1、ThreadGroup 与 Thread
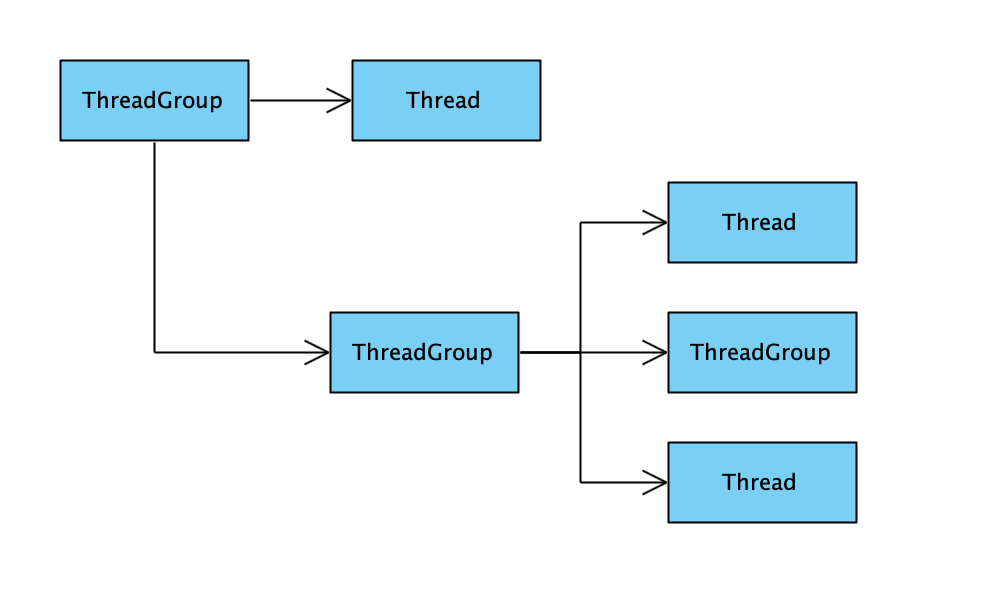
Java 程序中,默认情况下,新的线程都会被加入到 main 线程所在的 group 中,main 线程的 group 名字同线程名。父子 Thread、父子 ThreadGroup 以及 Thread 以及 ThreadGroup 之间的层次关系,如图所示:
2、ThreadGroup 详细介绍
2.1、创建 ThreadGroup
ThreadGroup 的构造函数
public ThreadGroup(String name) public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name)
/*** Constructs a new thread group. The parent of this new group is* the thread group of the currently running thread.* <p>* The <code>checkAccess</code> method of the parent thread group is* called with no arguments; this may result in a security exception.** @param name the name of the new thread group.* @exception SecurityException if the current thread cannot create a* thread in the specified thread group.* @see java.lang.ThreadGroup#checkAccess()* @since JDK1.0*/public ThreadGroup(String name) {// 默认取当线程所在的线程组设为 this 的父线程组this(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), name);}/*** Creates a new thread group. The parent of this new group is the* specified thread group.* <p>* The <code>checkAccess</code> method of the parent thread group is* called with no arguments; this may result in a security exception.** @param parent the parent thread group.* @param name the name of the new thread group.* @exception NullPointerException if the thread group argument is* <code>null</code>.* @exception SecurityException if the current thread cannot create a* thread in the specified thread group.* @see java.lang.SecurityException* @see java.lang.ThreadGroup#checkAccess()* @since JDK1.0*/public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name) {this(checkParentAccess(parent), parent, name);}private ThreadGroup(Void unused, ThreadGroup parent, String name) {this.name = name;this.maxPriority = parent.maxPriority;this.daemon = parent.daemon;this.vmAllowSuspension = parent.vmAllowSuspension;this.parent = parent;parent.add(this);}
示例代码:
package com.yj.thread_group;/*** @description: 创建线程组* @author: erlang* @since: 2021-02-25 23:21*/public class CreateThreadGroup {public static void main(String[] args) {ThreadGroup mainGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();// 只指定了线程组的名字,未指定父 group// 这里默认父 group 为当前线程所在的 group 即 curTheadGroupThreadGroup group1 = new ThreadGroup("Group_1");System.out.println(group1.getParent() == mainGroup);// 这里指定了线程组的名字和父线程组ThreadGroup group2 = new ThreadGroup(group1, "Group_2");System.out.println(group2.getParent() == group1);}}
2.2、复制 Thread 数组到 ThreadGroup 数组
在一个线程组中会加入若干个线程以及子线程组,线程组为我们提供了若干个方法,可以复制出线程和线程组。
2.2.1、复制 Thread 数组
下面两个方法,会将 ThreadGroup 中的 active 线程全部复制到线程数组中,其中 recurse 参数如果为 true,则该方法会将所有子线程组中的活跃线程都递归到线程数组中,
public int enumerate(Thread list[]) {checkAccess();return enumerate(list, 0, true);}public int enumerate(Thread list[], boolean recurse) {checkAccess();return enumerate(list, 0, recurse);}// recurse 为 true 时,递归累加子线程组里的存活线程private int enumerate(Thread list[], int n, boolean recurse) {int ngroupsSnapshot = 0;ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot = null;synchronized (this) {if (destroyed) {return 0;}int nt = nthreads;if (nt > list.length - n) {nt = list.length - n;}for (int i = 0; i < nt; i++) {if (threads[i].isAlive()) {list[n++] = threads[i];}}if (recurse) {ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;if (groups != null) {groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);} else {groupsSnapshot = null;}}}if (recurse) {for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {n = groupsSnapshot[i].enumerate(list, n, true);}}return n;}
示例代码:
package com.yj.thread_group;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** @description: 复制 Thread 数组* @author: erlang* @since: 2021-02-25 23:40*/public class EnumerateThread {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("CustomThreadGroup");Thread thread = new Thread(threadGroup, () -> {while (true) {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "Thread");thread.start();TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(2000);ThreadGroup mainGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();Thread[] threads = new Thread[mainGroup.activeCount()];int enumerates = mainGroup.enumerate(threads);System.out.println("第一次输出:" + enumerates);enumerates = mainGroup.enumerate(threads, false);System.out.println("第二次输出:" + enumerates);}}
