集合框架的概述
1.集合、数组都是对多个数据进行存储操作的结构,简称Java容器
说明:此时的存储,主要指的是内存层面的存储,不涉及到持久化的存储(.txt,.jpg,.avi,数据库中)
2.数组在存储多个数据方面的特点
>一旦初始化以后,其长度就确定了
>数组一旦定义好,其元素的类型也就确定了。我们也就只能操作指定类型的数据了
比如:String[] arr;int[] arr1;Object[] arrr2
3.数组存储多个数据方面的缺点
>一旦初始化以后,其长度就不可修改
>数组中提供的方法非常有限,对于添加、删除、插入数据等操作,非常不便,同时效率不高
>获取数组中实际元素的个数的需求,数组没有现成的属性或方法可用
>数组存储数据的特点:有序、可重复。对于无序、不可重复的需求,不能满足
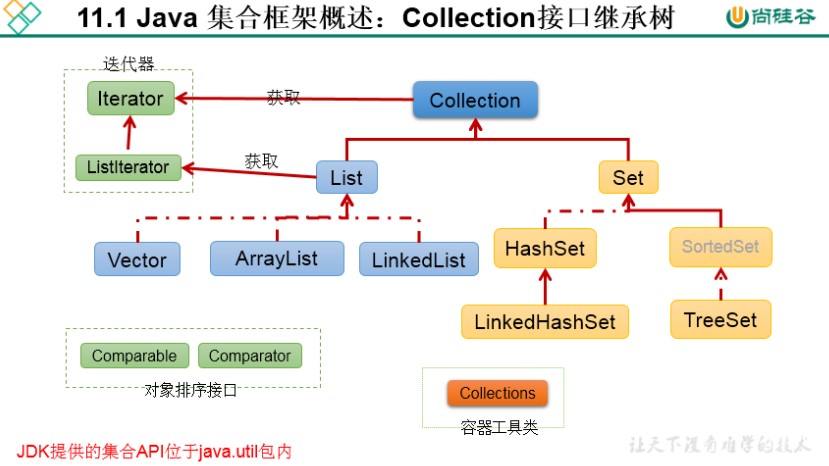
集合框架
Collection接口:单列集合,用来存储一个一个的对象
List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据 —- >”动态”数组
ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
set接口:存储无序的、不可重复的数据 —->高中讲的”集合”
HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet
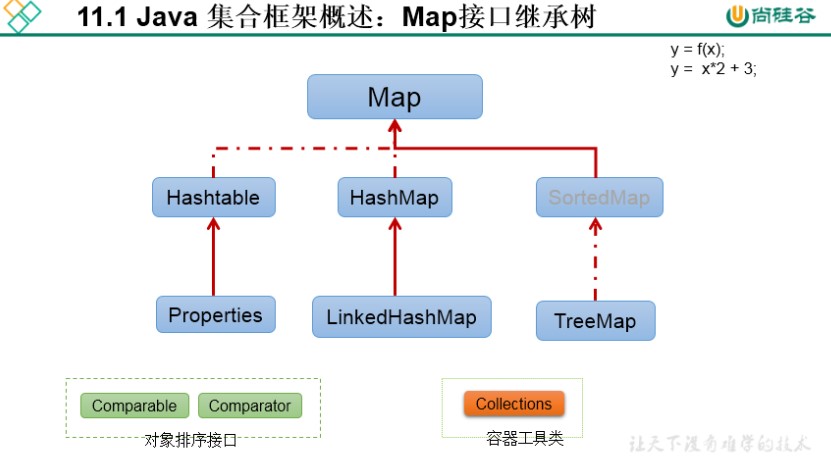
Map接口:双列集合,用来存储一对(key - value)一对的数据 —>高中函数
HashMap、LinkedHashMap/TreeMap/Hashable/Properties
Collection接口中常用方法
public void test1(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();//add(Object e):将元素e添加到集合coll中coll.add("AA");coll.add("BB");coll.add(123);//自动装箱coll.add(new Date());//size():获取添加的元素的个数System.out.println(coll.size());//4//addAll(Collection coll1):将coll1集合中的元素添加到当前的集合中Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();coll1.add(456);coll1.add("CC");coll.addAll(coll1);System.out.println(coll.size());//6//clear():清空集合元素coll.clear();System.out.println(coll);//[]//isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空System.out.println(coll.isEmpty());//true}
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.List;public class CollectionTest1 {@Testpublic void test1(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add(123);coll.add(456);coll.add("AA");coll.add(new String("Tom"));coll.add(false);coll.add(new People("jerry", 19));//1.contains(Object obj):判断当前集合中是否包含obj//我们在判断时会调用obj对象所在类的equals()boolean contains = coll.contains(123);System.out.println(contains);//trueSystem.out.println(coll.contains(new String("Tom")));//trueSystem.out.println(coll.contains(new People()));//true//2.containsAll(Collection coll1):判断形参从coll1中的所有元素是否都存在于当前集合中Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,456);System.out.println(coll.containsAll(coll1));//true}@Testpublic void test2(){//3.remove(Object obj):从当前集合中移除obj元素Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add(123);coll.add(456);coll.add("AA");coll.add(new String("Tom"));coll.add(false);coll.add(new People("jerry", 19));coll.remove(1234);//System.out.println(coll);coll.remove(new People("jerry", 19));System.out.println(coll);//4.removeAll(Collection coll1):从当前集合中移除coll1中所有的元素Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,456);coll.removeAll(coll1);System.out.println(coll);}@Testpublic void test3(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add(123);coll.add(456);coll.add("AA");coll.add(new String("Tom"));coll.add(false);coll.add(new People("jerry", 19));//5.retainAll(Collection coll1):交集:获取当前集合和coll1集合的交集,并返回给当前集合//Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,4567);//coll.retainAll(coll1);//System.out.println(coll);//6.equals(Object obj):Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();coll1.add(123);coll1.add(456);coll1.add("AA");coll1.add(new String("Tom"));coll1.add(false);coll1.add(new People("jerry", 19));System.out.println(coll.equals(coll1));//true}@Testpublic void test4(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add(123);coll.add(456);coll.add("AA");coll.add(new String("Tom"));coll.add(false);coll.add(new People("jerry", 19));//7.hashCode():返回当前对象的哈希值System.out.println(coll.hashCode());//8.集合--->数组:toArray():Object[] array = coll.toArray();for (int i = 0;i<array.length;i++){System.out.println(array[i]);}//拓展:数组--->集合:调用Arrays类的静态方法asList()List<String> strings = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"aa", "bb", "cc"});System.out.println(strings);//iterator():返回Iterator接口的实例,用于遍历集合元素}}
