- 全文检索
- 简介
- 安装
- kibana
- 核心概念 索引 映射 文档
- 高级查询 Query DSL
- 索引原理
- 分词器
- 过滤查询
- 聚合查询
- 整合应用
- 集群
全文检索
全文检索是计算机程序通过扫描文章中的每一个词,对每一个词建立一个索引,指明该词在文章中出现的次数和位置。当用户查询时根据建立的索引查找,类似于通过字典的检索字表查字的过程。
索: 建立索引 文本——>切分 —-> 词 文章出现过 出现多少次
检索: 查询 关键词—-> 索引中—> 符合条件文章 相关度排序
全文检索(Full-Text Retrieval)以文本作为检索对象,找出含有指定词汇的文本。全面、准确和快速是衡量全文检索系统的关键指标。
只处理文本、不处理语义搜索时英文不区分大小写结果列表有相关度排序
简介
什么是ElasticSearch
`ElasticSearch` 简称 `ES` ,是基于`Apache Lucene`构建的`开源搜索引擎`,是当前最流行的`企业级搜索引擎`。`Lucene本身就可以被认为迄今为止性能最好的一款开源搜索引擎工具包`,但是lucene的API相对复杂,需要深厚的搜索理论。很难集成到实际的应用中去。`ES是采用java语言编写,提供了简单易用的RestFul API,开发者可以使用其简单的RestFul API,开发相关的搜索功能,从而避免lucene的复杂性`。
ElasticSearch诞生
多年前,一个叫做`Shay Banon`的刚结婚不久的失业开发者,由于妻子要去伦敦学习厨师,他便跟着也去了。在他找工作的过程中,为了给妻子构建一个食谱的搜索引擎,他开始构建一个早期版本的`Lucene`。
直接基于Lucene工作会比较困难,所以Shay开始抽象Lucene代码以便Java程序员可以在应用中添加搜索功能。他发布了他的第一个开源项目,叫做“Compass”。
后来Shay找到一份工作,这份工作处在高性能和内存数据网格的分布式环境中,因此高性能的、实时的、分布式的搜索引擎也是理所当然需要的。然后他决定重写Compass库使其成为一个独立的服务叫做Elasticsearch。
第一个公开版本出现在2010年2月,在那之后Elasticsearch已经成为Github上最受欢迎的项目之一,代码贡献者超过300人。一家主营Elasticsearch的公司就此成立,他们一边提供商业支持一边开发新功能,不过Elasticsearch将永远开源且对所有人可用。
Shay的妻子依旧等待着她的食谱搜索……
目前国内大厂几乎无一不用Elasticsearch,阿里,腾讯,京东,美团 等等 …..
安装
- 传统方式安装 下载安装包—-> 平台 window macos linux(ubuntu)
- Docker 方式安装 推荐
传统方式安装
# 0.环境准备- centos7.x+、ubuntu、windows、macos- 安装jdk11.0+ 并配置环境变量 jdk8# 1.下载ES- https://www.elastic.co/cn/start
# 2.安装ES不用使用root用户,创建普通用户
# 添加用户名$ useradd chenyn# 修改密码$ passwd chenyn# 普通用户登录
# 3.解压缩ES安装包
$ tar -zxvf elasticsearch-7.14.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz$ ll总用量 650168drwxr-xr-x. 10 chenyn chenyn 167 8月 16 11:07 elasticsearch-7.14.0
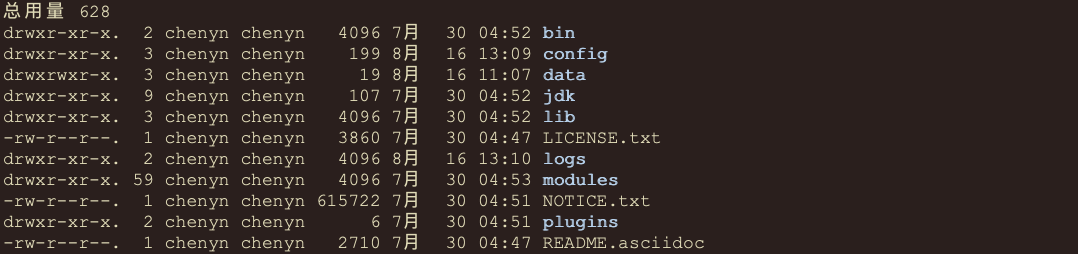
# 4.查看ES解压包中目录结构
[chenyn@localhost elasticsearch-7.14.0]$ ll- bin 启动ES服务脚本目录- config ES配置文件的目录- data ES的数据存放目录- jdk ES提供需要指定的jdk目录- lib ES依赖第三方库的目录- logs ES的日志目录- modules 模块的目录- plugins 插件目录
# 5.启动ES服务
[chenyn@localhost ~]$ ./elasticsearch-7.14.0/bin/elasticsearch

- 这个错误时系统jdk版本与es要求jdk版本不一致,es默认需要jdk11以上版本,当前系统使用的jdk8,需要从新安装jdk11才行!- 解决方案:1.安装jdk11+ 配置环境变量、2.ES包中jdk目录就是es需要jdk,只需要将这个目录配置到ES_JAVA_HOME环境变即可、
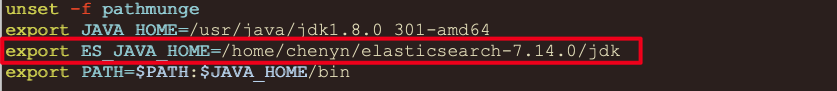
# 6.配置环境变量
$ vim /etc/profile- export ES_JAVA_HOME=指定为ES安装目录中jdk目录- source /etc/profile
# 7.从新启动ES服务

# 8.ES启动默认监听9200端口,访问9200
$ curl http://localhost:9200
开启远程访问
# 1.默认ES无法使用主机ip进行远程连接,需要开启远程连接权限- 修改ES安装包中config/elasticsearch.yml配置文件
$ vim elasticsearch.yml

# 2.重新启动ES服务- ./elasticsearch- 启动出现如下错误:`bootstrap check failure [1] of [4]: max file descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process is too low, increase to at least [65535]`bootstrap check failure [2] of [4]: max number of threads [3802] for user [chenyn] is too low, increase to at least [4096]`bootstrap check failure [3] of [4]: max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]`bootstrap check failure [4] of [4]: the default discovery settings are unsuitable for production use; at least one of [discovery.seed_hosts, discovery.seed_providers

# 3.解决错误-1
$ vim /etc/security/limits.conf
# 在最后面追加下面内容* soft nofile 65536* hard nofile 65536* soft nproc 4096* hard nproc 4096# 退出重新登录检测配置是否生效:ulimit -Hnulimit -Snulimit -Huulimit -Su
# 3.解决错误-2
#进入limits.d目录下修改配置文件。$ vim /etc/security/limits.d/20-nproc.conf# 修改为启动ES用户名 soft nproc 4096
