VUE
vue2,经典版本,现在绝大部分的企业项目都是vue2
vue3,新版本 ,趋势
VUE初体验
基于vue.js框架来编写项目需要以下几个步骤:
- 导入vue.js包(CDN)
<!-- 开发环境版本,包含了有帮助的命令行警告 --><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><!-- 生产环境版本,优化了尺寸和速度 --><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2"></script># 当然,也可以将文件下载下来再通过本地导入。
- 应用
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><!-- 1.引入vue.js文件 --><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><!-- 2.指定区域,该区域的内容希望由vue.js来接管。 --><div id="app"><h1>欢迎学习Vue.js</h1><div>我叫{{name}},微信{{wechat}}</div> <!-- {{}}会去vue对象的data属性里面找值--><input type="button" value="点我" v-on:click="clickMe"> <!-- v-on:click点击事件 当点击的时候执行vue对象里的clickMe函数--></div><script>// 3.创建Vue对象,并关联指定HTML区域。var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {name: '123',wechat: '123888'},methods: {clickMe: function () {// 获取值this.name// 修改值this.name = "xx"this.name = "455";this.wechat = "455666";}}})</script></body></html>
vue常见指令
想要使用vue.js来进行开发,就必须学会vue.js中提供的指令,明白每个指令是什么意思,才能更灵活的让他去显示我们想要的效果。
插值表达式
一般在显示文本内容的标签中使用。就是将js中的值显示在html标签中
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div>我叫{{name}},我喜欢{{hobby}},邮箱:{{dataInfo.email}}</div><ul><li>{{'456'}}</li> <!--{{}}里面可以引用vue中的值,也可以直接写一些值--><li>{{'456' + "土鳖"}}</li><li>{{ base + 1 + 1 }}</li><li>{{ 1===1 ?"456":"789"}}</li> <!--1===1条件成立就是456 不成立就是789 --></ul><ul><li>{{ condition?"12":"34"}}</li> <!--condition的值是用的vue对象里的值 --></ul><input type="button" value="点我" v-on:click="clickMe"></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {name: '123',hobby: '篮球',dataInfo: {id: 1,email: "xxx.com"},condition: false,base: 1},methods: {clickMe: function () {this.name = "小马哥";this.condition = true;this.dataInfo.email = "xmg@live.com";this.base += 100;}}})</script></body></html>
v-bind
一般用于对标签中的属性进行操作。
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><style>.ig {border: 2px solid red;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><img src='xx.png' class='c1' /><img alt="" v-bind:src="imageUrl" v-bind:class="cls"> <!--v-bind:src对应的imageUrl会去vue对象中找imageUrl然后复制过来 --></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {imageUrl: 'https://hcdn2.luffycity.com/media/frontend/public_class/PY1@2x_1566529821.1110113.png',cls: "ig",}})</script></body></html>
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><style>.ig {border: 2px solid red;}.info {color: red;}.danger {font-size: 10px;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><img src='xx.png' class='c1'/><img alt="" v-bind:src="imageUrl" v-bind:class="cls"><!--内部会判断v1和v2的值,值也是去vue对象中找,只会找值为True的并赋值给class --><h1 v-bind:class="{info:v1,danger:v2}">你好呀111</h1><!--clsDict也是去vue对象中找,会找值为True的将键放到此处 --><h1 v-bind:class="clsDict">你好呀</h1><!--会将vue对象的data对象中的a1 和 a2的值放到此处 --><h2 v-bind:class="[a1,a2]"></h2><!--条件成立是a1,不成立是‘y’,然后还有一个a1--><h2 v-bind:class="[1===1?a1:'y',a2]">111</h2><!--clr会去vue data对象中去找,size也是--><h3 v-bind:style="{ color:clr,fontSize:size+'px'}">222</h3><h3 style="color: red;font-size: 19px">333</h3><!--给input添加一个点击事件 当点击的时候执行vue data 属性里的clickme --><input type="button" value="点我" v-on:click="clickMe"></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {imageUrl: 'https://hcdn2.luffycity.com/media/frontend/public_class/PY1@2x_1566529821.1110113.png',cls: "ig",v1: true,v2: true,clsDict: {info: false,danger: false},a1: "info",a2: "danger",clr: "red",size: "19",},methods:{clickMe:function () {this.v1 = false;}}})</script></body></html>
v-bind注意:
- 简写的格式:
:属性名=xxx,例如:<h1 v-bind:class="v1"></h1><h1 :class="v1"></h1><img :src="xx" />
- v-bind属于单向绑定( JS修改->HTML修改 )。
v-model
一般用于在交互的表中中使用,例如:input、select、textarea等。【双向绑定】
JS修改->HTML修改
HTML修改 -> JS修改
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div>用户名:<input type="text" v-model="user"></div><div>密码:<input type="password" v-model="pwd"></div><input type="button" value="登录" v-on:click="clickMe"/><input type="button" value="重置" v-on:click="resetForm"/></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {user: "",pwd: "",},methods: {clickMe: function () {console.log(this.user, this.pwd)},resetForm: function () {this.user = "";this.pwd = "";}}})</script></body></html>
更多标签实例
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div>用户名:<input type="text" v-model="user"></div><div>密码:<input type="password" v-model="pwd"></div><div>性别:<input type="radio" v-model="sex" value="1">男<input type="radio" v-model="sex" value="2">女</div><div>爱好:<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobby" value="11">篮球<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobby" value="22">足球<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobby" value="33">评判求</div><div>城市:<select v-model="city"><option value="sh">上海</option><option value="bj">北京</option><option value="sz">深圳</option></select></div><div>擅长领域:<select v-model="company" multiple><option value="11">技术</option><option value="22">销售</option><option value="33">运营</option></select></div><div>其他:<textarea v-model="more"></textarea></div><input type="button" value="注 册" v-on:click="clickMe"/></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {user: "",pwd: "",sex: "2",hobby: ["22"],city: "sz",company: ["22", "33"],more: '...'},methods: {clickMe: function () {console.log(this.user, this.pwd, this.sex, this.hobby, this.city, this.company, this.more);},}})</script></body></html>
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div>用户名:<input type="text" v-model="info.user"></div><div>密码:<input type="password" v-model="info.pwd"></div><div>性别:<input type="radio" v-model="info.sex" value="1">男<input type="radio" v-model="info.sex" value="2">女</div><div>爱好:<input type="checkbox" v-model="info.hobby" value="11">篮球<input type="checkbox" v-model="info.hobby" value="22">足球<input type="checkbox" v-model="info.hobby" value="33">评判求</div><div>城市:<select v-model="info.city"><option value="sh">上海</option><option value="bj">北京</option><option value="sz">深圳</option></select></div><div>擅长领域:<select v-model="info.company" multiple><option value="11">技术</option><option value="22">销售</option><option value="33">运营</option></select></div><div>其他:<textarea v-model="info.more"></textarea></div><input type="button" value="注 册" v-on:click="clickMe"/></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {info: {user: "",pwd: "",sex: "2",hobby: ["22"],city: "sz",company: ["22", "33"],more: '...'}},methods: {clickMe: function () {console.log(this.info);},}})</script></body></html>
v-for
用户数据进行循环并展示。
示例1:
<div id="app"><ul><!--会生成三个li标签--><li v-for="item in dataList">{{ item }}</li></ul></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {dataList: ["郭德纲", "于谦", "三哥"],}})</script>
示例2:
<div id="app"><ul><!--可以得到值和索引 item是值 idx是索引--><li v-for="(item,idx) in dataList">{{idx}} - {{ item }}</li></ul></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {dataList: ["郭德纲", "于谦", "三哥"],}})</script>
示例3:
<div id="app"><ul><!--循环字典时 value 是值 key 是键--><li v-for="(value,key) in dataDict">{{key}} - {{ value }}</li></ul></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {dataDict: {id: 1,age: 18,name: "xxx"}}})</script>
示例4:
<div id="app"><ul><!--此时的item是一个字典,通过item.取值--><li v-for="(item,idx) in cityList">{{item.id}} - {{ item.text }}</li></ul></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {cityList: [{id: 11, text: "上海"},{id: 12, text: "北京"},{id: 13, text: "深圳"},]}})</script>
实例5:
<ul><li> <span>id 11</span> <span>text 上海</span> </li>。。。。</ul>
<div id="app"><ul><!--支持双层循环--><li v-for="(item,idx) in cityList"><span v-for="(v,k) in item">{{k}} {{v}}</span></li></ul></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {cityList: [{id: 11, text: "上海"},{id: 12, text: "北京"},{id: 13, text: "深圳"},]}})</script>
v-on
事件相关的指令,例如:
v-on:click 点击v-on:dblclick 双击v-on:mouseover,v-on:mouseout,v-on:changev-on:focus...
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><ul><li v-on:click="clickMe">点击</li><!--简便写法--><li @click="clickMe">点击</li><li v-on:dblclick="doSomething('双击')">双击</li><!--可以传参--><li v-on:mouseover="doSomething('进入')" v-on:mouseout="doSomething('离开')">进入&离开</li></ul></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {clickMe: function () {alert("点击了")},doSomething: function (msg) {console.log(msg);}}})</script></body></html>
案例
数据的管理包括对数据:展示、动态添加、删除、修改。
- 数据列表展示
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><style>.penal {border: 1px solid #dddddd;margin: 20px 0 0 0;padding: 10px;border-bottom: 0;background-color: #d9d9d9;}.table {width: 100%;border-collapse: collapse;border-spacing: 0;}.table > tbody > tr > td, .table > tbody > tr > th, .table > tfoot > tr > td, .table > tfoot > tr > th, .table > thead > tr > td, .table > thead > tr > th {padding: 8px;vertical-align: top;border: 1px solid #ddd;text-align: left;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><h3 class="penal">数据列表</h3><table class="table"><thead><tr><td>姓名</td><td>年龄</td></tr></thead><tbody><tr v-for="item in dataList"><td>{{item.name}}</td><td>{{item.age}}</td></tr></tbody></table></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {dataList: [{"name": "武沛齐", "age": 19},{"name": "alex", "age": 89},]}})</script></body></html>
- 数据添加
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><style>.penal {border: 1px solid #dddddd;margin: 20px 0 0 0;padding: 10px;border-bottom: 0;background-color: #d9d9d9;}.table {width: 100%;border-collapse: collapse;border-spacing: 0;}.table > tbody > tr > td, .table > tbody > tr > th, .table > tfoot > tr > td, .table > tfoot > tr > th, .table > thead > tr > td, .table > thead > tr > th {padding: 8px;vertical-align: top;border: 1px solid #ddd;text-align: left;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><h3 class="penal">表单区域</h3><div><div><label>姓名</label><input type="text" v-model="user"></div><div><label>年龄</label><input type="text" v-model="age"><input type="button" value="新建" @click="addUser"></div></div><h3 class="penal">数据列表</h3><table class="table"><thead><tr><td>姓名</td><td>年龄</td></tr></thead><tbody><tr v-for="item in dataList"><td>{{item.name}}</td><td>{{item.age}}</td></tr></tbody></table></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {user: "",age: "",dataList: [{name: "武沛齐", age: 19},{name: "alex", age: 89},]},methods: {addUser: function () {let row = {name: this.user, age: this.age};this.dataList.push(row);this.user = "";this.age = "";}}})</script></body></html>
- 删除数据
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><style>.penal {border: 1px solid #dddddd;margin: 20px 0 0 0;padding: 10px;border-bottom: 0;background-color: #d9d9d9;}.table {width: 100%;border-collapse: collapse;border-spacing: 0;}.table > tbody > tr > td, .table > tbody > tr > th, .table > tfoot > tr > td, .table > tfoot > tr > th, .table > thead > tr > td, .table > thead > tr > th {padding: 8px;vertical-align: top;border: 1px solid #ddd;text-align: left;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><h3 class="penal">表单区域</h3><div><div><label>姓名</label><input type="text" v-model="user"></div><div><label>年龄</label><input type="text" v-model="age"><input type="button" value="新建" @click="addUser"></div></div><h3 class="penal">数据列表</h3><table class="table"><thead><tr><td>姓名</td><td>年龄</td><td>操作</td></tr></thead><tbody><tr v-for="(item,idx) in dataList"><td>{{item.name}}</td><td>{{item.age}}</td><td>// :data-idx="idx" 会将idx的值传递给deleteRow函数<input type="button" value="删除" @click="deleteRow" :data-idx="idx"/></td></tr></tbody></table></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {user: "",age: "",dataList: [{name: "武沛齐", age: 19},{name: "alex", age: 89},]},methods: {addUser: function () {let row = {name: this.user, age: this.age};this.dataList.push(row);this.user = "";this.age = "";},deleteRow: function (event) {// event当前事件的触发对象是默认传递进来的// event.target.dataset默认格式// 根据索引删除dataList中的值let idx = event.target.dataset.idx;// 1是删除1个this.dataList.splice(idx, 1);}}})</script></body></html>
- 编辑修改数据
