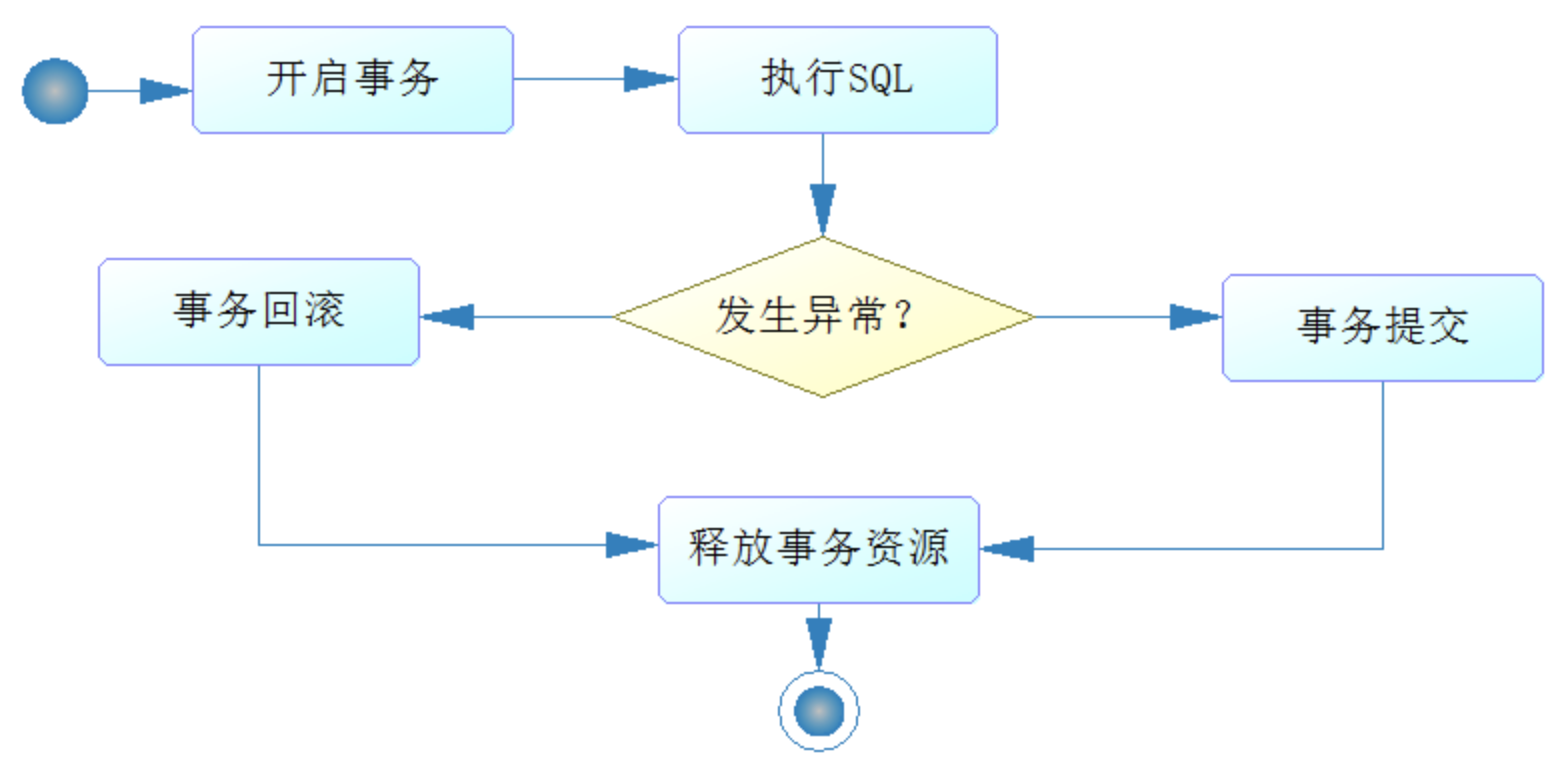
事务
执行SQL的事务流程
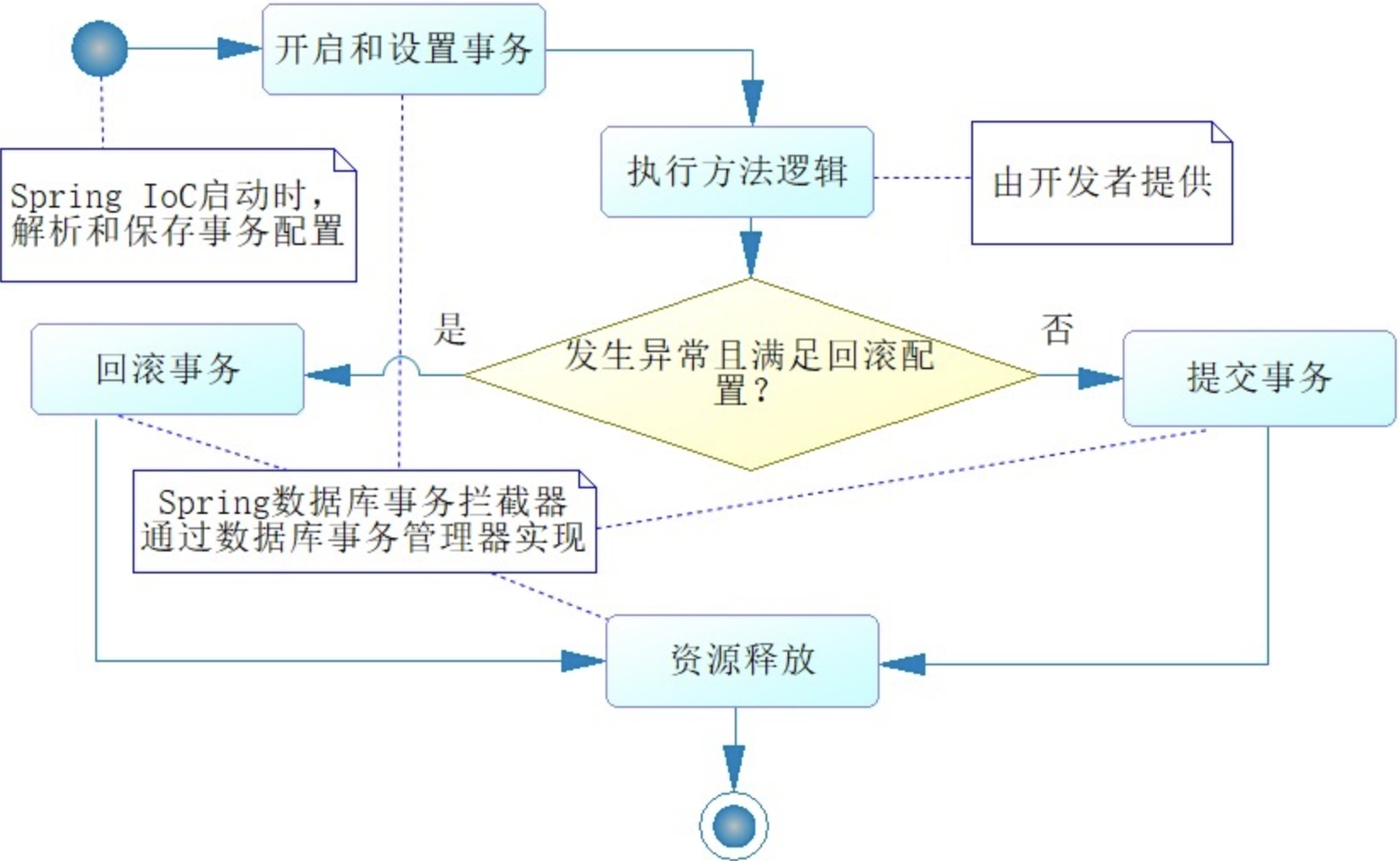
Spring 声明式事务
数据库事务
数据库事务具有以下4个基本特征,也就是著名的ACID。
Atomic(原子性)
事务中包含的操作被看作一个整体的业务单元,这个业务单元中的操作要么全部成功,要么全部失败,不会出现部分失败、部分成功的场景。
Consistency(一致性)
事务在完成时,必须使所有的数据都保持一致状态,在数据库中所有的修改都基于事务,保证了数据的完整性。
Isolation(隔离性)
这是我们讨论的核心内容,正如上述,可能多个应用程序线程同时访问同一数据,这样数据库同样的数据就会在各个不同的事务中被访问,这样会产生丢失更新。为了压制丢失更新的产生,数据库定义了隔离级别的概念,通过它的选择,可以在不同程度上压制丢失更新的发生。因为互联网的应用常常面对高并发的场景,所以隔离性是需要掌握的重点内容。
Durability(持久性)
事务结束后,所有的数据会固化到一个地方,如保存到磁盘当中,即使断电重启后也可以提供给应用程序访问。
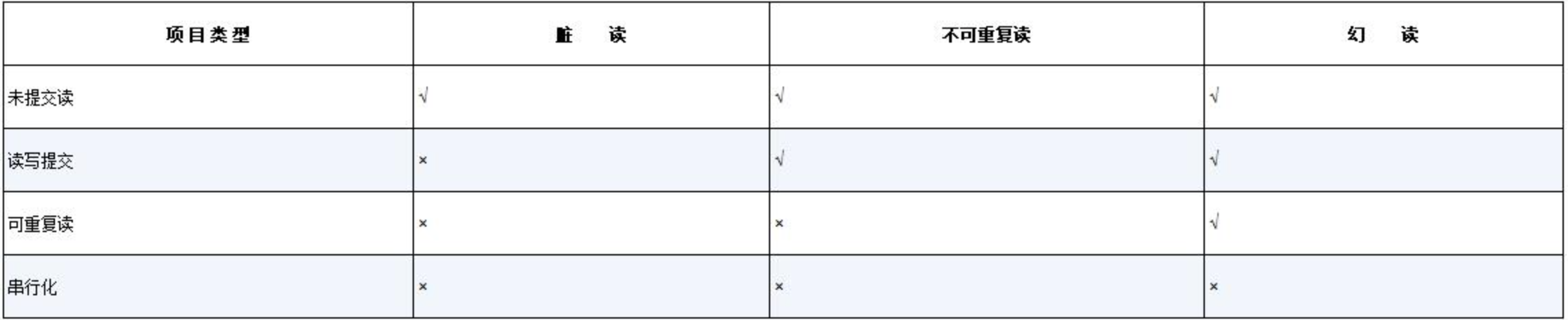
隔离级别
数据库标准
未提交读、读写提交、可重复读和串行化
未提交读
未提交读(read uncommitted)是最低的隔离级别,其含义是允许一个事务读取另外一个事务没有提交的数据。(脏读)
读写提交
读写提交(read committed)隔离级别,是指一个事务只能读取另外一个事务已经提交的数据,不能读取未提交的数据。(不可重复读)
可重复读
可重复读的目标是克服读写提交中出现的不可重复读的现象,因为在读写提交的时候,可能出现一些值的变化,影响当前事务的执行,这个时候数据库提出了可重复读的隔离级别。这样就能够克服不可重复读的现象
串行化
串行化(Serializable)是数据库最高的隔离级别,它会要求所有的SQL都会按照顺序执行,这样就可以克服上述隔离级别出现的各种问题,所以它能够完全保证数据的一致性。
/** Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors.** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.* You may obtain a copy of the License at** https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and* limitations under the License.*/package org.springframework.transaction.annotation;import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition;/*** Enumeration that represents transaction propagation behaviors for use* with the {@link Transactional} annotation, corresponding to the* {@link TransactionDefinition} interface.