# 3.解决错误-3
# 编辑sysctl.conf文件$ vim /etc/sysctl.confvm.max_map_count=655360 #centos7 系统vm.max_map_count=262144 #ubuntu 系统# 执行以下命令生效:$ sysctl -p
# 3.解决错误-4
# 编辑elasticsearch.yml配置文件$ vim conf/elasticsearch.ymlcluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
# 4.重启启动ES服务,并通过浏览器访问
{"name": "localhost.localdomain","cluster_name": "elasticsearch","cluster_uuid": "OWh3xLYwR-6lZ_fQNhVY3A","version": {"number": "7.14.0","build_flavor": "default","build_type": "tar","build_hash": "dd5a0a2acaa2045ff9624f3729fc8a6f40835aa1","build_date": "2021-07-29T20:49:32.864135063Z","build_snapshot": false,"lucene_version": "8.9.0","minimum_wire_compatibility_version": "6.8.0","minimum_index_compatibility_version": "6.0.0-beta1"},"tagline": "You Know, for Search"}
Docker方式安装
# 1.获取镜像- docker pull elasticsearch:7.14.0# 2.运行es- docker run -d -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" elasticsearch:7.14.0# 3.访问ES- http://10.15.0.5:9200/
Kibana
简介
Kibana Navicat是一个针对Elasticsearch mysql的开源分析及可视化平台,使用Kibana可以查询、查看并与存储在ES索引的数据进行交互操作,使用Kibana能执行高级的数据分析,并能以图表、表格和地图的形式查看数据。
安装
传统方式安装
# 1. 下载Kibana- https://www.elastic.co/downloads/kibana# 2. 安装下载的kibana- $ tar -zxvf kibana-7.14.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz# 3. 编辑kibana配置文件- $ vim /Kibana 安装目录中 config 目录/kibana/kibana.yml# 4. 修改如下配置- server.host: "0.0.0.0" # 开启kibana远程访问- elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"] #ES服务器地址# 5. 启动kibana- ./bin/kibana# 6. 访问kibana的web界面- http://10.15.0.5:5601/ #kibana默认端口为5601
Docker方式安装
# 1.获取镜像- docker pull kibana:7.14.0# 2.运行kibana- docker run -d --name kibana -p 5601:5601 kibana:7.14.0# 3.进入容器连接到ES,重启kibana容器,访问- http://10.15.0.3:5601# 4.基于数据卷加载配置文件方式运行- a.从容器复制kibana配置文件出来- b.修改配置文件为对应ES服务器地址- c.通过数据卷加载配置文件方式启动`docker run -d -v /root/kibana.yml:/usr/share/kibana/config/kibana.yml --name kibana -p 5601:5601 kibana:7.14.0
compose方式安装
version: "3.8"volumes:data:config:plugin:networks:es:services:elasticsearch:image: elasticsearch:7.14.0ports:- "9200:9200"- "9300:9300"networks:- "es"environment:- "discovery.type=single-node"- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"volumes:- data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data- config:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config- plugin:/usr/share/elasticsearch/pluginskibana:image: kibana:7.14.0ports:- "5601:5601"networks:- "es"volumes:- ./kibana.yml:/usr/share/kibana/config/kibana.yml
# kibana配置文件 连接到ESserver.host: "0"server.shutdownTimeout: "5s"elasticsearch.hosts: [ "http://elasticsearch:9200" ]monitoring.ui.container.elasticsearch.enabled: true
核心概念
索引
**一个索引就是一个拥有几分相似特征的文档的集合**。比如说,你可以有一个商品数据的索引,一个订单数据的索引,还有一个用户数据的索引。**一个索引由一个名字来标识**``(必须全部是小写字母的),并且当我们要对这个索引中的文档进行索引、搜索、更新和删除的时候,都要使用到这个名字。
映射
**映射是定义一个文档和它所包含的字段如何被存储和索引的过程**。在默认配置下,ES可以根据插入的数据自动地创建mapping,也可以手动创建mapping。 mapping中主要包括字段名、字段类型等
文档
**文档是索引中存储的一条条数据。一条文档是一个可被索引的最小单元**。ES中的文档采用了轻量级的JSON格式数据来表示。
基本操作
索引
创建
# 1.创建索引- PUT /索引名 ====> PUT /products- 注意:1.ES中索引健康转态 red(索引不可用) 、yellwo(索引可用,存在风险)、green(健康)2.默认ES在创建索引时回为索引创建1个备份索引和一个primary索引# 2.创建索引 进行索引分片配置- PUT /products{"settings": {"number_of_shards": 1, #指定主分片的数量"number_of_replicas": 0 #指定副本分片的数量}}

查询
# 查询索引- GET /_cat/indices?v

删除
# 3.删除索引- DELETE /索引名 =====> DELETE /products- DELETE /* `*代表通配符,代表所有索引`

映射
创建
字符串类型: keyword 关键字 关键词 、text 一段文本
数字类型:integer long
小数类型:float double
布尔类型:boolean
日期类型:date
# 1.创建索引&映射
PUT /products{"settings": {"number_of_shards": 1,"number_of_replicas": 0},"mappings": {"properties": {"title":{"type": "keyword"},"price":{"type": "double"},"created_at":{"type": "date"},"description":{"type": "text"}}}}

说明: ES中支持字段类型非常丰富,如:text、keyword、integer、long、ip 等。更多参见https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.15/mapping-types.html