结论:向Collection接口的实现类的对象中添加数据obj时,要求obj所在类要重写equals()
集合元素的遍历
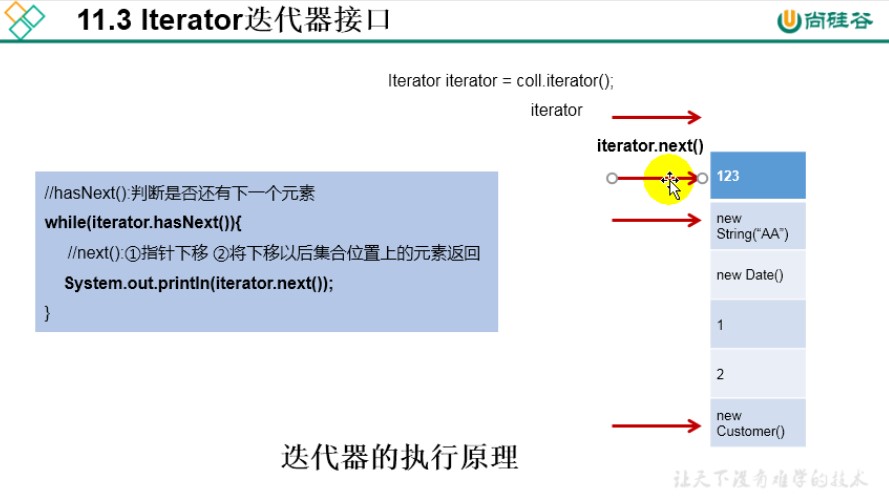
使用迭代器Iterator接口
1.内部方法:hasNext() 和 next()
2.集合对象每次调用iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象,默认游标都在集合的第一个元素之前
3.内部定义了rename(),可以在遍历的时候,删除集合中的元素,此方法不同于集合直接调用remove()
注:如果还未调用next()或在上一次调用next方法之后已经调用了remove方法,再调用remove都会报IllegalStateException
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.Iterator;public class IteratorTest {@Testpublic void test(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add(123);coll.add(456);coll.add(new String("Tom"));coll.add(false);coll.add(new People("jerry", 19));Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();//方式一System.out.println(iterator.next());//123System.out.println(iterator.next());//456System.out.println(iterator.next());//TomSystem.out.println(iterator.next());//falseSystem.out.println(iterator.next());//People{name='jerry', age=19}//报异常:NoSuchElementExceptionSystem.out.println(iterator.next());//方式二:不推荐for (int i = 0;i<coll.size();i++){System.out.println(iterator.next());}//方式三:推荐while(iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}}}
remove方法
public void test3(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add(123);coll.add(456);coll.add(new String("Tom"));coll.add(false);coll.add(new People("jerry", 19));//删除集合中的”Tom“Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){Object obj = iterator.next();if ("Tom".equals(obj)) {iterator.remove();}}//遍历集合iterator = coll.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}}
增强for循环
for(数组元素的类型 局部变量 :数组对象){
}
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;public class ForTest {@Testpublic void test1(){Collection coll = new ArrayList();coll.add(123);coll.add(456);coll.add(new String("Tom"));coll.add(false);coll.add(new People("jerry", 19));for (Object obj: coll){System.out.println(obj);}}@Testpublic void test2(){int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};for (int i : arr){System.out.println(i);}}}
ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector三者的异同
相同:三个类都实现了List接口,存储数据的特点相同:存储有序的、可重复的数据
不同:ArrayList:作为List接口的主要实现类,线程不安全的,效率高,底层使用Object[] elementData存储
LinkedList:对于频繁的插入、删除操作,使用此类效率比ArrayList高,底层使用双向链表存储
Vector:作为List接口的古老实现类,线程安全的,效率低,底层使用Object[] elementData存储
List接口的常用方法
public class ListTest {@Testpublic void test1(){ArrayList list = new ArrayList();list.add(123);list.add(456);list.add("AA");list.add(new People("Tom",12));System.out.println(list);//void add(int index,Object ele)list.add(1,"BB");//boolean addAll(int index,Collection eles)List list1 = Arrays.asList(1,2,3);list.addAll(list1);System.out.println(list);}@Testpublic void test2(){ArrayList list = new ArrayList();list.add(123);list.add(456);list.add("AA");list.add(new People("Tom",12));//int indexOf(Object obj)int