1.读取文件
1.1读文本文件
#3个步骤mode有rb和rt 以字节的形式读取就是2进制,以文本的方式读就是字符串,是从当前指针开始读的1.打开文件file = open('文件',mode='rb')# 将文件以rb的读取方式打开并赋值给file#将文件以rt的读取方式读取,编码为utf-8,打开并赋值给file , t模式默认是str也就是unicode编码file = open('文件', mode = 'rt', encoding='utf-8')2.读取文件内容data = file.read() #读取file文件的内容赋值给data3.关闭文件file.close()# 不指定encoding参数,操作系统会使用自己默认的编码# linux系统默认用utf8编码# windows系统默认用gbk编码
1.2读非文本文件,如图片视频
file = ('文件路径',mode='rb')data = file.read()file.close()
1.3 读操作常用功能
1.3.1 读所有 .read
1.3.2 读n个字符.read(个数)
file = open ('F:\xuexi\1.txt',mode = 'rt',encoding='utf-8')data = file.read(2) # 读两个字符data1= file.read(1) # 读的是第3个字符,因为此时的光标在第2个字符之后file.closeprint(data)# 在读字节的时候需要把读取模式换成rb就好,注意,3个字节是一个字符
1.3.3 读一行.readline()
file = open(r'F:\xuexi\1.txt',mode = 'r' , encoding='utf-8')data = file.readline()data1 = file.readline()file.close()# .readline()后面无发跟行数,如果写行数,是读几个字符和read一样#注意读几行的时候也要考虑光标的位置及程序运行的顺序循环读文件file = open(r'F:\xuexi\1.txt',mode = 'r' , encoding='utf-8')for line in file:print(line.strip())file.close()#此时输出会有两空行,是文件中的换行和print的换行,如果要去除可以结合字符串的strip()
1.3.4 读所有行,每行作为一个元素的列表 .readlines()
file = open('F:\xuexi\1.text',mode='r'.encoding='utf-8')data = file.readlines()file.close()# 读出所有的文件
1.3.5 写入硬盘.flush()
file = open('F:\xuexi\1.txt',mode='a',encoding='utf-8')file.write('你好') # 不是写到了硬盘是写到了缓冲区,系统会一段时间内刷到硬盘file.flush()#现在就刷到硬盘file.close()
1.3.6 移动光标位置(字节位单位)
a模式下,用write写的时候只能写入尾部,不会写道光标志的位置
a+ 模式下用read是可以结合seek()的
file=open('F:\xuexi\1.txt',mode='rt',encoding='utf-8')f.seek(3)np = file.raed()f.close()# 0 参照物是文件开头位置 在t模式和b模式下都可以使用# 1 参照物是当前指针所在位置 只能在b模式下# 2 参照物是文件末尾位置 只能在b模式下f.seek(9,0)# 从文件开头开始移动9个字节f.seek(3,1)
1.3.7 获取当前的光标位置(按字节算)
file=open(r'F:\xuexi\1.txt',mode='rt',encoding='utf-8')n = file.tell()file.read(2)n1 = file.tell()file.close()print(n,n1)# 输出 0 ,6#1个字符3个字节#注意模式,rb的话就是按字节去读
1.4 上下文管理with
对文件进行操作时,每次都要打开关闭文件,繁琐
可以使用with,可以实现自动关闭文件
with open(r'F:\xuexi\1.txt',mode='rt') as file:data = file.read()print(data)#file就是代指了打开文件这个操作
#python2.7后支持同时对多个文件进行上下文管理with open("xxxx.txt", mode='rb') as f1, open("xxxx.txt", mode='rb') as f2:pass
1.5 注意事项
绝对路径
file = open('c:\学习\1.text', mode = 'rt',encoding='utf-8')data = file.read()file.close()"""windows下写绝对路径容易出现转义的问题:如:c:\xx\ntr\1.text 会把\n转义为换行会报错,需要加两个\\,可以解决c:\xx\\ntr\1.text"""
相对路径
程序的运行目录
读文件时文件不存在会报错
判断文件路径是否存在
#需要引入os模块import osfile_path = 'c:\xuexi\1.text'exits = os.path.exists(file_path)#判断file_path路径是否存在返回bool值if exits:file = ('c:\xuexi\1.tetx',mode='rt',encoding='utf-8')data = file.read()file.close()
2.写文件
写文件的时候为了避免内存空间的占用,一般就打开一次文件等全部的写操作完成后再进行关闭
w在写文件的时候,文件不存在会先创建文件再写入,如果存在则清空文件再写入
2.1 写文本文件
1.打开文件file = open('c:\xuexi\1.text',mode='wb') #以2进制的形式写file = open('c:\xuexi\1.text',mode='wt',encoding='utf-8') # 以字符串的形式写,编码为utf8写到文件里2.写入内容file.write('nihao'.encode(utf-8)) #在以2进制的形式写的时候可以结合字符串的独有方法encode,这样写入的也是字符串3.关闭文件file.close()
2.2 写图片文件等
file1 = open('c:\tupian\1.png',mode='rb')file2 = file1.read()file1.close()file3 = open('c:\tupian\2.png',mode='wb')file3.write(file2)file3.close()#读取1.png,将其写入到2.png文件中w在写文件的时候会先清空内容然后再写入
3 文件的打开模式
- 只读:r rt rb
文件存在就读,不存在报错 - 只写: w wb wt
文件存在情况该文件写,不存在创建该文件写 - 只写: x xb xt
存在报错,不存在创建再写 - 只写 :a ab at 在尾部追加
存在在尾部追加,不存在创建再写 - 读写 r+ rb+ rt+ ,默认的光标是文件的开始位置
```python file = open (‘c:\xuexi\1.text’ ,mode = ‘rt+’,encoding=’utf-8’)
data = file.read() # 读到了最后