查询
# 1.查看某个索引的映射- GET /索引名/_mapping =====> GET /products/_mapping

文档
添加文档
POST /products/_doc/1 #指定文档id{"title":"iphone13","price":8999.99,"created_at":"2021-09-15","description":"iPhone 13屏幕采用6.1英寸OLED屏幕。"}
POST /products/_doc/ #自动生成文档id{"title":"iphone14","price":8999.99,"created_at":"2021-09-15","description":"iPhone 13屏幕采用6.8英寸OLED屏幕"}
{"_index" : "products","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "sjfYnXwBVVbJgt24PlVU","_version" : 1,"result" : "created","_shards" : {"total" : 1,"successful" : 1,"failed" : 0},"_seq_no" : 3,"_primary_term" : 1}
查询文档
GET /products/_doc/1
{"_index" : "products","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "1","_version" : 1,"_seq_no" : 0,"_primary_term" : 1,"found" : true,"_source" : {"title" : "iphone13","price" : 8999.99,"created_at" : "2021-09-15","description" : "iPhone 13屏幕采用6.1英寸OLED屏幕"}}
删除文档
DELETE /products/_doc/1
{"_index" : "products","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "1","_version" : 2,"result" : "deleted","_shards" : {"total" : 1,"successful" : 1,"failed" : 0},"_seq_no" : 2,"_primary_term" : 1}
更新文档
PUT /products/_doc/sjfYnXwBVVbJgt24PlVU{"title":"iphon15"}
说明: 这种更新方式是先删除原始文档,在将更新文档以新的内容插入。
POST /products/_doc/sjfYnXwBVVbJgt24PlVU/_update{"doc" : {"title" : "iphon15"}}
说明: 这种方式可以将数据原始内容保存,并在此基础上更新。
批量操作
POST /products/_doc/_bulk #批量索引两条文档{"index":{"_id":"1"}}{"title":"iphone14","price":8999.99,"created_at":"2021-09-15","description":"iPhone 13屏幕采用6.8英寸OLED屏幕"}{"index":{"_id":"2"}}{"title":"iphone15","price":8999.99,"created_at":"2021-09-15","description":"iPhone 15屏幕采用10.8英寸OLED屏幕"}
POST /products/_doc/_bulk #更新文档同时删除文档{"update":{"_id":"1"}}{"doc":{"title":"iphone17"}}{"delete":{"_id":2}}{"index":{}}{"title":"iphone19","price":8999.99,"created_at":"2021-09-15","description":"iPhone 19屏幕采用61.8英寸OLED屏幕"}
说明:批量时不会因为一个失败而全部失败,而是继续执行后续操作,在返回时按照执行的状态返回!
高级查询
说明
ES中提供了一种强大的检索数据方式,这种检索方式称之为`Query DSL` ,`Query DSL`是利用`Rest API传递JSON格式的请求体(Request Body)数据`与ES进行交互,这种方式的`丰富查询语法`让ES检索变得`更强大,更简洁`。
语法
# GET /索引名/_doc/_search {json格式请求体数据}# GET /索引名/_search {json格式请求体数据}
- 测试数据
# 1.创建索引 映射PUT /products/{"mappings": {"properties": {"title":{"type": "keyword"},"price":{"type": "double"},"created_at":{"type":"date"},"description":{"type":"text"}}}}# 2.测试数据PUT /products/_doc/_bulk{"index":{}}{"title":"iphone12 pro","price":8999,"created_at":"2020-10-23","description":"iPhone 12 Pro采用超瓷晶面板和亚光质感玻璃背板,搭配不锈钢边框,有银色、石墨色、金色、海蓝色四种颜色。宽度:71.5毫米,高度:146.7毫米,厚度:7.4毫米,重量:187克"}{"index":{}}{"title":"iphone12","price":4999,"created_at":"2020-10-23","description":"iPhone 12 高度:146.7毫米;宽度:71.5毫米;厚度:7.4毫米;重量:162克(5.73盎司) [5] 。iPhone 12设计采用了离子玻璃,以及7000系列铝金属外壳。"}{"index":{}}{"title":"iphone13","price":6000,"created_at":"2021-09-15","description":"iPhone 13屏幕采用6.1英寸OLED屏幕;高度约146.7毫米,宽度约71.5毫米,厚度约7.65毫米,重量约173克。"}{"index":{}}{"title":"iphone13 pro","price":8999,"created_at":"2021-09-15","description":"iPhone 13Pro搭载A15 Bionic芯片,拥有四种配色,支持5G。有128G、256G、512G、1T可选,售价为999美元起。"}
常见检索
查询所有[match_all]
match_all关键字: 返回索引中的全部文档
GET /products/_search{"query": {"match_all": {}}}
关键词查询(term)
term 关键字: 用来使用关键词查询
GET /products/_search{"query": {"term": {"price": {"value": 4999}}}}
NOTE1: 通过使用term查询得知ES中默认使用分词器为
标准分词器(StandardAnalyzer),标准分词器对于英文单词分词,对于中文单字分词。NOTE2: 通过使用term查询得知,
在ES的Mapping Type 中 keyword , date ,integer, long , double , boolean or ip 这些类型不分词,只有text类型分词。
范围查询[range]
