
作者简介:五月君,Software Designer,公众号「Nodejs技术栈」作者。
Async Hooks 功能是 Node.js v8.x 版本新增加的一个核心模块,它提供了 API 用来追踪 Node.js 程序中异步资源的声明周期,可在多个异步调用之间共享数据,本文从最基本入门篇开始学习,之后会有在某些场景下具体应用实践篇介绍。
executionAsyncId 和 triggerAsyncId
async hooks 模块提供了 executionAsyncId() 函数标志当前执行上下文的异步资源 Id,下文使用 asyncId 表示。还有一个 triggerAsyncId() 函数来标志当前执行上下文被触发的异步资源 Id,也就是当前异步资源是由哪个异步资源创建的。
每个异步资源都会生成 asyncId,该 id 会呈递增的方式生成,且在 Node.js 当前实例里全局唯一。
const asyncHooks = require('async_hooks');const fs = require('fs');const asyncId = () => asyncHooks.executionAsyncId();const triggerAsyncId = () => asyncHooks.triggerAsyncId();console.log(`Global asyncId: ${asyncHooks.executionAsyncId()}, Global triggerAsyncId: ${triggerAsyncId()}`);fs.open('hello.txt', (err, res) => {console.log(`fs.open asyncId: ${asyncId()}, fs.open triggerAsyncId: ${triggerAsyncId()}`);});
下面是我们运行的结果,全局的 asyncId 为 1,fs.open 回调里打印的 triggerAsyncId 为 1 由全局触发。
Global asyncId: 1, Global triggerAsyncId: 0fs.open asyncId: 5, fs.open triggerAsyncId: 1
默认未开启的 Promise 执行跟踪
默认情况下,由于 V8 提供的 promise introspection API 相对消耗性能,Promise 的执行没有分配 asyncId。这意味着默认情况下,使用了 Promise 或 Async/Await 的程序将不能正确的执行和触发 Promise 回调上下文的 ID。
即得不到当前异步资源 asyncId 也得不到当前异步资源是由哪个异步资源创建的 triggerAsyncId,如下所示:
Promise.resolve().then(() => {// Promise asyncId: 0. Promise triggerAsyncId: 0console.log(`Promise asyncId: ${asyncId()}. Promise triggerAsyncId: ${triggerAsyncId()}`);})
通过 asyncHooks.createHook 创建一个 hooks 对象启用 Promise 异步跟踪。
const hooks = asyncHooks.createHook({});hooks.enable();Promise.resolve().then(() => {// Promise asyncId: 7. Promise triggerAsyncId: 6console.log(`Promise asyncId: ${asyncId()}. Promise triggerAsyncId: ${triggerAsyncId()}`);})
异步资源的生命周期
asyncHooks 的 createHook() 方法返回一个用于启用(enable)和禁用(disable)hooks 的实例,该方法接收 init/before/after/destory 四个回调来标志一个异步资源从初始化、回调调用之前、回调调用之后、销毁整个生命周期过程。
init(初始化)
当构造一个可能发出异步事件的类时调用。
- async:异步资源唯一 id
- type:异步资源类型,对应于资源的构造函数名称,更多类型参考 async_hooks_type
- triggerAsyncId:当前异步资源由哪个异步资源创建的异步资源 id
- resource:初始化的异步资源
/*** Called when a class is constructed that has the possibility to emit an asynchronous event.* @param asyncId a unique ID for the async resource* @param type the type of the async resource* @param triggerAsyncId the unique ID of the async resource in whose execution context this async resource was created* @param resource reference to the resource representing the async operation, needs to be released during destroy*/init?(asyncId: number, type: string, triggerAsyncId: number, resource: object): void;
before(回调函数调用前)
当启动异步操作(例如 TCP 服务器接收新链接)或完成异步操作(例如将数据写入磁盘)时,系统将调用回调来通知用户,也就是我们写的业务回调函数。在这之前会先触发 before 回调。/*** When an asynchronous operation is initiated or completes a callback is called to notify the user.* The before callback is called just before said callback is executed.* @param asyncId the unique identifier assigned to the resource about to execute the callback.*/before?(asyncId: number): void;
after(回调函数调用后)
当回调处理完成之后触发 after 回调,如果回调出现未捕获异常,则在触发 uncaughtException 事件或域(domain)处理之后触发 after 回调。/*** Called immediately after the callback specified in before is completed.* @param asyncId the unique identifier assigned to the resource which has executed the callback.*/after?(asyncId: number): void;
