Context Hierarchy
DispatcherServlet 期望有一个 WebApplicationContext(普通 ApplicationContext 的扩展)用于自己的配置。WebApplicationContext 有一个与 ServletContext 和与之相关的 Servlet 的链接。它也被绑定到 ServletContext,这样应用程序就可以使用 RequestContextUtils 上的静态方法来查询 WebApplicationContext,如果他们需要访问它的话。
对于许多应用程序来说,有一个单一的 WebApplicationContext 是简单的,也是足够的。也可以有一个上下文层次结构,其中一个根 WebApplicationContext 被多个 DispatcherServlet(或其他 Servlet)实例共享,每个实例有自己的子 WebApplicationContext 配置。关于上下文层次结构特征的更多信息,请参见 ApplicationContext 的附加功能。
根 WebApplicationContext 通常包含基础设施 Bean,例如需要在多个 Servlet 实例中共享的数据存储库和业务服务。这些 Bean 有效地被继承,并且可以在 Servlet 特定的子 WebApplicationContext 中被覆盖(即重新声明),该子 WebApplicationContext 通常包含给定 Servlet 的本地 Bean。下面的图片显示了这种关系: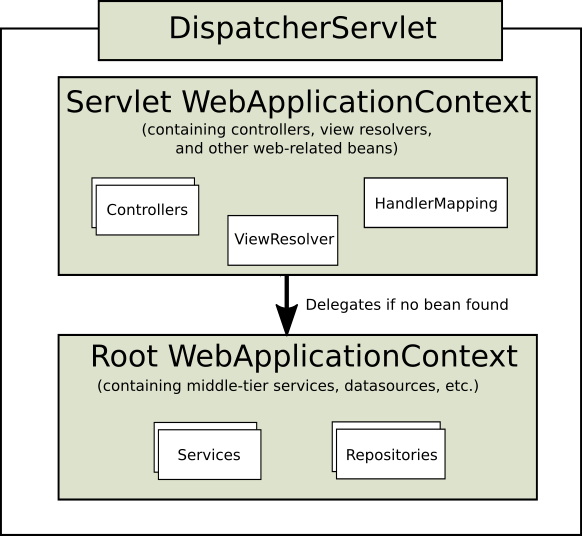
- Servlet WebApplicationContext :包含 controller、view 等其他 bean
- Root WebApplicationContext :包含 service、DataSource 等其他 bean
- Servlet 如果没有找到 bean 这委托 Root 上下文查找
下面的例子配置了一个 WebApplicationContext 的层次结构:
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {@Overrideprotected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {return new Class<?>[] { RootConfig.class };}@Overrideprotected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {return new Class<?>[] { App1Config.class };}@Overrideprotected String[] getServletMappings() {return new String[] { "/app1/*" };}}
:::tips
如果不需要应用上下文层次结构,应用程序可以通过 getRootConfigClasses()返回所有配置,而从 getServletConfigClasses()返回空配置。
:::
下面的例子显示了 web.xml 的对应关系:
<web-app><listener><listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class></listener><context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/root-context.xml</param-value></context-param><servlet><servlet-name>app1</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/app1-context.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>app1</servlet-name><url-pattern>/app1/*</url-pattern></servlet-mapping></web-app>
:::tips 如果不需要应用上下文层次结构,应用程序可以只配置一个 「root 」上下文,并将 contextConfigLocation Servlet 参数留空。 :::

