剪辑自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/HfqH-b8x8SsE6zb8pcF3Og
原文:https://medium.com/@kelispinor/簡介-self-supervised-learning-的近期發展-2018-2020-a3872662727d
前言
今年(2020) Self Supervised Learning (SSL) 的研究来到了新的高峰。
不仅在 AAAI 上 LeCun, Bengio 与 Hinton 都对这领域寄与厚望; 最近发表的文章也显示 SSL 得到的模型表现在 ImageNet dataset 上逐渐逼近了传统 Supervised Learning 的表现了。
近年 ResNet-50 在 ImageNet 上的表现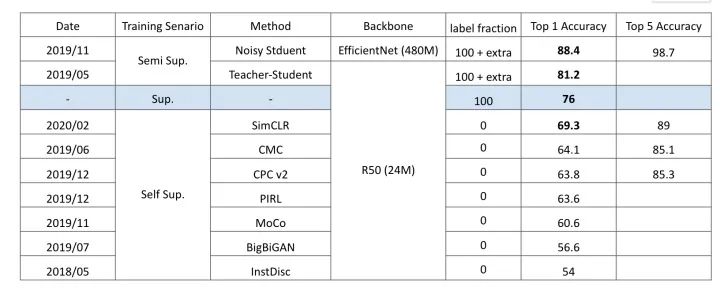
在实际应用中(例如业界中已经部署的模型), Self Supervised Learning 未必能直接有效的提升 Performance ,但阅读这些文章还是能得到不少启发。例如我们能对以下 Supervised Learning 问题有更多想法:
- 如果将 Deep Network 学习到有用的信息,人工标记 (Manual-Label) 是必要的吗?
- 数据( Data) 本身带有的信息是否比标记 (Label) 更加丰富?
- 我们能将每张图视为一个类别(Class); 甚至每一个 Pixel 都视为一个类别吗?
以上问题可能有点天马行空,如果在实际应用上我们能思考:
- 在 Representation Learning 中,如何能等价的增大 Batch Size?如何能维持 Embedding Space 的稳定性?
- 在 Deep Network 一定是最后一层具有最丰富的 Representation 吗?
- 听说 Deep Network 的 Capacity 很强大 ,但时至今日,我们是否已经达到 Model 能负荷的上限?(例如 ResNet-50 有 24M 个参数,号称拥有 ‘大数据’ 的人们,是否已经触碰到 Effective Upper-Bound of ResNet-50’s Model Complexity?)
- 如果 Model Complexity 远超乎我们想象,那什么样的 Training Procedure 能最有效率的将信息储存于 Deep Network 中?
- Data Augmentation 是学习 Deep Learning 一定会接触到的方法,它只是一个方便 Training 的 Trick 呢?还是他对 Network 有特殊意义?
这些问题目前没人能给出确切答案,但在接下来的文章中必然能带来更多想法与启发。
Before SSL Revolution:Pretext Task
早期在探索 SSL 的想法相对单纯,如果没有得到 Label ,就利用 Rule-Based 的方法生成一些 Label 。比较著名的方法为
- Rotation
- Jigsaw Puzzle
- Colorization
“Unsupervised Representation Learning by Predicting Image Rotations” 一文中提出 Rotation 可谓是 SSL 之滥觞。将给定的 Image 旋转固定的 0, 90, 180, 270 四种角度,让 Network 预测看到的图是原图被转了几度后的结果。
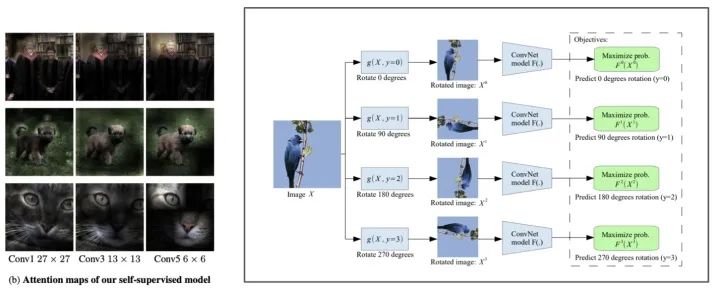
Unsupervised Representation Learning by Predicting Image Rotations https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.07728.pdf
乍听之下,预测旋转角度挺没意思的,但是如果 Training Data 是整个 ImageNet 时,这样的任务就变成相当有趣了。Network 必须了解了什么是对象后,才能了解旋转。这也贯策了 SSL 的基本想法:Knowledge Before Task.