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><style>.penal {border: 1px solid #dddddd;margin: 20px 0 0 0;padding: 10px;border-bottom: 0;background-color: #d9d9d9;}.table {width: 100%;border-collapse: collapse;border-spacing: 0;}.table > tbody > tr > td, .table > tbody > tr > th, .table > tfoot > tr > td, .table > tfoot > tr > th, .table > thead > tr > td, .table > thead > tr > th {padding: 8px;vertical-align: top;border: 1px solid #ddd;text-align: left;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><h3 class="penal">表单区域</h3><div><div><label>姓名</label><input type="text" v-model="user"></div><div><label>年龄</label><input type="text" v-model="age"><input type="button" :value="title" @click="addUser"></div></div><h3 class="penal">数据列表</h3><table class="table"><thead><tr><td>姓名</td><td>年龄</td><td>操作</td></tr></thead><tbody><tr v-for="(item,idx) in dataList"><td>{{item.name}}</td><td>{{item.age}}</td><td><input type="button" value="删除" @click="deleteRow" :data-idx="idx"/><input type="button" value="编辑" @click="editRow" :data-idx="idx"/></td></tr></tbody></table></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {editIndex: undefined,title: "新建",user: "",age: "",dataList: [{name: "武沛齐", age: 19},{name: "alex", age: 89},]},methods: {addUser: function () {if (this.editIndex) {// 修改this.dataList[this.editIndex].name = this.user;this.dataList[this.editIndex].age = this.age;} else {let row = {name: this.user, age: this.age};this.dataList.push(row);}this.user = "";this.age = "";this.editIndex = undefined;this.title = "新建";},deleteRow: function (event) {// 根据索引删除dataList中的值let idx = event.target.dataset.idx;this.dataList.splice(idx, 1);},editRow: function (event) {let idx = event.target.dataset.idx;// let name = this.dataList[idx].name;// let age = this.dataList[idx].age;// let {id, name} = {id: 1, name: "武沛齐"};// console.log(id, name);let {name, age} = this.dataList[idx];this.user = name;this.age = age;this.title = "编辑";this.editIndex = idx;}}})</script></body></html>
v-if指令
条件指令 用来做判断 条件不成立标签都不会渲染到页面
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app">//判断 isLogin 的值是否为True 是的话执行{{user}}<a v-if="isLogin">{{user}}</a>//v-else 就是else<a v-else>登录</a></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {isLogin: false,user: "武沛齐"}})</script></body></html>
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><h1 v-if="v1">阿里无人区</h1><h1 v-if="v2">去西藏</h1><h1 v-else>去新疆</h1><div v-if="v3 === '北京'"><h1>天安门</h1></div><div v-else-if="v3 === '新疆'"><h1>乌鲁木齐</h1></div><div v-else-if="v3 ==='西藏'"><h1>拉萨</h1></div><div v-else><h1>大理</h1></div></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {v1: true,v2: true,v3: "新疆"}})</script></body></html>
v-show
根据条件显示或隐藏(标签都会渲染到页面)。
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><h1 v-show="v1">可可西里</h1><h1 v-show="!v1">罗布泊</h1></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {v1: false,}})</script></body></html>
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><style>label {width: 60px;display: inline-block;text-align: right;margin-right: 8px;}</style></head><body><div id="app">// isSms=false 将isSms对应的值修改为false<input type="button" value="密码登录" @click="isSms=false"/><input type="button" value="短信登录" @click="isSms=true"/><div v-show="isSms"><p><label>手机号</label><input type="text" placeholder="手机号"></p><p><label>验证码</label><input type="text" placeholder="验证码"></p></div><div v-show="!isSms"><p><label>用户名</label><input type="text" placeholder="用户名"></p><p><label>密码</label><input type="password" placeholder="密码"></p></div></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {isSms: false,}})</script></body></html>
登录案例
在编写案例之前,现在来学下axios,他是一个HTTP 库,可以发送Http请求。
// 引入 axios库<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>// axios 里面放一个对象 params是url中携带的参数,data是请求体中携带的参数<script>axios({method: "post",url: 'https://api.luf...ord/login/',params: {v1:123,v2:456},data: {name:"武沛齐",pwd:"123"},headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then(function (res) {console.log(res.data);}).catch(function (error) {console.log(error);})</script>.then是发送请求后执行的回调函数res是请求返回的内容,catch回调函数是捕获错误信息的
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script><script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script><style>label {width: 60px;display: inline-block;text-align: right;margin-right: 8px;}</style></head><body><div id="app"><input type="button" value="密码登录" @click="isSms=false"/><input type="button" value="短信登录" @click="isSms=true"/><div v-show="isSms"><p><label>手机号</label><input type="text" placeholder="手机号" v-model="sms.mobile"></p><p><label>验证码</label><input type="text" placeholder="验证码" v-model="sms.code"></p></div><div v-show="!isSms"><p><label>用户名</label><input type="text" placeholder="用户名" v-model="info.username"></p><p><label>密码</label><input type="password" placeholder="密码" v-model="info.password"></p></div><input type="button" value="登 录" @click="loginForm"/></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {isSms: false,info: {username: "",password: "",},sms: {mobile: "",code: ""}},methods: {loginForm: function () {// 1.获取用户输入的值let dataDict = this.isSms ? this.sms : this.info;let url;if (this.isSms) {url = "https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/auth/mobile/login/?loginWay=mobile";} else {url = "https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/auth/password/login/?loginWay=password";}// 2.想某个地址发送网络请求 axios// https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/auth/password/login/?loginWay=password// {"username":"alex123","password":"999"}// https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/auth/mobile/login/?loginWay=mobile// {"mobile":"18630087660","code":"123123"}axios({method: "post",url: url,data: dataDict,headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then(function (res) {if (res.data.code === -1) {alert(res.data.msg);return;}// 登录成功后跳转window.location.href = "https://www.luffycity.com"}).catch(function (error) {alert("请求异常,请重新操作。")})}}})</script></body></html>
组件化开发
在开发过程中,我们可以将页面中 某一部分 的功能编写成一个组件,然后再在页面上进行引用。
- 有利于划分功能模块的开发(HTML、CSS、JavaScript等相关代码都集成到组件中)。
- 有利于重用
局部组件
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><h1>=======当前页面=======</h1>{{name}}<h1>=======引入子组件=======</h1><Demo></Demo> //使用组件<Demo></Demo> //组件可以复用<Bb></Bb><Bb></Bb><hr/><Bb></Bb></div><script>//创建子组件 template子组件模板 就是 html页面 {{msg}}是 data定义的函数的返回值一定是返回值才能在 模板中引用const Demo = {data:function() {return {msg: '哈哈哈哈哈'}},template: `<div><h1>{{msg}}</h1><input type="text" v-model="msg"/><input type="button" @click="showMeg" value="点我呀"></div>`,methods: {showMeg: function () {alert(this.msg);}}}//创建子组件const Bili = {// 组件中的data是一个方法,并返回值(与Vue对象创建不同)data:function() {return {dataList: [{"id": 1, "title": "路飞学城倒闭了"},{"id": 2, "title": "老板和保洁阿姨跑了"},]}},template: `<div><h1>数据列表</h1><table border="1"><thead><tr><th>ID</th><th>标题</th></tr></thead><tbody><tr v-for="item in dataList"><td>{{item.id}}</td><td>{{item.title}}</td></tr></tbody></table></div>`}var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {name: "武沛齐",},<!--components放的是待指组件的名字,想当于挂载组件-->components: {Demo,Bb: Bili},methods: {}})</script></body></html>
全局组件
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><h1>=======当前页面=======</h1>{{name}}<h1>=======引入子组件=======</h1><Demo></Demo><Demo></Demo><Bili></Bili><Bili></Bili></div><script>//创建子组件 Demo 组件的名字Vue.component('Demo', {data: function () {return {msg: '哈哈哈哈哈'}},template: `<div><h1>{{msg}}</h1><input type="text" v-model="msg"/><input type="button" @click="showMeg" value="点我呀"></div>`,methods: {showMeg: function () {alert(this.msg);}}});//创建子组件Vue.component('Bili', {// 组件中的data是一个方法,并返回值(与Vue对象创建不同)data: function () {return {dataList: [{"id": 1, "title": "路飞学城倒闭了"},{"id": 2, "title": "老板和保洁阿姨跑了"},]}},template: `<div><h1>数据列表</h1><table border="1"><thead><tr><th>ID</th><th>标题</th></tr></thead><tbody><tr v-for="item in dataList"><td>{{item.id}}</td><td>{{item.title}}</td></tr></tbody></table></div>`});var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {name: "武沛齐",},methods: {}})</script></body></html>
vue-router 组件
vue + vue-router组件可以实现 SPA(single Page Application),即:单页面应用。
单页面应用,简而言之就是项目只有一个页面。
一个页面如何呈现多种界面的效果呢?
- 基于vue开发多个组件,例如:活动组件、课程组件、咨询组件
- 在页面上 vue-router 用来管理这些组件,用户点击某个按钮,就显示特定的组件(数据基于Ajax获取)。
官方地址:https://router.vuejs.org/zh/
下载地址:https://unpkg.com/vue-router@4
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><!-- vue-router.js 依赖 vue.js --><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script></head><body></body></html>
注意:后期用脚手架开发时,可以直接使用npm下载和引用。
快速上手
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.container {width: 980px;margin: 0 auto;}.menu {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.menu a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}</style><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div class="menu"><div class="container">//router-link 相当于a标签 定义菜单一般使用router-link<router-link to="/">Logo</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/course">课程</router-link><router-link to="/news">资讯</router-link></div></div><div class="container">//router-view 里面放的是加载的组件<router-view></router-view></div></div><script>//定义了三个组件const Home = {template: '<div>首页内容...</div>'}const Course = {template: '<div>课程内容..</div>'}const News = {template: '<div>资讯内容..</div>'}//定义VueRouter 管理三个组件 访问'/'路径 加载Home组件const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/',component: Home},{path: '/home', component: Home},{path: '/course', component: Course},{path: '/news', component: News}],})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {name: "武沛齐",},methods: {},router: router //router 添加到router})</script></body></html>
案例 第一版
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.container {width: 1100px;margin: 0 auto;}.menu {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.menu a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}.course-list {display: flex;flex-wrap: wrap;justify-content: flex-start;}.course-list .item {width: 248px;padding: 10px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;margin-right: 5px;margin-top: 10px;}.course-list .item img {width: 100%;height: 120px;}</style>// 引入环境<script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script><script src="axios.min.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div class="menu"><div class="container"><router-link to="/">路飞学城</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/course">课程</router-link><router-link to="/news">资讯</router-link></div></div><div class="container"><router-view></router-view></div></div><script>const Home = {data: function () {return {title: "欢迎使用路飞学城"}},template: `<h2>{{title}}</h2>`}const Course = {data: function () {return {courseList: []}},created: function () {/* 组件创建完成之后自动触发【此时组件的对象已创建,但还未将页面相关的DOM创建并显示在页面上】- 可以去操作组件对象,例如:this.courseList = [11,22,33]- 不可以去操作DOM,例如:document.getElementById (未创建)*/axios({method: "get",url: 'https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/course/actual/?limit=5&offset=0',headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then((res) => {this.courseList = res.data.data.result;})},mounted: function () {/* DOM对象已在页面上生成,此时就可以 */},template: `<div class="course-list"><div class="item" v-for="item in courseList"><img :src="item.cover" alt=""><a>{{item.name}}</a></div></div>`}const News = {data: function () {return {dataList: []}},created: function () {/* 组件创建完成之后自动触发【此时组件的对象已创建,但还未将页面先关的DOM创建并显示在页面上】- 可以去操作组件对象,例如:this.courseList = [11,22,33]- 不可以去操作DOM,例如:document.getElementById (未创建)*/axios({method: "get",url: 'https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/course/actual/?limit=5&offset=10',headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then((res) => {this.dataList = res.data.data.result;})},template: `<ul><li v-for="item in dataList">{{item.name}}</li></ul>`}const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/', component: Home},{path: '/home', component: Home},{path: '/course', component: Course},{path: '/news', component: News}],//mode: 'history'})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {},router: router})</script></body></html>
路由和传值
当某个组件可以根据某些参数值的不同,展示不同效果时,需要用到动态路由。
例如:访问网站看到课程列表,点击某个课程,就可以跳转到课程详细页面(根据课程ID不同展示不同数据)。
如何来设置动态路由呢?