new_data = file.write(‘nihao’)#然后开始写,想当于追加了
r+ 写文件的时候从文件开头写会覆盖内容
file.close()
- 读写: w+ wb+ wt+ 默认的光标位置是文件的开始位置```pythonfile = open('F:\xuexi\1.txt',mode='wt+',encoding='utf-8')data = file.read()file.seek(0)#将光标重置到开始位置file.write('你好')file.close()#此时文件中的只有你好,因为光标重置了,w会清空再写
- 读写: x+ xb+ xt+ 默认光标位置是开始位置(创建新的文件)
- 读写: a+ ab+ at+ 默认光标的位置是:末尾
```python file = open (‘F:\xuexi\1.txt’,mode = ‘wt+’,encoding=’utf-8’)
file.write(‘你好吗’)
file.seek(0)
file.read()
<a name="834ae468"></a>### 4.csv文件操作```python需要引入os模块逗号分隔值,也叫字符分隔值,因为分隔字符可以不是逗号,其文件以纯文本的形式存储表格数据(数字和文本)对于这种格式的数据,需要用open()函数来读取文件,并根据逗号分隔的特点来进行处理
练习题案例:下载文档中的所有图片且以用户名为图片名称存储。
ID,用户名,头像26044585,Hush,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/51d46dc32abe7ac7f83b94c67bb88cacc46869954f478-aP4Q3V19318369,柒十一,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/703fdb063bdc37b11033ef794f9b3a7adfa01fd21a6d1-wTFbnO
import osimport requestswith open ("F:\xuexi\1.text",mode = 'r',encoding ='utf-8') as file:file.reade()for line in file:userid ,username,url=line.split(',')print(username,url)res = request.get(url = url, headers={"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/87.0.4280.88 Safari/537.36"})if not os.path.exists("images")os.makedirs('images')#创建目录with open ("images\{}.png".format(username),mode='wb') as images_file:images_file.write(res.content)
5.ini格式文件
ini文件是用于存储软件的配置文件,比如 mysql数据库的配置文件
需要引入 configparser模块
[mysqld] #节点datadir=/var/lib/mysql#键 值socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.socklog-bin=py-mysql-bincharacter-set-server=utf8collation-server=utf8_general_cilog-error=/var/log/mysqld.log# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security riskssymbolic-links=0[mysqld_safe]log-error=/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.logpid-file=/var/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid[client]default-character-set=utf8
import configparserconfig = configparser.configparser()config.read('F:\xuexi\1.ini',encoding='utf-8')1.读取所有节点conu = config.sections()print(conu)# ['mysqld','mysqld_safe'.'client']2.获取节点下的键值conu = config.items('client')print(conu)#[('log-error','/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log'),('pid-file','/var/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid')]for key,values in config.items('mysqld_safe'):print(key,values)3.获取某个节点下的键对应的值coun = config.get('clinet','default-character-set')print(coun)#utf84.是否存在节点v1 = config.has_section('clinet')5.添加一个节点config.add_section("group")6.删除节点config.remove_section('client')7.节点中设置键值config.set('SEC_1', 'k10', "123")config.set('SEC_1', 'name', "哈哈哈哈哈")7.内容写入文件config.write(open('files/new.ini', mode='w', encoding='utf-8'))9.删除节点中的键值config.remove_option("mysqld", "datadir")
6.xml格式的文件
可扩展标记语言,数据存储语言,xml被设计用与传输和存储数据
存储: 用来存储配置文件,如 java的配置文件
传输: 网络传输时用这种格式
<data><country name="Liechtenstein"><rank updated="yes">2</rank><year>2023</year><gdppc>141100</gdppc><neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" /><neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" /></country><country name="Singapore"><rank updated="yes">5</rank><year>2026</year><gdppc>59900</gdppc><neighbor direction="N" name="Malaysia" /></country><country name="Panama"><rank updated="yes">69</rank><year>2026</year><gdppc>13600</gdppc><neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" /><neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" /></country></data>
