两种情况// try to bias towards thread in case object is anonymously biased// 在内存中 创建一个匿名可偏向 header 101markOop header = (markOop) ((uintptr_t) mark & ((uintptr_t)markOopDesc::biased_lock_mask_in_place |(uintptr_t)markOopDesc::age_mask_in_place |epoch_mask_in_place));if (hash != markOopDesc::no_hash) {header = header->copy_set_hash(hash);}// 又创建一个偏向自己的new_header thread_id + 101markOop new_header = (markOop) ((uintptr_t) header | thread_ident);// debugging hintDEBUG_ONLY(entry->lock()->set_displaced_header((markOop) (uintptr_t) 0xdeaddead);)// CAS 如果是匿名偏向,就改为偏向自己,将new_header 设置到锁的markword当中去if (lockee->cas_set_mark(new_header, header) == header) {if (PrintBiasedLockingStatistics)(* BiasedLocking::anonymously_biased_lock_entry_count_addr())++;}else {//CAS失败CALL_VM(InterpreterRuntime::monitorenter(THREAD, entry), handle_exception);}success = true;}}// 当前偏向的线程不是自己// traditional lightweight lockingif (!success) {//首先产生一个无锁的markwordmarkOop displaced = lockee->mark()->set_unlocked();entry->lock()->set_displaced_header(displaced);bool call_vm = UseHeavyMonitors;// CAS将这个无锁的markword替换到锁记录中,如果成功则轻量级锁加锁成功if (call_vm || lockee->cas_set_mark((markOop)entry, displaced) != displaced) {//进入这个if表示轻量级锁加锁失败//是否是重入的场景if (!call_vm && THREAD->is_lock_owned((address) displaced->clear_lock_bits())) {entry->lock()->set_displaced_header(NULL);} else {//重量级锁CALL_VM(InterpreterRuntime::monitorenter(THREAD, entry), handle_exception);}}}//执行CPU的下一条指令UPDATE_PC_AND_TOS_AND_CONTINUE(1, -1);} else {istate->set_msg(more_monitors);UPDATE_PC_AND_RETURN(0); // Re-execute}}CASE(_monitorexit): {oop lockee = STACK_OBJECT(-1);CHECK_NULL(lockee);// derefing's lockee ought to provoke implicit null check// find our monitor slotBasicObjectLock* limit = istate->monitor_base();BasicObjectLock* most_recent = (BasicObjectLock*) istate->stack_base();while (most_recent != limit ) {if ((most_recent)->obj() == lockee) {BasicLock* lock = most_recent->lock();markOop header = lock->displaced_header();most_recent->set_obj(NULL);if (!lockee->mark()->has_bias_pattern()) {bool call_vm = UseHeavyMonitors;// If it isn't recursive we either must swap old header or call the runtimeif (header != NULL || call_vm) {markOop old_header = markOopDesc::encode(lock);if (call_vm || lockee->cas_set_mark(header, old_header) != old_header) {// restore object for the slow casemost_recent->set_obj(lockee);CALL_VM(InterpreterRuntime::monitorexit(THREAD, most_recent), handle_exception);}}}UPDATE_PC_AND_TOS_AND_CONTINUE(1, -1);}most_recent++;}// Need to throw illegal monitor state exceptionCALL_VM(InterpreterRuntime::throw_illegal_monitor_state_exception(THREAD), handle_exception);ShouldNotReachHere();}
批量重偏向
偏向撤销
批量重偏向-轻量级锁降级为偏向锁
当一个线程创建了大量对象并执行了初始的同步操作,后来另一个线程也来将这些对象作为锁对象进行操作,会导偏向锁重偏向的操作。JVM 认为如果对同一个类的对象进行了20次偏向撤销,就会产生批量重偏向。
此时锁 由 轻量级锁 =》偏向锁。
批量撤销
批量撤销-禁用偏向锁
JVM 认为如果对同一个类的对象进行了40次单个撤销,JVM会认为代码设计有问题,对所有该类的对象进行批量撤销,并且从此对这个类禁用偏向锁,修改类class文件中的markword为001。
在超过40次本应该为可偏向状态偏向锁101的新对象,在经历过批量重偏向和批量撤销后直接在实例化后转为无锁001。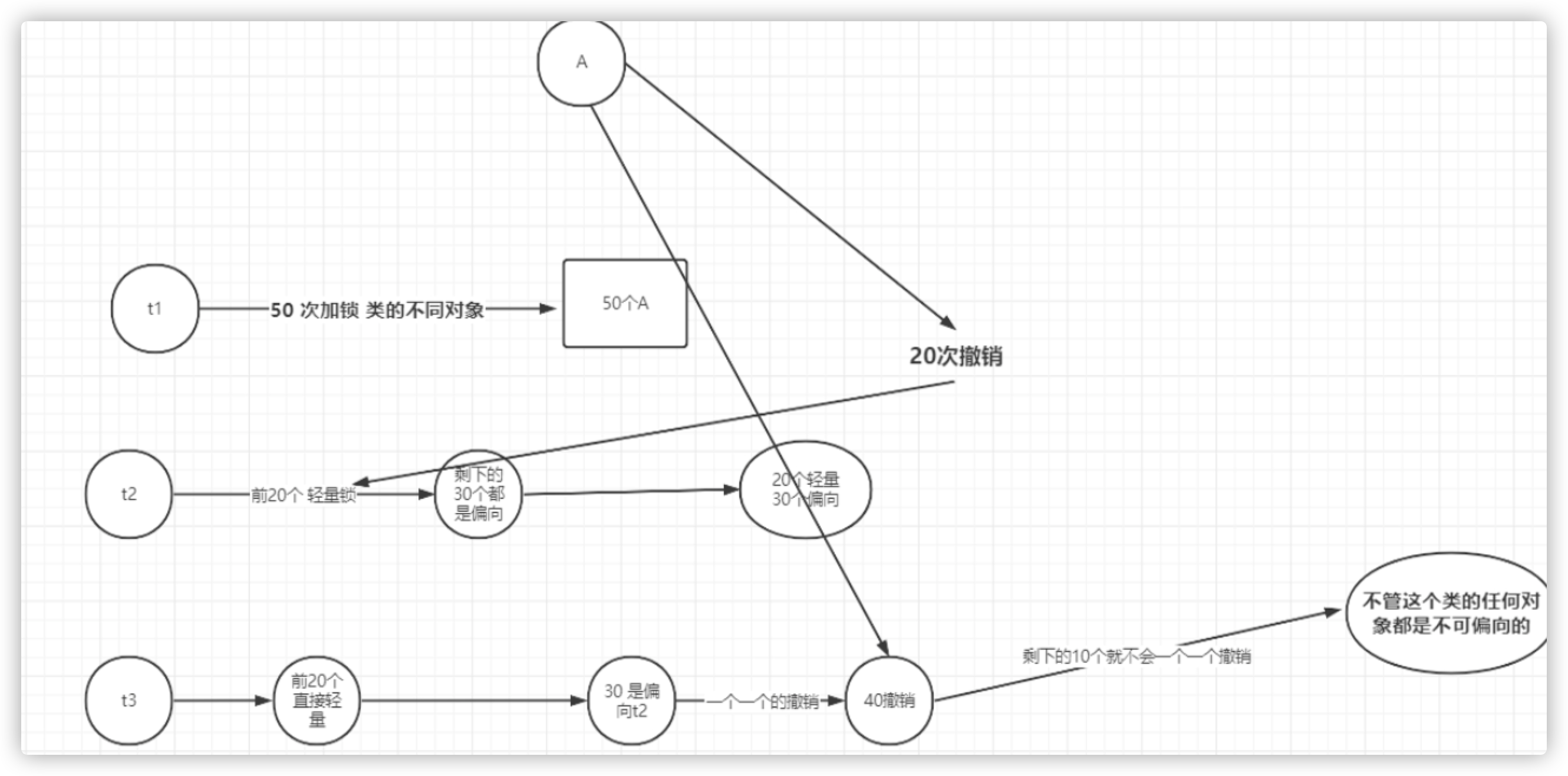
- 批量重偏向和批量撤销是针对类的优化,和对象无关。
- 偏向锁重偏向一次之后不可再次重偏向。
- 当某个类已经触发批量撤销机制后,JVM会默认当前类产生了严重的问题,剥夺了该类的新实例对象使用偏向锁的权利
偏向过期
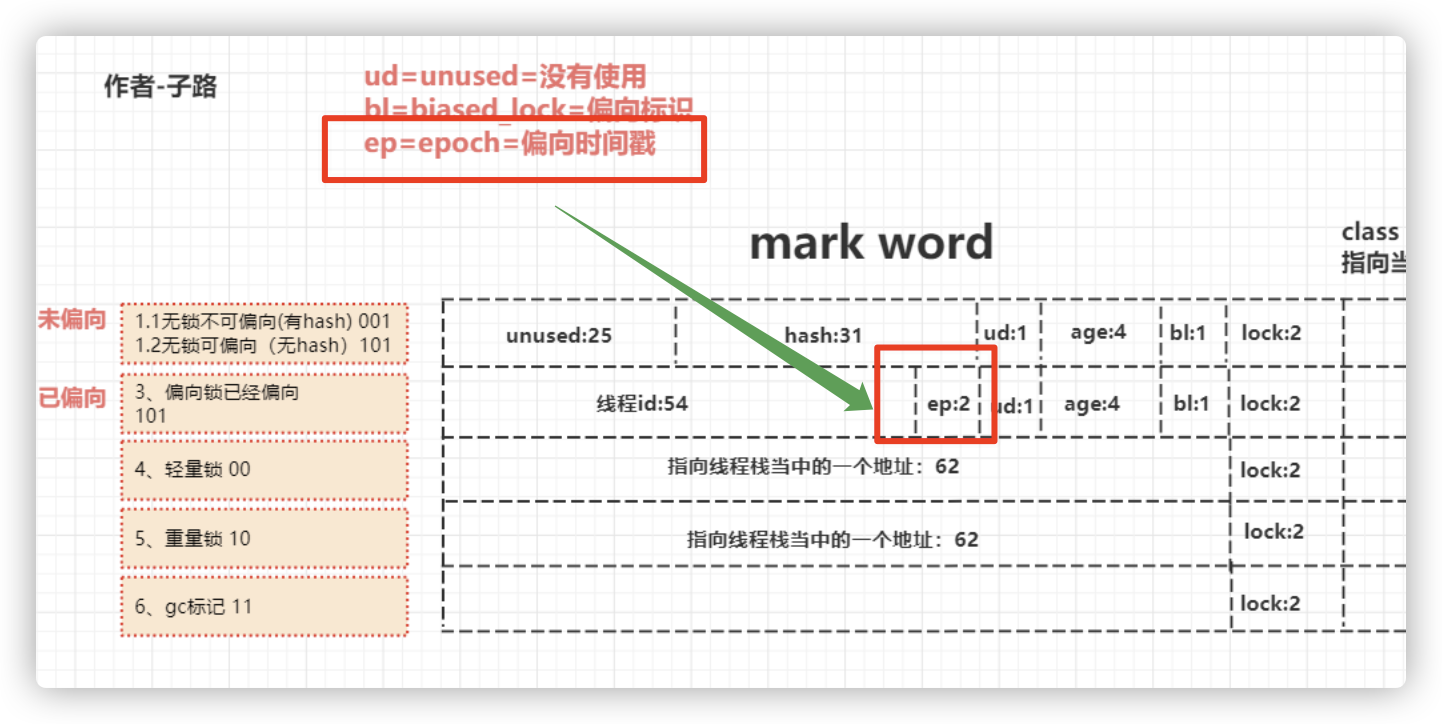
当一个类被加载到元空间后,这个类的类信息会成为创建这个类的对象的模板,这个epoch的值就是存在于类信息中的模板值,默认为01。
当发生批量重偏向时,就会对元空间中这个类的epoch值 +1。
当一个线程访问偏向锁,发现epoch值不等于初始值时,就认为这个偏向锁过期了,可以直接把该锁设置为偏向自己。