- 定义路由
const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{ path: '/', component: Home}, //component是组件的名字{ path: '/course', component: Course, name: "Course"} // name待指这个路由{ path: '/detail/:id', component: Detail, name: "Detail"} //:id 表示/detail/可以跟参数],})
- HTML展示
<div><router-link to="/">首页</router-link><router-link to="/course">课程</router-link><router-link to="/detail/123">课程</router-link><router-link :to="{path:'/course'}">课程</router-link><router-link :to="{path:'/course?size=19&page=2'}">课程</router-link><router-link :to="{path:'/course', query:{size:19,page:2}">课程</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Course'}">课程</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Course', query:{size:19,page:2} }">课程</router-link>//query就是在url中传参,?size-123&<router-link :to="{path:'/detail/22',query:{size:123}}">Linux</router-link>//params:{id:3}是指给/detail/:id中的:id传参数<router-link :to="{name:'Detail',params:{id:3}, query:{size:29}}">网络安全</router-link></div><h1>内容区域</h1><router-view></router-view>
- 组件获取URL传值和GET参数
const Detail = {data: function () {return {title: "详细页面",paramDict: null,queryDict: null,}},created: function () {this.paramDict = this.$route.params; //this.$route.params读的是'/detail/:id'这种格式传的值this.queryDict = this.$route.query;//this.$route.query读的是url中传过来的值?后的值// 发送axios请求},template: `<div><h2>{{title}}</h2><div>当前请求的数据 {{paramDict}} {{queryDict}}</div></div>`}
案例:路飞学城(第2版)
点击课程,查看课程详细页面。
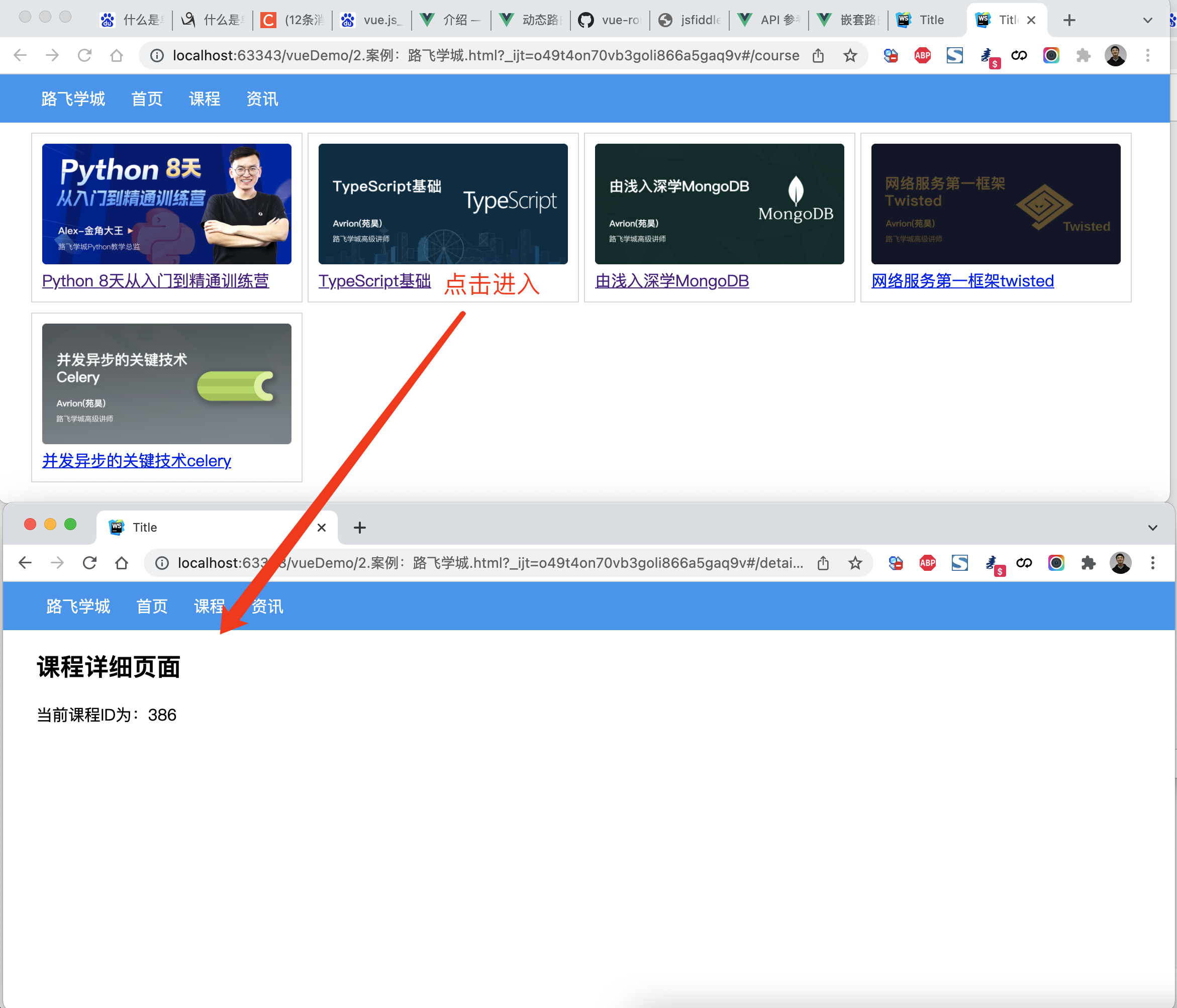
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.container {width: 1100px;margin: 0 auto;}.menu {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.menu a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}.course-list {display: flex;flex-wrap: wrap;justify-content: flex-start;}.course-list .item {width: 248px;padding: 10px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;margin-right: 5px;margin-top: 10px;}.course-list .item img {width: 100%;height: 120px;}</style><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script><script src="axios.min.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div class="menu"><div class="container"><router-link to="/">路飞学城</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/course">课程</router-link><router-link to="/news">资讯</router-link></div></div><div class="container"><router-view></router-view></div></div><script>const Home = {data: function () {return {title: "欢迎使用路飞学城"}},template: `<h2>{{title}}</h2>`}const Course = {data: function () {return {courseList: []}},created: function () {/* 组件创建完成之后自动触发【此时组件的对象已创建,但还未将页面先关的DOM创建并显示在页面上】- 可以去操作组件对象,例如:this.courseList = [11,22,33]- 不可以去操作DOM,例如:document.getElementById (未创建)*/axios({method: "get",url: 'https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/course/actual/?limit=5&offset=0',headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then((res) => {this.courseList = res.data.data.result;})},mounted: function () {/* DOM对象已在页面上生成,此时就可以 */},template: `<div class="course-list"><div class="item" v-for="item in courseList"><router-link :to="{name:'Detail',params:{id:item.id}}"><img :src="item.cover" alt=""><a>{{item.name}}</a></router-link></div></div>`}const News = {data: function () {return {dataList: []}},created: function () {/* 组件创建完成之后自动触发【此时组件的对象已创建,但还未将页面先关的DOM创建并显示在页面上】- 可以去操作组件对象,例如:this.courseList = [11,22,33]- 不可以去操作DOM,例如:document.getElementById (未创建)*/axios({method: "get",url: 'https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/course/actual/?limit=5&offset=10',headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then((res) => {this.dataList = res.data.data.result;})},template: `<ul><li v-for="item in dataList">{{item.name}}</li></ul>`}const Detail = {data: function () {return {title: "详细页面",courseId: null}},created: function () {this.courseId = this.$route.params.id;// 此处可以根据课程ID,发送ajax请求获取课程详细信息},template: `<div><h2>课程详细页面</h2><div>当前课程ID为:{{courseId}}</div></div>`}const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/', component: Home},{path: '/home', component: Home},{path: '/course', component: Course},{path: '/news', component: News},{path: '/detail/:id', component: Detail, name: 'Detail'}],//mode: 'history'})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {},router: router})</script></body></html>
页面无法刷新问题
上述编写案例是没有问题,但如果在开发中会涉及到 同一个路由的跳转(默认不会重新加载页面,数据无法获取)。
例如:在详细页面再出现一个课程推荐,即:在课程详细,点击推荐的课程后跳转到课程详细页面(课程ID不同),此时课程的ID还是原来加载的ID,无法获取推荐课程的ID。
如何解决呢?
在课程详细的组件中设置watch属性即可,watch会监测$route 值,一旦发生变化,就执行相应的函数。
const Detail = {data: function () {return {title: "详细页面",courseId: null,}},created: function () {this.courseId = this.$route.params.id;this.getCourseDetail();},watch: {//监听路由里面的值发生改变就执行定义的这个函数 to表示要跳转到的那个路由相关的值,from表示原来页面的值$route:function(to, from) {this.courseId = to.params.id;// this.getCourseDetail();}},methods: {getCourseDetail: function () {// 根据this.courseId获取课程详细信息}},template: `<div><h2>{{title}}</h2><div>当前请求的数据 {{paramDict}} {{queryDict}}</div></div>`}
案例:路飞学城(第3版)
在详细页面实现推荐课程
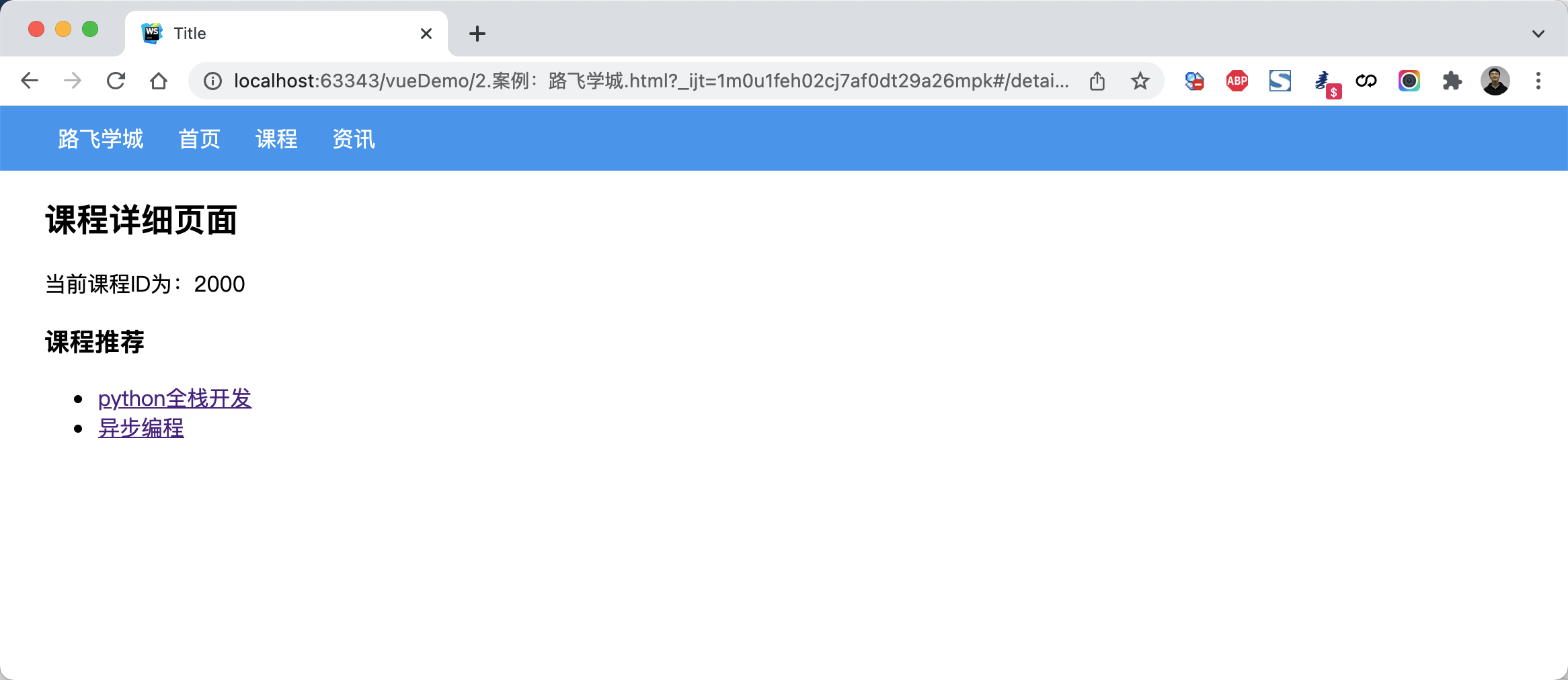
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.container {width: 1100px;margin: 0 auto;}.menu {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.menu a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}.course-list {display: flex;flex-wrap: wrap;justify-content: flex-start;}.course-list .item {width: 248px;padding: 10px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;margin-right: 5px;margin-top: 10px;}.course-list .item img {width: 100%;height: 120px;}</style><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script><script src="axios.min.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div class="menu"><div class="container"><router-link to="/">路飞学城</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/course">课程</router-link><router-link to="/news">资讯</router-link></div></div><div class="container"><router-view></router-view></div></div><script>const Home = {data: function () {return {title: "欢迎使用路飞学城"}},template: `<h2>{{title}}</h2>`}const Course = {data: function () {return {courseList: []}},created: function () {/* 组件创建完成之后自动触发【此时组件的对象已创建,但还未将页面先关的DOM创建并显示在页面上】- 可以去操作组件对象,例如:this.courseList = [11,22,33]- 不可以去操作DOM,例如:document.getElementById (未创建)*/axios({method: "get",url: 'https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/course/actual/?limit=5&offset=0',headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then((res) => {this.courseList = res.data.data.result;})},mounted: function () {/* DOM对象已在页面上生成,此时就可以 */},template: `<div class="course-list"><div class="item" v-for="item in courseList"><router-link :to="{name:'Detail',params:{id:item.id}}"><img :src="item.cover" alt=""><a>{{item.name}}</a></router-link></div></div>`}const News = {data: function () {return {dataList: []}},created: function () {/* 组件创建完成之后自动触发【此时组件的对象已创建,但还未将页面先关的DOM创建并显示在页面上】- 可以去操作组件对象,例如:this.courseList = [11,22,33]- 不可以去操作DOM,例如:document.getElementById (未创建)*/axios({method: "get",url: 'https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/course/actual/?limit=5&offset=10',headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then((res) => {this.dataList = res.data.data.result;})},template: `<ul><li v-for="item in dataList">{{item.name}}</li></ul>`}const Detail = {data: function () {return {title: "详细页面",courseId: null,hotCourseList: [{id: 1000, title: "python全栈开发"},{id: 2000, title: "异步编程"},],}},created: function () {this.courseId = this.$route.params.id;// 此处可以根据课程ID,发送ajax请求获取课程详细信息this.getCourseDetail();},watch: {$route: function (to, from) {this.courseId = to.params.id;this.getCourseDetail();}},methods: {getCourseDetail: function () {// 根据this.courseId获取课程详细信息}},template: `<div><h2>课程详细页面</h2><div>当前课程ID为:{{courseId}}</div><h3>课程推荐</h3><ul><li v-for="item in hotCourseList"><router-link :to="{name:'Detail', params:{id:item.id}}">{{item.title}}</router-link></li></ul></div>`}const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/', component: Home},{path: '/home', component: Home},{path: '/course', component: Course},{path: '/news', component: News},{path: '/detail:id', component: Detail, name: 'Detail'}],//mode: 'history'})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {},router: router})</script></body></html>