6.1 读取文件和内容
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET# ET去打开xml文件tree = ET.parse("files/xo.xml")# 获取根标签root = tree.getroot()print(root) # <Element 'data' at 0x7f94e02763b0>
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ETcontent = """<data><country name="Liechtenstein"><rank updated="yes">2</rank><year>2023</year><gdppc>141100</gdppc><neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" /><neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" /></country><country name="Panama"><rank updated="yes">69</rank><year>2026</year><gdppc>13600</gdppc><neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" /><neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" /></country></data>"""root = ET.XML(content)print(root) # <Element 'data' at 0x7fdaa019cea0>
6.2 读取节点数据
# 获取根标签root = ET.xml(content)print(root) # data# 获取data标签的孩子标签for child in root:# child.tag = conntry# child.attrib = {"name":"Liechtenstein"}print(child.tag, child.attrib)#country {'name': 'Liechtenstein'}#country {'name': 'Panama'}for node in child:print(node.tag, node.attrib, node.text)"""输出内容rank {} 2year {} 2023gdppc {} 141100neighbor {'direction': 'E', 'name': 'Austria'} Noneneighbor {'direction': 'W', 'name': 'Switzerland'} Nonerank {} 69year {} 2026gdppc {} 13600neighbor {'direction': 'W', 'name': 'Costa Rica'} Noneneighbor {'direction': 'E', 'name': 'Colombia'} None"""root = ET.XML(content)for child in root.iter('year'):print(child.tag, child.text)"""year 2023year 2026"""root = ET.XML(content)v1 = root.findall('country')print(v1)v2 = root.find('country').find('rank')print(v2.text)"""[<Element 'country' at 0x0000025989E7CB30>, <Element 'country' at 0x0000025989E7CD10>]2"""
6.3 修改删除节点
# 修改节点内容和属性rank = root.find('country').find('rank')print(rank.text)rank.text = "999"rank.set('update', '2020-11-11')print(rank.text, rank.attrib)############ 保存文件 ############tree = ET.ElementTree(root)tree.write("new.xml", encoding='utf-8')# 删除节点root.remove( root.find('country') )print(root.findall('country'))############ 保存文件 ############tree = ET.ElementTree(root)tree.write("newnew.xml", encoding='utf-8')
6.4 构建文档
<home><son name="儿1"><grandson name="儿11"></grandson><grandson name="儿12"></grandson></son><son name="儿2"></son></home>=============================================from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET# 创建根标签root = ET.Element("home")# 创建节点大儿子son1 = ET.Element('son', {'name': '儿1'})# 创建小儿子son2 = ET.Element('son', {"name": '儿2'})# 在大儿子中创建两个孙子grandson1 = ET.Element('grandson', {'name': '儿11'})grandson2 = ET.Element('grandson', {'name': '儿12'})son1.append(grandson1)son1.append(grandson2)# 把儿子添加到根节点中root.append(son1)root.append(son2)tree = ET.ElementTree(root)tree.write('oooo.xml', encoding='utf-8', short_empty_elements=False)
<famliy><son name="儿1"><age name="儿11">孙子</age></son><son name="儿2"></son></famliy>from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET# 创建根节点root = ET.Element("famliy")# 创建节点大儿子son1 = ET.SubElement(root, "son", attrib={'name': '儿1'})# 创建小儿子son2 = ET.SubElement(root, "son", attrib={"name": "儿2"})# 在大儿子中创建一个孙子grandson1 = ET.SubElement(son1, "age", attrib={'name': '儿11'})grandson1.text = '孙子'et = ET.ElementTree(root) #生成文档对象et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8")