range 关键字: 用来指定查询指定范围内的文档
GET /products/_search{"query": {"range": {"price": {"gte": 1400,"lte": 9999}}}}
前缀查询[prefix]
prefix 关键字: 用来检索含有指定前缀的关键词的相关文档
GET /products/_search{"query": {"prefix": {"title": {"value": "ipho"}}}}
通配符查询[wildcard]
wildcard 关键字: 通配符查询 **? 用来匹配一个任意字符 用来匹配多个任意字符
GET /products/_search{"query": {"wildcard": {"description": {"value": "iphon*"}}}}
多id查询[ids]
ids 关键字 : 值为数组类型,用来根据一组id获取多个对应的文档
GET /products/_search{"query": {"ids": {"values": ["verUq3wBOTjuBizqAegi","vurUq3wBOTjuBizqAegk"]}}}
模糊查询[fuzzy]
fuzzy 关键字: 用来模糊查询含有指定关键字的文档
GET /products/_search{"query": {"fuzzy": {"description": "iphooone"}}}
注意:
fuzzy 模糊查询 最大模糊错误 必须在0-2之间
- 搜索关键词长度为 2 不允许存在模糊
- 搜索关键词长度为3-5 允许一次模糊
- 搜索关键词长度大于5 允许最大2模糊
布尔查询[bool]
bool 关键字: 用来组合多个条件实现复杂查询
**must: 相当于&& 同时成立****should: 相当于|| 成立一个就行****must_not: 相当于! 不能满足任何一个**
GET /products/_search
多字段查询[multi_match]
GET /products/_search{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"term": {"price": {"value": 4999}}}]}}}注意: 字段类型分词,将查询条件分词之后进行查询改字段 如果该字段不分词就会将查询条件作为整体进行查询
默认字段分词查询[query_string]
GET /products/_search{"query": {"query_string": {"default_field": "description","query": "屏幕真的非常不错"}}}注意: 查询字段分词就将查询条件分词查询 查询字段不分词将查询条件不分词查询
高亮查询[highlight]
highlight 关键字: 可以让符合条件的文档中的关键词高亮
GET /products/_search{"query": {"term": {"description": {"value": "iphone"}}},"highlight": {"fields": {"*":{}}}}
自定义高亮html标签: 可以在highlight中使用
pre_tags和post_tags
GET /products/_search{"query": {"term": {"description": {"value": "iphone"}}},"highlight": {"post_tags": ["</span>"],"pre_tags": ["<span style='color:red'>"],"fields": {"*":{}}}}
多字段高亮 使用
require_field_match开启多个字段高亮
GET /products/_search{"query": {"term": {"description": {"value": "iphone"}}},"highlight": {"require_field_match": "false","post_tags": ["</span>"],"pre_tags": ["<span style='color:red'>"],"fields": {"*":{}}}}
返回指定条数[size]
size 关键字: 指定查询结果中返回指定条数。 默认返回值10条
GET /products/_search{"query": {"match_all": {}},"size": 5}
分页查询[form]
from 关键字: 用来指定起始返回位置,和size关键字连用可实现分页效果
GET /products/_search{"query": {"match_all": {}},"size": 5,"from": 0}
指定字段排序[sort]
GET /products/_search{"query": {"match_all": {}},"sort": [{"price": {"order": "desc"}}]}
返回指定字段[_source]
_source 关键字: 是一个数组,在数组中用来指定展示那些字段
GET /products/_search{"query": {"match_all": {}},"_source": ["title","description"]}
索引原理
倒排索引
倒排索引(Inverted Index)也叫反向索引,有反向索引必有正向索引。通俗地来讲,正向索引是通过key找value,反向索引则是通过value找key。ES底层在检索时底层使用的就是倒排索引。
索引模型
现有索引和映射如下:
{"products" : {"mappings" : {"properties" : {"description" : {"type" : "text"},"price" : {"type" : "float"},"title" : {"type" : "keyword"}}}}}
先录入如下数据,有三个字段title、price、description等
| _id | title | price | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 蓝月亮洗衣液 | 19.9 |
蓝月亮洗衣液很高效 |
| 2 | iphone13 | 19.9 |
很不错的手机 |
| 3 | 小浣熊干脆面 | 1.5 | 小浣熊很好吃 |
在ES中除了text类型分词,其他类型不分词,因此根据不同字段创建索引如下:
title字段:
| term | _id(文档id) | | —- | —- | | 蓝月亮洗衣液 | 1 | | iphone13 | 2 | | 小浣熊干脆面 | 3 |price字段
| term | _id(文档id) | | —- | —- | | 19.9 | [1,2] | | 1.5 | 3 |description字段
| term | _id | term | _id | term | _id | | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | —- | | 蓝 | 1 | 不 | 2 | 小 | 3 | | 月 | 1 | 错 | 2 | 浣 | 3 | | 亮 | 1 | 的 | 2 | 熊 | 3 | | 洗 | 1 | 手 | 2 | 好 | 3 | | 衣 | 1 | 机 | 2 | 吃 | 3 | | 液 | 1 | | | | | | 很 | [1:1:9,2:1:6,3:1:6] | | | | | | 高 | 1 | | | | | | 效 | 1 | | | | |
**注意: Elasticsearch分别为每个字段都建立了一个倒排索引。因此查询时查询字段的term,就能知道文档ID,就能快速找到文档。**
分词器
Analysis 和 Analyzer