路由嵌套
const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/pins/',component: Pins,// children是子路由children: [{// 当 /pins/hot 匹配成功,// Hot组件 会被渲染在 Pins 的 <router-view> 中path: 'hot',component: Hot},{// 当 /pins/following 匹配成功,// Following组件 会被渲染在 Pins 的 <router-view> 中path: 'following',component: Following}]}]})
案例:路飞学城(第4版)
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.container {width: 1100px;margin: 0 auto;}.menu {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.menu a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}.course-list {display: flex;flex-wrap: wrap;justify-content: flex-start;}.course-list .item {width: 248px;padding: 10px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;margin-right: 5px;margin-top: 10px;}.course-list .item img {width: 100%;height: 120px;}</style><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script><script src="axios.min.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div class="menu"><div class="container"><router-link to="/">路飞学城</router-link><router-link to="/pins">沸点</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/course">课程</router-link><router-link to="/news">资讯</router-link></div></div><div class="container"><router-view></router-view></div></div><script>const Home = {data: function () {return {title: "欢迎使用路飞学城"}},template: `<h2>{{title}}</h2>`}const Course = {data: function () {return {courseList: []}},created: function () {/* 组件创建完成之后自动触发【此时组件的对象已创建,但还未将页面先关的DOM创建并显示在页面上】- 可以去操作组件对象,例如:this.courseList = [11,22,33]- 不可以去操作DOM,例如:document.getElementById (未创建)*/axios({method: "get",url: 'https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/course/actual/?limit=5&offset=0',headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then((res) => {this.courseList = res.data.data.result;})},mounted: function () {/* DOM对象已在页面上生成,此时就可以 */},template: `<div class="course-list"><div class="item" v-for="item in courseList"><router-link :to="{name:'Detail',params:{id:item.id}}"><img :src="item.cover" alt=""><a>{{item.name}}</a></router-link></div></div>`}const News = {data: function () {return {dataList: []}},created: function () {/* 组件创建完成之后自动触发【此时组件的对象已创建,但还未将页面先关的DOM创建并显示在页面上】- 可以去操作组件对象,例如:this.courseList = [11,22,33]- 不可以去操作DOM,例如:document.getElementById (未创建)*/axios({method: "get",url: 'https://api.luffycity.com/api/v1/course/actual/?limit=5&offset=10',headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"}}).then((res) => {this.dataList = res.data.data.result;})},template: `<ul><li v-for="item in dataList">{{item.name}}</li></ul>`}const Detail = {data: function () {return {title: "详细页面",courseId: null,hotCourseList: [{id: 1000, title: "python全栈开发"},{id: 2000, title: "异步编程"},],}},created: function () {this.courseId = this.$route.params.id;// 此处可以根据课程ID,发送ajax请求获取课程详细信息this.getCourseDetail();},watch: {$route: function (to, from) {this.courseId = to.params.id;this.getCourseDetail();}},methods: {getCourseDetail: function () {// 根据this.courseId获取课程详细信息}},template: `<div><h2>课程详细页面</h2><div>当前课程ID为:{{courseId}}</div><h3>课程推荐</h3><ul><li v-for="item in hotCourseList"><router-link :to="{name:'Detail', params:{id:item.id}}">{{item.title}}</router-link></li></ul></div>`}const Pins = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><h2>沸点专区</h2><router-link :to="{name:'Hot'}">热点</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Following'}">关注</router-link>//因为有了路由嵌套的关系 点击热点 组件是加载在这个router-view里,而不是全局的router-view<router-view></router-view></div>`};const Hot = {template: `<div><h2>Hot页面</h2></div>`};const Following = {template: `<div><h2>Following页面</h2></div>`};const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/', component: Home},{path: '/home', component: Home},{path: '/course', component: Course},{path: '/news', component: News},{path: '/detail:id', component: Detail, name: 'Detail'},{path: '/pins',component: Pins,name: 'Pins',children: [{// 当 /pins/hot 匹配成功,// Hot组件 会被渲染在 Pins 的 <router-view> 中path: 'hot',component: Hot,name:'Hot'},{// 当 /pins/following 匹配成功,// Following组件 会被渲染在 Pins 的 <router-view> 中path: 'following',component: Following,name:'Following'}]}],//mode: 'history'})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {},router: router})</script></body></html>
案例:后台分类菜单
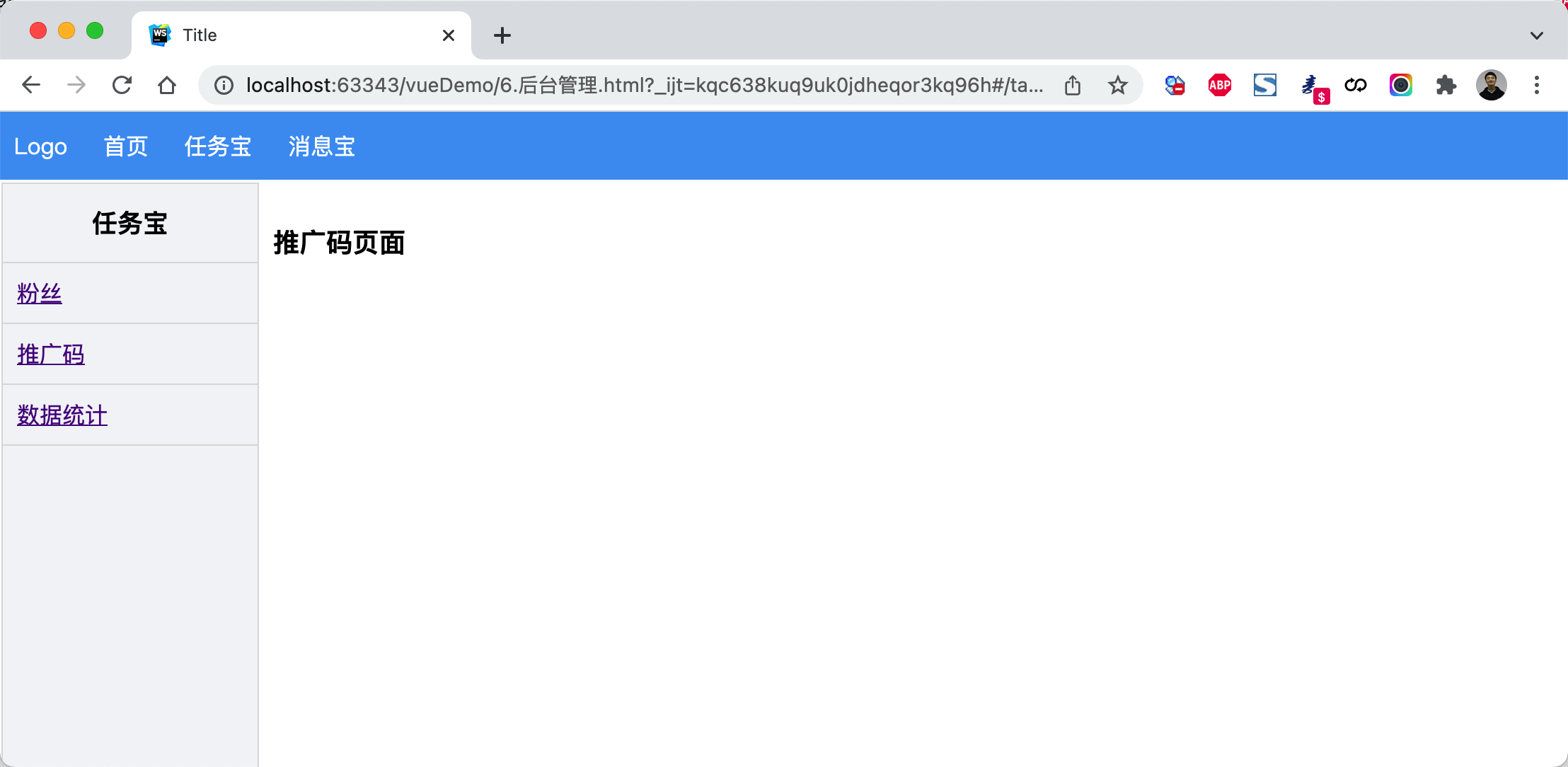
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.header {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.header a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}.body .left-menu {width: 180px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;border-bottom: 0;position: absolute;left: 1px;top: 50px;bottom: 0;overflow: auto;background-color: #f3f5f7;}.body .left-menu .head {border-bottom: 1px solid #dddddd;text-align: center;font-size: 18px;font-weight: bold;padding: 15px;}.body .left-menu a {display: block;padding: 10px;border-bottom: 1px solid #dddddd;}.body .right-body {position: absolute;left: 183px;top: 50px;right: 0;bottom: 0;overflow: auto;padding: 10px;}</style><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script><script src="axios.min.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div class="header"><router-link to="/">Logo</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/task">任务宝</router-link><router-link to="/message">消息宝</router-link></div><div class="body"><router-view></router-view></div></div><script>const Home = {data: function () {return {title: "欢迎使用xx系统"}},template: `<h2>{{title}}</h2>`};const Task = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><div class="left-menu"><div class="head">任务宝</div><router-link :to="{name:'Fans'}">粉丝</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Spread'}">推广码</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Statistics'}">数据统计</router-link></div><div class="right-body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Fans = {template: `<h3>粉丝页面</h3>`};const Spread = {template: `<h3>推广码页面</h3>`};const Statistics = {template: `<h3>数据统计页面</h3>`};const Message = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><div class="left-menu"><div class="head">消息宝</div><router-link :to="{name:'Sop'}">SOP</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Send'}">推送管理</router-link></div><div class="right-body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Sop = {template: `<h3>SOP页面</h3>`};const Send = {template: `<h3>推送管理页面</h3>`};const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/', component: Home},{path: '/home', component: Home},{path: '/task',component: Task,name: 'Task',children: [{path: '',// component: Fans,// redirect:'/task/fans'//重订向redirect: {name: 'Fans'}},{path: 'fans',component: Fans,name: 'Fans'},{path: 'spread',component: Spread,name: 'Spread'},{path: 'statistics',component: Statistics,name: 'Statistics'}]},{path: '/message',component: Message,name: 'Message',children: [{path: 'sop',component: Sop,name: 'Sop'},{path: 'send',component: Send,name: 'Send'}]}]})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {},router: router})</script></body></html>
编程式导航
除了使用 <router-link> 创建 a 标签来定义导航链接,我们还可以借助 router 的实例方法,通过编写代码来实现。