<user><![CDATA[你好呀]]</user>from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET# 创建根节点root = ET.Element("user")root.text = "<![CDATA[你好呀]]"et = ET.ElementTree(root) # 生成文档对象et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8")
7.excel 文件操作
需要引入第三方模块
pip install openpyxl模块名称
7.1 读excel load_workbook
from openpyxl import load_workbookwb = load_workbook("F:\1.xlsx")
7.1.1 获取excel文件中的所有shet名称.sheetnames
wb = load_workbook("F:\1.xlsx")wb.sheetnames
7.1.2 选择sheet基于名称
sheet = wb["数据导出"]cell = sheet.cell(1, 2)print(cell.value)
7.1.3 选择sheet基于索引.worksheets[0]
sheet = wb.worksheets[0]cell = sheet.cell(1,2)print(cell.value)
7.1.4 循环所有的sheet
"""for name in wb.sheetnames:sheet = wb[name]cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)print(cell.value)""""""for sheet in wb.worksheets:cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)print(cell.value)""""""for sheet in wb:cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)print(cell.value)"""
7.2 读sheet中单元格的数据
from openpyxl import load_workbookwb = load_workbook("F:\1.xlsx")
7.2.1 获取第n行第n列的单元格(位置从1开始)
cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)print(cell.value)print(cell.style)print(cell.font)print(cell.alignment)
7.2.2 获取某个单元格
c1 = sheet["A2"]print(c1.value)c2 = sheet['D4']print(c2.value)
7.2.3 获取第n行所有的单元格
for cell in sheet[1]:print(cell.value)
7.2.4 所有行的数据(获取某一列数据)
for row in sheet.rows:print(row[0].value, row[1].value)
7.2.5 获取所有列的数据
for col in sheet.columns:print(col[1].value)
7.2.6 读合并单元格
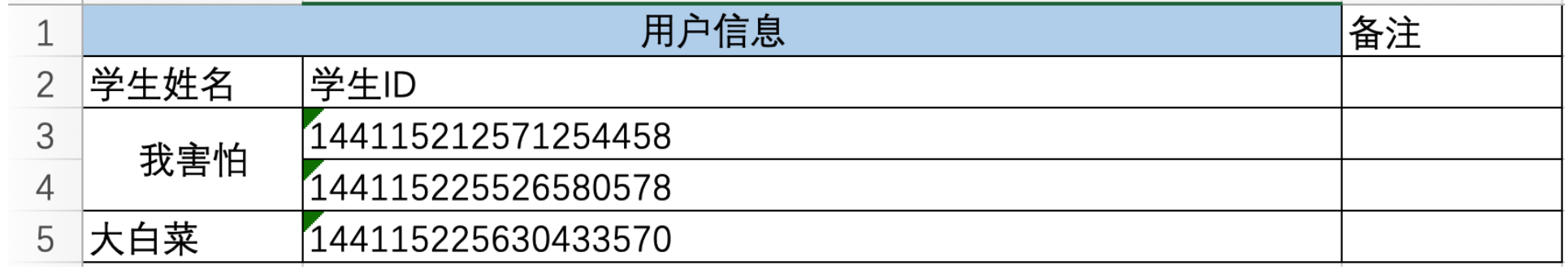
from openpyxl import load_workbookwb = load_workbook("files/p1.xlsx")sheet = wb.worksheets[2]# 获取第N行第N列的单元格(位置是从1开始)c1 = sheet.cell(1, 1)print(c1) # <Cell 'Sheet1'.A1>print(c1.value) # 用户信息c2 = sheet.cell(1, 2)print(c2) # <MergedCell 'Sheet1'.B1>print(c2.value) # None
from openpyxl import load_workbookwb = load_workbook('files/p1.xlsx')sheet = wb.worksheets[2]for row in sheet.rows:print(row)""">>> 输出结果(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A1>, <MergedCell 'Sheet1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C1>)(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C2>)(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C3>)(<MergedCell 'Sheet1'.A4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C4>)(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C5>)"""
7.3 写excel
7.3.1 在原excel基础上写
from openpyxl import load_workbookwb = load_workbook('files/p1.xlsx')sheet = wb.worksheets[0]# 找到单元格,并修改单元格的内容cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)cell.value = "新的开始"# 将excel文件保存到p2.xlsx文件中wb.save("files/p2.xlsx")
7.3.2 新创建excel写
from openpyxl import workbook# 创建excel且默认会创建一个sheet(名称为Sheet)wb = workbook.Workbook()sheet = wb.worksheets[0] # 或 sheet = wb["Sheet"]# 找到单元格,并修改单元格的内容cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)cell.value = "新的开始"# 将excel文件保存到p2.xlsx文件中wb.save("files/p2.xlsx")
7.3.3 其他操作
