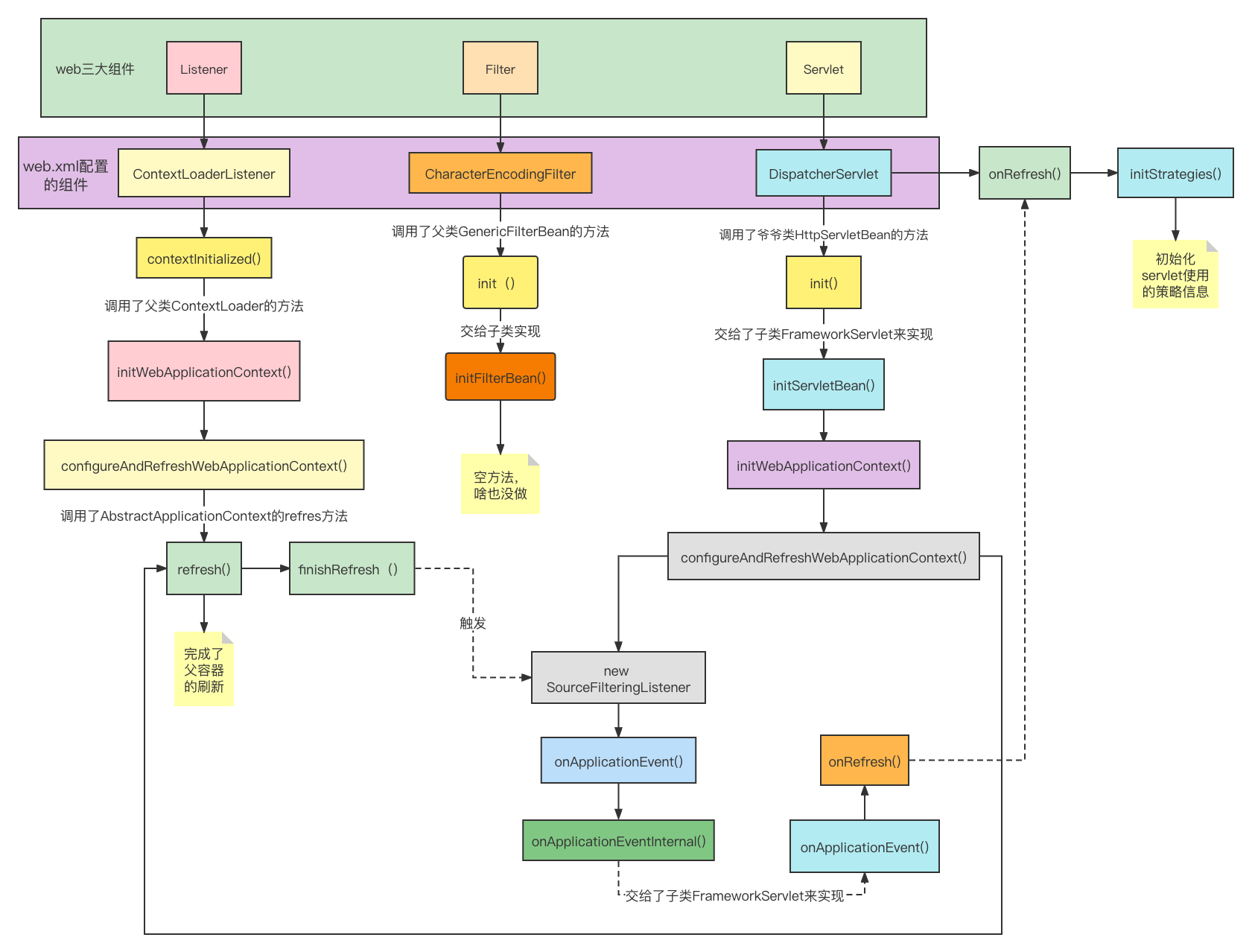
SpringMVC最后是通过Tomcat来进行部署的。当在Servlet中进行进行应用部署时,主要步骤为:
When a web application is deployed into a container, the following steps must be performed, in this order, before the web application begins processing client requests.
- Instantiate an instance of each event listener identified by a element in the deployment descriptor.
- For instantiated listener instances that implement ServletContextListener , call the contextInitialized() method.
- Instantiate an instance of each filter identified by a element in the deployment descriptor and call each filter instance’s init() method.
- Instantiate an instance of each servlet identified by a element that includes a element in the order defined by the load-on-startup element values, and call each servlet instance’s init() method.
