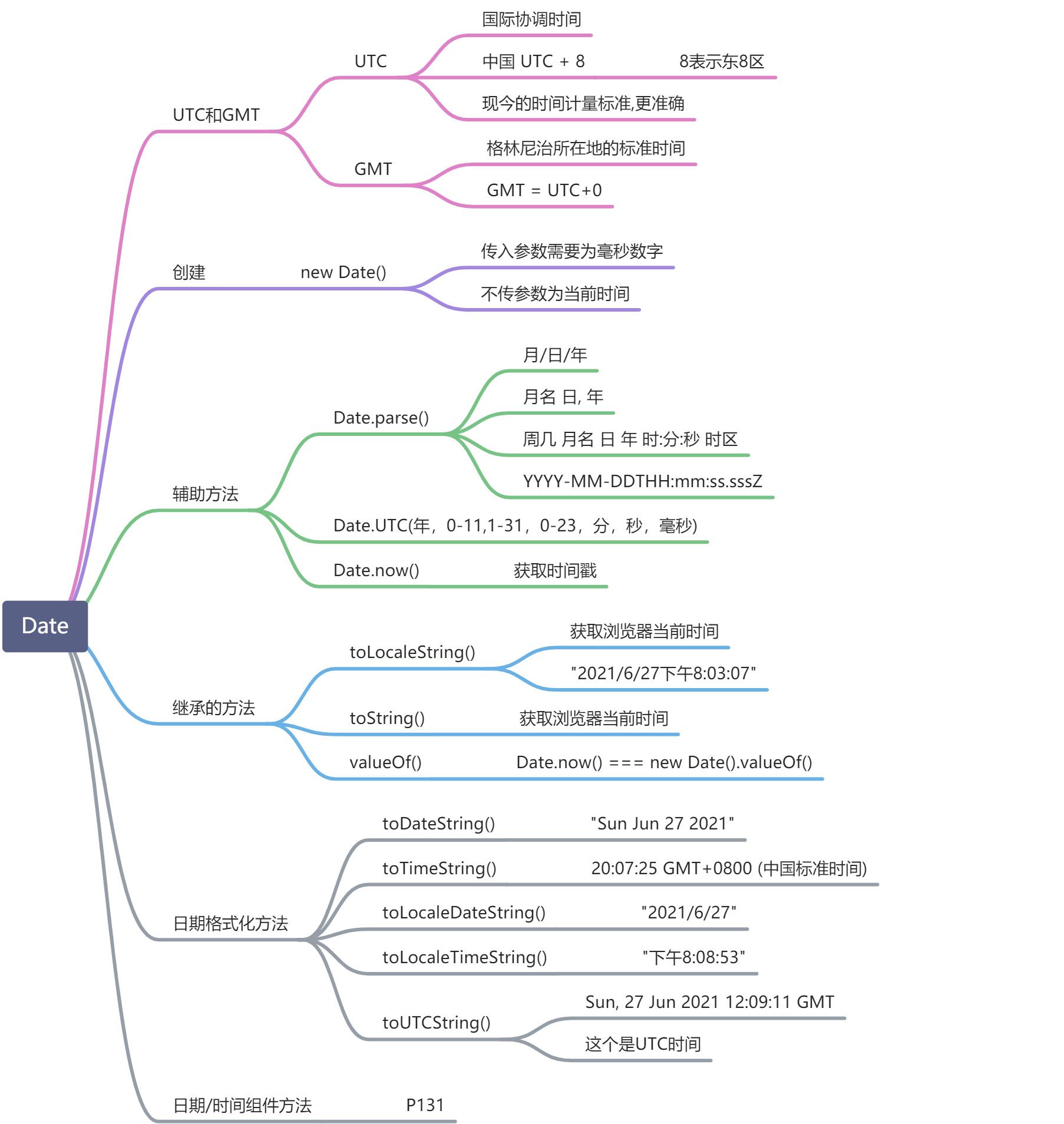
Date
RegExp
标记
- g —全局匹配
- i — 忽略大小写
- m — 多行匹配
- y — 粘附, 只查找lastindex开始及其之后的字符串
- u — unicode匹配
s — doall,表示. 匹配任何字符(包括\n 和 \r)
元字符
( [ { \ ^ $ | ) ] } ? * + . — 需要\进行转义
/*** @description 如果字符串没有经过处理直接正则匹配会报错,所以需要转换* @param {string} string 当前传入的字符串* @returns 返回处理好的字符串*/function regExpase(string) {const reg = /[\\"'()[\]{}|*.?+$^]/g;let regSource = RegExp(reg.source);/* $&匹配到的每一项,前面加\ */return (string && regSource.test(string)) ? string.replace(reg, '\\$&') : (string || '');}
实例属性
global — bool 是否开启全局匹配
- ignoreCase — bool 是否忽略大小写
- unicode — bool 是否设置了u匹配标记
- sticky — bool 是否开启y匹配
- lastIndex — number 下一次搜索的位置
- multiline — bool 是否多行匹配
- dotAll — bool 是否全匹配
- source — 拿到当前匹配的字符串 字面量
-
实例方法
exec — 返回第一个匹配信息的数组,没有找到返回null,包含两个额外属性,index:当前匹配的起始位置,input:要查到的字符串。如果使用了全局模式,每一次都会继续向下查找而不是从第一个查找。
let text = "mom and dad and baby";let pattern = /mom( and dad( and baby)?)?/gi;let matches = pattern.exec(text);console.log(matches.index); // 0console.log(matches.input); // "mom and dad and baby"console.log(matches[0]); // "mom and dad and baby"console.log(matches[1]); // " and dad and baby"console.log(matches[2]); // " and baby"
test —- 接受字符串,返回true和false,测试是否匹配
继承方法
// 都会返回当前字面量let pattern = new RegExp("\\[bc\\]at", "gi");console.log(pattern.toString()); // /\[bc\]at/giconsole.log(pattern.toLocaleString()); // /\[bc\]at/gi
构造函数属性
RegExp 构造函数的所有属性都没有任何 Web 标准出处,因此不要在生产环境中使 用它们。
input — $_ 最后搜索的字符串(非标准特性)
- lastMatch — $& 最后匹配的文本
- lastParen — $+ 最后匹配的捕获组(非标准特性)
- leftContext — $` input 字符串中出现在 lastMatch 前面的文本
- rightContext — $’ input 字符串中出现在 lastMatch 后面的文本
let text = "this has been a short summer";let pattern = /(.)hort/g;if (pattern.test(text)) {console.log(RegExp.input); // this has been a short summerconsole.log(RegExp.leftContext); // this has been aconsole.log(RegExp.rightContext); // summerconsole.log(RegExp.lastMatch); // shortconsole.log(RegExp.lastParen); // s}