学习目标:
- 了解Swagger的作用和概念
- 了解前后端分离
- 在springboot中集成Swagger
- Swagger简介:
前后端分离:
Vue+springboot
Vue是有双向绑定的 他的前端视图都是用js渲染的,我们只需要通过后端吧前端的js页面数据生成就行了后端时代:
前端只用管理静态页面;html,js,css==》后端。使用模板引擎 JSP =》后端是主力前后端分离时代:
前端:
前端控制层(vue双向绑定,通过data渲染), 视图层(views)【在公司前端团队搞】
1.伪造后端数据 ,在js文件里面放入JSON数据。数据已经存在了,不需要后端,前端的工程也能跑起来,数据请求的是前端本地的js,在真实上线数据应该请求的后端接口 如前端js文件数据留有
{
“code” :0,
“msg” :””,
“data” : {“username” : “青江”,
“sex” : “男”,
“role” : 1}
}
后端:
后端控制层(Controller),服务层(Service),数据访问层(Dao)【在公司后端团队搞】
进行交互的时候 后台提供的API返回的也应该是一模一样的数据
{
“code” :0,
“msg” :””,
“data” : {“username” : “青江”,
“sex” : “男”,
“role” : 1}
}
前后端如何交互?
前端让后端提供API接口 并且跟他说好这个接口返回的json数据是什么格式 ,后端说我知道了 我马上就去按照你的要求写一个接口,并返回你要求的json数据
前后端相对独立
前后端相对独立,松耦合度 ,甚至他们两个可以部署在不同的服务器上 如前端8080端口 后端9090端口
产生问题:
前后端集成联调,前端和后端人员无法做到及时协商,来尽早解决。如果前端临时加需求,后端要写大量的代码,最终导致问题集中爆发导致工程延期
解决方案:
- 首先制定schema【计划的提纲】,实时更新最新的API,降低集成的风险;
- 早些年:制定world计划文档;
前后端分离:
需要一种后端更新了,前端需要生成一个界面来使用我的API,前端还可以测试我的API是否可以链接成功<br /> 1.前端需要测试后端的接口 :postman工具可以来测试<br /> 2.后端提供接口,需要实时更新最新的消息及改动