想要导航到不同的 URL,则使用 router.push 方法。这个方法会向 history 栈添加一个新的记录,所以,当用户点击浏览器后退按钮时,则回到之前的 URL。
- router.push
往history 栈添加元素 ,同时跳转过去
// 字符串router.push('home')// 对象router.push({ path: 'home' })// 命名的路由 name就是路由里的name,并携带参数router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId: '123' }}) //// 带查询参数,变成 /register?plan=privaterouter.push({ path: 'register', query: { plan: 'private' }})
- router.replace
把当前页面替换成某个页面
// 字符串router.replace('home')// 对象router.replace({ path: 'home' })// 命名的路由router.replace({ name: 'user', params: { userId: '123' }})// 带查询参数,变成 /register?plan=privaterouter.replace({ path: 'register', query: { plan: 'private' }})# 跟 router.push 很像,唯一的不同就是,它不会向 history 添加新记录,而是跟它的方法名一样 —— 替换掉当前的 history 记录。
- router.go 这个方法的参数是一个整数,意思是在 history 记录中向前或者后退多少步
// 在浏览器记录中前进一步,等同于 history.forward()router.go(1)// 后退一步记录,等同于 history.back()router.go(-1)// 前进 3 步记录router.go(3)// 如果 history 记录不够用,那就默默地失败呗router.go(-100)router.go(100)
案例:登录跳转(含顶部)
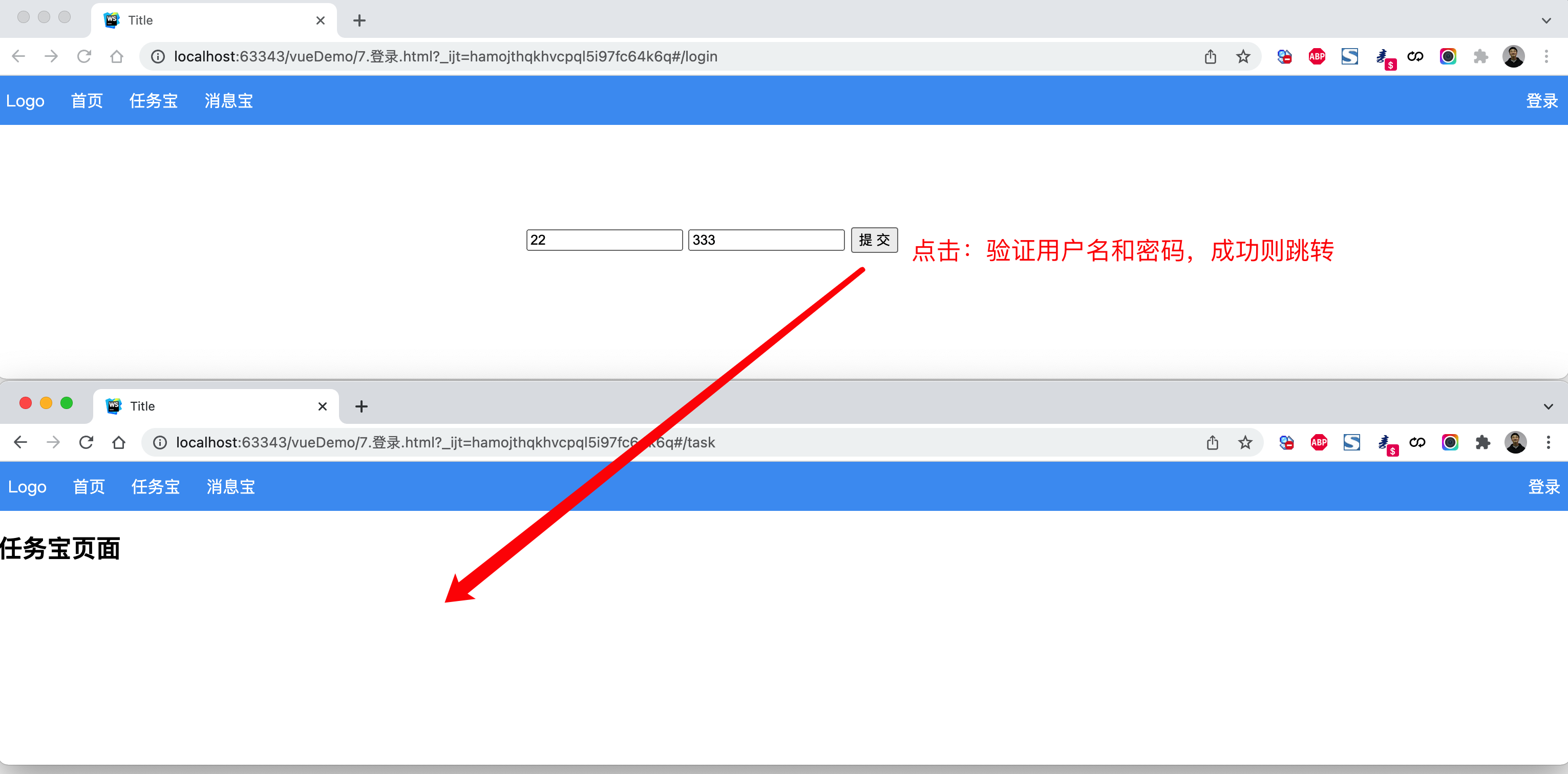
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.header {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.header a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}</style><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><div class="header"><router-link to="/">Logo</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/task">任务宝</router-link><router-link to="/message">消息宝</router-link><div style="float: right;"><router-link to="/login">登录</router-link></div></div><div class="body"><router-view></router-view></div></div><script>const Home = {data: function () {return {title: "欢迎使用xx系统"}},template: `<h2>{{title}}</h2>`};const Task = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><h2>任务宝页面</h2></div>`};const Message = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><h2>消息宝页面</h2></div>`};const Login = {data: function () {return {user: '',pwd: ''}},methods: {doLogin: function () {if (this.user.length > 0 && this.pwd.length > 0) {this.$router.push({name: 'Task'});// this.$router.replace({name: 'Task'});}}},template: `<div style="width: 500px;margin: 100px auto"><input type="text" placeholder="用户名" v-model="user"/><input type="text" placeholder="密码" v-model="pwd" /><input type="button" value="提 交" @click="doLogin" /></div>`};const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/', component: Home},{path: '/home', component: Home},{path: '/login', component: Login, name: 'Login'},{path: '/task', component: Task, name: 'Task'},{path: '/message', component: Message, name: 'Message'}]})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {},router: router})</script></body></html>
案例:登录跳转(不含顶部)
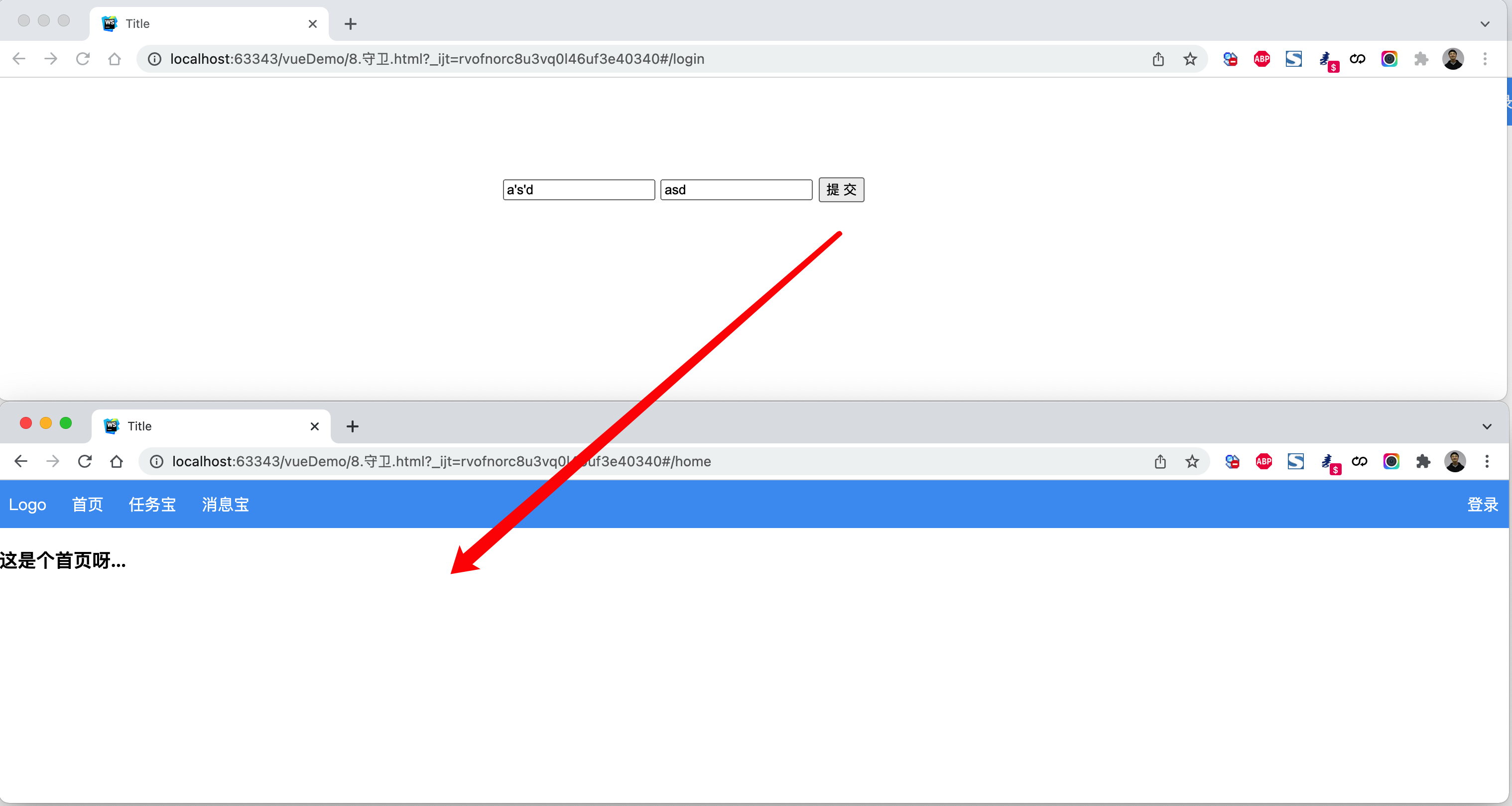
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.header {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.header a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}.body .left-menu {width: 180px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;border-bottom: 0;position: absolute;left: 1px;top: 50px;bottom: 0;overflow: auto;background-color: #f3f5f7;}.body .left-menu .head {border-bottom: 1px solid #dddddd;text-align: center;font-size: 18px;font-weight: bold;padding: 15px;}.body .left-menu a {display: block;padding: 10px;border-bottom: 1px solid #dddddd;}.body .right-body {position: absolute;left: 183px;top: 50px;right: 0;bottom: 0;overflow: auto;padding: 10px;}</style><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><router-view></router-view></div><script>const Home = {data: function () {return {title: "欢迎使用xx系统"}},template: `<div><div class="header"><router-link to="/">Logo</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Task'}">任务宝</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Message'}">消息宝</router-link><div style="float: right;"><router-link to="/login">登录</router-link></div></div><div class="body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Index = {template: '<h3>这是个首页呀...</h3>'}const Task = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><div class="left-menu"><div class="head">任务宝</div><router-link :to="{name:'Fans'}">粉丝</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Spread'}">推广码</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Statistics'}">数据统计</router-link></div><div class="right-body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Fans = {template: `<h3>粉丝页面</h3>`};const Spread = {template: `<h3>推广码页面</h3>`};const Statistics = {template: `<h3>数据统计页面</h3>`};const Message = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><div class="left-menu"><div class="head">消息宝</div><router-link :to="{name:'Sop'}">SOP</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Send'}">推送管理</router-link></div><div class="right-body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Sop = {template: `<h3>SOP页面</h3>`};const Send = {template: `<h3>推送管理页面</h3>`};const Login = {data: function () {return {user: '',pwd: ''}},methods: {doLogin: function () {if (this.user.length > 0 && this.pwd.length > 0) {this.$router.push({name: 'Index'});// this.$router.replace({name: 'Task'});}}},template: `<div style="width: 500px;margin: 100px auto"><input type="text" placeholder="用户名" v-model="user"/><input type="text" placeholder="密码" v-model="pwd" /><input type="button" value="提 交" @click="doLogin" /></div>`};const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/',// component: Home,redirect: '/login'},{path: '/login', component: Login, name: 'Login'},{path: '/home',component: Home,children: [{path: '',component: Index,name: "Index"},{path: 'task',component: Task,name: 'Task',children: [{path: 'fans',component: Fans,name: 'Fans'},{path: 'spread',component: Spread,name: 'Spread'},{path: 'statistics',component: Statistics,name: 'Statistics'}]},{path: 'message',component: Message,name: 'Message',children: [{path: 'sop',component: Sop,name: 'Sop'},{path: 'send',component: Send,name: 'Send'}]}],},]})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {},router: router})</script></body></html>
导航守卫
在基于vue-router实现访问跳转时,都会执行一个钩子。
const router = new VueRouter({ ... })# router.beforeEach 每个url执行之前router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {// to: Route: 即将要进入的目标 路由对象// from: Route: 当前导航正要离开的路由// next() 继续向后执行// next(false) 中断导航,保持当前所在的页面。// next('/') next({path:'/'}) next({name:'Login'}) 跳转到指定页面})
注意:可以基于他实现未登录跳转登录页面。
案例:登录拦截(全局)
未登录时,访问后台管理页面,自动跳转到登录页面。
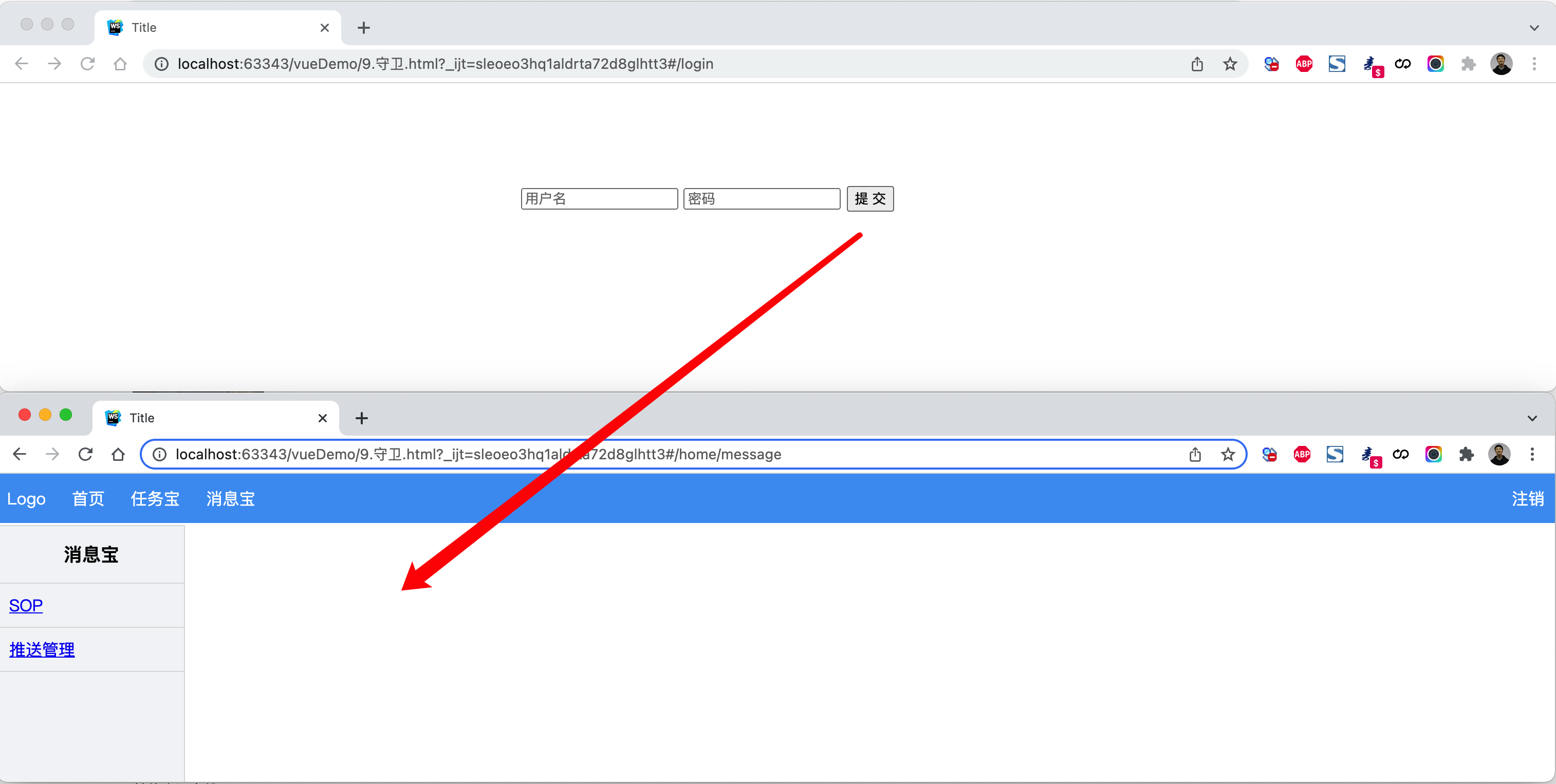
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.header {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.header a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}.body .left-menu {width: 180px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;border-bottom: 0;position: absolute;left: 1px;top: 50px;bottom: 0;overflow: auto;background-color: #f3f5f7;}.body .left-menu .head {border-bottom: 1px solid #dddddd;text-align: center;font-size: 18px;font-weight: bold;padding: 15px;}.body .left-menu a {display: block;padding: 10px;border-bottom: 1px solid #dddddd;}.body .right-body {position: absolute;left: 183px;top: 50px;right: 0;bottom: 0;overflow: auto;padding: 10px;}</style><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><router-view></router-view></div><script>const Home = {data: function () {return {title: "欢迎使用xx系统"}},methods: {doLogout: function () {sessionStorage.clear();this.$router.push({name: "Login"});}},template: `<div><div class="header"><router-link to="/">Logo</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Task'}">任务宝</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Message'}">消息宝</router-link><div style="float: right;"><a @click="doLogout">注销</a></div></div><div class="body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Index = {template: '<h3>这是个首页呀...