Unsupervised Learning of Visual Representations by Solving Jigsaw Puzzles https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.09246
后来的 Jigsaw 与 Colorization 基本上延续了这种探索 Image 本质的想法,设计出能帮助理解 Content 的辅助任务,因此这类方法统称为 Pretext Task (委托任务)。其中 Colorization 这个方法,能延伸出 Tracking 的效果,着实让人震惊。
Huge Improvement:Contrastive Learning
“Data-Centric” Loss
另一派做法是从设计 Loss Function 下手,找出能探索数据本身性质的 Loss。
其中 Energy-Based Model 算是 LeCun 从以前到现在不断推广的,这种模型与具有强烈的物理意义,可能会是明日之星; 而这篇文章整理的是另一种以 Mutual Information 为主的 Loss Function。
AutoRegressive Model
说到理解数据,最直观的机率模型就是建立 Data Likelihood,而在 Computer Vision 的领域中,最强大的莫过于 PixelCNN 这种 Pixel-by-Pixel 的建模方法了。使用 Chain Rule,Network 能够完整 Encode 所有信息。
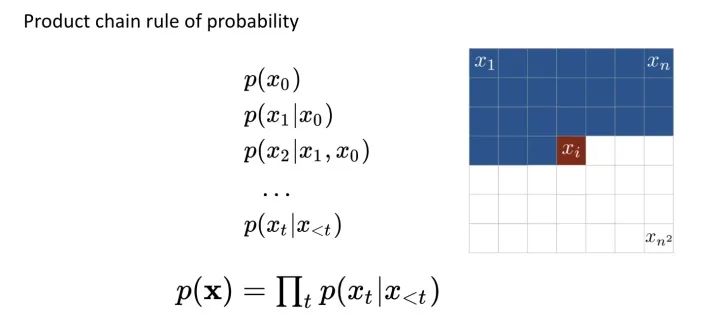
Conditional Image Generation with PixelCNN Decoders https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6527-conditional-image-generation-with-pixelcnn-decoders.pdf
但是 Representation Learning 在乎的并不是整个 Data Distribution; 而是怎么得到更抽象、High-level 的表示法。End-to-End Training 让人们发现,Deep Neural Network 是有能力解构数据的 Hierarchical Internal Representation 的,何不利用这种强大的能力呢?
也就是Learn the dataset, not the data points.
InfoNCE
DeepMind 在 2017 年(https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.03748)提出一种基于Mutual Information修改 AutoRegrssive 的 Loss Function,称为 InfoNCE 。
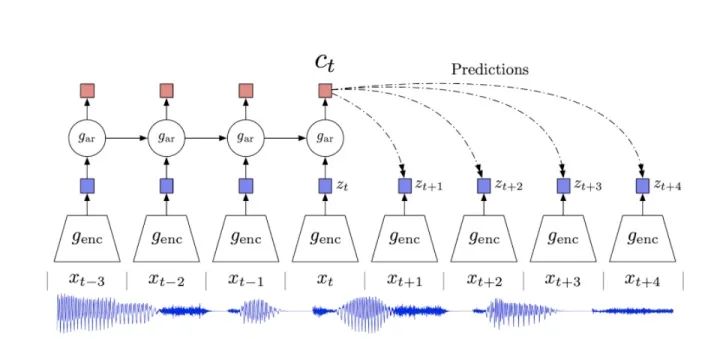
https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.03748
