FutureTask源码结构
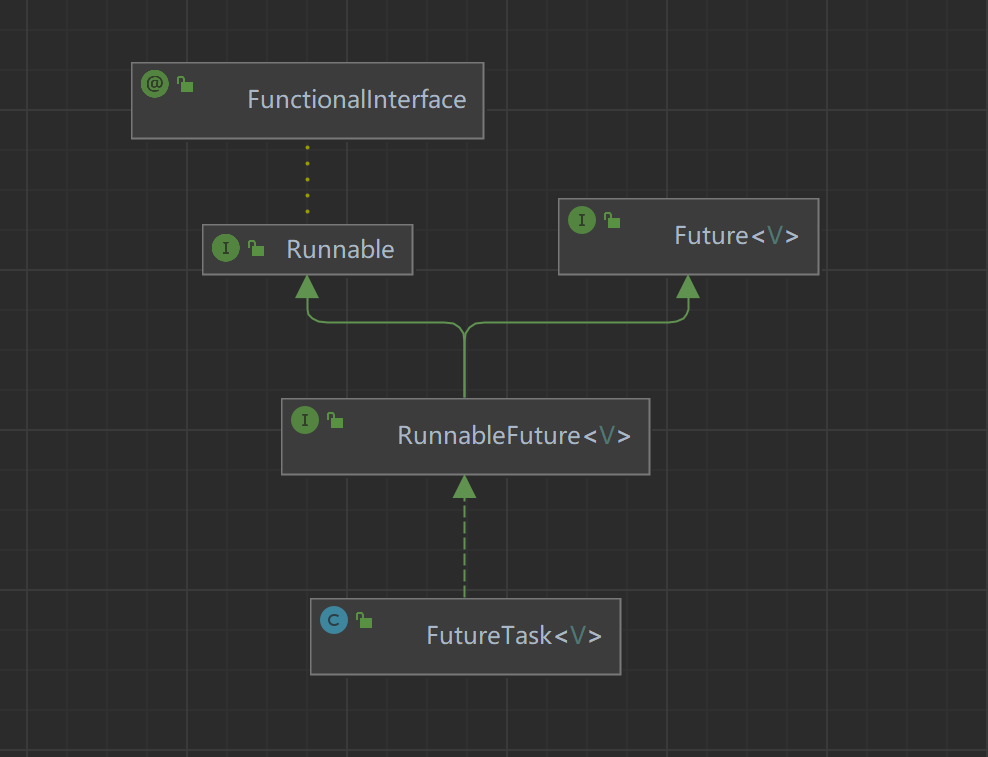
- 作为线程:实现Runnable接口
- 异步处理:实现了Future接口
有返回值:构造注入Callable
提供了Callable功能 /*** Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the* given {@code Callable}.** @param callable the callable task* @throws NullPointerException if the callable is null*/public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {if (callable == null)throw new NullPointerException();this.callable = callable;this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable}
FutureTask 实例用法
FutureTask 往往搭配Callable接口使用:
@Testvoid contextLoads() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 匿名内部类的方式,实现Callable接口 + FutureTask (可以拿到返回结果,可以处理异常)FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -----come in");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);return "task over";});Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask, "t1");t1.start();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 忙其他任务");// 阻塞等待整个线程完成,获取返回结果System.out.println(futureTask.get());}
get()缺点
futureTask.get() 调用get()方法求结果,如果计算机没有完成容易导致程序阻塞
实际开发这并不这样写,这样的写发并不优雅,调get()容易造成阻塞,可以写成,多线程任务什么时候完成了isDone(),什么时候去调用
@Testvoid contextLoads() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 匿名内部类的方式,实现Callable接口 + FutureTask (可以拿到返回结果,可以处理异常)FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -----come in");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);return "task over";});Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask, "t1");t1.start();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 忙其他任务");// 阻塞等待整个线程完成,获取返回结果// System.out.println(futureTask.get());// 每500 毫秒判断是否完成while (true){if (futureTask.isDone()){System.out.println(futureTask.get());break;}else {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);System.out.println("正在处理中");}}}
isDone()缺点
- 轮询的方式会耗费无谓的cpu资源,而且也不见得能及时得到计算结果,如果想要异步获取结果,通常都会以轮询的方式获取结果尽量不要阻塞
Future对于结果的获取不是很友好,只能通过阻塞或轮询方式得到任务结果
CompletableFuture
get()方法在Future计算完成之前会一直处于阻塞状态下,
isDone()方法容易消耗CPU资源