</h3>'}const Task = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><div class="left-menu"><div class="head">任务宝</div><router-link :to="{name:'Fans'}">粉丝</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Spread'}">推广码</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Statistics'}">数据统计</router-link></div><div class="right-body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Fans = {template: `<h3>粉丝页面</h3>`};const Spread = {template: `<h3>推广码页面</h3>`};const Statistics = {template: `<h3>数据统计页面</h3>`};const Message = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><div class="left-menu"><div class="head">消息宝</div><router-link :to="{name:'Sop'}">SOP</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Send'}">推送管理</router-link></div><div class="right-body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Sop = {template: `<h3>SOP页面</h3>`};const Send = {template: `<h3>推送管理页面</h3>`};const Login = {data: function () {return {user: '',pwd: ''}},methods: {doLogin: function () {if (this.user.length > 0 && this.pwd.length > 0) {sessionStorage.setItem("isLogin", true);this.$router.push({name: 'Index'});}}},template: `<div style="width: 500px;margin: 100px auto"><input type="text" placeholder="用户名" v-model="user"/><input type="text" placeholder="密码" v-model="pwd" /><input type="button" value="提 交" @click="doLogin" /></div>`};const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/',component: Home,redirect: '/home'},{path: '/home',component: Home,name: "Home",children: [{path: '',component: Index,name: "Index"},{path: 'task',component: Task,name: 'Task',children: [{path: 'fans',component: Fans,name: 'Fans'},{path: 'spread',component: Spread,name: 'Spread'},{path: 'statistics',component: Statistics,name: 'Statistics'}]},{path: 'message',component: Message,name: 'Message',children: [{path: 'sop',component: Sop,name: 'Sop'},{path: 'send',component: Send,name: 'Send'}]}],},{path: '/login', component: Login, name: 'Login'},]})router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {// 如果已登录,则可以继续访问目标地址// sessionStorage存储到游览器上的一个值if (sessionStorage.getItem('isLogin')) {next();return;}// 未登录,访问登录页面if (to.name === "Login") {next();return;}// 未登录,跳转登录页面// next(false); 保持当前所在页面,不跳转next({name: 'Login'});})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {},router: router})</script></body></html>
案例:登录拦截(路由)
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>body {margin: 0;}.header {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.header a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}.body .left-menu {width: 180px;border: 1px solid #dddddd;border-bottom: 0;position: absolute;left: 1px;top: 50px;bottom: 0;overflow: auto;background-color: #f3f5f7;}.body .left-menu .head {border-bottom: 1px solid #dddddd;text-align: center;font-size: 18px;font-weight: bold;padding: 15px;}.body .left-menu a {display: block;padding: 10px;border-bottom: 1px solid #dddddd;}.body .right-body {position: absolute;left: 183px;top: 50px;right: 0;bottom: 0;overflow: auto;padding: 10px;}</style><script src="vue.js"></script><script src="vue-router.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><router-view></router-view></div><script>const Home = {data: function () {return {title: "欢迎使用xx系统"}},methods: {doLogout: function () {sessionStorage.clear();this.$router.push({name: "Login"});}},template: `<div><div class="header"><router-link to="/">Logo</router-link><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Task'}">任务宝</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Message'}">消息宝</router-link><div style="float: right;"><a @click="doLogout">注销</a></div></div><div class="body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Index = {template: '<h3>这是个首页呀...</h3>'}const Task = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><div class="left-menu"><div class="head">任务宝</div><router-link :to="{name:'Fans'}">粉丝</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Spread'}">推广码</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Statistics'}">数据统计</router-link></div><div class="right-body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Fans = {template: `<h3>粉丝页面</h3>`};const Spread = {template: `<h3>推广码页面</h3>`};const Statistics = {template: `<h3>数据统计页面</h3>`};const Message = {data: function () {return {}},template: `<div><div class="left-menu"><div class="head">消息宝</div><router-link :to="{name:'Sop'}">SOP</router-link><router-link :to="{name:'Send'}">推送管理</router-link></div><div class="right-body"><router-view></router-view></div></div>`};const Sop = {template: `<h3>SOP页面</h3>`};const Send = {template: `<h3>推送管理页面</h3>`};const Login = {data: function () {return {user: '',pwd: ''}},methods: {doLogin: function () {if (this.user.length > 0 && this.pwd.length > 0) {sessionStorage.setItem("isLogin", true);this.$router.push({name: 'Index'});}}},template: `<div style="width: 500px;margin: 100px auto"><input type="text" placeholder="用户名" v-model="user"/><input type="text" placeholder="密码" v-model="pwd" /><input type="button" value="提 交" @click="doLogin" /></div>`};const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/',component: Home,redirect: '/home'},{path: '/home',component: Home,name: "Home",children: [{path: '',component: Index,name: "Index"},{path: 'task',component: Task,name: 'Task',children: [{path: 'fans',component: Fans,name: 'Fans'},{path: 'spread',component: Spread,name: 'Spread'},{path: 'statistics',component: Statistics,name: 'Statistics'}]},{path: 'message',component: Message,name: 'Message',children: [{path: 'sop',component: Sop,name: 'Sop'},{path: 'send',component: Send,name: 'Send'}]}],beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {if (sessionStorage.getItem('isLogin')) {next();return;}// 未登录,跳转登录页面// next(false); 保持当前所在页面,不跳转next({name: 'Login'});}},{path: '/login', component: Login, name: 'Login'},]})var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {},methods: {},router: router})</script></body></html>
补充:
- cookie
- localStorage
setItem (key, value)getItem (key)removeItem (key)clear ()key (index)
- sessionStorage
脚手架
基于vue+vue-router单文件开发,可以完成小规模的页面的开发,但如果项目大+组件多+依赖多,开发起来就非常不方便。
此时,脚手架(vue cli - Vue Command Line Interface )是一个基于 Vue.js 进行快速开发的完整系统。
官方的说法:Vue CLI 致力于将 Vue 生态中的工具基础标准化。它确保了各种构建工具能够基于智能的默认配置即可平稳衔接,这样你可以专注在撰写应用上,而不必花好几天去纠结配置的问题。
通俗的说法:他帮助我们构内置了很多组件来帮助我们更便捷的的开发vue.js项目。
安装
- 第一步:安装node.js ``` Vue CLI 4.x+ 需要 Node.js v8.9 或更高版本 (推荐 v10 以上)。
https://nodejs.org/en/download/
<br />- 第二步:关于npm
安装上node之后,自带了npm包管理工具,类似于Python中的pip。
如果想要更新npm到最新版,可以执行命令: sudo npm install npm@latest -g
<br />- 第三步:npm淘宝源,以后基于npm安装包就会快了(相当于豆瓣的pip源)
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org
- 第四步:全局安装vue-cli
安装(最新版)
sudo npm install -g @vue/cli
安装(指定版本)
sudo npm install -g @vue/cli@4.5.14
卸载
sudo npm uninstall -g @vue/cli
<br /><a name="39da6755"></a>## 创建项目```javascriptcd /Users/wupeiqi/WebstormProjectsvue create mysite
提示:babel是一个将ES6语法转化成ES5的工具,eslint是做语法检查。
a few moments later…
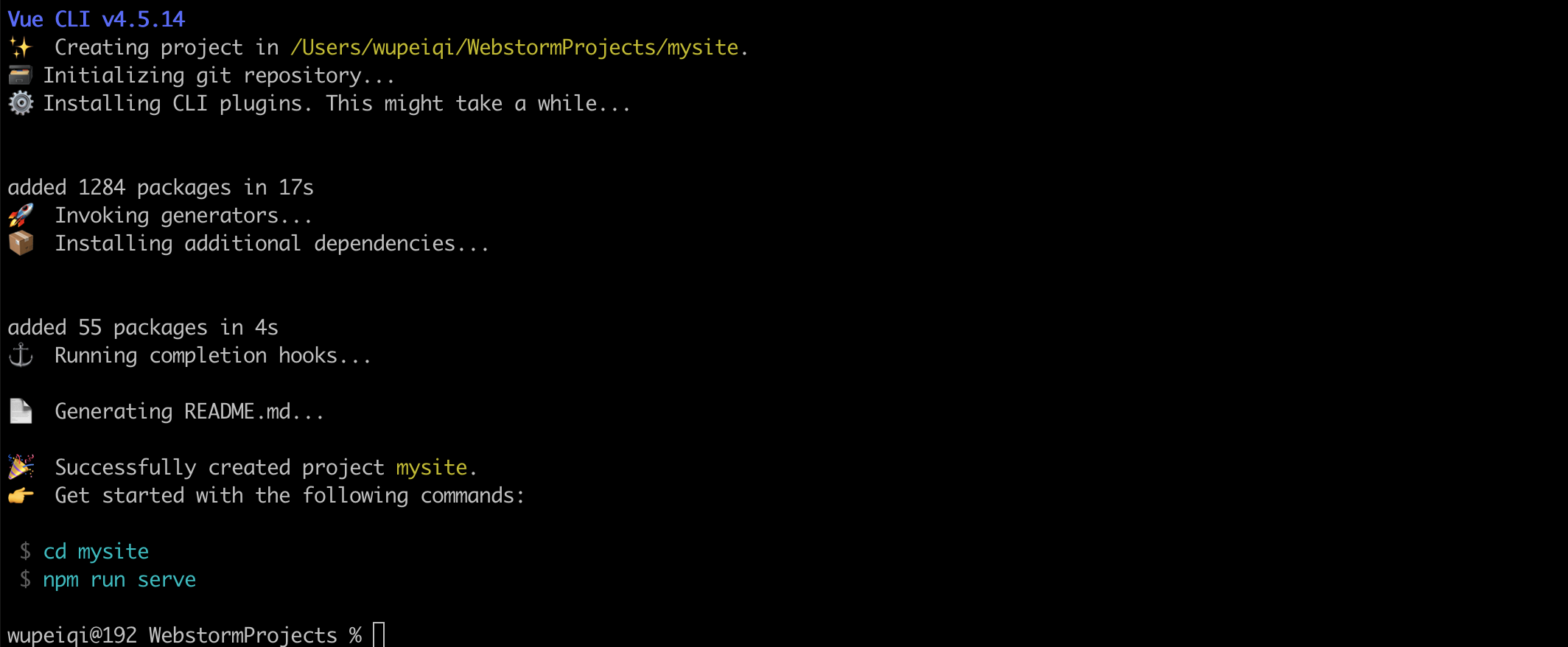
按照提示执行如下命令,脚手架就会给我们大家一个Web服务去运行编写的vue项目(便于开发测试)。
cd mysitenpm run serve

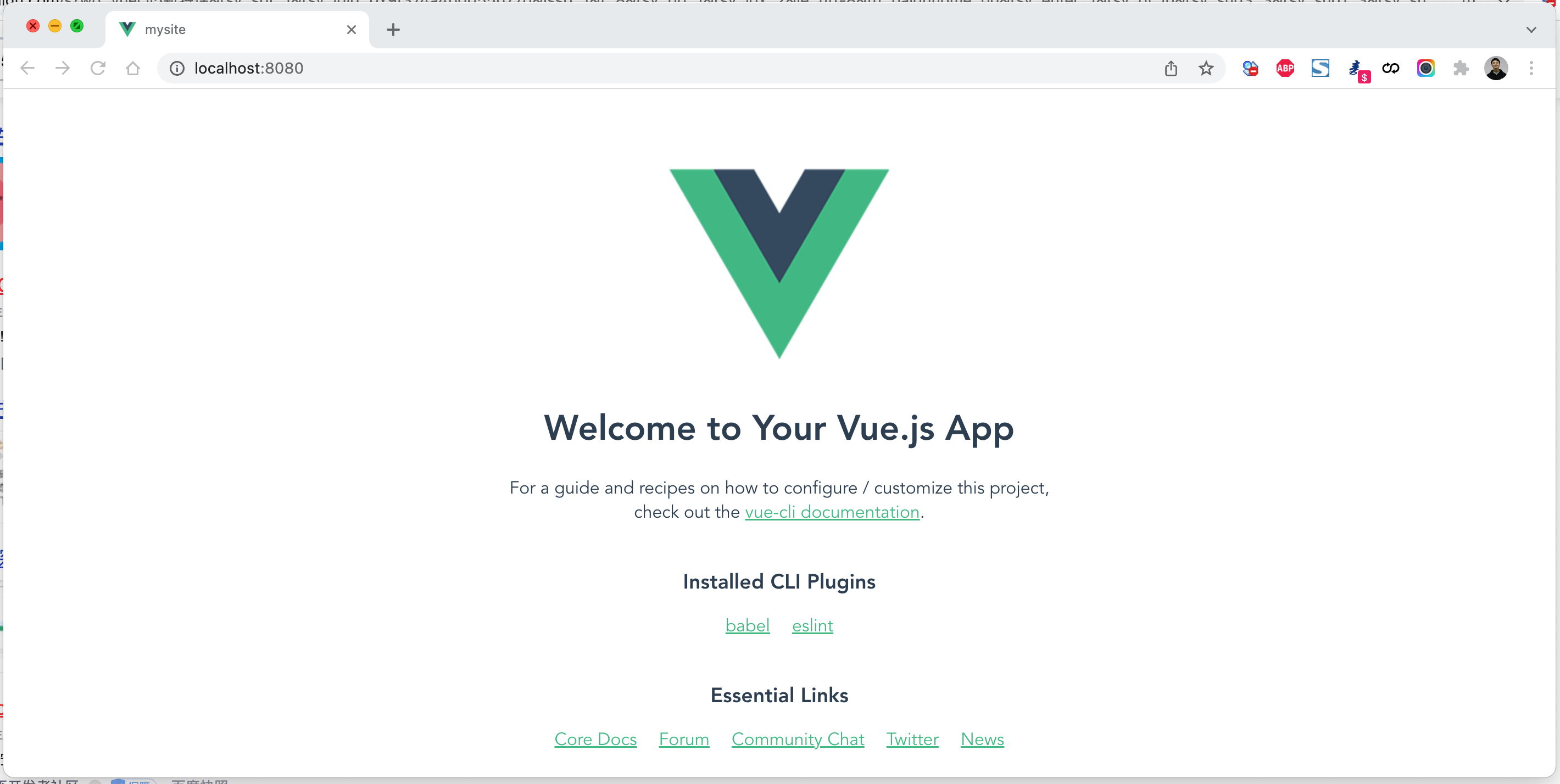
编译和部署
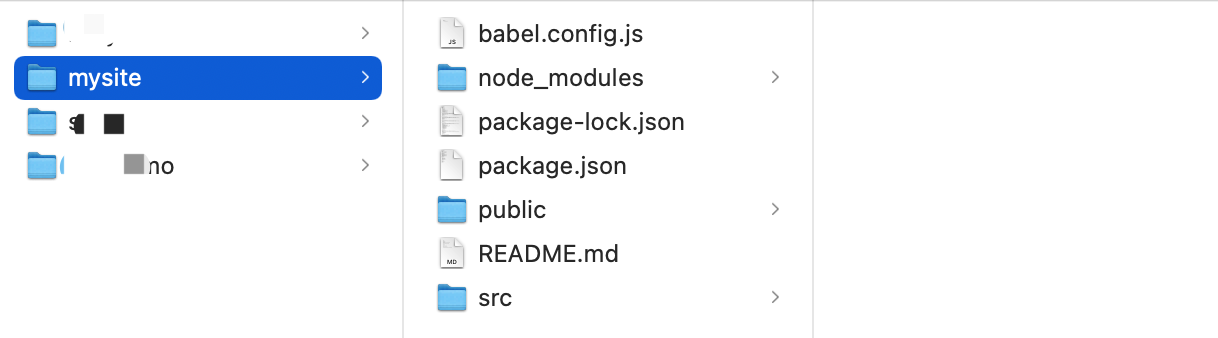
项目创建完,脚手架会默认会生成如下文件(包含项目依赖、配置文件、默认代码)。
如果以后项目开发完毕,想要进行项目部署,是不需要这些文件的,执行命令:
cd 项目目录npm run build
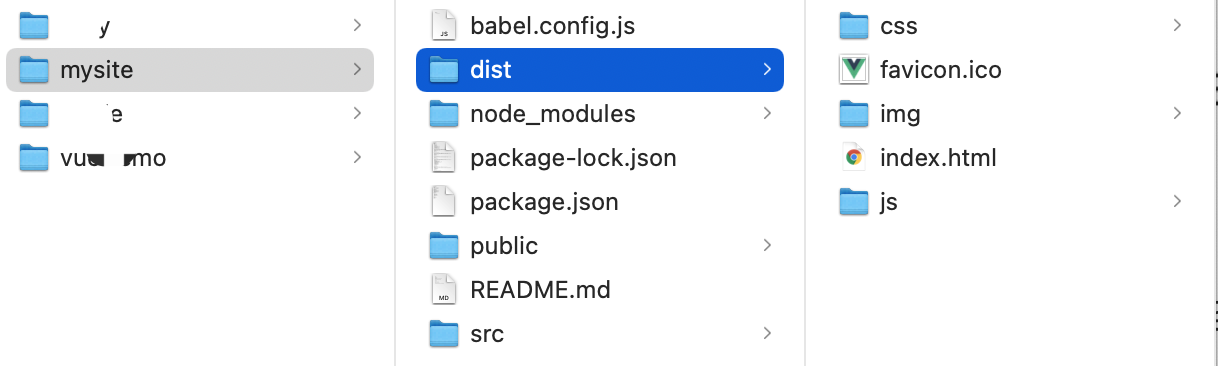
build会将项目中的依赖和代码自动编译成HTML、CSS、JavaScript代码,后续只需要将此代码上传至服务器部署即可。
目录结构
- babel.config.js babel是ES6转换ES5的组件,这是他所需的配置文件(一般不需要动)。- package.json 项目所需的包的版本信息。- package-lock.json 保存项目所需的包细节以及包的依赖等信息。- node-modules 项目安装依赖包的文件保存的地方。例如:npm install axiosaxios包会保存在此目录、信息也会写在 package.json、package-lock.json中- src- main.js 项目的启动 npm run serve ,用户访问时程序的入门。new vue()- App.vue 主组件- components 子组件- assets 静态文件(自己的静态文件,会被压缩和合并)- public 【此目录下的文件直接被复制到dist/目录下,一般放不动的数据,引入第三方】- index.html 主HTML文件(模板引擎)- favicon.icon 图标- README.md 项目说明文档