Swagger
号称世界上最流行的Api框架;
- RestFul Api 文档在线自动生成工具 =》Api文档与Api定义同步更新
- 直接允许,可以在线测试api接口;
-
Swagger官网
https://swagger.io/
使用Swagger开源和专业工具集简化用户、团队和企业的API开发。了解Swagger如何帮助您按比例设计和记录API。在项目中使用Swagger需要spring box;
Swagger2
- ui
在springBoot中集成Swagger
1.新建一个springboot-web项目
Swagger-text.zip2.导入相关依赖分别是

<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui --><dependency><groupId>io.springfox</groupId><artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId><version>2.9.2</version></dependency><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 --><dependency><groupId>io.springfox</groupId><artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId><version>2.9.2</version></dependency>
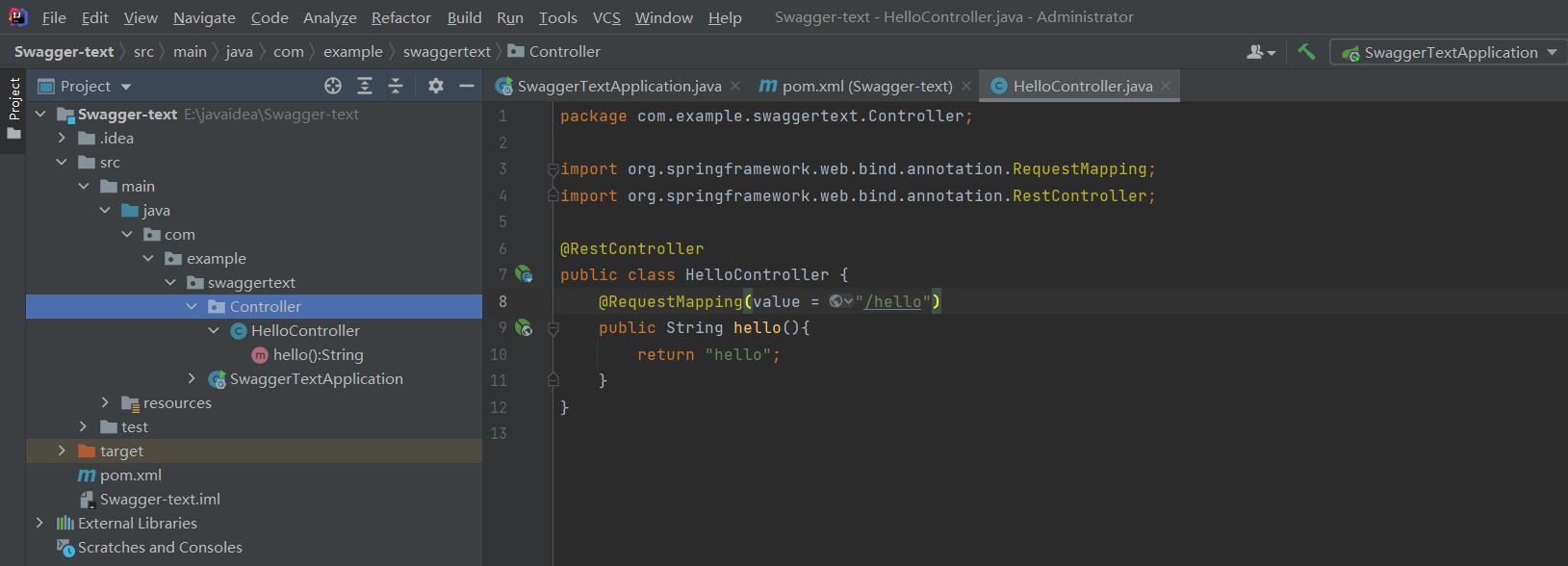
3.编写一个hello工程
4.配置Swagger==>Config
@Configuration
只要加了就会配置到配置里面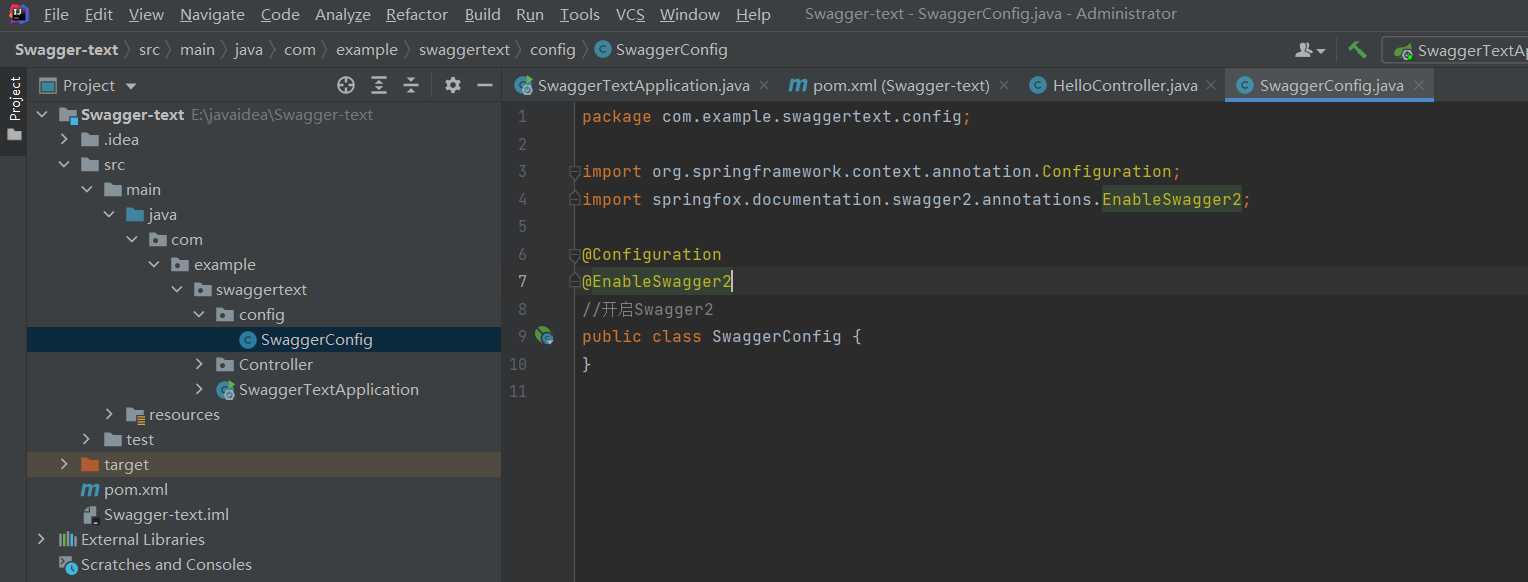
加入@EnableSwagger2注解就会开启Swagger2
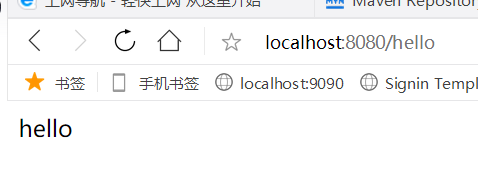
