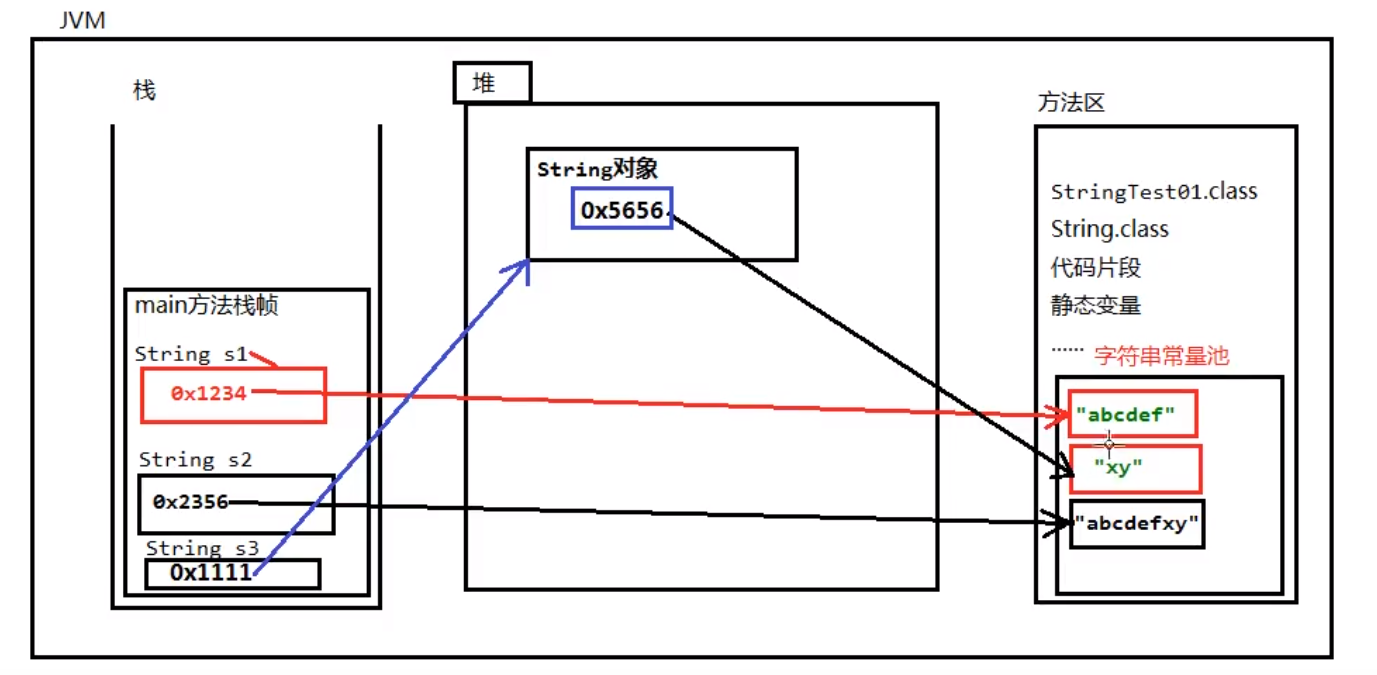
1.1 字符串对象内存分析
package com.string;/* 1、Java JDK中内置的一个类,java.lang.String 2、使用双引号括起来的都是String对象 3、双引号括起来的字符串是不可变的 4、在JDK中双引号括起来的字符串中,字符串存储在方法区的字符串常量池当中 - 字符串在实际开发中太频繁,为了执行效率 */public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { // s1 是引用,存储 字符串对象'abcdef' 的内存地址,'abcdef' 存储在方法区的字符串常量池中 // 两行代码创建了三个字符串对象,都是在字符串常量池中 String s1 = "abcdef"; // 连接表示创建一个新的字符串对象 String s2 = "abcdef" + "xy"; // 分析代码中的 xy 从哪里来的? // 凡是双引号括起来的都在字符串常量池中,new 对象是在堆里边开辟内存 String s3 = new String("xy"); }}
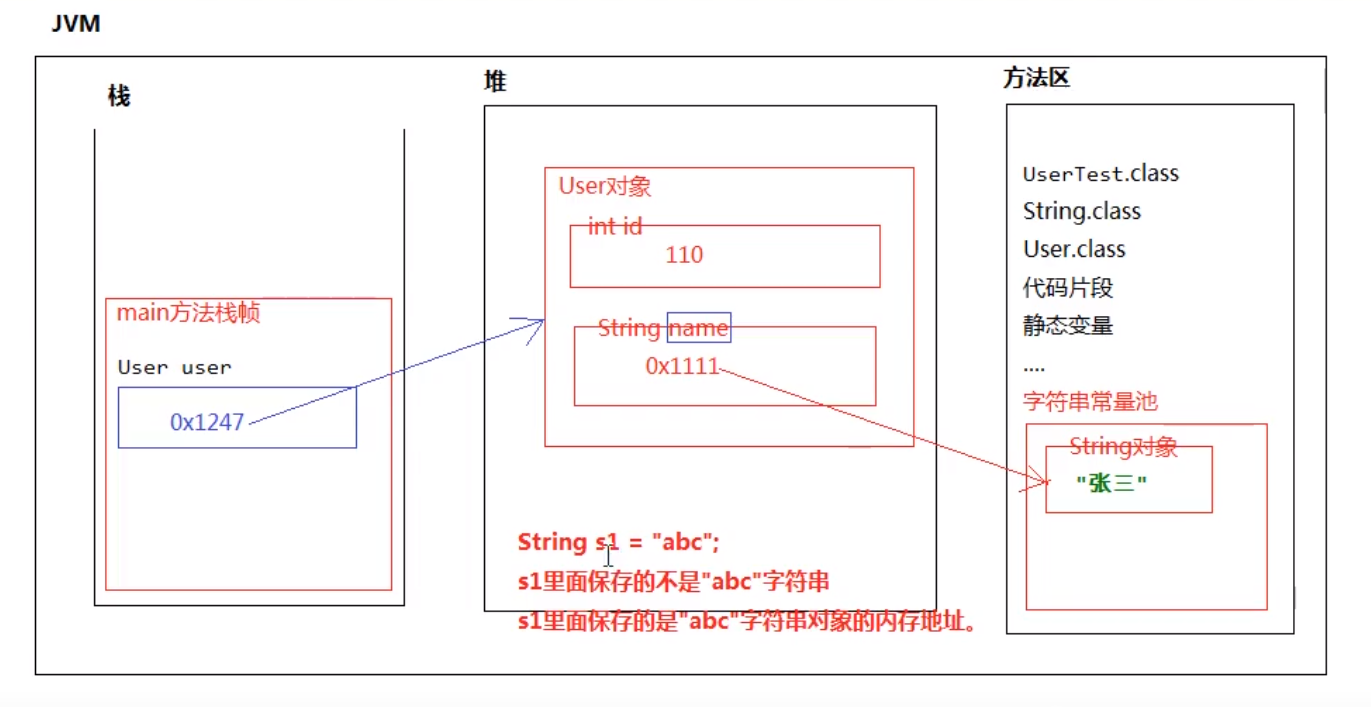
package com.string;public class UserTest { public static void main(String[] args) { User user = new User(110,"张三"); }}
1.2 对象间的比较
package com.string;public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "abcdef"; String s2 = "abcdef"; // 分析结果是 true 还是false // == 比较的是对象的内存地址 System.out.println(s1 == s2);// false // String类的equals方法,只要是字符串对象都可以使用equals方法 // 方法一 System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // 方法二 可以避免空指针异常,String k = null;不可调用equals方法 // String k = null; String k = new String("teststring"); System.out.println(k.equals(s2)); }}
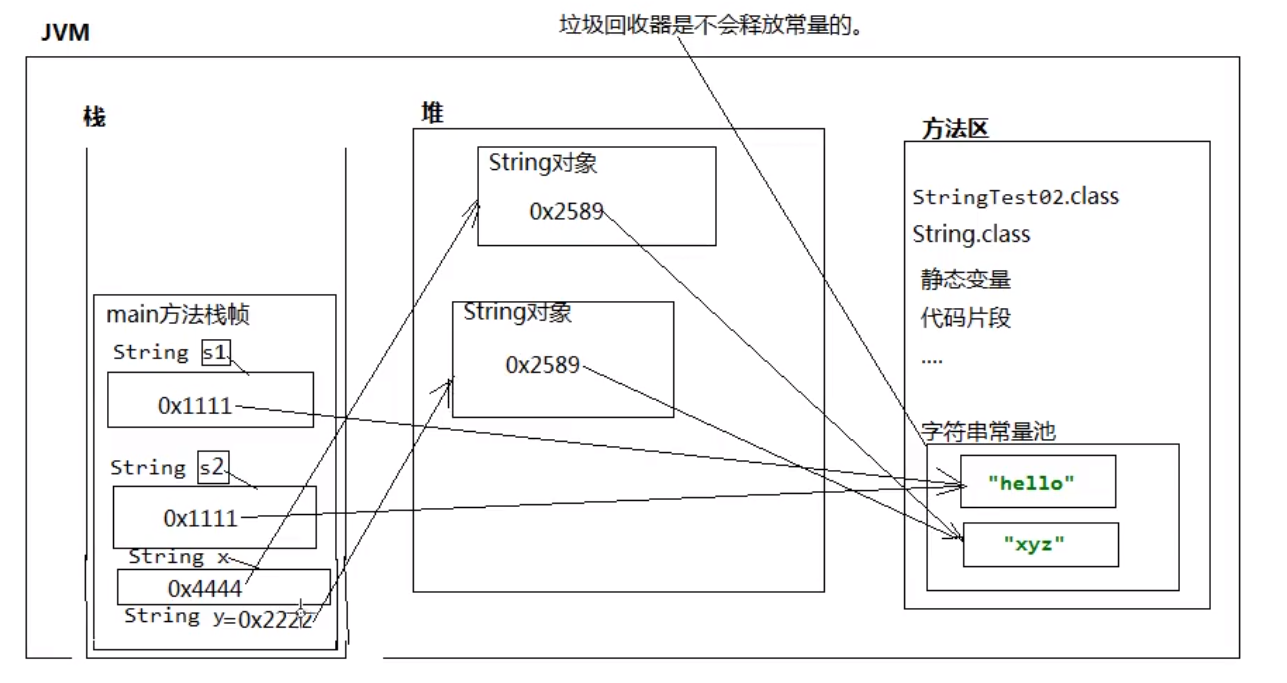
1.3 面试题
package com.string;/* 分析以下程序,一共创建了几个对象 */public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { /* 一共3个对象 方法区字符串常量池中1个 "hello" 对象 堆内存中两个String对象 一共3个 */ String s1 = new String("hello"); String s2 = new String("hello"); }}
1.4 常用的构造方法