从图上说明是相当直观的,模型基于看过的 Data 提取 Context (也就是 Feature) 并且对未来做预测。并且 Loss Function 的目标是让 Data 和 Context 的 Mutual Information 越大越好。
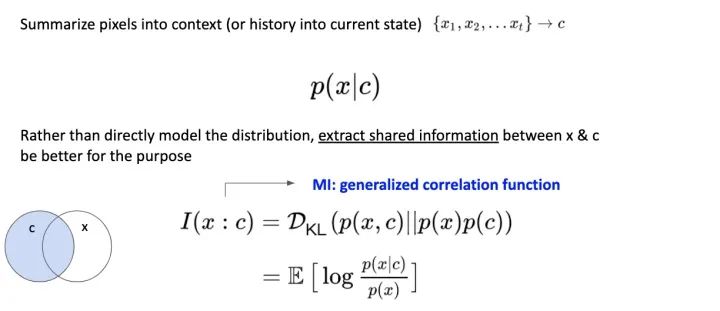
Mutual Information 是广义上的 Correlation Function。(当我们完全不了解系统的 Dynamics 或更深入的行为时,Mutual Information 依旧能作为估算) 它量化了我们能从 Context 中得到多少 Data 的信息,称为 Data 与 Context 之间的 Mutual Information。
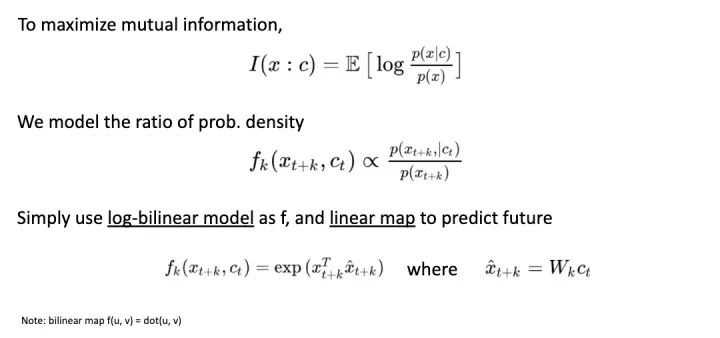
首先,为了最大化 Mutual Information 让 Network Model Distribution Ratio (而不像 generative model 是单纯 model distribution); 并且用简单的 Linear Map 作为从 Context 到 Future Data 的预测函数。
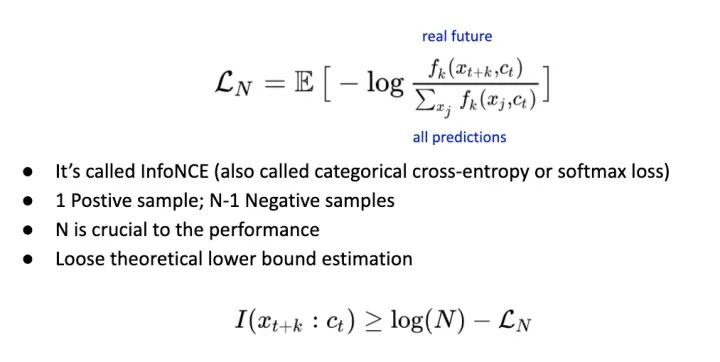
InfoNCE 写法如下。其实他与常用的 Cross Entropy Loss 并没有太大区别,差异只在于这个 Loss 并不是用于分类,而是注重在对数据的本身做预测。如果用先前 Time Series 的例子就是预测未来。
Learning Deep Representations of Fine-grained Visual Descriptions
我们把所唯一正确的预测称为 Positive Sample; 其它的预测通通为 Negative Samples。文章接下来都使用 Contrastive Loss 来表示这种 Training 方法。
另外 InfoNCE 有一个 Weak Lower-Bound 在描述 N 的重要,也就是越多的 Negative Samples 时,Loss Function 越能控制 Mutual Information,并且是以 Log 的方式 Scale (这给了 Metric Learning 一点 Hint, Batch Size 可能随着 log scale)。
CPC:Contrastive Predictive
第一个成功在 Image Classification 实践出 InfoNCE 的是 CPC 这篇文章 (基本上是 DeepMind 同一个 team 的作品)。很直观的利用在图片上裁切 Patch 的方式,做出 Positive & Negative samples,实现 Contrastive Loss 。
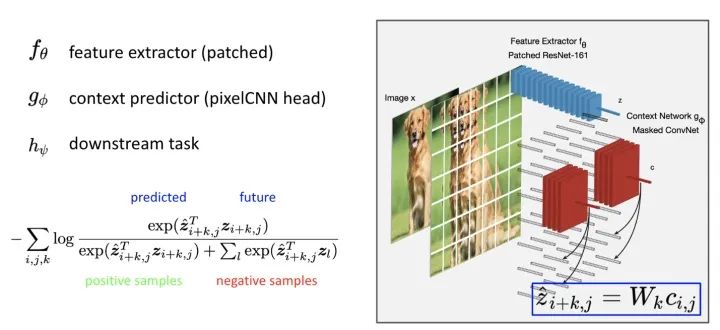
Data-Efficient Image Recognition with Contrastive Predictive https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.09272