5.我们访问:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html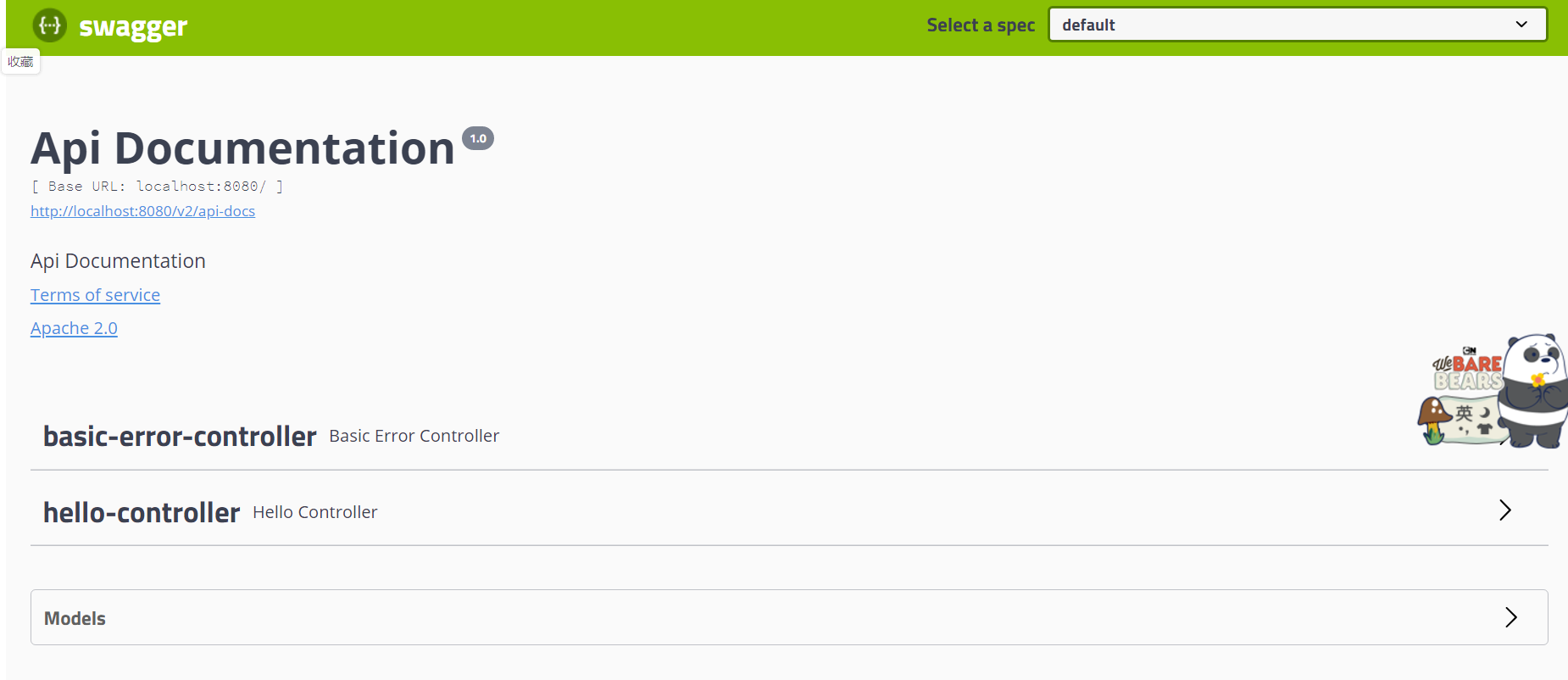
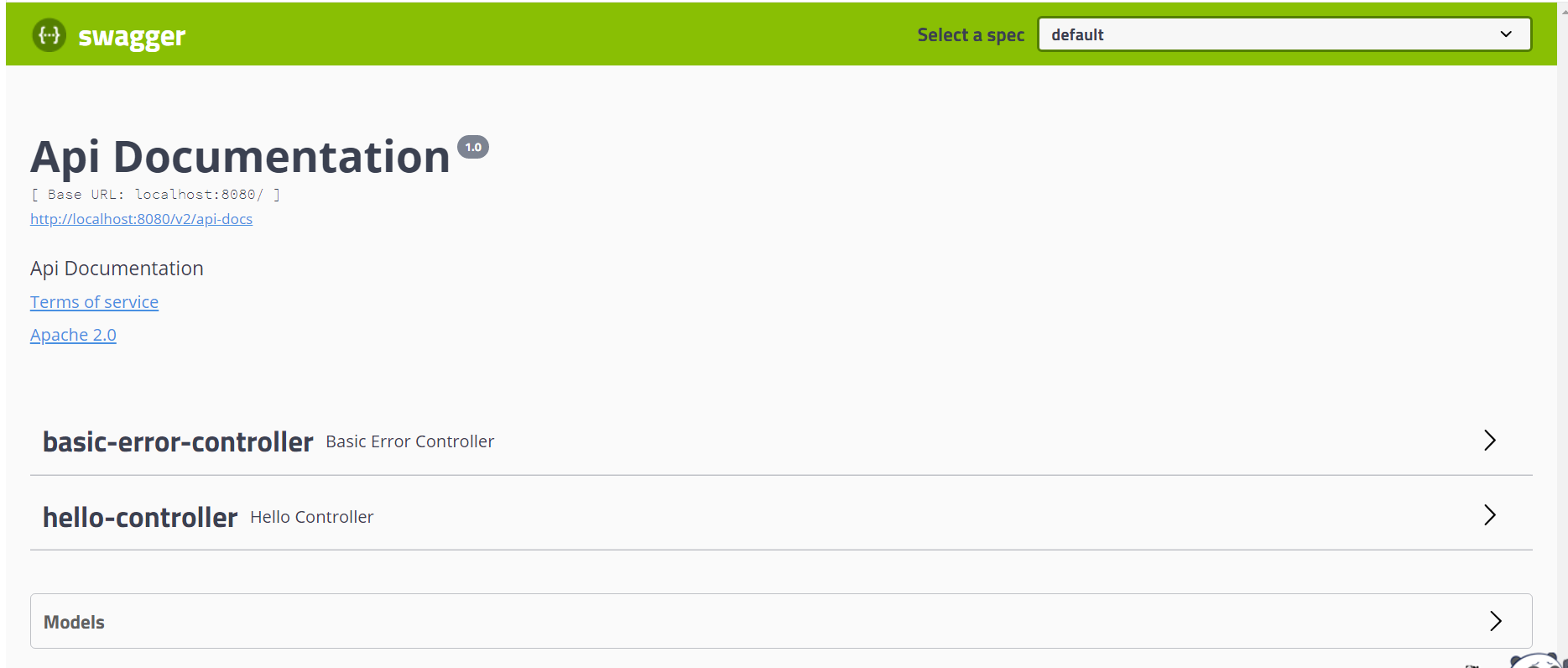
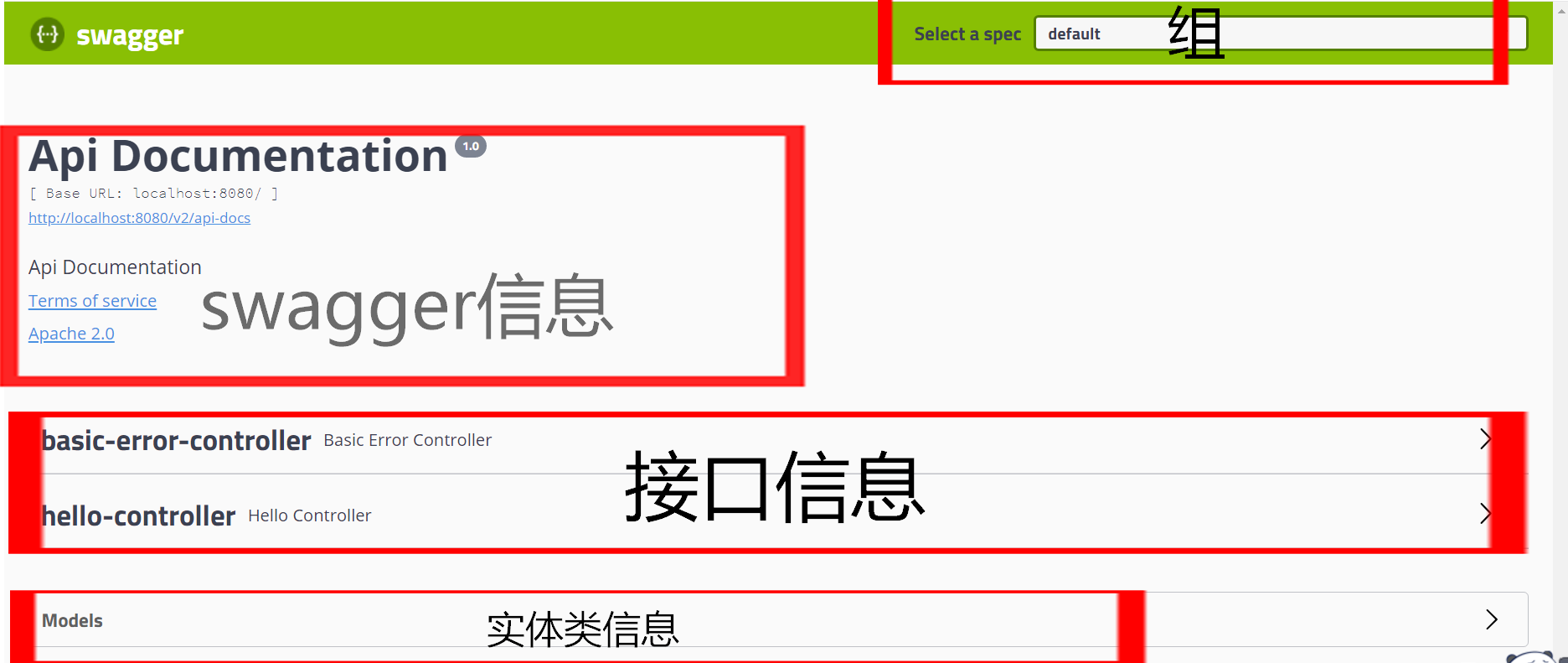
配置Swagger基本信息
Swagger 的 bean 实例Docket
配置基本信息
package com.example.swaggertext.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;import java.util.ArrayList;@Configuration@EnableSwagger2//开启Swagger2public class SwaggerConfig {//作者信息public static final Contact DEFAULT_CONTACT = new Contact("", "", "");//配置了Swagger 的Docket的bean实例@Beanpublic Docket docket(){return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo());}//配置Swagger信息=apiInfoprivate ApiInfo apiInfo(){return new ApiInfo("Api Documentation","Api Documentation","1.0","urn:tos",DEFAULT_CONTACT,"Apache 2.0","http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0", new ArrayList());}}
Swagger配置扫描接口以及开关
默认的扫描接口是所有的扫描都写了
select()方法可以自定义扫描接口
@Beanpublic Docket docket(){return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo()).select()//RequestHandlerSelectors配置要扫描接口的方式.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example.swaggertext.Controller"))//any() 扫描全部的接口//.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())//none()默认不扫描//.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.none())//withClassAnnotation扫描类上的注解 参数只能是 注解的.class//.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withClassAnnotation(Generated.class))// withMethodAnnotation 扫描方法上的注解//.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withMethodAnnotation(Generated.class))//.paths 过滤器 我首先扫描Controller包里面的东西 使用paths方法过滤只要 helloController里面的接口.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/helloController/**")).build();
配置是否启动Swagger
public Docket docket(){return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo())//enable配置是否启动Swagger 如果未false 则 sweeger不能在浏览器中访问.enable(false);
我只希望我的swagger只在生产环境中使用 在发布的时候不使用
- 判断是不是生产环境 flag = false
将flag赋值给enable就可以.enable(flag)
如何判断我们的端口号是哪个?