对于真正的异步处理,希望是可以通过传入回调函数,在Future结束时自动调用该回调函数,这样我们就不用等待结果
阻塞的方式和异步编程的设计理念相违背,而轮询的方式耗费无谓的CPU资源。因此
JDK8设计CompaletableFuture。
CompltetableFuture提供了一种观模式类似的机制,可以让任务执行完成后通知监听的一方。
类架构说明
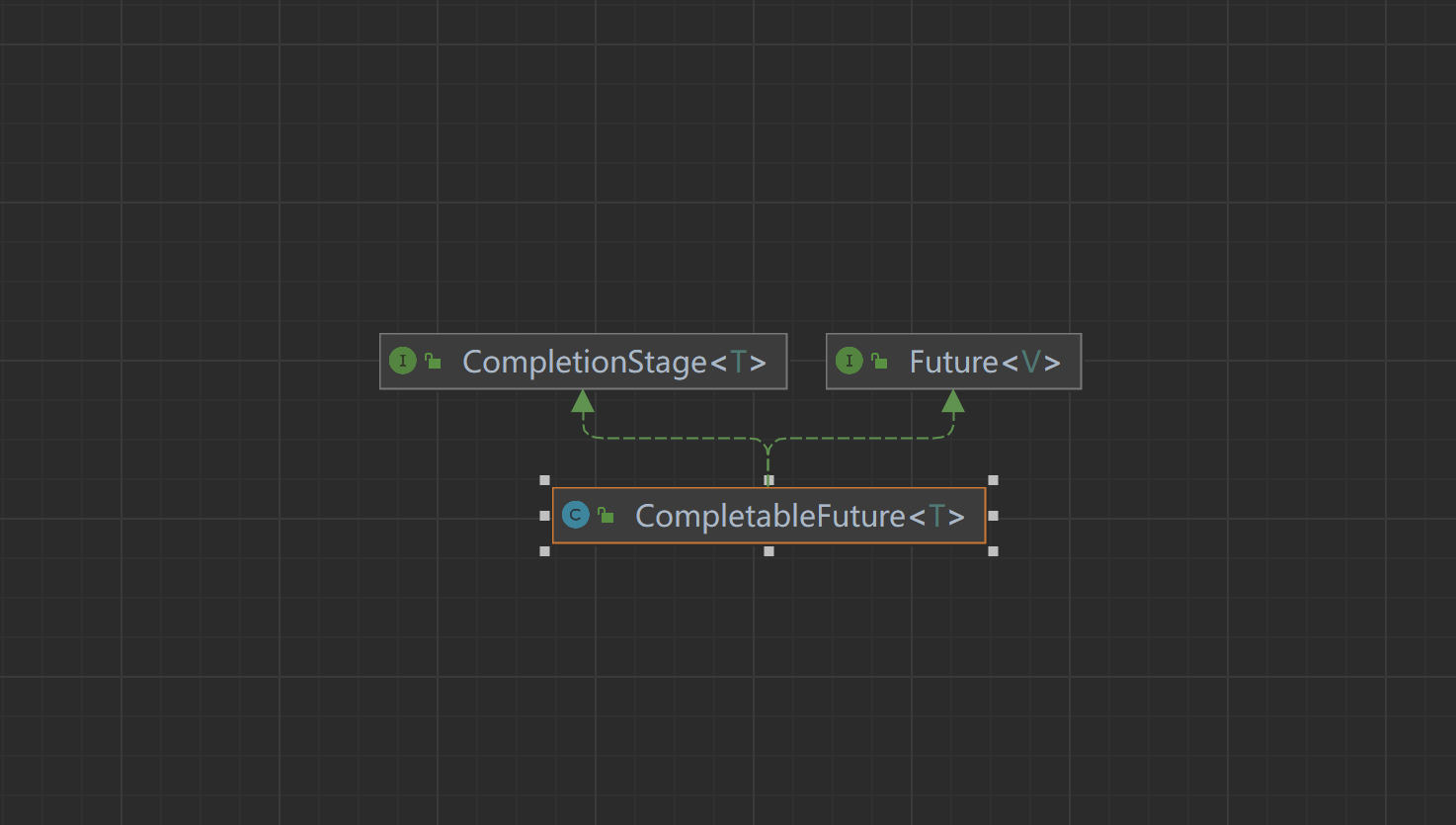
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T>
CompletionStage
- CompletionStage代表异步计算过程中的某一个阶段,一个阶段完成后可能会触发另外一个阶段
- 一个阶段的计算执行是一个Function,Consumer或者Runnable。比如:stage.thenApply(
- 一个阶段的执行可能是被单个阶段的完成触发,也可能是由多个阶段一起触发
代表异步计算过成中的某一个阶段,一个阶段完成后可能会触发另外一个阶段,有些类似Linux系统的管道分隔符穿参数。
介绍
在java8中,CompletabeleFuture提供了非常强大的Future的扩展功能,可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性,并且提供了函数式编程能力,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,也提供了转换和组合CompletableFuture的方法。
它可能代表一个明确完成的Future,也可能代表一个完成阶段(CompletionStage),它支持在计算完成以后触发一些函数或执行某些动作。
它实现了Future和CompletionStage接口
创建方式
没有指定Executor的方法,直接用默认的ForkJoinPool.commonPool()作为它的线程池执行异步代码。
如果指定线程池,则使用自定义或者特别指定的线程池执行异步代码
runAsync 无返回值
- public static CompletableFuture
runAsync(Runnable runnable) - public static CompletableFuture
runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor) @Testpublic void test1() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}});System.out.println(voidCompletableFuture.get());}
supplyAsync 有返回值
public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier)
public static CompletableFuture supplyAsync(Supplier supplier, Executor executor)
CompletableFuture 回调方法
whenComplete
public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);try {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---come in");int i = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("---- 1秒后出结果" + i);return i;}, threadPool).whenComplete((v, e) -> {if (e == null) {System.out.println("----计算完成,更新系统:" + v);}}).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("一场情况" + e.getCause() + "\t" + e.getMessage());return null;});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程去忙其他任务了");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {threadPool.shutdown();}}