Analysis: 文本分析是把全文本转换一系列单词(term/token)的过程,也叫分词(Analyzer)。Analysis是通过Analyzer来实现的。分词就是将文档通过Analyzer分成一个一个的Term(关键词查询),每一个Term都指向包含这个Term的文档。
Analyzer 组成
- 注意: 在ES中默认使用标准分词器: StandardAnalyzer 特点: 中文单字分词 单词分词
我是中国人 this is good man——> analyzer——> 我 是 中 国 人 this is good man
分析器(analyzer)都由三种构件组成的:
character filters,tokenizers,token filters。
character filter字符过滤器- 在一段文本进行分词之前,先进行预处理,比如说最常见的就是,过滤html标签(hello —> hello),& —> and(I&you —> I and you)
tokenizers分词器- 英文分词可以根据空格将单词分开,中文分词比较复杂,可以采用机器学习算法来分词。
Token filtersToken过滤器- 将切分的单词进行加工。大小写转换(例将“Quick”转为小写),去掉停用词(例如停用词像“a”、“and”、“the”等等),加入同义词(例如同义词像“jump”和“leap”)。
注意:
- 三者顺序: Character Filters—->Tokenizer—->Token Filter
- 三者个数:Character Filters(0个或多个) + Tokenizer + Token Filters(0个或多个)
内置分词器
- Standard Analyzer - 默认分词器,英文按单词词切分,并小写处理
- Simple Analyzer - 按照单词切分(符号被过滤), 小写处理
- Stop Analyzer - 小写处理,停用词过滤(the,a,is)
- Whitespace Analyzer - 按照空格切分,不转小写
- Keyword Analyzer - 不分词,直接将输入当作输出
内置分词器测试
- 标准分词器
- 特点: 按照单词分词 英文统一转为小写 过滤标点符号 中文单字分词
POST /_analyze{"analyzer": "standard","text": "this is a , good Man 中华人民共和国"}
- Simple 分词器
- 特点: 英文按照单词分词 英文统一转为小写 去掉符号 中文按照空格进行分词
POST /_analyze{"analyzer": "simple","text": "this is a , good Man 中华人民共和国"}
- Whitespace 分词器
- 特点: 中文 英文 按照空格分词 英文不会转为小写 不去掉标点符号
POST /_analyze{"analyzer": "whitespace","text": "this is a , good Man"}
创建索引设置分词
PUT /索引名{"settings": {},"mappings": {"properties": {"title":{"type": "text","analyzer": "standard" //显示指定分词器}}}}
中文分词器
在ES中支持中文分词器非常多 如 smartCN、IK 等,推荐的就是 IK分词器。
安装IK
开源分词器 Ik 的github:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik
注意IK分词器的版本要你安装ES的版本一致注意Docker 容器运行 ES 安装插件目录为 /usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins
# 1. 下载对应版本- [es@linux ~]$ wget https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/download/v7.14.0/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.14.0.zip# 2. 解压- [es@linux ~]$ unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.2.4.zip #先使用yum install -y unzip# 3. 移动到es安装目录的plugins目录中- [es@linux ~]$ ls elasticsearch-6.2.4/plugins/[es@linux ~]$ mv elasticsearch elasticsearch-6.2.4/plugins/[es@linux ~]$ ls elasticsearch-6.2.4/plugins/elasticsearch[es@linux ~]$ ls elasticsearch-6.2.4/plugins/elasticsearch/commons-codec-1.9.jar config httpclient-4.5.2.jar plugin-descriptor.propertiescommons-logging-1.2.jar elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.2.4.jar httpcore-4.4.4.jar# 4. 重启es生效# 5. 本地安装ik配置目录为- es安装目录中/plugins/analysis-ik/config/IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml
IK使用
IK有两种颗粒度的拆分:
ik_smart: 会做最粗粒度的拆分ik_max_word: 会将文本做最细粒度的拆分
POST /_analyze{"analyzer": "ik_smart","text": "中华人民共和国国歌"}

POST /_analyze{"analyzer": "ik_max_word","text": "中华人民"}

扩展词、停用词配置
IK支持自定义扩展词典和停用词典
**扩展词典**就是有些词并不是关键词,但是也希望被ES用来作为检索的关键词,可以将这些词加入扩展词典。**停用词典**就是有些词是关键词,但是出于业务场景不想使用这些关键词被检索到,可以将这些词放入停用词典。
定义扩展词典和停用词典可以修改IK分词器中config目录中IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml这个文件。
1. 修改vim IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd"><properties><comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment><!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 --><entry key="ext_dict">ext_dict.dic</entry><!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典--><entry key="ext_stopwords">ext_stopword.dic</entry></properties>2. 在ik分词器目录下config目录中创建ext_dict.dic文件 编码一定要为UTF-8才能生效vim ext_dict.dic 加入扩展词即可3. 在ik分词器目录下config目录中创建ext_stopword.dic文件vim ext_stopword.dic 加入停用词即可4.重启es生效
注意:词典的编码必须为UTF-8,否则无法生效!