package com.string;/** * 关于String类的构造方法 * String s1 = new String("") * String s2 = "" 最常用 * String s3 = new String(char数组) * String s4 = new String(char数组,offset,length) * String s5 = new String(byte数组) * String s6 = new String(byte数组,offset,length) */public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { byte [] bytes = {97,98,99}; String s2 = new String(bytes); // 输出一个引用,自动调用toString()方法,默认object的话,会自动输出对象的内存地址 // 结果不是内存地址,String类已经重写了toString()方法 System.out.println(s2);//abc System.out.println(s2.toString());// abc String s1 = new String(bytes,1,2); System.out.println(s1);//bc char[] chars = {'我','是','中','国','人'}; String s3 = new String(chars); String s4 = new String(chars,2,3); System.out.println(s3);// 我是中国人 System.out.println(s4);// 中国人 }}
1.5 方法练习
package com.string;public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { // String 类当中常用方法 // 1、char charAt(int index) char c1 = "我是中国人".charAt(2); System.out.println(c1);// 中 //2、compareTo(String anotherString) int result1 = "abcd".compareTo("abcd");// 前后相同 System.out.println(result1);// 0 int result2 = "abcd".compareTo("abcde");// 前小后大 System.out.println(result2);// -1 int result3 = "abcde".compareTo("abcd");// 前大后小 System.out.println(result3);// 1 int result4 = "abc".compareTo("ycd");// 两个字符串的某个位置的有比较结果后,后边的字符不需要比较 System.out.println(result4);// -24 // 3、boolean contains(CharSequence s) System.out.println("https://pypi.douban.com/simple".contains("https://"));//true System.out.println("https://pypi.douban.coom/simple".contains("xigua"));//false }}