这边用到了三个 Network,分别是 feature extractor, context prediction 跟 downstream task network。这是因问 SSL 的 evaluation 方式不同的关系,这边简单说明一下。
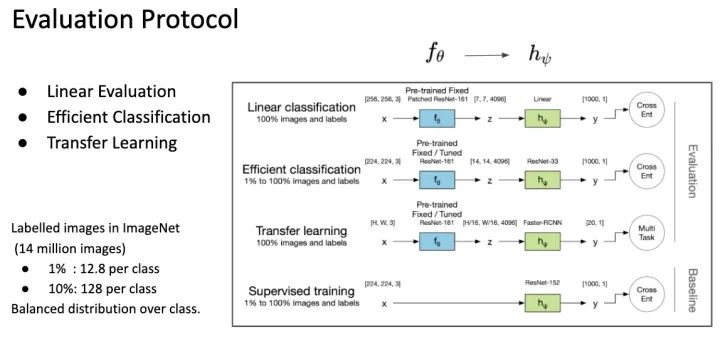
SSL 训练出来的模型基本上不能直接使用,通常只能作为很强的 Pretrained Model。因此要评估 Pretrained Model 好坏通常做 Linear Evaluation ,Fine-tune 一个 Linear Classifier 看能达到多少的准确度(为了公平,通常这个 classifier 会用 grid search 得到)。
研究后来发现, SSL Pretrained Model 不仅得到 Linear Separable 的 Feature Space; 并且这些 Feature 是很丰富的,因为只需要少量的 Data 就可以达到很好的效果,这称为 Efficient Classification Evaluation。像常常会测试,拿 ImageNet (有 1000 类一千四百万张图片) 1% 的资料量(也就是每个类别 Randomly choose 12 张图片) 来训练。这种 Evaluation 凸显出 Feature 是能广泛描述各种类别的,因此只要取少少的 Samples 就可以达到效果。
第三种 Evaluation 就是将 Pretrained Model 运用在各种 Vision Task 上,例如拿到 Object Detection 或 Segmentation 任务上依旧能表现不错。
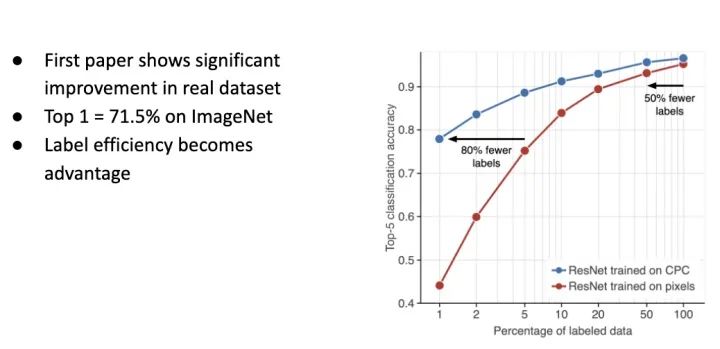
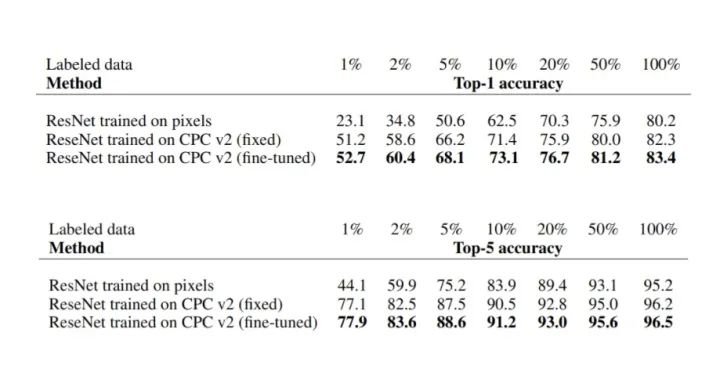
回到 CPC 这篇文章,ResNet-50 Linear Protocol 能达到 Top-1 71.5% 的准确率; 在 Efficient Classification Protocol 上,能比原本 Supervised Learning 的方式省掉至少 50% ~ 80% 的资料(这边是参数更多的 ResNet)。意味着通过 SSL Pretrained Model,我能够少一些人工标记一样能达到原本 Supervised Learning 的准确度。
What Important?
CPC 带来巨大的好处,但什么事情是重要的?难道以后都需要将一张图切很多 Patch 来预测吗?并不尽然。
在 CMC 这边文章中表明了,使用不同场景 (View Point, Depth, Color Space) 来计算 Contrastive Loss 能达到非常好的效果,因此 Contrastive 本身 (也就是辨认 Positive & Negative Sample 之间的 Consistency) 才是关键。
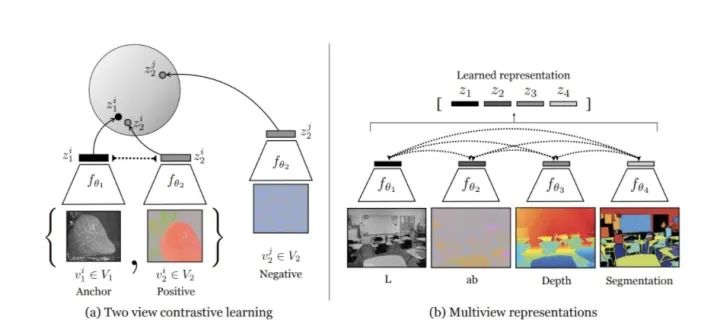
Contrastive Multiview Coding https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.05849