destory(销毁)
当 asyncId 对应的异步资源被销毁后调用 destroy 回调。
一些资源的销毁依赖于垃圾回收,因此如果对传递给 init 回调的资源对象有引用,则有可能永远不会调用 destory 从而导致应用程序中出现内存泄漏。如果资源不依赖垃圾回收,这将不会有问题。/*** Called after the resource corresponding to asyncId is destroyed* @param asyncId a unique ID for the async resource*/destroy?(asyncId: number): void;
promiseResolve
当传递给 Promise 构造函数的 resolve() 函数执行时触发 promiseResolve 回调。
以下代码会触发两次 promiseResolve() 回调,第一次是我们直接调用的 resolve() 函数,第二次是在 .then() 里虽然我们没有显示的调用,但是它也会返回一个 Promise 所以还会被再次调用。 ```typescript const hooks = asyncHooks.createHook({ promiseResolve(asyncId) { syncLog(‘promiseResolve: ‘, asyncId); } }); new Promise((resolve) => resolve(true)).then((a) => {});/*** Called when a promise has resolve() called. This may not be in the same execution id* as the promise itself.* @param asyncId the unique id for the promise that was resolve()d.*/promiseResolve?(asyncId: number): void;
// 输出结果 promiseResolve: 2 promiseResolve: 3
<a name="Y9H2s"></a>## 注意 init 回调里写日志造成 “栈溢出” 问题一个异步资源的生命周期中第一个阶段 init 回调是当构造一个可能发出异步事件的类时会调用,要注意由于使用 console.log() 输出日志到控制台是一个异步操作,在 AsyncHooks 回调函数中使用类似的异步操作将会再次触发 init 回调函数,进而导致无限递归出现 **```RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded```** 错误,也就是 “ **栈溢出**”。<br />调试时,一个简单的记录日志的方式是使用 fs.writeFileSync() 以同步的方式写入日志,这将不会触发 AsyncHooks 的 init 回调函数。```javascriptconst syncLog = (...args) => fs.writeFileSync('log.txt', `${util.format(...args)}\n`, { flag: 'a' });const hooks = asyncHooks.createHook({init(asyncId, type, triggerAsyncId, resource) {syncLog('init: ', asyncId, type, triggerAsyncId)}});hooks.enable();fs.open('hello.txt', (err, res) => {syncLog(`fs.open asyncId: ${asyncId()}, fs.open triggerAsyncId: ${triggerAsyncId()}`);});
输出以下内容,init 回调只会被调用一次,因为 fs.writeFileSync 是同步的是不会触发 hooks 回调的。
init: 2 FSREQCALLBACK 1fs.open asyncId: 2, fs.open triggerAsyncId: 1
异步之间共享上下文
Node.js v13.10.0 增加了 async_hooks 模块的 AsyncLocalStorage 类,可用于在一系列异步调用中共享数据。
如下例所示,asyncLocalStorage.run() 函数第一个参数是存储我们在异步调用中所需要访问的共享数据,第二个参数是一个异步函数,我们在 setTimeout() 的回调函数里又调用了 test2 函数,这一系列的异步操作都不影响我们在需要的地方去获取 asyncLocalStorage.run() 函数中存储的共享数据。
const { AsyncLocalStorage } = require('async_hooks');const asyncLocalStorage = new AsyncLocalStorage();asyncLocalStorage.run({ traceId: 1 }, test1);async function test1() {setTimeout(() => test2(), 2000);}async function test2() {console.log(asyncLocalStorage.getStore().traceId);}
AsyncLocalStorage 用途很多,例如在服务端必不可少的日志分析,一个 HTTP 从请求到响应整个系统交互的日志输出如果能通过一个 traceId 来关联,在分析日志时也就能够清晰的看到整个调用链路。
下面是一个 HTTP 请求的简单示例,模拟了异步处理,并且在日志输出时去追踪存储的 id
const http = require('http');const { AsyncLocalStorage } = require('async_hooks');const asyncLocalStorage = new AsyncLocalStorage();function logWithId(msg) {const id = asyncLocalStorage.getStore();console.log(`${id !== undefined ? id : '-'}:`, msg);}let idSeq = 0;http.createServer((req, res) => {asyncLocalStorage.run(idSeq++, () => {logWithId('start');setImmediate(() => {logWithId('processing...');setTimeout(() => {logWithId('finish');res.end();}, 2000)});});}).listen(8080);
下面是运行结果,我在第一次调用之后直接调用了第二次,可以看到我们存储的 id 信息与我们的日志一起成功的打印了出来。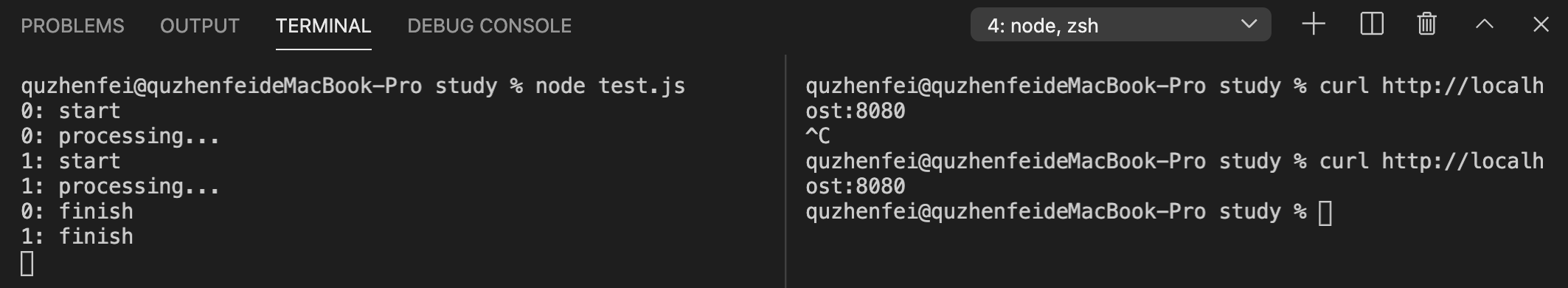
在下一节会详细介绍, 如何在 Node.js 中使用 async hooks 模块的 AsyncLocalStorage 类处理请求上下文, 也会详细讲解 AsyncLocalStorage 类是如何实现的本地存储。