index = list.indexOf(4567);System.out.println(index);//-1//int lastIndexOf(Object obj)System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(456));//1//Object remove(int index)Object obj = list.remove(0);System.out.println(obj);//123System.out.println(list);//[456, AA, People{name='Tom', age=12}]//Object set(int index,Object ele)list.set(1,"CC");System.out.println(list);//[456, CC, People{name='Tom', age=12}]//List subList(int formIndex,int toIndex)List list1 = list.subList(2, 3);System.out.println(list1);//[People{name='Tom', age=12}]System.out.println(list);//[456, CC, People{name='Tom', age=12}]}}
总结
增:add(int index,Object ele)
删:remove(int index)
改:set(int index,Object ele)
查:get(int index)
插:add(int index,Object ele)
长度:size()
遍历:
public void test3(){ArrayList list = new ArrayList();list.add(123);list.add(456);list.add("AA");//方式一:Iterator迭代器方式Iterator iterator = list.iterator();while(iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}//方式二:增强for循环for (Object obj : list){System.out.println(obj);}//方式三:普通for循环for (int i = 0;i < list.size();i++){System.out.println(list.get(i));}}
Set接口
TreeSet排序
1.向TreeSet中添加的数据,要求是相同类型的对象
2.两种排序方式:自然排序(实现Comparable接口)和定制排序(Comparator)
3.自然排序中,比较两个对象是否相同的标准为:compareTo()返回0,不再是equals()
4.定制排序中,比较两个对象是否相同的标准为:compareTo()返回0,不再是equals()
public void test3() throws RuntimeException {Comparator com = new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {if (o1 instanceof People && o2 instanceof People)People p3 = (People) o1;People p2 = (People) o2;return Integer.compare(u1.getAge(),u2.getAge());}else{throw new RuntimeException("输入的数据类型不匹配");}}}TreeSet set = new TreeSet(com);set.add(new People("Tom",12));set.add(new People("Jack",22));set.add(new People("Mike",52));set.add(new People("Timi",2));Iterator iterator = set.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}
实例
public class MyDate implements Comparable{private int year;private int month;private int day;public MyDate(){}public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {this.year = year;this.month = month;this.day = day;}public int getYear() {return year;}public void setYear(int year) {this.year = year;}public int getMonth() {return month;}public void setMonth(int month) {this.month = month;}public int getDay() {return day;}public void setDay(int day) {this.day = day;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "MyDate{" +"year=" + year +", month=" + month +", day=" + day +'}';}//方式二:@Overridepublic int compareTo(Object o) {if (o instanceof MyDate){MyDate m = (MyDate) o;//比较年int minusYear = this.getYear() - m.getYear();if (minusYear != 0){return minusYear;}//比较月int minusMonth = this.getMonth() - m.getMonth();if (minusMonth != 0){return minusMonth;}//比较日return this.getDay() - m.getDay();}throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据类型不一致");}}
public class Employee implements Comparable{private String name;private int age;private MyDate birthday;public Employee() {}public Employee(String name, int age, MyDate birthday) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.birthday = birthday;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public MyDate getBirthday() {return birthday;}public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {this.birthday = birthday;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Employee{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", birthday=" + birthday +'}';}//按 name 排序@Overridepublic int compareTo(Object o) {if(o instanceof Employee){Employee e = (Employee) o;return this.name.compareTo(e.name);}//return 0;throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据类型不一致");}}