- dev是我们的测试环境端口号为8989,生产环境是我们的pro端口号为9999
- 在application.properties中spring.profiles.active=dev 来激活我们的测试端口
在代码里面获取环境:
//看一下项目到底是测试的,生产的,还是默认的public Docket docket(Environment environment){//设置要显示的Swagger环境Profiles profiles = Profiles.of("dev");//通过environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles); 判断是否处在自己设定的环境当中 如果是“dev”//flag就是ture 不是就是falseboolean flag = environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles);
配置API文档分组以及接口注释
我们首先到默认端口 8080上
- 我们现在有ABC三个人员协同开发 让他们每个人分别负责 A B C三个模块
新建ABC三个分组
@Beanpublic Docket docket1(){return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("A");}@Beanpublic Docket docket2(){return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("B");}@Beanpublic Docket docket3(){return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("C");}
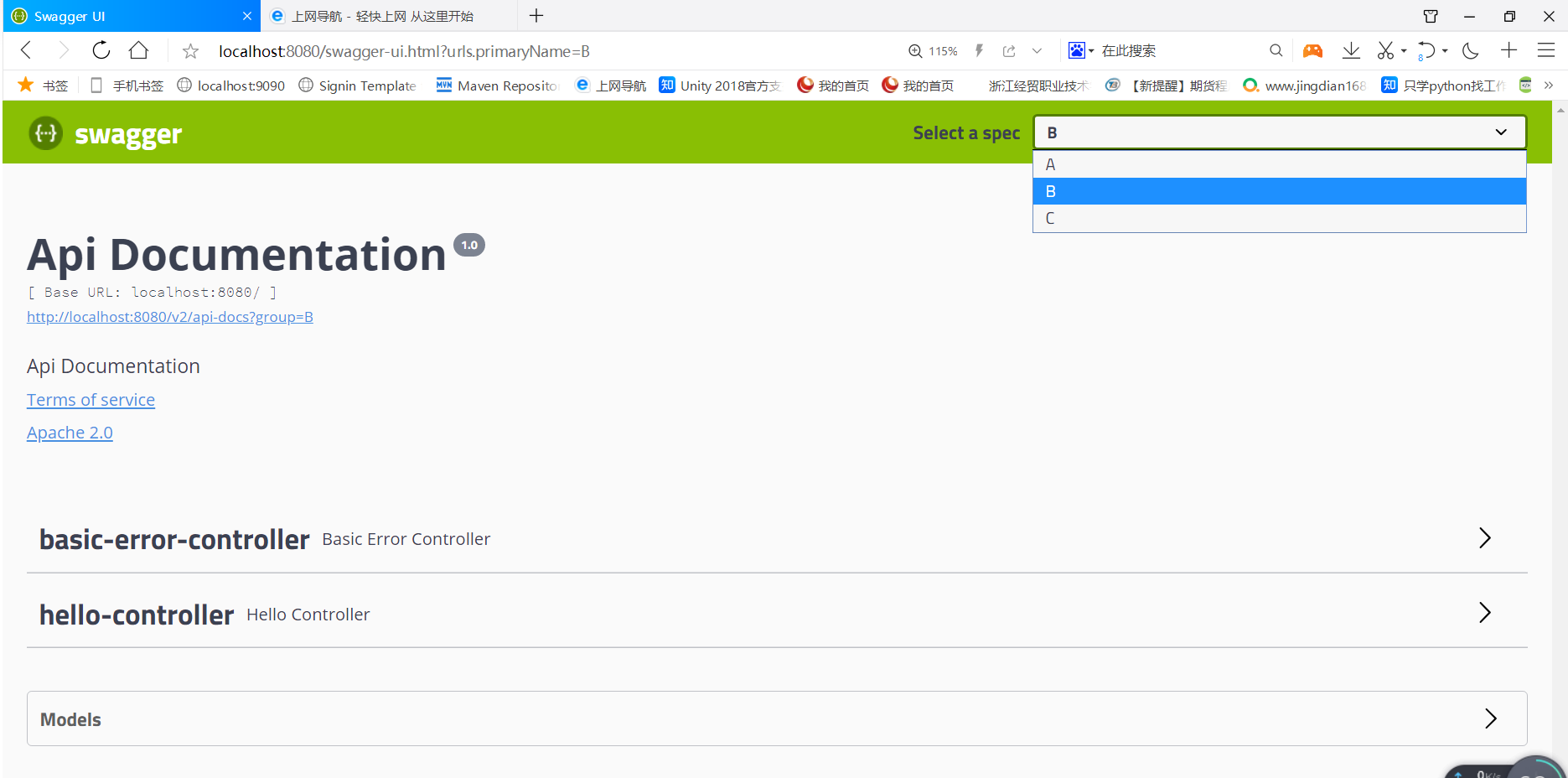
我们新建一个实体类User ```java package com.example.swaggertext.pojo;