当应用部署到容器时,在应用相应客户的请求之前,需要执行以下步骤:
- 创建并初始化由元素标记的事件监听器。
- 对于事件监听器,如果实现了ServletContextListener接口,那么调用其contextInitialized()方法。
- 创建和初始化由元素标记的过滤器,并调用其init()方法。
- 根据中定义的顺序创建和初始化由元素标记的servlet,并调用其init()方法。所以在Tomcat下部署的应用,会先初始化listener,然后初始化filter,最后初始化servlet。
现在根据配置文件和Oracle所说的初始化流程分析一下,SpringMVC是如何来一步步启动容器,并加载相关信息的。
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"version="3.1"><!--告诉加载器,去这个位置去加载spring的相关配置--><context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value></context-param><!--配置前端控制器--><servlet><servlet-name>springMvc</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><!--SpringMVC配置文件--><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>springMvc</servlet-name><url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping><listener><listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class></listener><!--解决乱码问题的filter--><filter><filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name><filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class><init-param><param-name>encoding</param-name><param-value>utf-8</param-value></init-param></filter><filter-mapping><filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></filter-mapping></web-app>
1.初始化Listener
我们在配置文件定义的Listener类是ContextLoaderListener.
继承关系:ContextLoaderListener 类继承了 ContextLoader 类并且实现了 ServletContextListener 接口,按照启动程序,会调用其 contextInitialized() 方法。
/**
* 这个方法:初始化应用上下文
* @param event
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
//这里就进入了初始化web容器的核心
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* 初始化web应用的上下文
* ServletContext官方叫servlet上下文。服务器会为每一个工程创建一个对象,这个对象就是ServletContext对象。
* 这个对象全局唯一,而且工程内部的所有servlet都共享这个对象。所以叫全局应用程序共享对象。
* @param servletContext servlet 上下文
* @return
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
/*
* 首先通过 WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE 这个String类型的静态变量获取一个Root ioc 容器,
* 根据 ioc 容器作为全局变量存储在 application 对象中,如果存在则有且只能有一个
*
* 如果在初始化 Root WebApplicationContext 即, Root ioc 容器的时候发现已经存在,则直接抛出异常,
* 因此web.xml中只允许存在一个ContextLoader类或其子类对象。
* */
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
/*如果context不存在,则直接进行创建*/
if (this.context == null) {
/*step into*/
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
/*配置并刷新应用的root ioc 容器,这里会进行bean的创建和初始化工作,
* 这里最终会调用 AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法。
* 并且ioc容器中的bean类会被放在application中。*/
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//以属性的配置方式将application配置servletContext中,因为servletContext是整个应用唯一的,所以可以根据key值获取到application,从而能够获取到应用的所有信息