main.js
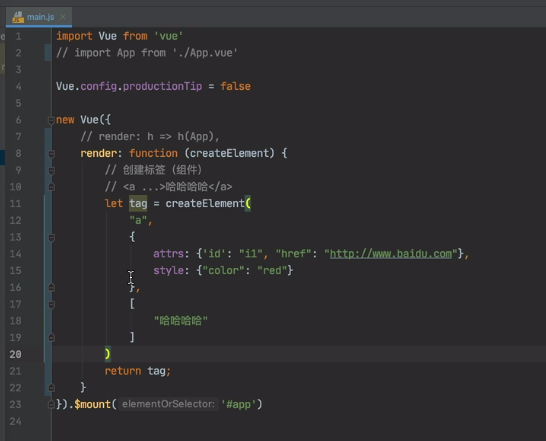
render返回什么页面就看到什么,createElement是创建标签的
App.vue
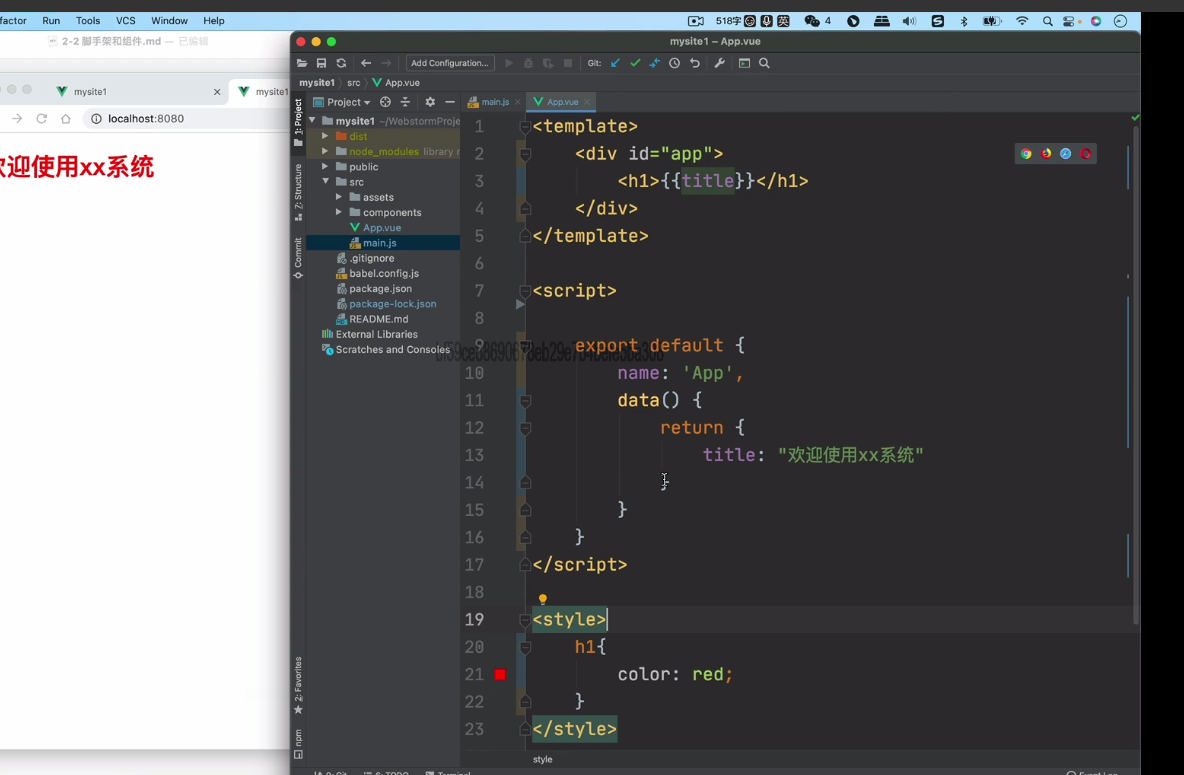
template 放html代码 script放js style放样式
cd 项目npm install #会根据package-lock.json 自动下载所需要的包
本质上,其实就是将原来的代码做了拆分来进行开发,开发完毕之后再编译整合起来。
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script></head><body><div id="app"><h1>欢迎学习Vue.js</h1><div>我叫{{name}},微信{{wechat}}</div></div><script>var app = new Vue({el: '#app',data: {name: '武沛齐',wechat: 'wupeiqi888'},methods: {clickMe: function () {this.name = "alex";this.wechat = "wupeiqi666";}}})</script></body></html>
快速上手
axios组件
安装:
cd 项目目录npm install axiosnpm install vue-axios
导入:main.js文件中引入
import Vue from 'vue'import axios from 'axios'import VueAxios from 'vue-axios'Vue.use(VueAxios, axios) #这两个组件挂载到vue中
使用:
Vue.axios.get(api).then((response) => {console.log(response.data)})this.axios.get(api).then((response) => {console.log(response.data)})this.$http.get(api).then((response) => {console.log(response.data)})
vue-router组件
安装:
cd 项目目录npm install vue-router@3
引入:
// src/router/index.jsimport Vue from 'vue'import VueRouter from 'vue-router'import Home from '../components/Home'Vue.use(VueRouter)const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/home',name: "Home",component: Home},]})export default router #导出router对象 外部就可以使用
// main.jsimport Vue from 'vue'import axios from 'axios'import VueAxios from 'vue-axios'import App from './App.vue'// 导入router文件import router from "./router"Vue.use(VueAxios, axios)Vue.config.productionTip = truenew Vue({router: router, #组件使用必须放在new Vue里render: h => h(App),}).$mount('#app')
使用:App.vue
<template><div><router-link to="/home">点我</router-link><router-view></router-view></div></template>
案例:路飞学城
基于vue-cli快速开发:路飞学城(第一版)
线上部署
- 第一步:编译
npm run build
- 第二步:将编译后的代码dist文件上传到服务器(阿里云、腾讯云)
- 第三步:安装nginx + 配置 + 启动
yum install nginx
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.confuser nginx;worker_processes auto;error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;pid /run/nginx.pid;# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic.include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;events {worker_connections 1024;}http {log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;sendfile on;tcp_nopush on;tcp_nodelay on;keepalive_timeout 65;types_hash_max_size 4096;include /etc/nginx/mime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;server {listen 80;listen [::]:80;server_name _;# 项目目录root /data/mysite;# Load configuration files for the default server block.include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;error_page 404 /404.html;location = /404.html {}error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;location = /50x.html {}}}
- 第四步:访问
vuex
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
就是将组件中需要共享的数据交给vuex来帮我们进行管理,例如:用户登录状态、加入购物车。

案例:登录
vue create vxdemonpm install vue-router@3npm install vuex@3
- main.js
import Vue from 'vue'import App from './App.vue'import router from "./router"import store from "./store"Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue({router: router,store: store, //store挂载到vuerender: h => h(App),}).$mount('#app')
- App.vue
<template><div id="app"><div class="menu"><div class="container"><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/course">课程</router-link><div style="float: right"><a v-if="this.$store.state.isLogin">{{this.$store.state.userInfo.username}}</a><router-link v-else to="/login">登录</router-link></div></div></div><div class="container"><router-view></router-view></div></div></template><script>export default {name: 'App',data() {return {}},components: {},}</script><style>body {margin: 0;}.container {width: 1100px;margin: 0 auto;}.menu {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.menu a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}</style>
- src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'Vue.use(Vuex)export default new Vuex.Store({//state存储数据的state: {isLogin: false, //是否登录userInfo: null //用户信息},//通过mutations中的函数来修改state中的值//state默认就是当前的,传过来的值在infomutations: {login: function (state, info) {state.userInfo = info;state.isLogin = true;},},actions: {}})
- router/index.js
// router/index.jsimport Vue from 'vue'import VueRouter from 'vue-router'import Home from '../components/Home'import Course from '../components/Course'import Login from '../components/Login'Vue.use(VueRouter)const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/home',name: "Home",component: Home},{path: '/course',name: "Course",component: Course},{path: '/login',name: "Login",component: Login},]})export default router
- components/Login.vue
<template><div><input type="text" v-model="info.username" placeholder="用户名"><input type="password" v-model="info.password" placeholder="密码"><input type="button" value="登录" @click="doLogin"/></div></template><script>export default {name: "Login",data() {return {info: {username: "",password: ""}}},methods: {doLogin: function () {// 1.用户登录this.$store.commit('login', this.info);// 2.登录成功修改状态this.$router.push({name: 'Home'});}}}</script><style scoped></style>
关于computed属性
在vue的组件中有一个computed属性(计算属性),监听关联的数据,如果发生变化则重新计算并显示。
<template><div><h1>主页 {{v1}} {{ v2}}</h1>//{{totalData}} 是通过computed计算出来的,就是去读取computed中的totalData属性,并执行get方法,返回值放到此处<div>总数:{{totalData}}</div><input type="button" value="点我" @click="addData"/></div></template><script>export default {name: "Home",data() {return {v1: 123,v2: 456}},computed: {totalData: {get() {let data = this.v1 + this.v2;return data + 1000;},set(value) {this.v1 = value;}}},methods: {addData() {// 给totalData设置值的时候就会执行 set方法this.totalData = 999;// this.v2 = 1000;}}}</script><style scoped></style>
所以,上述案例也可以用computed属性来实现,例如:App.vue改成:
<template><div id="app"><div class="menu"><div class="container"><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/course">课程</router-link><div style="float: right"><a v-if="userState">{{userName}}</a><router-link v-else to="/login">登录</router-link></div></div></div><div class="container"><router-view></router-view></div></div></template><script>export default {name: 'App',data() {return {}},computed: {userState: {get() {return this.$store.state.isLogin;}},userName() {return this.$store.state.userInfo.username;},},components: {},}</script><style>body {margin: 0;}.container {width: 1100px;margin: 0 auto;}.menu {height: 48px;background-color: #499ef3;line-height: 48px;}.menu a {color: white;text-decoration: none;padding: 0 10px;}</style>
案例:购物车

vue store存储commit和dispatchthis.$store.commit('toShowLoginDialog', true);this.$store.dispatch('toShowLoginDialog',false)主要区别是:dispatch:含有异步操作,例如向后台提交数据,写法: this.$store.dispatch('mutations方法名',值)commit:同步操作,写法:this.$store.commit('mutations方法名',值)
关于Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
代码示例:
const store = createStore({state: {count: 0},mutations: {increment (state) {state.count+=1;}},actions: {increment (context) {// 触发mutationscontext.commit('increment')}}})
在组件中如果要触发actions中的increment,则应该执行:
this.$store.dispatch('increment')
这就有点像脱裤子放屁,意义何在呢? 当有异步操作时,应该使用action、而不是mutation,例如:
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'Vue.use(Vuex)export default new Vuex.Store({state: {isLogin: false, //是否登录userInfo: null, //用户信息carNumber: 0,xxxxx: 10},mutations: {login: function (state, info) {state.userInfo = info;state.isLogin = true;},addCar: function (state) {state.carNumber += 1;},fetchAsync: function (state) {// ajax//setTimeout 1000毫秒以后才执行函数setTimeout(function () {state.xxxxx += 1;}, 1000);}},actions: {}})
