一、集合知识回顾
二、集合类体系结构
三、Collection
1、概述
Collection集合
是单例集合的顶层接口,它表示一组对象,这些对象也称为Collection的元素。
JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现,它提供更具体的子接口(如Set和List)实现。
2、创建Collection对象
多态的方式
具体实现类ArrayList
3、Collection集合常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 添加元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 从集合中移除指定的元素 |
| void clear() | 清空集合中的元素 |
| boolean contains(Objcet o) | 判断集合中是否存在指定的元素 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| int size() | 集合的长度,也就是集合中元素的个数 |
4、Collection集合遍历
Iterator:迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式
Iterator
迭代器是通过集合的iterator()方法得到的,所以我们说它是依赖于集合而存在的。
Iterator中的常用方法
E next():返回迭代中的下一个元素
boolean hasNext():如果迭代具有更多元素,则返回true
5、集合的使用步骤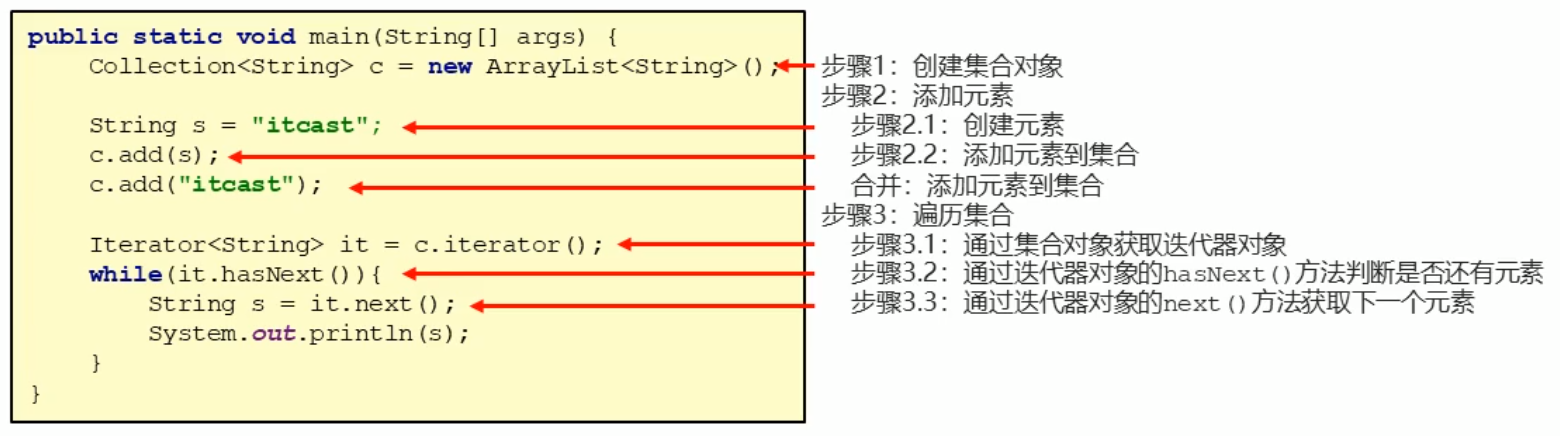
四、List集合
1、概述
有序集合(也称为序列),用户可以精确控制列表中每个元素的插入位置。用户可以通过整数索引访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
与Set集合不同,列表通常允许重复元素
2、List集合的特点
有序:存储和取出的元素顺序一致
可重复:存储的元素可以重复
3、List集合的特有方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void add(int index,E element) | 在此集合中的指定位置插入元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除指定索引处的元素 |
| E set(int index,E elemnt) | 修改指定索引处的元素,返回别修改的元素 |
| E get(int index) | 返回指定索引的元素 |
4、并发修改异常
ConcurrentModificationException:当不允许这样修改时,可以通过检测到对象的并发修改的方法来抛出此异常。(通过文档查询异常产生原因)
出错范例:
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();list.add("java");list.add("mysql");list.add("world");//报错Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){String s= iterator.next() ;if(s.equals("mysql")){list.add("spring");}}//可以使用for循环遍历,添加}
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {Iterator<E> iterator();boolean add(E e);}
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{public Iterator<E> iterator() {return new Itr();}private class Itr implements Iterator<E>{int cursor; // index of next element to returnint lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no suchint expectedModCount = modCount;public boolean hasNext() {return cursor != size;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public E next() {checkForComodification();int i = cursor;if (i >= size)throw new NoSuchElementException();Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;if (i >= elementData.length)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();cursor = i + 1;return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];}public void remove() {if (lastRet < 0)throw new IllegalStateException();checkForComodification();try {ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);cursor = lastRet;lastRet = -1;expectedModCount = modCount;} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}@Override@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);final int size = ArrayList.this.size;int i = cursor;if (i >= size) {return;}final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;if (i >= elementData.length) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);}// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write trafficcursor = i;lastRet = i - 1;checkForComodification();}final void checkForComodification() {if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;}}
final void checkForComodification()方法中,
modCount:是实际修集合的次数,
expectedModCount:是预期修改集合的次数,
如果这两者不相等,就会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
modCount来自AbstractList类
List调用add的时候,会对modeCount++
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {protected transient int modCount = 0;}
五、ListIterator(列表迭代器)
1、概念
通过List集合的listIterator()方法得到,所以说它是List集合特有的迭代器
用于允许程序员沿任一方向遍历列表的列表迭代器,在迭代期间修改列表,并获取列表中迭代器的当前位置
2、常用方法
E next():返回迭代中的下一个元素
boolean hasNext():如果迭代具有更多元素,则返回true