过滤查询
过滤查询
过滤查询,其实准确来说,ES中的查询操作分为2种: 查询(query)和过滤(filter)。查询即是之前提到的query查询,它 (查询)默认会计算每个返回文档的得分,然后根据得分排序。而过滤(filter)只会筛选出符合的文档,并不计算 得分,而且它可以缓存文档 。所以,单从性能考虑,过滤比查询更快。 换句话说**过滤适合在大范围筛选数据,而查询则适合精确匹配数据。一般应用时, 应先使用过滤操作过滤数据, 然后使用查询匹配数据。**

使用
GET /ems/emp/_search{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"match_all": {}} //查询条件],"filter": {....} //过滤条件}}
注意:- 在执行 filter 和 query 时,先执行 filter 在执行 query
- Elasticsearch会自动缓存经常使用的过滤器,以加快性能。
类型
常见过滤类型有: term 、 terms 、ranage、exists、ids等filter。
term 、 terms Filter
GET /ems/emp/_search # 使用term过滤{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"term": {"name": {"value": "小黑"}}}],"filter": {"term": {"content":"框架"}}}}}GET /dangdang/book/_search #使用terms过滤{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"term": {"name": {"value": "中国"}}}],"filter": {"terms": {"content":["科技","声音"]}}}}}
ranage filter
GET /ems/emp/_search{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"term": {"name": {"value": "中国"}}}],"filter": {"range": {"age": {"gte": 7,"lte": 20}}}}}}
exists filter
过滤存在指定字段,获取字段不为空的索引记录使用
GET /ems/emp/_search{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"term": {"name": {"value": "中国"}}}],"filter": {"exists": {"field":"aaa"}}}}}
ids filter
过滤含有指定字段的索引记录
GET /ems/emp/_search{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"term": {"name": {"value": "中国"}}}],"filter": {"ids": {"values": ["1","2","3"]}}}}}
整合应用
引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId></dependency>
配置客户端
@Configurationpublic class RestClientConfig extends AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration {@Override@Beanpublic RestHighLevelClient elasticsearchClient() {final ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = ClientConfiguration.builder().connectedTo("172.16.91.10:9200").build();return RestClients.create(clientConfiguration).rest();}}
客户端对象
- ElasticsearchOperations
- RestHighLevelClient 推荐
ElasticsearchOperations
- 特点: 始终使用面向对象方式操作 ES
- 索引: 用来存放相似文档集合
- 映射: 用来决定放入文档的每个字段以什么样方式录入到 ES 中 字段类型 分词器..
- 文档: 可以被索引最小单元 json 数据格式
相关注解
@Document(indexName = "products", createIndex = true)public class Product {@Idprivate Integer id;@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)private String title;@Field(type = FieldType.Float)private Double price;@Field(type = FieldType.Text)private String description;//get set ...}//1. @Document(indexName = "products", createIndex = true) 用在类上 作用:代表一个对象为一个文档-- indexName属性: 创建索引的名称-- createIndex属性: 是否创建索引//2. @Id 用在属性上 作用:将对象id字段与ES中文档的_id对应//3. @Field(type = FieldType.Keyword) 用在属性上 作用:用来描述属性在ES中存储类型以及分词情况-- type: 用来指定字段类型
索引文档
@Testpublic void testCreate() throws IOException {Product product = new Product();product.setId(1); //存在id指定id 不存在id自动生成idproduct.setTitle("怡宝矿泉水");product.setPrice(129.11);product.setDescription("我们喜欢喝矿泉水....");elasticsearchOperations.save(product);}
删除文档
@Testpublic void testDelete() {Product product = new Product();product.setId(1);String delete = elasticsearchOperations.delete(product);System.out.println(delete);}
查询文档
@Testpublic void testGet() {Product product = elasticsearchOperations.get("1", Product.class);System.out.println(product);}
更新文档
@Testpublic void testUpdate() {Product product = new Product();product.setId(1);product.setTitle("怡宝矿泉水");product.setPrice(129.11);product.setDescription("我们喜欢喝矿泉水,你们喜欢吗....");elasticsearchOperations.save(product);//不存在添加,存在更新}
删除所有
@Testpublic void testDeleteAll() {elasticsearchOperations.delete(Query.findAll(), Product.class);}
查询所有
@Testpublic void testFindAll() {SearchHits<Product> productSearchHits = elasticsearchOperations.search(Query.findAll(), Product.class);productSearchHits.forEach(productSearchHit -> {System.out.println("id: " + productSearchHit.getId());System.out.println("score: " + productSearchHit.getScore());Product product = productSearchHit.getContent();System.out.println("product: " + product);});}
RestHighLevelClient
创建索引映射
@Testpublic void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("fruit");createIndexRequest.mapping("{\n" +" \"properties\": {\n" +" \"title\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"price\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"double\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"created_at\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"date\"\n" +" },\n" +" \"description\":{\n" +" \"type\": \"text\"\n" +" }\n" +" }\n" +" }\n" , XContentType.JSON);CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = restHighLevelClient.indices().create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged());restHighLevelClient.close();}
索引文档
@Testpublic void testIndex() throws IOException {IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("fruit");indexRequest.source("{\n" +" \"id\" : 1,\n" +" \"title\" : \"蓝月亮\",\n" +" \"price\" : 123.23,\n" +" \"description\" : \"这个洗衣液非常不错哦!\"\n" +" }",XContentType.JSON);IndexResponse index = restHighLevelClient.index(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(index.status());}
更新文档