public class User { public String username; public String password; }
在写一个User的API```java//只要我们的接口中,返回值中存在实体类 他就会被扫描到Swagger中@PostMapping("/user")public User user(){return new User();}
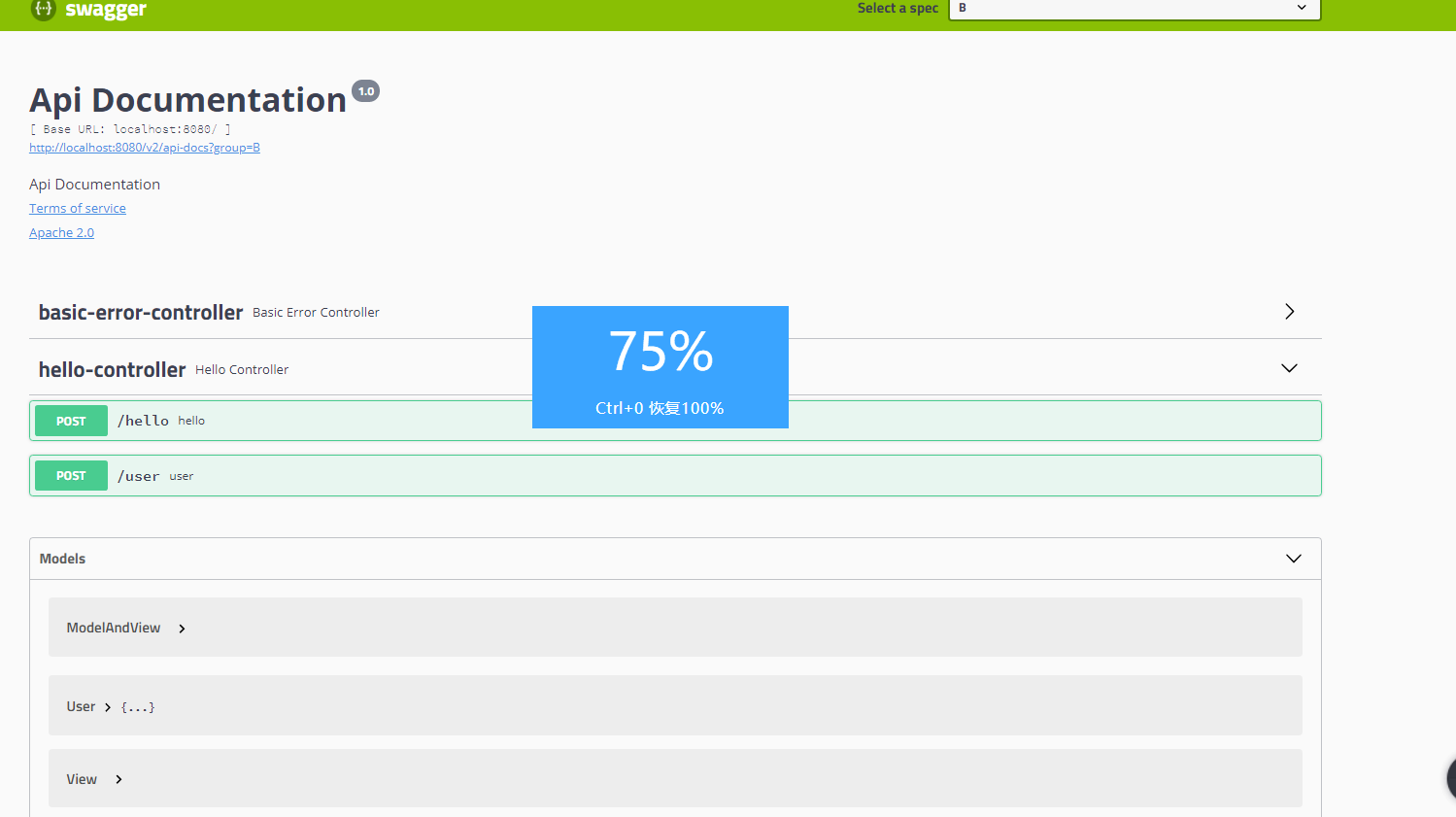
可以看到Controller 和model都有user
- 我们还可以给生成的文档加注释 ```java @ApiModel(“用户实体类”) public class User { @ApiModelProperty(“用户名”) public String username; @ApiModelProperty(“密码”) public String password; }
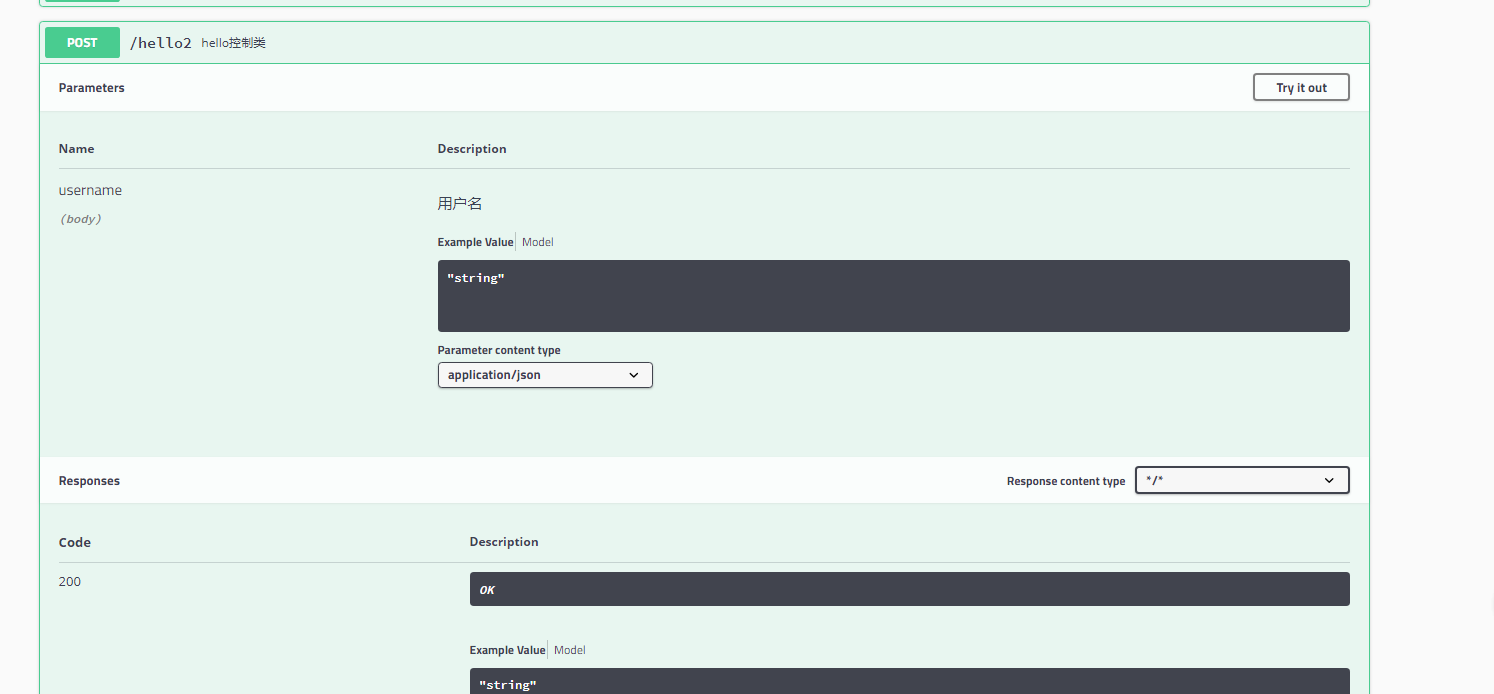