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
//将ServletContext设置到application的属性中
wac.setServletContext(sc);
//获取web.xml中配置的contextConfigLocation参数值
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
//调用应用的refresh方法,进行IOC容器的装载
wac.refresh();
}
思考与沉淀
我们在web.xml配置文件定义的Listener类是ContextLoaderListener类.继承关系:ContextLoaderListener 类继承了 ContextLoader 类并且实现了 ServletContextListener 接口,按照启动程序,会调用其 contextInitialized() 方法。这个方法主要是调用了initWebApplicationContext()来初始化web应用的上下文,再通过configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()加载web.xml里面指定的配置文件,然后调用ioc容器的刷新方法。
2.初始化Filter
在完成了对于 listener 的初始化操作以后,会进行 filter 的创建和初始化操作。我们这里使用的是 CharacterEncodingFilter 。我们先看一下这个类的具体类图信息 ctrl+H。
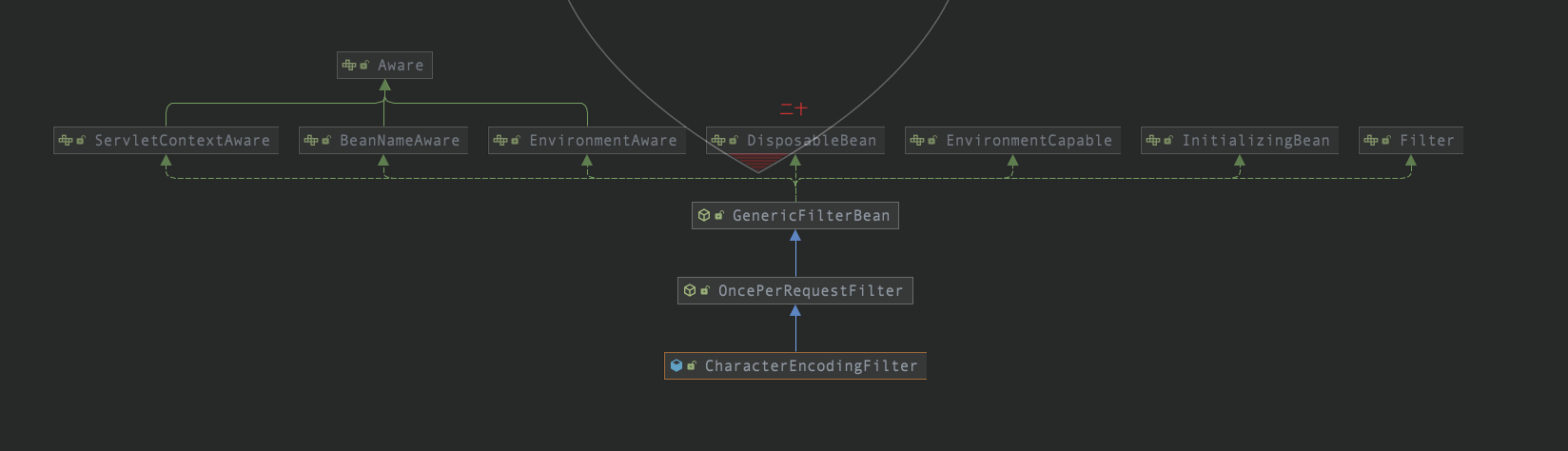
因为其实现了 Filter 接口,所以会调用其对应的 init(FilterConfig filterConfig) 方法。在其父类 GenericFilterBean 中有该方法的实现。
/**
* filter的初始化方法
* @param filterConfig
* @throws ServletException
*/
@Override
public final void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
Assert.notNull(filterConfig, "FilterConfig must not be null");
this.filterConfig = filterConfig;
// 将设置的初始化参数信息设置到pvs中
PropertyValues pvs = new FilterConfigPropertyValues(filterConfig, this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
//将具体的filter类进行包装
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
//创建对应的资源加载器
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(filterConfig.getServletContext());
Environment env = this.environment;
if (env == null) {
env = new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, env));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
String msg = "Failed to set bean properties on filter '" +
filterConfig.getFilterName() + "': " + ex.getMessage();
logger.error(msg, ex);
throw new NestedServletException(msg, ex);
}
}
// 交给子类实现
initFilterBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Filter '" + filterConfig.getFilterName() + "' configured for use");
}
}
protected void initFilterBean() throws ServletException {
//这里并未进行任何的初始化操作。其实Filter的主要作用还是在有请求过来时,进行的 doFilter() 中的处理,在启动阶段,处理比较少。
}
思考与沉淀
在完成了对于 listener 的初始化操作以后,会进行 filter 的创建和初始化操作。通常在web.xml文件配置的是:CharacterEncodingFilter 。通过这个类的继承关系,再结合实际源码分析:因为其实现了 Filter 接口,所以会调用其对应的 init(FilterConfig filterConfig) 方法。在其父类 GenericFilterBean 中有该方法的实现。然后又交给了子类,但是实际上啥也没做,其实Filter的主要作用还是在有请求过来时,进行的 doFilter() 中的处理,在启动阶段,处理比较少。
3.初始化Servlet
web应用启动的最后一个步骤就是创建和初始化 Servlet ,我们就从我们使用的 DispatcherServlet 这个类来进行分析,这个类是前端控制器,主要用于分发用户请求到具体的实现类,并返回具体的响应信息。
这里面有一个看源码的技巧,当分析到某一个类的时候,不知道如何再往下分析了,也就是缺少相应的抓手,怎么办?