** @author Colin Sampaleanu* @author Juergen Hoeller* @since 1.2*/public enum Propagation {/*** 需要事务,它是默认传播行为,如果当前存在事务,就沿用当前事务,* 否则新建一个事务运行子方法** Support a current transaction, create a new one if none exists.* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p>This is the default setting of a transaction annotation.*/REQUIRED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED),/*** 支持事务,如果当前存在事务,就沿用当前事务;如果不存在,* 则继续采用无事务的方式运行子方法** Support a current transaction, execute non-transactionally if none exists.* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p>Note: For transaction managers with transaction synchronization,* {@code SUPPORTS} is slightly different from no transaction at all,* as it defines a transaction scope that synchronization will apply for.* As a consequence, the same resources (JDBC Connection, Hibernate Session, etc)* will be shared for the entire specified scope. Note that this depends on* the actual synchronization configuration of the transaction manager.* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#setTransactionSynchronization*/SUPPORTS(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS),/*** 必须使用事务,如果当前没有事务,则会抛出异常,* 如果存在当前事务,就沿用当前事务** Support a current transaction, throw an exception if none exists.* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.*/MANDATORY(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY),/*** 无论当前事务是否存在,都会创建新事务运行方法,* 这样新事物就可以拥有新的锁和隔离级别等特性,与当前事务相互独立** Create a new transaction, and suspend the current transaction if one exists.* Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager},* which requires the {@code javax.transaction.TransactionManager} to be* made available to it (which is server-specific in standard Java EE).* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager*/REQUIRES_NEW(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW),/*** 不支持事务,当前存在事务时,将挂起事务,运行方法** Execute non-transactionally, suspend the current transaction if one exists.* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager},* which requires the {@code javax.transaction.TransactionManager} to be* made available to it (which is server-specific in standard Java EE).* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager*/NOT_SUPPORTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED),/*** 不支持事务,如果当前方法存在事务,则抛出异常,否则继续使用无事务机制运行** Execute non-transactionally, throw an exception if a transaction exists.* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.*/NEVER(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER),/*** 在当前方法调用字方法时,如果子方法发生异常* 只回滚字方法执行过的SQL, 而不会滚当前方法的事务** Execute within a nested transaction if a current transaction exists,* behave like {@code REQUIRED} otherwise. There is no analogous feature in EJB.* <p>Note: Actual creation of a nested transaction will only work on specific* transaction managers. Out of the box, this only applies to the JDBC* DataSourceTransactionManager. Some JTA providers might support nested* transactions as well.* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager*/NESTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED);private final int value;Propagation(int value) {this.value = value;}public int value() {return this.value;}}