另外 Google 做了大规模的定性实验,找出了几个对 Visual Representation 最有影响的因子,因为篇幅关系就节录下列重点
- Pretext Task 不一定能在 Downstream Task 上達到好的效果
- ResNet 的 skip-connection 能防止 feature quality 下降
- 增大 Model Size 和增加 Embedding Dimension 能有效提升 Performance
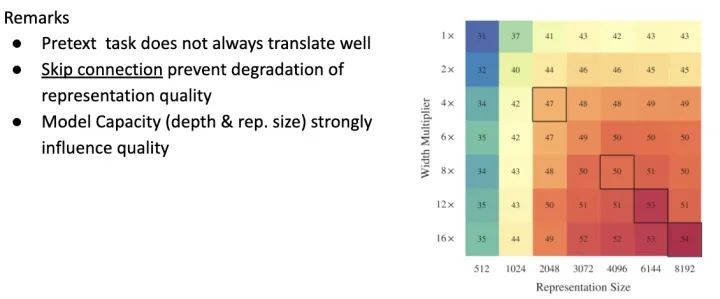
Revisiting Self-Supervised Visual Representation Learning https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.09005
到目前为止基本上定调了 SSL 的走向
- Contrastive Learning 能从 Data 中获得相当丰富的信息,不需要拘泥在 Patch 上
- 使用 ResNet 这种 Backbone (而非早期 paper 强调 VGG 能得到更好的 representation)
接下来的文章,都基于这样的前提来 Improve 。
MoCo:Momentum Contrast
这篇 MoCo 是 Kaiming He 在 FAIR (又是与 RGB 一起)第一次对 SSL 问题提出的文章。算是一个相当 Engineering 的解法,来有效增加 Batch Size,提升 Performance。
Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.05722
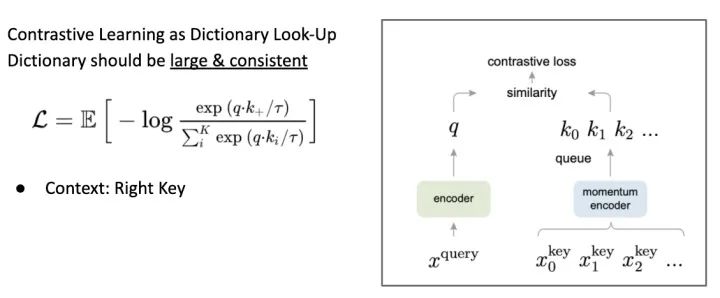
首先,我们可以完全忘掉过去 AutoRegressive 预测未来的观点; 或切 Patch 预测图片结构。MoCo 完全专注在 Contrastive Loss 上,将这个问题想象成有一个很大的 Dictionary ,Network 的目的就是一个 Encoder 要将图片 Encode 成唯一的一把 Key ,此时要如何做到让 Key Space Large and Consistent 是最重要的。
首先借鉴了另一篇 SSL 的文章 Memory Bank ,建一个 Bank 来存下所有的 Key (或称为 Feature) 。此方法相对把所有图塞进 Batch 少用很多内存,但对于很大的 Dataset 依旧难以 Scale Up。
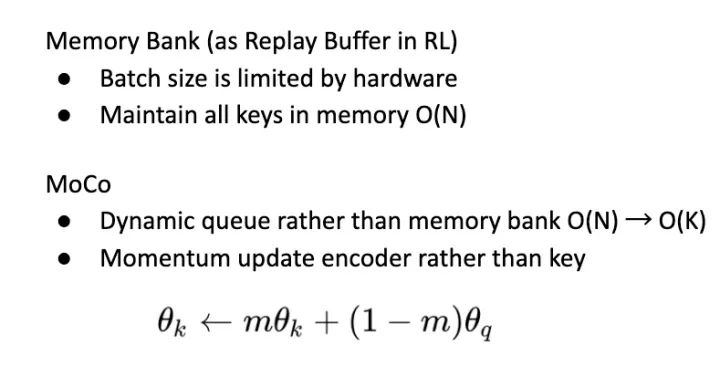
Unsupervised Feature Learning via Non-Parametric Instance-level Discrimination https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.01978
MoCo 改善了 Bank,用一个 Dynamic Queue 来取代,但是单纯这样做的话是行不通的,因为每次个 Key 会受到 Network 改变太多,Contrastive Loss 无法收敛。因此 MoCo 将种子 feature extractor 拆成两个独立的 Network:Encoder 和 Momentum Encoder。