@Testpublic void testUpdate() throws IOException {UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("fruit","qJ0R9XwBD3J1IW494-Om");updateRequest.doc("{\"title\":\"好月亮\"}",XContentType.JSON);UpdateResponse update = restHighLevelClient.update(updateRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(update.status());}
删除文档
@Testpublic void testDelete() throws IOException {DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("fruit","1");DeleteResponse delete = restHighLevelClient.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(delete.status());}
基于 id 查询文档
@Testpublic void testGet() throws IOException {GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("fruit","1");GetResponse getResponse = restHighLevelClient.get(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(getResponse.getSourceAsString());}
查询所有
@Testpublic void testSearch() throws IOException {SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("fruit");SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);//System.out.println(searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();for (SearchHit hit : hits) {System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());}}
综合查询
@Testpublic void testSearch() throws IOException {SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("fruit");SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();sourceBuilder.from(0).size(2).sort("price", SortOrder.DESC).fetchSource(new String[]{"title"},new String[]{}).highlighter(new HighlightBuilder().field("description").requireFieldMatch(false).preTags("<span style='color:red;'>").postTags("</span>")).query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("description","错"));searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println("总条数: "+searchResponse.getHits().getTotalHits().value);SearchHit[] hits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();for (SearchHit hit : hits) {System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());Map<String, HighlightField> highlightFields = hit.getHighlightFields();highlightFields.forEach((k,v)-> System.out.println("key: "+k + " value: "+v.fragments()[0]));}}
聚合查询
简介
聚合:英文为Aggregation,是es除搜索功能外提供的针对es数据做统计分析的功能。聚合有助于根据搜索查询提供聚合数据。聚合查询是数据库中重要的功能特性,ES作为搜索引擎兼数据库,同样提供了强大的聚合分析能力。它基于查询条件来对数据进行分桶、计算的方法。有点类似于 SQL 中的 group by 再加一些函数方法的操作。
注意事项:text类型是不支持聚合的。
测试数据
# 创建索引 index 和映射 mappingPUT /fruit{"mappings": {"properties": {"title":{"type": "keyword"},"price":{"type":"double"},"description":{"type": "text","analyzer": "ik_max_word"}}}}# 放入测试数据PUT /fruit/_bulk{"index":{}}{"title" : "面包","price" : 19.9,"description" : "小面包非常好吃"}{"index":{}}{"title" : "旺仔牛奶","price" : 29.9,"description" : "非常好喝"}{"index":{}}{"title" : "日本豆","price" : 19.9,"description" : "日本豆非常好吃"}{"index":{}}{"title" : "小馒头","price" : 19.9,"description" : "小馒头非常好吃"}{"index":{}}{"title" : "大辣片","price" : 39.9,"description" : "大辣片非常好吃"}{"index":{}}{"title" : "透心凉","price" : 9.9,"description" : "透心凉非常好喝"}{"index":{}}{"title" : "小浣熊","price" : 19.9,"description" : "童年的味道"}{"index":{}}{"title" : "海苔","price" : 19.9,"description" : "海的味道"}
使用
根据某个字段分组
# 根据某个字段进行分组 统计数量GET /fruit/_search{"query": {"term": {"description": {"value": "好吃"}}},"aggs": {"price_group": {"terms": {"field": "price"}}}}
求最大值
# 求最大值GET /fruit/_search{"aggs": {"price_max": {"max": {"field": "price"}}}}
求最小值
# 求最小值GET /fruit/_search{"aggs": {"price_min": {"min": {"field": "price"}}}}
求平均值
# 求平均值GET /fruit/_search{"aggs": {"price_agv": {"avg": {"field": "price"}}}}
求和
# 求和GET /fruit/_search{"aggs": {"price_sum": {"sum": {"field": "price"}}}}
整合应用
// 求不同价格的数量@Testpublic void testAggsPrice() throws IOException {SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("fruit");SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();sourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.terms("group_price").field("price"));searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);Aggregations aggregations = searchResponse.getAggregations();ParsedDoubleTerms terms = aggregations.get("group_price");List<? extends Terms.Bucket> buckets = terms.getBuckets();for (Terms.Bucket bucket : buckets) {System.out.println(bucket.getKey() + ", "+ bucket.getDocCount());}}
// 求不同名称的数量@Testpublic void testAggsTitle() throws IOException {SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("fruit");SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();sourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.terms("group_title").field("title"));searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);Aggregations aggregations = searchResponse.getAggregations();ParsedStringTerms terms = aggregations.get("group_title");List<? extends Terms.Bucket> buckets = terms.getBuckets();for (Terms.Bucket bucket : buckets) {System.out.println(bucket.getKey() + ", "+ bucket.getDocCount());}}
// 求和@Testpublic void testAggsSum() throws IOException {SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("fruit");SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();sourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.sum("sum_price").field("price"));searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);SearchResponse searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);ParsedSum parsedSum = searchResponse.getAggregations().get("sum_price");System.out.println(parsedSum.getValue());}
