一般说来,读取 SpringBoot 配置文件的方式大致可以分为三种(见下↓)。更详细的分类包括是否使用自定义配置文件、自定义配置文件的文件类型(.properties还是.yml)以及配置的 key 是否使用”前缀”等等。
- @Value + [@PropertySource]
- setXxx() + @ConfigurationProperties + [@PropertySource]
- environment.getProperty(“xxx”)
多说无益,直接上一个综合的栗子,一切不言自明。
需求场景: 一个接口需要从 application.properties 、diy.properties 以及 diy.yml 中读取配置给变量赋值(包括给静态变量赋值),然后再进行其它的业务逻辑的操作。
代码目录结构: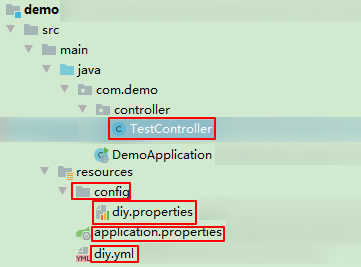
package com.demo.controller;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controller//@PropertySource("classpath:config/diy.properties")//@PropertySources({// @PropertySource("classpath:config/diy.properties"),// @PropertySource("classpath:diy.yml")}//)@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:config/diy.properties", "classpath:diy.yml"})@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")public class TestController {//@Value("${name}")//注意事项:读取 .properties 中的配置时,变量名必须加上前缀,否则运行报错@Value("${person.name}")private String name;private Integer age;public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}// 静态变量获取配置文件中的配置private static String password;@Value("${person.password}")//注意事项:注意不是使用默认的 setXxx,而是去掉"static"的 setXxx 方法public void setPassword(String password) {TestController.password = password;}@Autowiredpublic Environment environment;//@Value("${person.num}")//注意事项:读取 .yml 中的配置时,变量名不能添加前缀,否则运行报错@Value("${num}")private int num;private int num2;public void setNum2(int num2) {this.num2 = num2;}@RequestMapping("/test")@ResponseBodypublic String test() {System.out.println("name = " + name);System.out.println("age = " + age);System.out.println("password = " + password);System.out.println("num = " + num);System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);// 0,无法设置前缀,导致无法获取到值,结论:形如 person.num2 使用 @Value 获取,不要使用 @setXxx 方式System.out.println("environment.getProperty(\"person.sex\"):" + environment.getProperty("person.sex"));return "springboot 访问成功!";}}
diy.yml
person:num: 2020num2: 2022
application.properties
person.name=from applictionn.properties
diy.properties
person.name=name from diy.propertiesperson.age=20person.password=pwd form diy.propertiesperson.sex=sex form diy.properties
访问 http://localhost:8080/test 测试,运行结果:
- 控制台输出:
name = from applictionn.propertiesage = 20password = pwd form diy.propertiesnum = 2020num2 = 0environment.getProperty("person.sex"):sex form diy.properties
- 浏览器:
【小结】
- 当一个配置在
application.properties和自定义配置文件中同时存在时,取application.properties。也就是说application.properties 的优先级高于自定义配置文件。 - 当使用
@Value读取配置信息时,
① 如果读取的是.properties文件,@Value("${xxx.xxx}")必须使用配置中 key全称(即加上”前缀”),且如果是自定义配置文件,还要加上@PropertySource("classpath:xxx/xxx.properties)指定配置文件位置。
② 如果读取的是.yml文件,@Value("${xxx}")使用的配置的 key 需要去掉”前缀”。同样如果是自定义配置文件,也要指定配置文件位置。 - 使用
@Value时,如果获取的是application.properties中的配置,则不需要在@PropertySource("classpath:xxx/xxx.properties")设置文件路径。也不需要在@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "xxx")中设置”前缀”(因为@Value获取.properties中的配置,必须使用配置中 key 的全称)。 - 大多数情况下,一个类文件中只读取一个配置文件,使用
@PropertySource("classpath:xxx/xxx.properties")即可。实在需要使用多个配置文件的情况下,使用@PropertySources({ @PropertySource("classpath:config/diy.properties"), @PropertySource("classpath:diy.yml")} )或者@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:config/diy.properties", "classpath:diy.yml"}) - 静态变量读取配置信息,需要使用
setXxx,这里尤其要注意使用public void setXxx(E e)的形式,不要使用编辑器默认生成的setXxx方法 —public static void setXxx(E e)形式,否则将无法读取到配置信息。