上面的代码运行结果如下,最后一个输出会比第一个少 1,这是因为代码中将递归 recurse 设置为了 false,CustomThreadGroup 中的线程不会包含在内。
第一次输出:3第二次输出:2
注意:
- enumerate 方法获取的线程仅仅是个预估值,并不能百分之百的保证当前线程组的活跃线程。比如,在调用复制之后,某个线程结束了生命周期或者新的线程加入了进来,都会导致数据的不准确
- enumerate 方法的返回值比 threads 的长度真实
2.2.1、复制 ThreadGroup 数组
和前面介绍的复制线程数组类似,下面两个方法,主要用于复制当前 ThreadGroup 的子线程组,同样 recurse 会决定是否以递归的方式复制。
public int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[]) {checkAccess();return enumerate(list, 0, true);}public int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[], boolean recurse) {checkAccess();return enumerate(list, 0, recurse);}private int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[], int n, boolean recurse) {int ngroupsSnapshot = 0;ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot = null;synchronized (this) {if (destroyed) {return 0;}int ng = ngroups;if (ng > list.length - n) {ng = list.length - n;}if (ng > 0) {System.arraycopy(groups, 0, list, n, ng);n += ng;}if (recurse) {ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;if (groups != null) {groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);} else {groupsSnapshot = null;}}}if (recurse) {for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {n = groupsSnapshot[i].enumerate(list, n, true);}}return n;}
示例代码:
package com.yj.thread_group;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** @description: 复制 ThreadGroup 数组* @author: erlang* @since: 2021-02-25 23:40*/public class EnumerateThreadGroup {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ThreadGroup threadGroup1 = new ThreadGroup("CustomThreadGroup_1");ThreadGroup threadGroup2 = new ThreadGroup(threadGroup1, "CustomThreadGroup_2");TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(2);ThreadGroup mainGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();ThreadGroup[] threads = new ThreadGroup[mainGroup.activeGroupCount()];int enumerates = mainGroup.enumerate(threads);System.out.println("第一次输出:" + enumerates);enumerates = mainGroup.enumerate(threads, false);System.out.println("第二次输出:" + enumerates);}}
上面的代码运行结果如下,这是因为 threadGroup1 的父线程组为 currentThreadGroup,而 threadGroup2 的父线程组为 threadGroup1。
第一次输出:2第二次输出:1
2.4、ThreadGroup 操作
2.4.1、ThreadGroup 的基本操作
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| activeCount | 用于获取线程组中活跃的线程数量,这个值是估计值,并不能保证百分之百准确。原因:该方法会递归获取其他子线程组中的活跃线程数量 |
| activeGroupCount | 用于获取线程组中活跃的子线程组数量,这也是一个估计值,该方法也会递归获取所有的子线程组数量 |
| getMaxPriority | 用于获取线程组的优先级。默认情况下,线程组的优先级为 10,在该线程组中,所有线程的优先级都不能大于线程组的优先级 |
| getName | 获取线程组的名字 |
| getParent | 用于获取当前线程组的父线程组,如果父线程组不存在,则会返回 null。比如:system group 的父线程组为 null |
| list | 没有返回值,执行该方法会将线程组中所有的活跃线程信息全部输出到控制台,即 System.out |
| parentOf(ThreadGroup g) | 会判断当前线程组是不是给定线程组的父线程组,另外如果给定的线程组的就是自己本身,那么该方法也会返回 true |
| setMaxPriority(int pri) | 会指定线程组的最大优先级,但最大优先级不能超过父线程组的最大优先级,执行该方法不仅会改变当前线程组的最大优先级,还会改变所有子线程组的最大优先级 |
示例代码:
package com.yj.thread_group;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** @description: ThreadGroup 方法使用* @author: erlang* @since: 2021-03-01 20:29*/public class ThreadGroupMethod {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("ThreadGroup_1");Thread thread = new Thread(threadGroup, () -> {while (true) {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "Thread");thread.start();TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(1);ThreadGroup mainGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();System.out.println("activeCount=" + mainGroup.activeCount());System.out.println("activeGroupCount=" + mainGroup.activeGroupCount());System.out.println("getMaxPriority=" + mainGroup.getMaxPriority());System.out.println("getName=" + mainGroup.getName());System.out.println("mainGroup.getParent=" + mainGroup.getParent());System.out.println("\r\nlist: ");mainGroup.list();System.out.println("threadGroup.getParent=" + threadGroup.getParent());System.out.println("parentOf=" + mainGroup.parentOf(threadGroup));System.out.println("parentOf=" + mainGroup.parentOf(mainGroup));}}
运行结果如下:
activeCount=3activeGroupCount=1getMaxPriority=10getName=mainmainGroup.getParent=java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=system,maxpri=10]list:java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main,maxpri=10]Thread[main,5,main]Thread[Monitor Ctrl-Break,5,main]java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=ThreadGroup_1,maxpri=10]Thread[Thread,5,ThreadGroup_1]threadGroup.getParent=java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main,maxpri=10]parentOf=trueparentOf=true
2.4.2、ThreadGroup 的 interrupt
中断一个线程组会导致该线程组中所有的活跃线程都被中断,即该线程组中每一个线程都被设置了 interrupt 标识。下面是 ThreadGroup.interrupt 方法的源码,从源码中可以看出在 interrupt 内部会执行所有线程的 interrupt 方法。
public final void interrupt() {int ngroupsSnapshot;ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;synchronized (this) {checkAccess();for (int i = 0 ; i < nthreads ; i++) {threads[i].interrupt();}ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;if (groups != null) {groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);} else {groupsSnapshot = null;}}for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {groupsSnapshot[i].interrupt();}}
示例代码:
package com.yj.thread_group;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** @description: 线程组中断* @author: erlang* @since: 2021-03-01 21:02*/public class ThreadGroupInterrupt {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("ThreadGroup_1");new Thread(threadGroup, () -> {while (true) {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {break;}}System.out.println("thread1 is End!");}, "thread1").start();new Thread(threadGroup, () -> {while (true) {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {break;}}System.out.println("thread2 is End!");}, "thread2").start();TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(2);threadGroup.interrupt();}}
执行结果:
thread2 is End!thread1 is End!
2.4.3、ThreadGroup 的 destroy
destroy 用于销毁线程组,该方法只是针对一个没有任何活跃线程的线程组进行一次 destroy 标记,调用该方法的直接结果是在父线程组中将自己移除。
示例代码:
package com.yj.thread_group;/*** @description: 线程组的销毁方法* @author: erlang* @since: 2021-03-01 21:13*/public class ThreadGroupDestroy {public static void main(String[] args) {ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("ThreadGroup");ThreadGroup mainGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();System.out.println("threadGroup.isDestroyed=" + threadGroup.isDestroyed());mainGroup.list();threadGroup.destroy();System.out.println("====================================================");System.out.println("threadGroup.isDestroyed=" + threadGroup.isDestroyed());mainGroup.list();}}
执行结果:
threadGroup.isDestroyed=falsejava.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main,maxpri=10]Thread[main,5,main]Thread[Monitor Ctrl-Break,5,main]java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=ThreadGroup,maxpri=10]====================================================threadGroup.isDestroyed=truejava.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main,maxpri=10]Thread[main,5,main]Thread[Monitor Ctrl-Break,5,main]
2.4.4、守护 ThreadGroup
线程可以设置为守护线程,线程组也可以设置为守护线程组,但是若将一个线程组设置为守护线程组(daemon),并不会影响线程的 daemon 属性。如果一个线程组的 daemon 被设置为 true,那么在线程组没有任何活跃的时候该线程组将自动销毁。示例代码:
package com.yj.thread_group;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** @description: 守护线程组* @author: erlang* @since: 2021-03-01 21:21*/public class ThreadGroupDaemon {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ThreadGroup threadGroup1 = new ThreadGroup("ThreadGroup_1");new Thread(threadGroup1, () -> {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "ThreadGroup_1-thread1").start();ThreadGroup threadGroup2 = new ThreadGroup("ThreadGroup_2");new Thread(threadGroup2, () -> {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "ThreadGroup_2-thread2").start();threadGroup2.setDaemon(true);TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println("threadGroup1.isDestroyed=" + threadGroup1.isDestroyed());System.out.println("threadGroup2.isDestroyed=" + threadGroup2.isDestroyed());}}
执行结果:
threadGroup1.isDestroyed=falsethreadGroup2.isDestroyed=true
3、总结
本文详细介绍了线程组和线程之间的关系,并简单介绍了 ThreadGroup 的大部分的 API。线程组并不是管理线程的,而是针对线程的一个组织。