1.看类的继承关系,从类的继承关系触发,寻找相应的方法
2.看初始化这种的方法
ctrl+H 查看类的继承关系,DispatcherServlet 实现了Servlet 接口,所以按照加载过程,最终会调用其 init(ServletConfig config)方法。从DispatcherServlet中寻找init方法发现没有,这个时候怎么办?按照类的继承关系,逐步向上寻找。最终定位到 GenericServlet 中,但是这里什么也没有做,只是交给了子类去实现,那就继续寻找,最终定位到抓手:HttpServletBean。
/**
* 这个方法几乎是web-ioc容器的核心入口
* 当前类是DispatcherServlet的爷爷类
* 加载DispatcherServlet的时候,他的爷爷类会先加载的并且 init方法会执行
* @throws ServletException
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// 设置属性信息
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
//使用装饰器模式,对具体的实现类进行一个包装
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
//将web.xml里面的属性信息设置到 bw 里面。
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
//交给子类来实现
initServletBean();
}
来到子类:FrameworkServlet。
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//初始化web应用容器
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
//初始化框架servlet
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
/**
* 这里主要是进行了web应用容器上下文的创建,并进行了初始化工作。
* 跟踪一下初始化的具体流程
* @return
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//获取到 root ioc 容器
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
//将 root ioc 容器设置成 servlet 的ioc容器的父类
//如果当前servlet存在一个 WebApplicationContext 即:子IOC容器
//并且上下文获取的root ioc 容器存在,则将root ioc 容器作为子 ioc 容器的父容器
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//配置并刷新子容器,加载子容器中对应的bean实体类
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
//如果当前servlet中不存在子ioc容器,则去查找
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
//如果查找不到,就去创建一个
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
//根据类信息初始化一个ConfigurableWebApplicationContext对象
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
//设置web上下文环境信息
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
//设置其父类为root ioc 容器,root ioc 容器是整个应用唯一的。
wac.setParent(parent);
//设置其具体的配置信息的位置,这里是 classpath:spring-mvc.xml
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
//配置并刷新web应用的ioc容器
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
//配置容器的相关信息
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
//配置容器应用加载的监听器
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
//应用初始化信息
applyInitializers(wac);
//刷新加载里面的bean实体类
wac.refresh();
}
这里其实可以看到,在这个其实主要是根据配置文件信息进行类加载的工作,并且配置了一个容器加载信息的监听器 SourceFilteringListener。在最后通过 refresh 方法进行了容器中实体类的加载过程。这个refresh方法和我们在listener中实现类的初始化过程使用的是同一个方法。到此为止,在我们应用中配置的所有的类都能够扫描到,并且配置了我们的ioc容器中。因为我们配置了相关的容器加载的监听器,在refresh方法中调用了 finishRefresh 方法时,发送对应的容器加载完成广播信息,从而能够调用我们所注册的监听器 SourceFilteringListener。看一下里面的逻辑~
protected void onApplicationEventInternal(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (this.delegate == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Must specify a delegate object or override the onApplicationEventInternal method");
}
//这里的delegate,是传入的具体的代理类,所以在此回到了我们的FrameworkServlet
this.delegate.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
//最终调用了FrameworkServlet的onApplicationEvent方法
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}
}
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
// 又是一个扩展点,交给子类去实现
}
终于来到了我们的DispatcherServlet。
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
//通过重写父类的扩展点来到这里
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* 初始化servlet使用的策略信息,子类可以通过覆写该方法类增加更多的呃策略方法
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
//初始化MultipartResolver,可以支持文件的上传
initMultipartResolver(context);
//初始化本地解析器
initLocaleResolver(context);
//初始化主题解析器
initThemeResolver(context);
//处理器映射器,将请求和方法进行映射关联
initHandlerMappings(context);
//处理器适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
//处理器异常解析器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
//从请求到视图名的转换器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//视图解析器
initViewResolvers(context);
//FlashMap管理器
initFlashMapManager(context);
/*
* 可以看到里面主要是初始化了我们的所使用到的一些解析器和处理器等。
* 当接收到请求后,就可以根据这些解析器来进行请求的解析处理、方法的调用、异常的处理等等。
* 到此为止,Servlet的初始化工作就整个完成了。想当的复杂,主要是将很多的方法实现在父类中进行了处理。层级比较复杂,需要一点点跟踪分析。
*/
}
思考与沉淀
web应用启动的最后一个步骤就是创建和初始化 Servlet ,我们就从我们使用的 DispatcherServlet 这个类来进行分析,这个类是前端控制器,主要用于分发用户请求到具体的实现类,并返回具体的响应信息。看这个类的继承关系:在HttpServlet(他的爷爷类)中,实现了servlet的init方法(其实再往里追源码,实际是从源码里面实现的,算是一个扩展点吧),这里主要是委派给了子类FrameworkServlet(dispatcherServlet的父类)的initServletBean(),这个方法主要是初始化web应用。通过initWebApplicationContext()配置并刷新子容器,这里其实可以看到,在这个其实主要是根据配置文件信息进行类加载的工作,并且配置了一个容器加载信息的监听器 SourceFilteringListener。在最后通过 refresh 方法进行了容器中实体类的加载过程。这个refresh方法和我们在listener中实现类的初始化过程使用的是同一个方法。到此为止,在我们应用中配置的所有的类都能够扫描到,并且配置了我们的ioc容器中。因为我们配置了相关的容器加载的监听器,在refresh方法中调用了 finishRefresh 方法时,发送对应的容器加载完成广播信息,从而能够调用我们所注册的监听器 SourceFilteringListener。看一下里面的逻辑~这里面实际上又调用了传入的代理类的onRefresh()。这个代理类是谁?其实就是DispatcherServlet。他的onRefresh()实际上就是调用了initStrategies(),可以看到里面主要是初始化了我们的所使用到的一些解析器和处理器等。当接收到请求后,就可以根据这些解析器来进行请求的解析处理、方法的调用、异常的处理等等。到此为止,Servlet的初始化工作就整个完成了。