MoCo Algorithm
我们可以想象成这样的情境,Momentum Encoder 随着 Training Update 很慢,因此能提供很稳定的 Key ,也就是 Momentum Encoder 把这个 Key Space 先摆好; 当新的 Positive 经过 Encoder 进来时,跟所有其他的 Negative Sample 计算 Similarity ,如果 New Key 与原本的 Key 太近容易混淆,这时候的 Loss 绝大部分会 Update 给 Encoder (相当于找一个比较空的区域放 Key, 而不影响原本的其他 Key)。

等 Encoder Update 完后,在用 Momentum Update Slow Encoder。并将这次的 Batch 放进 Dynamic Queue 中。
从以下实验可以看到,MoCo 的表现几乎与暴力将 Batch Size 增大得到的效果一样,但是 Batch Size 没办法 Scale Up; Memory Bank 与 MoCo 有着一样的 Scaling Property,但 MoCo 的 Momentum Update 提供稳定的 Key Space 让整体 Performance 可以提升约 2%。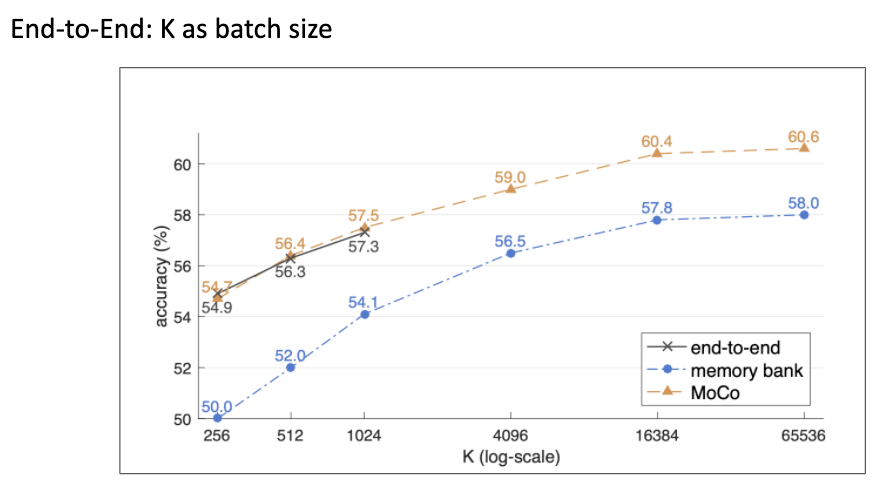
SimCLR:Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning
在 MoCo 之后发出来的论文是出自今年 (2020) 产量很高的 Hinton 之手。并且达到 SSL 当前 Linear Protocol State-of-The-Art 的记录。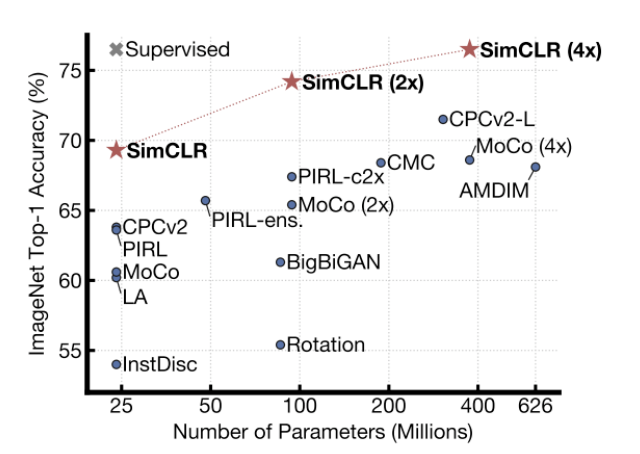
A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.05709
文章更专注在 Contrastive Loss ,并且发现几点重要因素,包括先前已知的 Batch Size, Embedding Size (与 Normalization)。
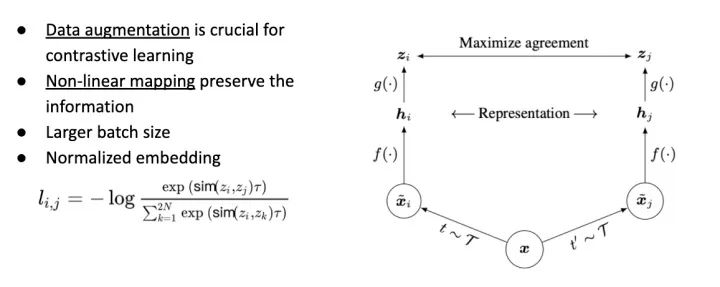
另外两点相当有意思,一点是 Data Augmentation 对 Contrastive Learning 的重要性; 一点是利用一个 Non-Linear Map 来避免 Feature 的 Information Loss。
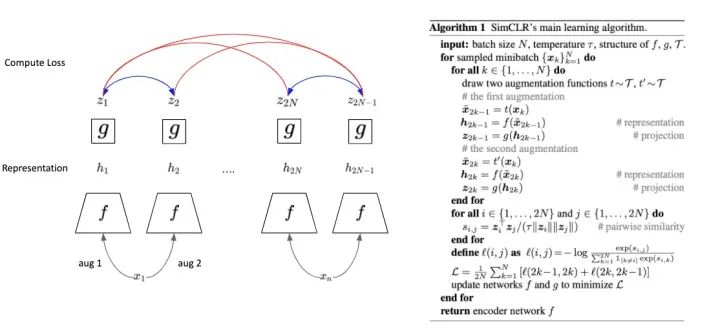
SimCLR 做了大量的 Augmentation ,并且是 Augmentation 的组合。
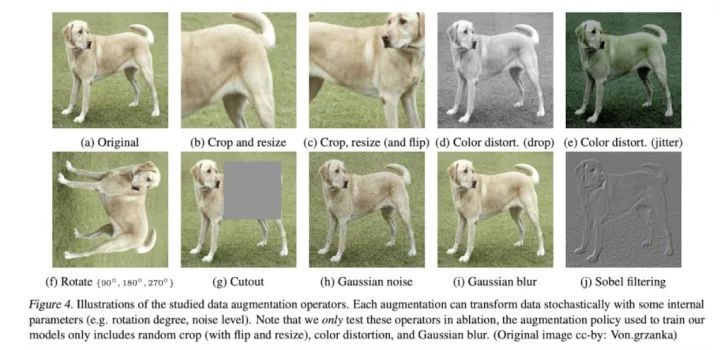
用几种常见的 Data Augmentation