# 1. 修改sheet名称"""sheet = wb.worksheets[0]sheet.title = "数据集"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 2. 创建sheet并设置sheet颜色"""sheet = wb.create_sheet("工作计划", 0)sheet.sheet_properties.tabColor = "1072BA"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 3. 默认打开的sheet"""wb.active = 0wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 4. 拷贝sheet"""sheet = wb.create_sheet("工作计划")sheet.sheet_properties.tabColor = "1072BA"new_sheet = wb.copy_worksheet(wb["Sheet"])new_sheet.title = "新的计划"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 5.删除sheet"""del wb["用户列表"]wb.save('files/p2.xlsx')"""
from openpyxl import load_workbookfrom openpyxl.styles import Alignment, Border, Side, Font, PatternFill, GradientFillwb = load_workbook('files/p1.xlsx')sheet = wb.worksheets[1]# 1. 获取某个单元格,修改值"""cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)cell.value = "开始"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 2. 获取某个单元格,修改值"""sheet["B3"] = "Alex"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 3. 获取某些单元格,修改值"""cell_list = sheet["B2":"C3"]for row in cell_list:for cell in row:cell.value = "新的值"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 4. 对齐方式"""cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)# horizontal,水平方向对齐方式:"general", "left", "center", "right", "fill", "justify", "centerContinuous", "distributed"# vertical,垂直方向对齐方式:"top", "center", "bottom", "justify", "distributed"# text_rotation,旋转角度。# wrap_text,是否自动换行。cell.alignment = Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='distributed', text_rotation=45, wrap_text=True)wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 5. 边框# side的style有如下:dashDot','dashDotDot', 'dashed','dotted','double','hair', 'medium', 'mediumDashDot', 'mediumDashDotDot','mediumDashed', 'slantDashDot', 'thick', 'thin'"""cell = sheet.cell(9, 2)cell.border = Border(top=Side(style="thin", color="FFB6C1"),bottom=Side(style="dashed", color="FFB6C1"),left=Side(style="dashed", color="FFB6C1"),right=Side(style="dashed", color="9932CC"),diagonal=Side(style="thin", color="483D8B"), # 对角线diagonalUp=True, # 左下 ~ 右上diagonalDown=True # 左上 ~ 右下)wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 6.字体"""cell = sheet.cell(5, 1)cell.font = Font(name="微软雅黑", size=45, color="ff0000", underline="single")wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 7.背景色"""cell = sheet.cell(5, 3)cell.fill = PatternFill("solid", fgColor="99ccff")wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 8.渐变背景色"""cell = sheet.cell(5, 5)cell.fill = GradientFill("linear", stop=("FFFFFF", "99ccff", "000000"))wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 9.宽高(索引从1开始)"""sheet.row_dimensions[1].height = 50sheet.column_dimensions["E"].width = 100wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 10.合并单元格"""sheet.merge_cells("B2:D8")sheet.merge_cells(start_row=15, start_column=3, end_row=18, end_column=8)wb.save("p2.xlsx")""""""sheet.unmerge_cells("B2:D8")wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 11.写入公式"""sheet = wb.worksheets[3]sheet["D1"] = "合计"sheet["D2"] = "=B2*C2"wb.save("p2.xlsx")""""""sheet = wb.worksheets[3]sheet["D3"] = "=SUM(B3,C3)"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 12.删除"""# idx,要删除的索引位置# amount,从索引位置开始要删除的个数(默认为1)sheet.delete_rows(idx=1, amount=20)sheet.delete_cols(idx=1, amount=3)wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 13.插入"""sheet.insert_rows(idx=5, amount=10)sheet.insert_cols(idx=3, amount=2)wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 14.