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Comparator;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.TreeSet;public class EmployeeTest {@Testpublic void test2(){TreeSet set = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {if (o1 instanceof Employee && o2 instanceof Employee){Employee e1 = (Employee) o1;Employee e2 = (Employee) o2;MyDate b1 = e1.getBirthday();MyDate b2 = e2.getBirthday();//方式一://比较年//int minusYear = b1.getYear() - b2.getYear();//if (minusYear != 0){// return minusYear;//}//比较月//int minusMonth = b1.getMonth() - b2.getMonth();//if (minusMonth != 0){// return minusMonth;//}//比较日//return b1.getDay() - b2.getDay();//方式二:return b1.compareTo(b2);}//return 0;throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据类型不一致");}});Employee e1 = new Employee("liudehua",55,new MyDate(1965,5,4));Employee e2 = new Employee("zhangxueyou",43,new MyDate(1987,5,4));Employee e3 = new Employee("guofucheng",44,new MyDate(1987,5,9));Employee e4 = new Employee("liangzhaowei",21,new MyDate(1978,12,4));Employee e5 = new Employee("liming",51,new MyDate(1954,8,12));set.add(e1);set.add(e2);set.add(e3);set.add(e4);set.add(e5);Iterator iterator = set.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}}@Testpublic void test1(){TreeSet set = new TreeSet();Employee e1 = new Employee("liudehua",55,new MyDate(1965,5,4));Employee e2 = new Employee("zhangxueyou",43,new MyDate(1987,5,4));Employee e3 = new Employee("guofucheng",44,new MyDate(1987,5,9));Employee e4 = new Employee("liangzhaowei",21,new MyDate(1978,12,4));Employee e5 = new Employee("liming",51,new MyDate(1954,8,12));set.add(e1);set.add(e2);set.add(e3);set.add(e4);set.add(e5);Iterator iterator = set.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}}}
Map接口
Map实现类结构
Map结构的理解
Map中的key:无序的、不可重复的,使用Set存储所有的key —->key所在的类要重写equals()和hasCode()
Map中的value:无序的、可重复的,使用Collection存储所有的value—->value所在的类要重写equals()
一个键值对:key-value构成了一个Entry对象
Map中的entry:无序的、不可重复的,使用Set存储所有的entry


Map常用方法
Map的遍历
public class MapTest {@Testpublic void test1(){Map map = new HashMap();map.put("AA",123);map.put(45,123);map.put("BB",56);//遍历所有的key集:keySet()Set set = map.keySet();Iterator iterator = set.iterator();while(iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}//遍历所有的value集:values()Collection values = map.values();for (Object obj : values){System.out.println(obj);}//遍历所有的key-value//方式一:entrySet()Set entrySet = map.entrySet();Iterator iterator1 = entrySet.iterator();while (iterator1.hasNext()){Object obj = iterator1.next();Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) obj;System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--->" + entry.getValue());}//方式二:Set keySet = map.keySet();Iterator iterator2 = keySet.iterator();while (iterator2.hasNext()) {Object key = iterator2.next();Object value = map.get(key);System.out.println(key + "===" + value);}}}
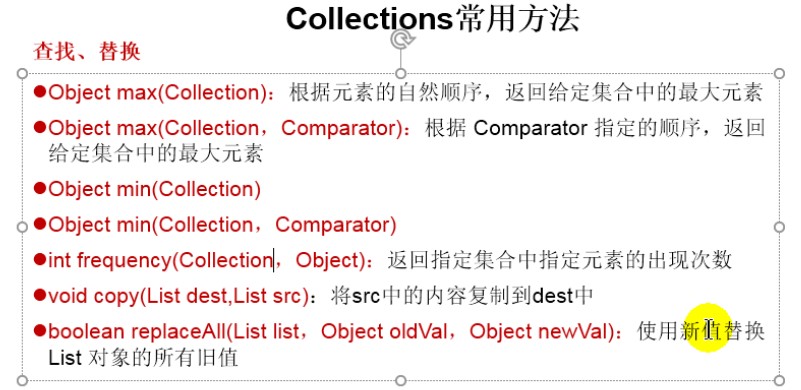
Collection常用方法