固定运行顺序
wait-notify 实现
采用 wait-notify 机制可以实现对线程执行顺序的控制,我们只需要一个执行标志即可,如下代码所示:
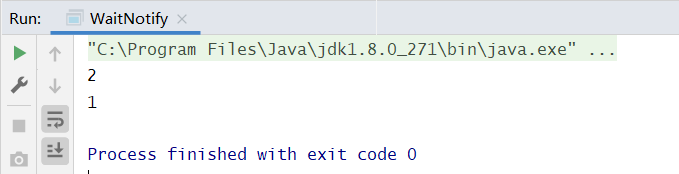
public class WaitNotify {// 用来同步的对象static Object obj = new Object();// t2 运行标记, 代表 t2 是否执行过static boolean t2runed = false;public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {synchronized (obj) {// 如果 t2 没有执行过while (!t2runed) {try {// t1 先等一会obj.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}System.out.println(1);});Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(2);synchronized (obj) {// 修改运行标记t2runed = true;// 通知 obj 上等待的线程(可能有多个,因此需要用 notifyAll)obj.notifyAll();}});t1.start();t2.start();}}
park-unpark 实现
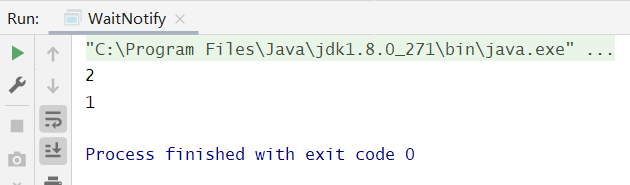
public class ParkUnpark {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {LockSupport.park();System.out.println("1");}, "t1");Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {System.out.println("2");LockSupport.unpark(t1);}, "t2");t1.start();t2.start();}}
交替运行顺序
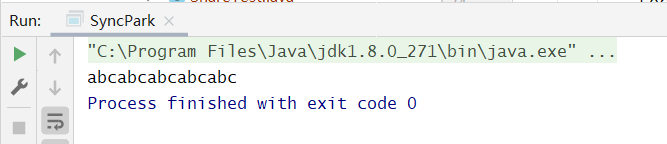
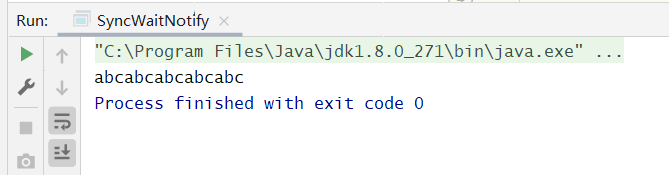
要求依次“线程1输出a,线程2输出b,线程3输出c”,这样循环5次。即利用三个线程输出“abcabcabcabcabc”这样的结构。
wait-notify 实现
public class SyncWaitNotify {private int flag;private final int loopNums;public SyncWaitNotify(int flag, int loopNums) {this.flag = flag;this.loopNums = loopNums;}@SneakyThrowspublic void print(int curFlag, int nextFlag, String content) {for (int i = 0; i < loopNums; i++) {synchronized (this) {//如果curFlag 和当前线程执行 flag 不相同while (this.flag != curFlag) {wait();}System.out.print(content);flag = nextFlag;notifyAll();}}}public static void main(String[] args) {SyncWaitNotify syncWaitNotify = new SyncWaitNotify(1, 5);//线程1打印 a -->flag=1new Thread(() -> {syncWaitNotify.print(1, 2, "a");}).start();//线程2打印 b -->flag=2new Thread(() -> {syncWaitNotify.print(2, 3, "b");}).start();//线程3打印 c -->flag=3new Thread(() -> {syncWaitNotify.print(3, 1, "c");}).start();}}
await-signal 实现
public class AwaitSignal extends ReentrantLock {// 循环次数private final int loopNumber;public AwaitSignal(int loopNumber) {this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}public void start(Condition first) {this.lock();try {first.signal();} finally {this.unlock();}}public void print(String str, Condition current, Condition next) {for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {this.lock();try {current.await();System.out.print(str);next.signal();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {this.unlock();}}}public static void main(String[] args) {AwaitSignal as = new AwaitSignal(5);//线程1的等待室Condition aWaitSet = as.newCondition();//线程2的等待室Condition bWaitSet = as.newCondition();//线程3的等待室Condition cWaitSet = as.newCondition();//线程1打印 anew Thread(() -> {as.print("a", aWaitSet, bWaitSet);}).start();//线程2打印 bnew Thread(() -> {as.print("b", bWaitSet, cWaitSet);}).start();//线程3打印 cnew Thread(() -> {as.print("c", cWaitSet, aWaitSet);}).start();//先唤醒 aWaitSet 中的线程1as.start(aWaitSet);}}
park-unpark 实现
public class SyncPark {private final int loopNumber;private Thread[] threads;public SyncPark(int loopNumber) {this.loopNumber = loopNumber;}public void setThreads(Thread... threads) {this.threads = threads;}public void print(String str) {for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {LockSupport.park();System.out.print(str);//输出str后,让下一个线程运行LockSupport.unpark(nextThread());}}private Thread nextThread() {Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int index = 0;for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {if (threads[i] == current) {index = i;break;}}if (index < threads.length - 1) {return threads[index + 1];} else {return threads[0];}}public void start() {for (Thread thread : threads) {thread.start();}//先让 threads[0] 执行LockSupport.unpark(threads[0]);}public static void main(String[] args) {SyncPark syncPark = new SyncPark(5);Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {syncPark.print("a");});Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {syncPark.print("b");});Thread t3 = new Thread(() -> {syncPark.print("c");});syncPark.setThreads(t1, t2, t3);syncPark.start();}}