在实验中发现,Color Distortion + Random Crop 效果提升的相当显著。这是因为原本的 Random Crop 切出来的图片 Distribution 其实相差不大,可以说是无效的 Patch (尤其对于 Contrastive Learning 来说相当不好),这两种 Operation 混合后会让 Distribution 大相径庭,能产生更多有效的 Negative Samples。
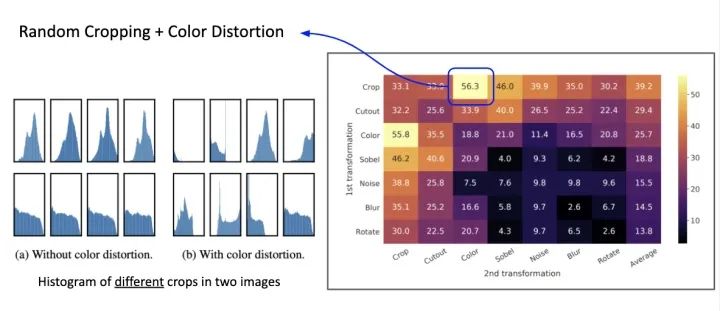
如果有仔细看 CPC 原文的读者也会发现,CPC 中提到的使用 Layer Normalization 取代 Batch Normalization 以避免 Model 太容易受到 Patch 的统计性质混淆有异曲同工之妙。
文章另一个亮点是,在算 Loss 之前加上一个 Layer,避免 Visual Representation 直接丢给 Contrastive Loss Function 计算。原因是这种比较 Similarity 的 Loss Function 可能会把一些信息给丢掉。
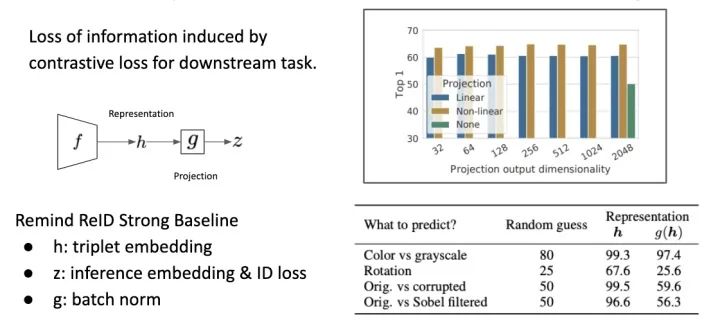
Bag of Tricks and A Strong Baseline for Deep Person Re-identification http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPRW_2019/papers/TRMTMCT/Luo_Bag_of_Tricks_and_a_Strong_Baseline_for_Deep_Person_CVPRW_2019_paper.pdf
文中做了一些实验,像是颜色、旋转这种信息,就会大幅度的被删除; 而加上一个 Nonlinar Map,这样可以大幅度地保存 Information。这跟 ReID 中一篇有名的文章 Bag of Tricks and A Strong Baseline for Deep Person Re-identification 的一种架构有点相似,让不同层的 Feature 给不同的 Loss 免于 Information Loss。
最后呢,有钱人的研究也是朴实无华且枯燥的,这就是标题 Simple 的来源。
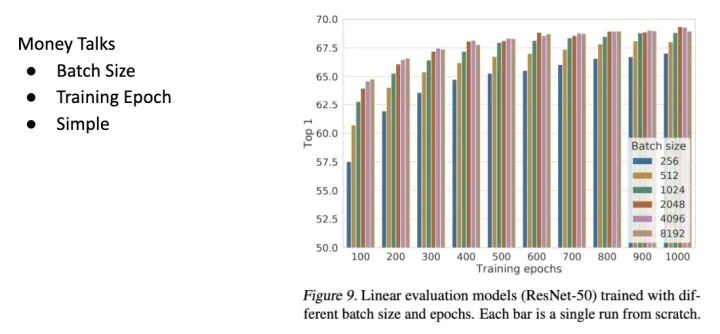
这张图表现出了一件事, Contrastive Learning 是一种能从 Data 本身获取信息的 Loss Function ; 而且 Data 本身的信息量远远多出 Label 很多,因此就算经过非常长时间的 Training,Model 并没有任何 Overfit 的迹象。
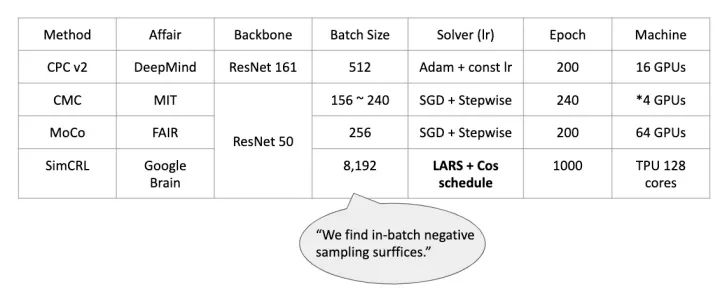
各方法用到的 Resources
Self-Supervised Learning 到目前为止展现了相当大的潜力,尤其是 Contrastive Learning 的方法,在资源丰沛的情况下,可以佣简单的架构便达到逼近 Supervised Learning 的效果,甚至在 Model Capacity 增加的情况下,能与 Supervised Learning 平起平坐。但如果要完全超过 Supervised Learning 的表现要怎么做呢?