1.6 String类方法练习
package com.string;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;import java.util.Locale;public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { // String 类当中常用方法 // 1、char charAt(int index) char c1 = "我是中国人".charAt(2); System.out.println(c1);// 中 //2、compareTo(String anotherString) int result1 = "abcd".compareTo("abcd");// 前后相同 System.out.println(result1);// 0 int result2 = "abcd".compareTo("abcde");// 前小后大 System.out.println(result2);// -1 int result3 = "abcde".compareTo("abcd");// 前大后小 System.out.println(result3);// 1 int result4 = "abc".compareTo("ycd");// 两个字符串的某个位置的有比较结果后,后边的字符不需要比较 System.out.println(result4);// -24 // 3、boolean contains(CharSequence s) System.out.println("https://pypi.douban.com/simple".contains("https://"));//true System.out.println("https://pypi.douban.coom/simple".contains("xigua"));//false // 4、boolean endsWith(String suffix) System.out.println("test.txt".endsWith(".java"));//false System.out.println("test.txt".endsWith(".txt"));//true // 5、boolean equals(Object anObject) System.out.println("abc".equals("abc"));//true //6、boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) System.out.println("abc".equalsIgnoreCase("ABc"));//true System.out.println("abc".equalsIgnoreCase("ABcd"));//false //7、byte[] getBytes() byte[] bytes = "abcdef".getBytes(); for (byte charS: bytes) { System.out.print(charS + " "); } //8、int indexOf(String str) System.out.println("abcdecfg".indexOf("c")); // 