1、什么是异常
1.1 定义

1.2 分类

1.3 异常体系结构
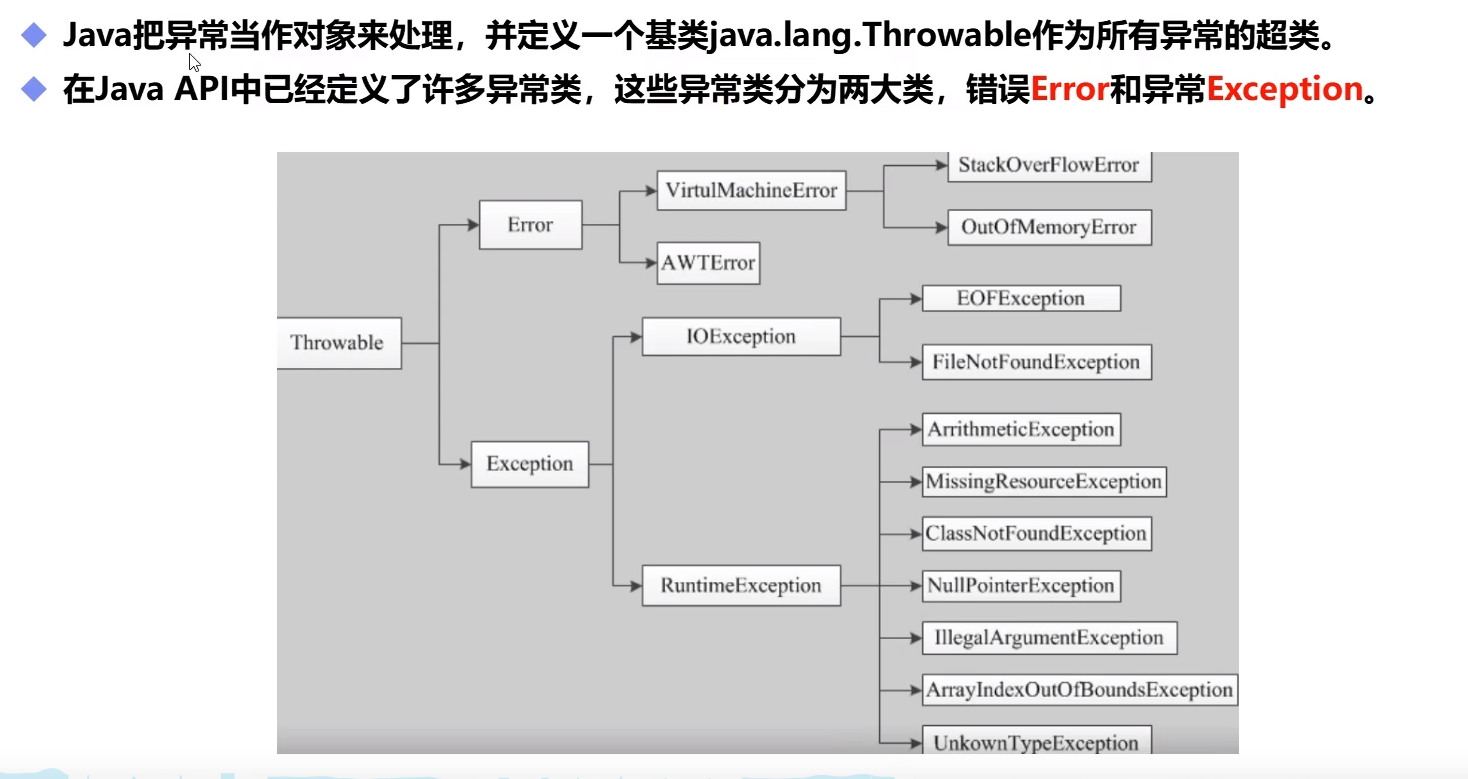
1.4 Error

1.5 Exception

2、Java异常处理机制

2.1 处理异常
package com.exception;public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 0; Demo01 demo01 = new Demo01(); demo01.test(a,b);// 捕获多个异常,从小到大 try{ System.out.println(a/b); }catch (ArithmeticException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (Error e) { System.out.println("Error: " + e); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace();// 打印错误的栈信息 System.out.println("exception: " + e); }catch (Throwable t){ System.out.println("Throwable: " + t); }finally { System.out.println("finaly"); } } public int test(int a, int b) throws ArithmeticException{// 假设方法上处理不了,方法上处理异常 if (b == 0){ throw new ArithmeticException();// 主动抛出异常,一般在方法中使用 } return a/b; }}
3、自定义异常

// MyExceptionpackage com.exception;public class MyException extends Throwable { // 传递数字 > 10 private int detail; public MyException(int a){ this.detail = a; } // 异常打印 @Override public String toString(){ return "MyException{" + detail + "}"; }}// Demo01package com.exception;public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 0; int b = 0; Demo01 demo01 = new Demo01(); try { demo01.test(a); } catch (MyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }// 捕获多个异常,从小到大 } public void test(int a) throws MyException {// 假设方法上处理不了,方法上处理异常 if (a == 0){ throw new MyException(a);// 主动抛出异常,一般在方法中使用 } System.out.println("ok"); }}
4、总结










