UI层
Flutter Widget组件的概念受到React.js框架的启发。核心思想是通过Widget构建UI层。
Widget简介
Widget用于绘制UI层,最基础的Flutter App调用runApp()函数。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';void main() {runApp(Center(child: Text('Hello, world!',textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,),),);}
runApp() 函数取得 Widget 并把它做为 Widget tree 的根节点。
基础组件(Basic Widget)
Text
Row, Column
基于Web的flexbox布局模型,用于创建在水平(Row)和垂直(Column)方向上的灵活布局。
Stack
不同于线性方向(水平或垂直)布局,Stack允许按照绘制顺序将Widget堆叠在一起,然后可以在Stack组件内部使用基于Positioned的自组件,分别相对于外层Stack组件的上、右、下、左边距进行定位。Stack相当于Web页面的绝对定位布局方式。
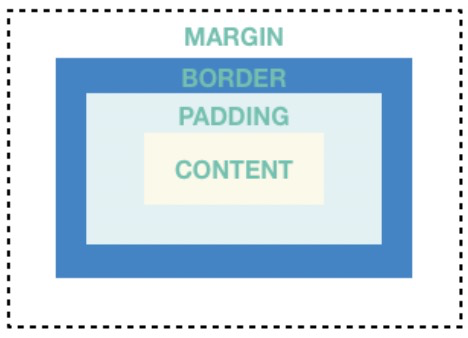
Container
Container允许创建矩形可视元素。Container可以使用BoxDecoration进行装饰,如:背景、边框或阴影。Container也可以包括 margins、padding及可以应用在其上的尺寸约束条件。另外,Container可以使用matrix在三维空间中进行变换。
手势控制
详细内容参考:GestureDetector
StatelessWidget 和 StatefulWidget
StatelessWidget和StatefulWidget的区别在于Widget是否管理状态。
StatelessWidget从它的父组件获取参数,并将他们保存在 final 成员变量中。
为构建更复杂的体验,例如:以更有趣的方式对用户输入作出反应,应用程序通常带有一些状态。Flutter使用StatefulWidget来实现这个想法。StatefulWidget 是特殊的 Widget,它知道如何生成保持 state 的状态对象。
class Counter extends StatefulWidget {// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the// values (in this case nothing) provided by the parent and used by the build// method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are always marked "final".@override_CounterState createState() => _CounterState();}class _CounterState extends State<Counter> {int _counter = 0;void _increment() {setState(() {// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that// something has changed in this State, which causes it to rerun// the build method below so that the display can reflect the// updated values. If you change _counter without calling// setState(), then the build method won't be called again,// and so nothing would appear to happen._counter++;});}@overrideWidget build(BuildContext context) {// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance// as done by the _increment method above.// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning// build methods fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that// needs updating rather than having to individually change// instances of widgets.return Row(children: <Widget>[RaisedButton(onPressed: _increment,child: Text('Increment'),),Text('Count: $_counter'),],);}}
你可能好奇,为什么StatefulWidget和State是两个分开的对象。在Flutter中,这两种类型的对象有不同的生命周期。Widgets 是临时对象,用于在当前状态下构建应用程序的展示。而状态对象从另一个角度讲,在 build() 函数被调用之前,用于保存信息。
在Fultter中,Widget 要么是stateful的,要么是stateless的。如果Widget可以根据用户交互行为发生改变,那么它肯定是 stateful的。组件的state被存储在 State 对象中,将widget的状态和显示分隔开。state包含了可以被修改的值,当widget的状态需要被改变是,state对象调用 setState() 方法通知flutter框架重绘组件。
创建Stateful组件
要点:
- 一个Stateful组件实现了两个类:
- StatefuleWidget子类
- State子类
- state类包含了组件的可变更状态和组件的
build()方法。
管理Widget状态
- 管理状态的方式有多种
- 作为组件的设计者,可以选择不同的状态管理方法
- Widget管理自己的状态
- 父组件管理组件状态
- 采用 mix-and-match 方法管理状态
- 如果有疑问,请先从父组件管理状态开始
状态管理的几种方式
如果决定用什么方式来管理状态呢?Flutter官方给出了一些原则性建议。
- 如果 state 是用户数据,例如:checkbox的状态是选中还是未选中,slider的位置等信息,最好的方式是由父组件去管理状态。
- 如果state是展示样式性的,例如:动画效果等,最好让组件自己去管理这些状态。
如果还有疑问,那么就用父组件去管理状态吧。
Flutter 中的布局
Widget是可以构建UI的类
Widget可以做为布局和UI元素使用
可以通过组合简单Widget使其成为复杂Widget
分类布局组件(Layout Widget)
https://flutter.dev/docs/development/ui/widgets/layout
Single-child布局组件
Material应用程序
采用Material Design设计标准实现的Material library,Flutter允许使用Scaffold Widget组件。它提供了默认的Banner、背景色,并提供了drawers、sanck bars及底部菜单等组件。
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {@overrideWidget build(BuildContext context) {return MaterialApp(title: 'Flutter layout demo',home: Scaffold(appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Flutter layout demo'),),body: Center(child: Text('Hello World'),),),);}}
No-material应用程序
默认的No-material App不包含AppBar,title及背景颜色。如果需要在non-material app中创建这些特性,需要自己创建。
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {@overrideWidget build(BuildContext context) {return Container(decoration: BoxDecoration(color: Colors.white),child: Center(child: Text('Hello World',textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,style: TextStyle(fontSize: 32,color: Colors.black87,),),),);}}
尺寸Widget
当布局尺寸太大,无法适应设备时,黄黑相间的条纹将会显现在设备上。为了解决这个问题,可以通过使用Expended 组件。它能使组件在Row或Column的纬度适应设备尺寸。
通用布局组件(Common layout widget)
标准组件
- Container:可以为Widget添加padding、margin、边框、背景色或其他装饰