9、boolean isEmpty() // 判断数组长度是length属性,判断字符串长度是length方法 System.out.println("".isEmpty());//true System.out.println("abc".isEmpty()); //false // 10、int lastIndexOf(String str) System.out.println("dbc#abcc#abcd#abc".lastIndexOf("abc")); // 11、String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) System.out.println("http://www.baidu.com".replace("http","https")); // 12、String[] split(String regex) String[] params = "name=wangbq&password=123456&age=18".split("&"); for (String param: params) { System.out.println(param); } // 13、boolean startsWith(String prefix) System.out.println("https://www.baidu.com".startsWith("http"));//true // 14、String substring(int beginIndex) System.out.println("https://www.baidu.com".substring(3));//ps://www.baidu.com // 15、String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) System.out.println("https://www.baidu.com".substring(3,5));//ps 开包 尾不包 // 16、char[] toCharArray() char[] chars = "我是中国人".toCharArray(); for (char charS: chars) { System.out.println(charS); } //17、String toLowerCase() System.out.println("https://www.baidu.com".toLowerCase()); //18、String toUpperCase() System.out.println("https://www.baidu.com".toUpperCase()); // 19、static String valueOf(char c) System.out.println(String.valueOf(true));//true System.out.println(String.valueOf(100));//100 System.out.println(String.valueOf(new Customer()));//我是一个VIP客户 }}class Customer{ @Override public String toString() { return "我是一个VIP客户"; }}