Semi-Supervised Learning
Teacher-Student
Teacher-Student (Knowledge Distillation)是一种相当有效率的做法,他的精神类似 SSL 并且能从 Data 本身获取更多的信息。
Billion-scale semi-supervised learning for image classification https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.00546
利用有 Label 的数据训练 Teacher,并让 Teacher 标记 Unlabel Data ,再交给 Student 学习。在实验上也可以发现,这种方法能随这数据量越多越有效,并且在 Supervised Learning 方法已经 Overfit 时,Semi-Supervised 还可以继续学习。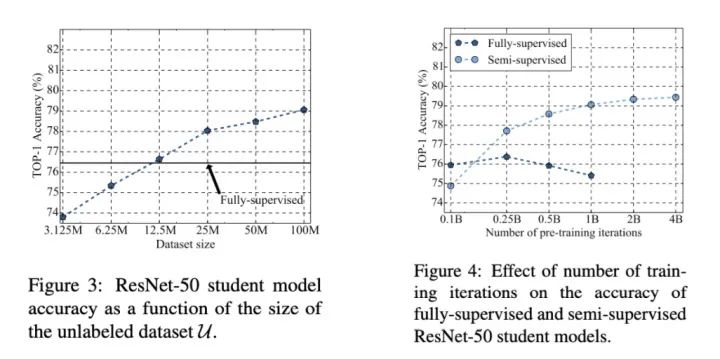
Noisy-Student
Google 也在这个方法上做了修改,让 Student 随着过程中能增大,并且加入更多干扰,确保学到的东西能 General 到真实情况。
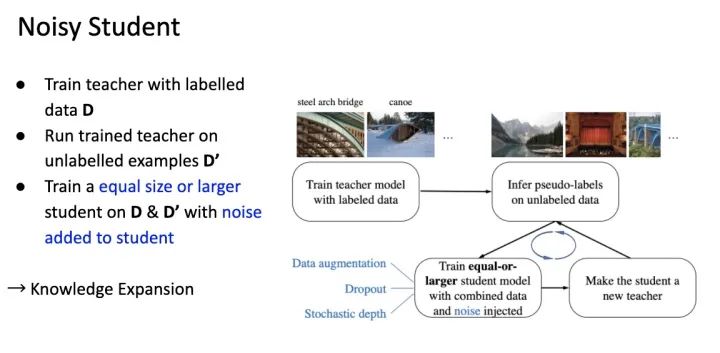
Self-training with Noisy Student improves ImageNet classification https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.04252
这里的干扰有两个:Data 上的 Augmentation 和 Architecture 上的 Randomness。
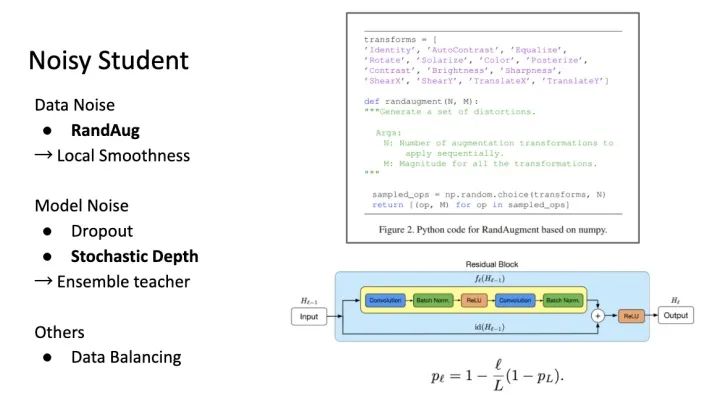
Deep Networks with Stochastic Depth https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.09382
RandAugment:Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.13719
一方面让 Student 有 Ensemble 的特性; 一放面让 Student 随着 Knowledge 增加可以增大。此方法下能达到目前 ImageNet 最高分 Top-1 Accuracy 88.4%。

最后用这张图总结数据与 Network 的发展:
- 如果在单纯 Supervised Learning 的情况下,研究 Architecture 带来的效果是相当显著的,人类目前得到 10% 的进步。
- 如果在限定架构的情况下,通过有效率的 Training 流程,从 Data 本身学习 (Unlabelled Data) ,也能得到显著提升。从 76% 能到 81.2%; 从 85.5% 能到当前 SOTA (88.4%)
Self-Supervised Learning 与 Semi-Supervised Learning 想传达的概念不尽相同,如果我们能从 Data 本身中,有效率的获取信息,那将比传统的 Manual Labelling 表现更好、学到的信息更丰富并且更能随着问题 Scaling Up。
References
1.Unsupervised Representation Learning by Predicting Image Rotations
2.Unsupervised Learning of Visual Representations by Solving Jigsaw Puzzles
3.Tracking Emerges by Colorizing Videos
4.Conditional Image Generation with PixelCNN Decoders
5.Representation Learning with Contrastive Predictive 编码
6.Learning Deep Representations of Fine-grained Visual Descriptions
7.Data-Efficient Image Recognition with Contrastive Predictive 编码编码
8.Contrastive Multiview 编码
9.Revisiting Self-Supervised Visual Representation Learning
10.Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning
11.Unsupervised Feature Learning via Non-Parametric Instance-level Discrimination
12.A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations
13.Billion-scale semi-supervised learning for image classification
14.Self-training with Noisy Student improves ImageNet classification
15.Deep Networks with Stochastic Depth
16.RandAugment:Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space