循环写内容"""sheet = wb["Sheet"]cell_range = sheet['A1:C2']for row in cell_range:for cell in row:cell.value = "xx"for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=5, min_col=1, max_col=7, max_row=10):for cell in row:cell.value = "oo"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 15.移动"""# 将H2:J10范围的数据,向右移动15个位置、向上移动1个位置sheet.move_range("H2:J10",rows=1, cols=15)wb.save("p2.xlsx")""""""sheet = wb.worksheets[3]sheet["D1"] = "合计"sheet["D2"] = "=B2*C2"sheet["D3"] = "=SUM(B3,C3)"sheet.move_range("B1:D3",cols=10, translate=True) # 自动翻译公式wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 16.打印区域"""sheet.print_area = "A1:D200"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""# 17.打印时,每个页面的固定表头"""sheet.print_title_cols = "A:D"sheet.print_title_rows = "1:3"wb.save("p2.xlsx")"""
8.压缩文件
内置的shutil模块可以实现对压缩文件的操作
import shutil# 1. 压缩文件"""# base_name,压缩后的压缩包文件# format,压缩的格式,例如:"zip", "tar", "gztar", "bztar", or "xztar".# root_dir,要压缩的文件夹路径"""# shutil.make_archive(base_name=r'datafile',format='zip',root_dir=r'files')# 2. 解压文件"""# filename,要解压的压缩包文件# extract_dir,解压的路径# format,压缩文件格式"""# shutil.unpack_archive(filename=r'datafile.zip', extract_dir=r'xxxxxx/xo', format='zip')
9.路径相关(*)
import shutilimport os# 1. 获取当前脚本绝对路径"""abs_path = os.path.abspath(__file__)print(abs_path)"""# 2. 获取当前文件的上级目录"""base_path = os.path.dirname( os.path.dirname(路径) )print(base_path)"""# 3. 路径拼接"""p1 = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx')print(p1)p2 = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx', 'oo', 'a1.png')print(p2)"""# 4. 判断路径是否存在"""exists = os.path.exists(p1)print(exists)"""# 5. 创建文件夹"""os.makedirs(路径)""""""path = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx', 'oo', 'uuuu')if not os.path.exists(path):os.makedirs(path)"""# 6. 是否是文件夹"""file_path = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx', 'oo', 'uuuu.png')is_dir = os.path.isdir(file_path)print(is_dir) # Falsefolder_path = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx', 'oo', 'uuuu')is_dir = os.path.isdir(folder_path)print(is_dir) # True"""# 7. 删除文件或文件夹"""os.remove("文件路径")""""""path = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx')shutil.rmtree(path)"""# 8. 拷贝文件夹"""shutil.copytree("/Users/wupeiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/","/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files")"""# 9.拷贝文件"""shutil.copy("/Users/wupeiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/WX20201123-112406@2x.png","/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/")shutil.copy("/Users/wupeiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/WX20201123-112406@2x.png","/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/x.png")"""# 10.文件或文件夹重命名"""shutil.move("/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/x.png","/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/xxxx.png")shutil.move("/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files","/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/images")"""
10.转义
windows路径使用的是\,linux路径使用的是/。
特别的,在windows系统中如果有这样的一个路径 D:\nxxx\txxx\x1,程序会报错。因为在路径中存在特殊符 \n(换行符)和\t(制表符),Python解释器无法自动区分。
所以,在windows中编写路径时,一般有两种方式:
- 加转义符,例如:
"D:\\nxxx\\txxx\\x1" - 路径前加r,例如:`r”D:\nxxx\txxx\x1”