E previous():返回列表中的上一个元素
boolean hasPrevious():如果此列表迭代器在相反方向遍历列表时具有更多元素,则返回true
void add(E e):将指定的元素插入列表
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();list.add("java");list.add("mysql");list.add("world");Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){String s= iterator.next() ;if(s.equals("mysql")){list.add("spring"); //错误方法}}ListIterator<String> lit = list.listIterator();while (lit.hasNext()){String s=lit.next();if(s.equals("mysql")){lit.add("spring");//使用列表迭代器添加}}}
3、源码分析
List
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {
Iterator<E> iterator();
ListIterator<E> listIterator();
boolean add(E e);
}
ArrayList
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E>{
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
}
ArrayList中listIterator()方法,返回ListItr
ListItr继承Itr,和实现了ListIterator接口
ListItr的add方法中,把modCount赋值给expectedModCount
AbstractList
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {
protected transient int modCount = 0;
}
ListIterator
public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> {
}
六、增强for循环
增强for:简化数组和Collection集合的遍历
实现Iterable接口的类允许其对象成为增强型for语句的目标
它是JDK5之后出现的,其内部原理是一个Iteratot迭代器
格式:
for(元素数据类型 变量名:数组或者Collection集合){
//在此处使用变量即可,该变量就是元素
}
七、List集合子类的特点
List集合常用子类:ArrayList,LinkedList
ArrayList:底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢
LinkedList:底层数据结构是链表,查询慢,增删快
八、LinkedList:集合的特有功能
因为底层是链表,所以可以有一些针对头节点和尾节点的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void addFirst(E e) | 在该列表开头插入指定的元素 |
| public void addLast(E e) | 将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾 |
| public E getFirst() | 返回此列表中的第一个元素 |
| public E getLast() | 返回此列表中的最后一个元素 |
| public E removeFirst() | 从此列表中删除并返回第一个元素 |
| public E removeLast() | 从此列表中删除并返回最后一个元素 |
九、Set集合
1、特点
不包含重复元素的集合
没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
十、哈希值
哈希值:是JDK根据对象的地址或者字符串或者数字算出来的int类型的数值
Object类中有一个方法可以获取到对象的哈希值
public int hasCode():返回对象的哈希码值
对象的哈希值特点
同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值是相同的
默认情况下,不同对象的哈希值是不同的。而重写hashCode()方法,可以实现让不同的对象的哈希值相同
十一、HashSet
1、特点
底层数据结构是哈希表
对集合的迭代顺序不做任何保证,也就是说不保证存储和取出的元素顺序一致
没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
由于是Set集合,所以是不包含重复数据的
2、HashSet保证元素唯一性源码分析
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
//hash值和元素的hashCode()方法相关
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//如果哈希表未初始化,就对其进行初始化
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//根据对象的哈希值计算对象的存储位置,如果该位置没有元素就存储元素
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
/**
存入的元素和以前的元素比较哈希值
如果哈希值不同,会继续向下执行,把元素添加到集合
如果哈希值相同,会调用对象的equals()方法比较
如果返回false,会继续向下执行,把元素添加到集合
如果返回true,说明元素重复,不存储
*/
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
}
过程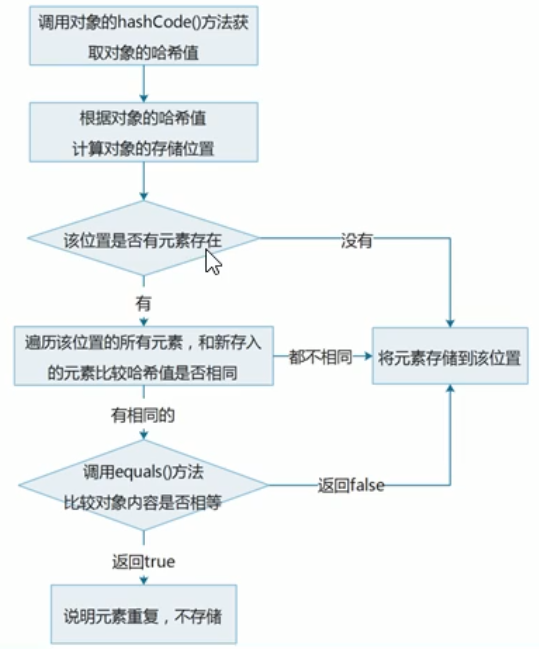
HashSet集合存储元素:
要保证元素唯一性,需要重写hashCode()和equals()
十二、哈希表
JDK8之前,底层采用数组+链表实现,可以说是一个元素为链表的数组
JDK8以后,在长度比较长的时候,底层实现了优化
十三、LinkedHashSet
1、特点
哈希表和链表实现的Set接口,具有可预测的迭代次序
由链表保证元素有序,也就是说元素的存储和取出顺序是一致的
由哈希表保证元素唯一性,也就是说没有重复元素
十四、TreeSet
1、特点
元素有序,这里的顺序不是指存储和取出顺序,而是按照一定的规则进行排序,具体排序方式取决于构造方法
TreeSet():根据元素的自然排序进行排序
TreeSet(Comparator comparator):根据指定的比较器进行排序
没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
由于是Set集合,所以不包含重复元素的集合
十五、自然排序Comparable的使用
用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,无参构造方法使用的是自然排序对元素进行排序的
自然排序,就是让元素所属的类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(T o)方法
重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
十六、比较器排序Comparator
用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,带参构造方法使用的是比较器排序对元素进行排序的
比较器排序,就是让集合构造方法接收Comparator实现类对象,重写compareTo(T o1,T o2)方法
重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写