集群 Cluster
相关概念
集群
一个集群就是由一个或多个节点组织在一起,它们共同持有你整个的数据,并一起提供索引和搜索功能。一个集群由一个唯一的名字标识,这个名字默认就是elasticsearch。这个名字是重要的,因为一个节点只能通过指定某个集群的名字,来加入这个集群。
节点
一个节点是你集群中的一个服务器,作为集群的一部分,它存储你的数据,参与集群的索引和搜索功能。和集群类似,一个节点也是由一个名字来标识的,默认情况下,这个名字是一个随机的漫威漫画角色的名字,这个名字会在启动的时候赋予节点。
索引
一组相似文档的集合
映射
用来定义索引存储文档的结构如:字段、类型等。
文档
索引中一条记录,可以被索引的最小单元
分片
Elasticsearch提供了将索引划分成多份的能力,这些份就叫做分片。当你创建一个索引的时候,你可以指定你想要的分片的数量。每个分片本身也是一个功能完善并且独立的“索引”,这个“索引”可以被放置 到集群中的任何节点上。
复制
Index的分片中一份或多份副本。
搭建集群
集群规划
# 1.准备3个ES节点和一个kibana 节点 ES 9200 9300- web: 9201 tcp:9301 node-1 elasticsearch.yml- web: 9202 tcp:9302 node-2 elasticsearch.yml- web: 9203 tcp:9303 node-3 elasticsearch.yml- kibana: 5602
- 注意
- 所有节点集群名称必须一致 cluster.name
- 每个节点必须有一个唯一名字 node.name
- 开启每个节点远程连接 network.host: 0.0.0.0
- 指定使用 IP地址进行集群节点通信 network.publish_host:
- 修改 web 端口 tcp 端口 http.port: transport.tcp.port
- 指定集群中所有节点通信列表 discovery.seed_hosts: node-1 node-2 node-3 相同
- 允许集群初始化 master 节点节点数: cluster.initial_master_nodes: [“node-1”, “node-2”,”node-3”]
- 集群最少几个节点可用 gateway.recover_after_nodes: 2
- 开启每个节点跨域访问http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: “*”
配置文件
# node-1 配置文件
# 指定集群名称 3个节点必须一致cluster.name: es-cluster# 指定节点名称 每个节点名字唯一node.name: node-1# 开放远程链接network.host: 0.0.0.0# 指定使用发布地址进行集群间通信network.publish_host: 192.168.124.3# 指定 web 端口http.port: 9201# 指定 tcp 端口transport.tcp.port: 9301# 指定所有节点的 tcp 通信discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.124.3:9301", "192.168.124.3:9302","192.168.124.3:9303"]# 指定可以初始化集群的节点名称cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2","node-3"]# 集群最少几个几点可用gateway.recover_after_nodes: 2# 解决跨域问题http.cors.enabled: truehttp.cors.allow-origin: "*"
# node-2 配置文件
# 指定集群名称 3个节点必须一致cluster.name: es-cluster# 指定节点名称 每个节点名字唯一node.name: node-2# 开放远程链接network.host: 0.0.0.0# 指定使用发布地址进行集群间通信network.publish_host: 192.168.124.3# 指定 web 端口http.port: 9202# 指定 tcp 端口transport.tcp.port: 9302# 指定所有节点的 tcp 通信discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.124.3:9301", "192.168.124.3:9302","192.168.124.3:9303"]# 指定可以初始化集群的节点名称cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2","node-3"]# 集群最少几个几点可用gateway.recover_after_nodes: 2# 解决跨域问题http.cors.enabled: truehttp.cors.allow-origin: "*"
# node-3 配置文件
# 指定集群名称 3个节点必须一致cluster.name: es-cluster# 指定节点名称 每个节点名字唯一node.name: node-2# 开放远程链接network.host: 0.0.0.0# 指定使用发布地址进行集群间通信network.publish_host: 192.168.124.3# 指定 web 端口http.port: 9202# 指定 tcp 端口transport.tcp.port: 9302# 指定所有节点的 tcp 通信discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.124.3:9301", "192.168.124.3:9302","192.168.124.3:9303"]# 指定可以初始化集群的节点名称cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2","node-3"]# 集群最少几个几点可用gateway.recover_after_nodes: 2# 解决跨域问题http.cors.enabled: truehttp.cors.allow-origin: "*"
编写 compose 文件
version: "3.8"networks:escluster:services:es01:image: elasticsearch:7.14.0ports:- "9201:9201"- "9301:9301"networks:- "escluster"volumes:- ./node-1/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data- ./node-1/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml- ./node-1/plugins/ik:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/ikenvironment:- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"es02:image: elasticsearch:7.14.0ports:- "9202:9202"- "9302:9302"networks:- "escluster"volumes:- ./node-2/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data- ./node-2/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml- ./node-2/plugins/ik:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/ikenvironment:- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"es03:image: elasticsearch:7.14.0ports:- "9203:9203"- "9303:9303"networks:- "escluster"volumes:- ./node-3/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data- ./node-3/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml- ./node-3/plugins/ik:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/ikenvironment:- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"kibana:image: kibana:7.14.0ports:- "5602:5601"networks:- "escluster"volumes:- ./kibana.yml:/usr/share/kibana/config/kibana.yml
kibana 配置文件
# kibana配置文件 连接到ESserver.host: "0"server.shutdownTimeout: "5s"elasticsearch.hosts: [ "http://192.168.124.3:9201" ] #链接任意节点即可monitoring.ui.container.elasticsearch.enabled: true
查看集群状态
http://10.102.115.3:9200/_cat/health?v
安装head插件
1. 访问github网站搜索: elasticsearch-head 插件2. 安装gityum install git3. 将elasticsearch-head下载到本地git clone git://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head.git4. 安装nodejs#注意: 没有wget的请先安装yum install -y wgetwget http://cdn.npm.taobao.org/dist/node/latest-v8.x/node-v8.1.2-linux-x64.tar.xz5. 解压缩nodejsxz -d node-v10.15.3-linux-arm64.tar.xztar -xvf node-v10.15.3-linux-arm64.tar6. 配置环境变量mv node-v10.15.3-linux-arm64 nodejsmv nodejs /usr/nodejsvim /etc/profileexport NODE_HOME=/usr/nodejsexport PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$NODE_HOME/bin7. 进入elasticsearch-head的目录npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.orgnpm installnpm run start8. 启动访问head插件 默认端口9100http://ip:9100 查看集群状态