this.$store.commit("fetchAsync");
从效果上看是没有问题的,但是通过开发者工具就会发现,监测到的state的数据不准确。
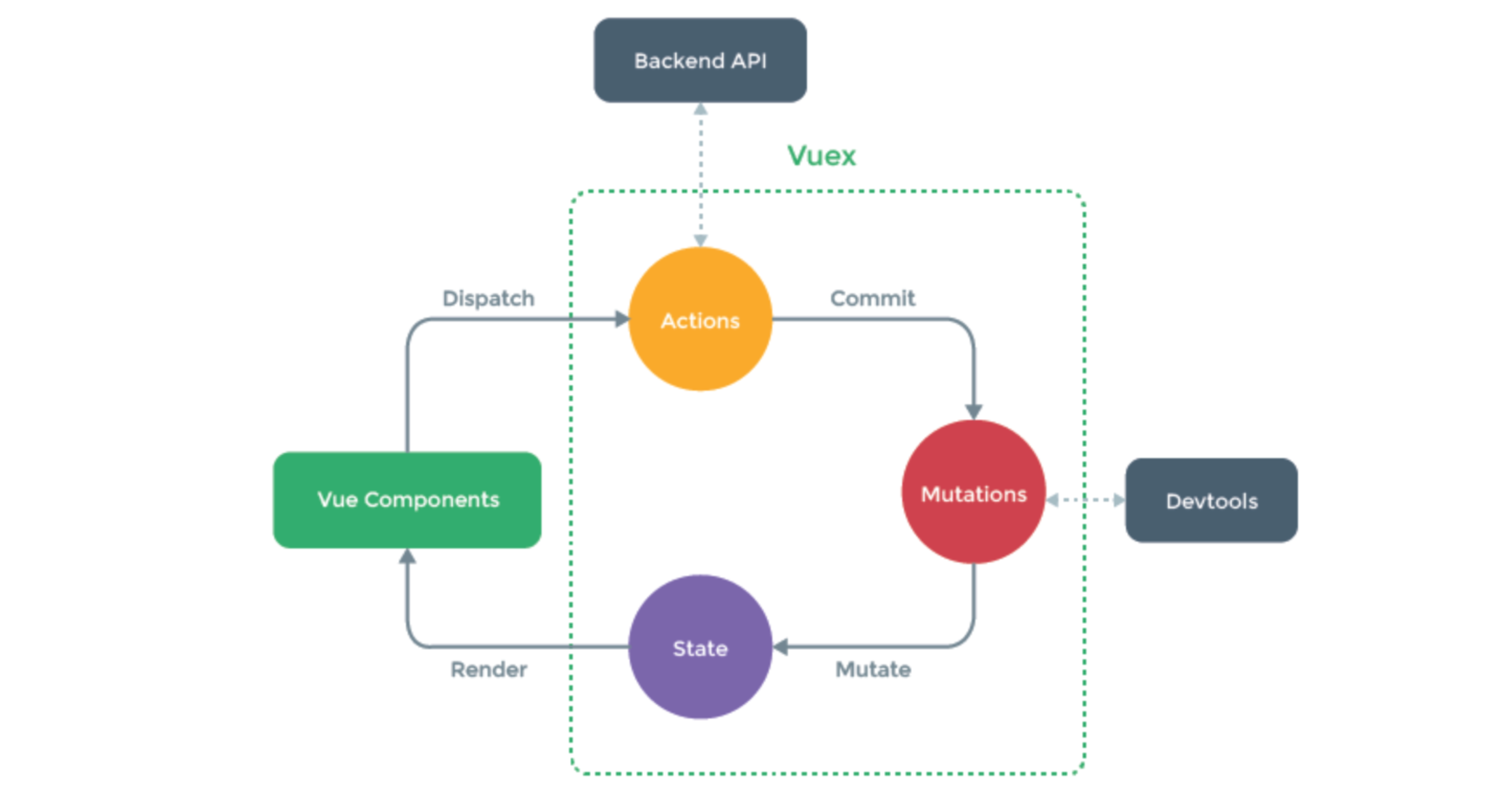
Action里面做异步操作,回调函数执行mutations,mutations里面修改state里面的值
所以,这种情况可以选择用Action。
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'Vue.use(Vuex)export default new Vuex.Store({state: {isLogin: false, //是否登录userInfo: null, //用户信息carNumber: 0,xxxxx: 10},mutations: {login: function (state, info) {state.userInfo = info;state.isLogin = true;},addCar: function (state) {state.carNumber += 1;},fetchAsync: function (state,data) {state.xxxxx += 1;console.log(data);}},actions: {fetchAsync: function (context,data) {setTimeout(function () {context.commit("fetchAsync",data);}, 1000);}}})
再触发时,调用:
this.$store.dispatch('fetchAsync',{ amount: 10})
flex布局
在CSS3中flex可以非常便捷的可以帮助我们实现对页面的布局。
- 传统的页面布局,基于div+float来实现。
- flex可以快速实现页面的布局(很方便)。
关于flex布局你必须要了解的有一下几点:
<div class="menu" 样式><div class="item" 样式>112</div><div class="item">113</div></div>
容器
flex布局
在容器元素上应用
<div class="menu"><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">113</div></div><style>.menu{border: 1px solid red;width: 500px;display: flex; // 表示flex布局}</style>
元素的方向(主轴和副轴)
<div class="menu"><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">113</div></div><style>.menu{border: 1px solid red;width: 500px;display: flex; // 表示flex布局flex-direction: row; // 主轴是横向,副轴是纵向。column}</style>
元素排列方式
justify-content,主轴上的元素的排列方式align-items,副轴上的元素的排列方式。

<div class="menu"><div class="item">11</div><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">112</div></div><style>.menu {width: 500px;border: 1px solid red;display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: flex-start; /* 主轴=横向,横向从左开始 */justify-content: flex-end; /* 主轴=横向,横向从右开始 */justify-content: space-between; /* 主轴=横向,左右定格,中间元素等分空白 */justify-content: space-around; /* 主轴=横向,所有元素等分空白 */justify-content: space-evenly; /* 主轴=横向,元素间距一样 */}.item {border: 1px solid green;padding: 5px 50px;height: 50px;width: 40px;}</style>
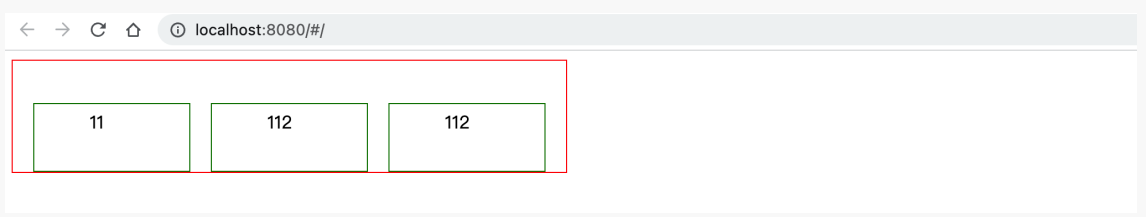
<div class="menu"><div class="item">11</div><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">112</div></div><style>.menu {width: 500px;height: 300px;border: 1px solid red;display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: flex-start; /* 主轴=横向,横向从左开始 */justify-content: flex-end; /* 主轴=横向,横向从右开始 */justify-content: space-between; /* 主轴=横向,左右定格,中间元素等分空白 */justify-content: space-around; /* 主轴=横向,所有元素等分空白 */justify-content: space-evenly; /* 主轴=横向,元素间距一样 */align-items: center; /* 副轴=纵向,元素居中*/align-items: flex-start; /* 副轴=纵向,元素顶部*/align-items: flex-end; /* 副轴=纵向,元素底部*/}.item {border: 1px solid green;padding: 5px 50px;height: 50px;width: 40px;}</style>
换行
flex-wrap: nowrap;元素超过容器,不换行flex-wrap: wrap;元素超过容器,换行
示例1:不换行
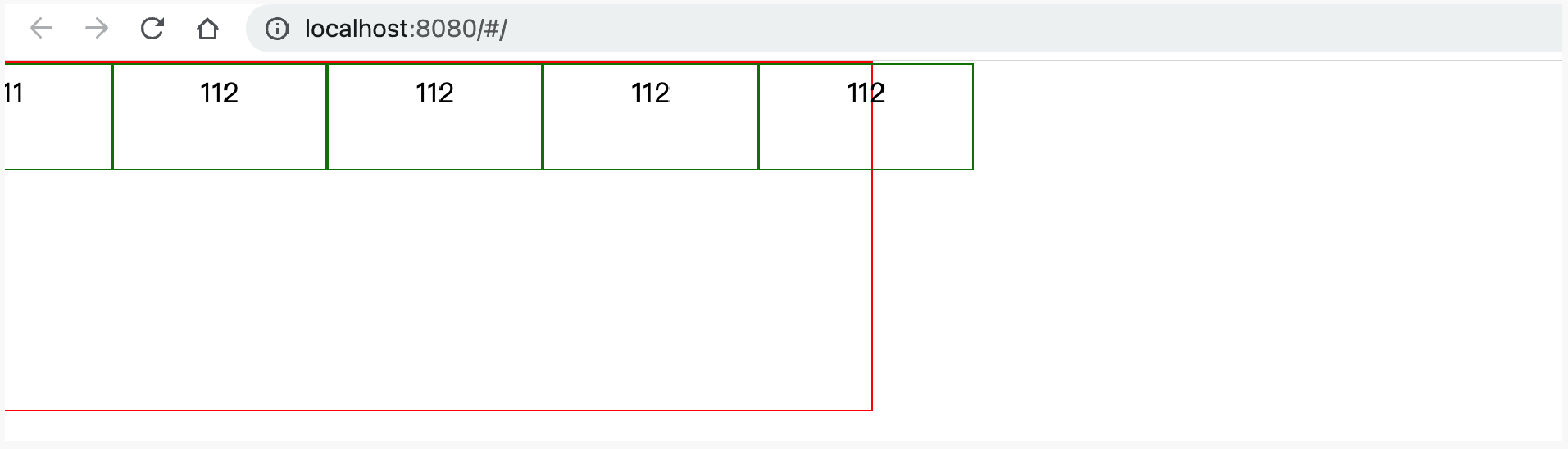
<div class="menu"><div class="item">11</div><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">112</div></div><style>.menu {width: 500px;height: 200px;border: 1px solid red;display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: space-evenly; /* 主轴=横向,元素间距一样 */align-items: flex-start; /* 副轴=纵向,元素顶部*/flex-wrap: nowrap;}.item {border: 1px solid green;padding: 5px 50px;height: 50px;width: 40px;}</style>
示例2:换行

<div class="menu"><div class="item">111</div><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">112</div><div class="item">112</div></div><style>body{margin: 0;}.menu {width: 500px;height: 200px;border: 1px solid red;display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: space-evenly; /* 主轴=横向,元素间距一样 */align-items: flex-start; /* 副轴=纵向,元素顶部*/flex-wrap: wrap;}.item {border: 1px solid green;padding: 5px 50px;height: 50px;width: 40px;}</style>
多行对齐方式
align-content用于控制多行元素的对齐方式,如果元素只有一行则不会起作用;默认stretch,即在元素没设置高度,或高度为auto情况下让元素填满整个容器。
flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | space-evenly | stretch(默认);
元素
顺序
order,默认0,用于决定项目排列顺序,数值越小,项目排列越靠前。
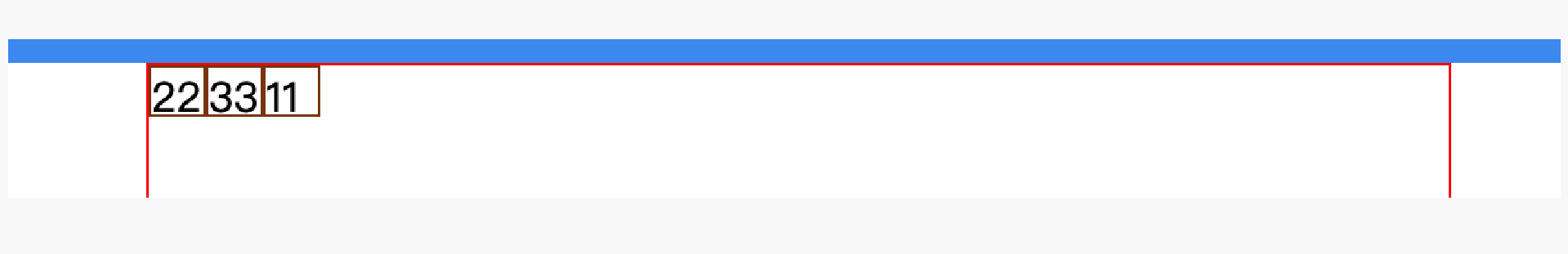
<div class="father"><div class="son" style="order: 2">11</div><div class="son" style="order: 0">22</div><div class="son" style="order: 1">33</div></div><style scoped>.father {border: 1px solid red;width: 500px;height: 300px;display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: flex-start;}.father .son {border: 1px solid saddlebrown;width: 20px;height: 18px;}</style>
剩余空间
flex-grow,默认0,用于决定项目在有剩余空间的情况下是否放大,默认不放大;

<div class="father"><div class="son">11</div><div class="son" style="flex-grow: 1">22</div><div class="son" style="flex-grow: 1">33</div></div>
案例:flex页面布局

<template><div><div class="row1"><div class="company"></div><div class="pic"></div><div class="pic"></div><div class="pic"></div></div><div class="row2"><div class="title"><div>手机</div><div>查看更多</div></div><div class="pic-list"><div class="big"></div><div class="right-list"><div class="group"><div class="phone"></div><div class="phone"></div><div class="phone"></div><div class="phone"></div></div><div class="group"><div class="phone"></div><div class="phone"></div><div class="phone"></div><div class="phone"></div></div></div></div></div><div class="course-list"><div class="item"></div><div class="item"></div><div class="item"></div><div class="item"></div><div class="item"></div></div></div></template><script>export default {name: "Mi"}</script><style scoped>.row1 {display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: space-between;}.row1 .company {width: 210px;height: 180px;background-color: saddlebrown;}.row1 .pic {width: 266px;height: 180px;background-color: cadetblue;}.row2 .title {display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: space-between;}.row2 .pic-list {display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: space-between;}.row2 .pic-list .big {background-color: aquamarine;height: 610px;width: 210px;margin-right: 20px;}.row2 .pic-list .right-list {/*background-color: antiquewhite;*/flex-grow: 1;}.row2 .pic-list .right-list .group {display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: space-between;flex-wrap: wrap;}.row2 .pic-list .right-list .phone {margin-bottom: 10px;border: 1px solid red;width: 200px;height: 300px;}.course-list {display: flex;justify-content: space-between;flex-wrap: wrap;}.course-list .item {width: 24%;height: 100px;background-color: skyblue;margin-top: 15px;}// 如果最后一个元素,是第3个,右边距=一个位置 + 所有空白位置/3(有三个空白位置).course-list .item:last-child:nth-child(4n - 1) {margin-right: calc(24% + 4% / 3);}// 如果最后一个元素,是第2个,右边距=两个位置 + 所有空白位置/3*2(有三个空白位置).course-list .item:last-child:nth-child(4n - 2) {margin-right: calc(48% + 8% / 3);}</style>
至此,结合以上的知识点,我们就可以来开发一个项目,但很多的页面按钮、标签、提示框等都需要自己手动,太费劲。
所以,接下来就要给大家的来聊一个UI框架 - ElementUI,他的内部提供了很多方便的样式和组件,可以加速我们开发。
ElementUI
Element,是有 饿了吗 团队开发一套为开发者、设计师和产品经理准备的基于 Vue 2.0 的组件库(也支持vue3.x)。
在他的基础上来开发,可以大大提升开发进度。

想要在项目中进行使用element-ui需要提前安装并引入。
引入
方式1:完整引入
- 安装
cd 项目目录npm install element-ui
- 引入 ```javascript import Vue from ‘vue’; import ElementUI from ‘element-ui’; import ‘element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css’; import App from ‘./App.vue’;
Vue.use(ElementUI);
new Vue({ render: h => h(App), }).$mount(‘#app’)
- 在组件中使用```html<el-button type="success">哈哈哈</el-button>
方式2:局部引入
- 安装
cd 项目目录npm install element-ui
- 引入 ```javascript import Vue from ‘vue’; import { Button, Select } from ‘element-ui’; import ‘element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css’; import App from ‘./App.vue’;
Vue.use(Button) Vue.use(Select)
new Vue({ render: h => h(App), }).$mount(‘#app’)
- 在组件中使用```html<el-button type="success">哈哈哈</el-button>
完整组件名称:https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN/component/quickstart
组件的使用
参见官方文档,在后续的项目开发中来应用并使用。