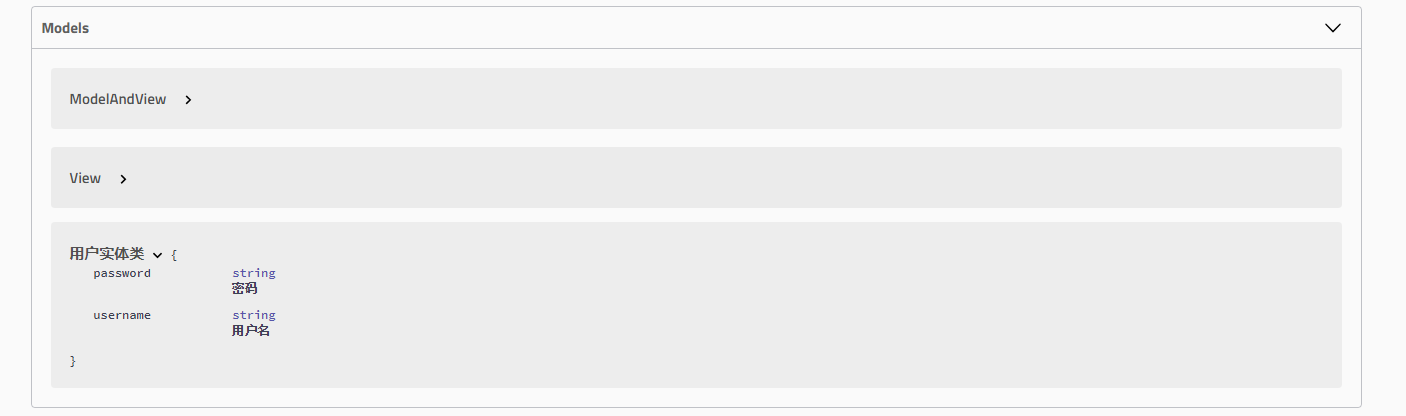- 还可以给API加注释我们新建一个API hello2```java@ApiOperation("hello控制类")@PostMapping(value = "/hello2")public String hello2(@ApiParam("用户名") @RequestBody String username ){System.out.println(username);return "hello"+username;}
swagger的测试功能
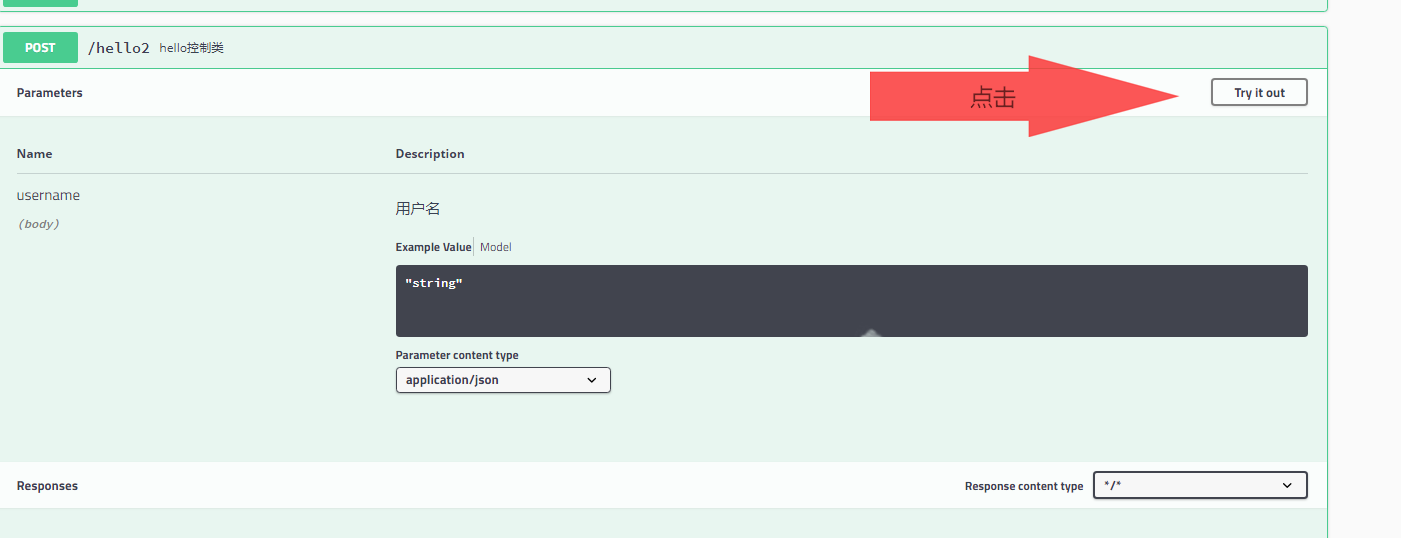
点击Try it out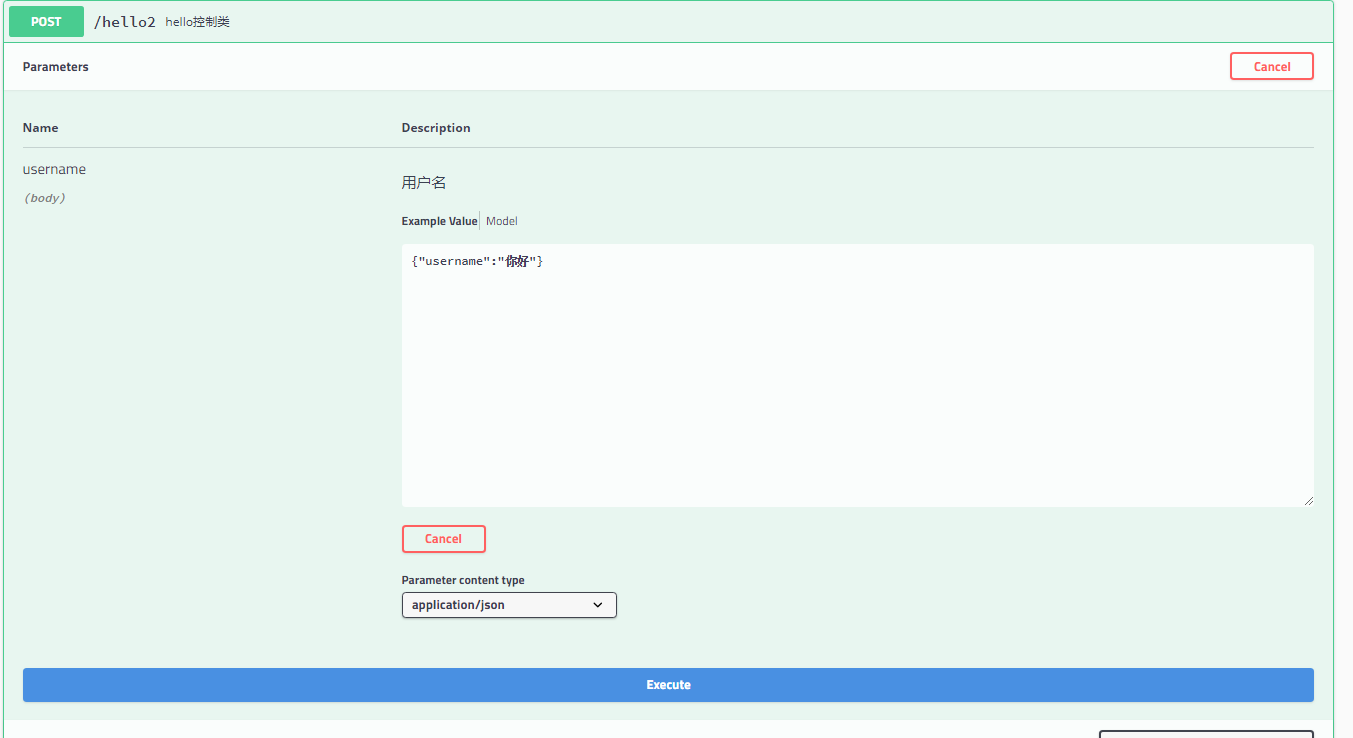
我们给后端发送请求 字符串
{“username”:”你好”}
“username”:”你好”
“你好”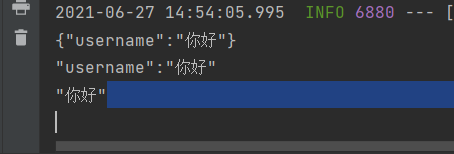
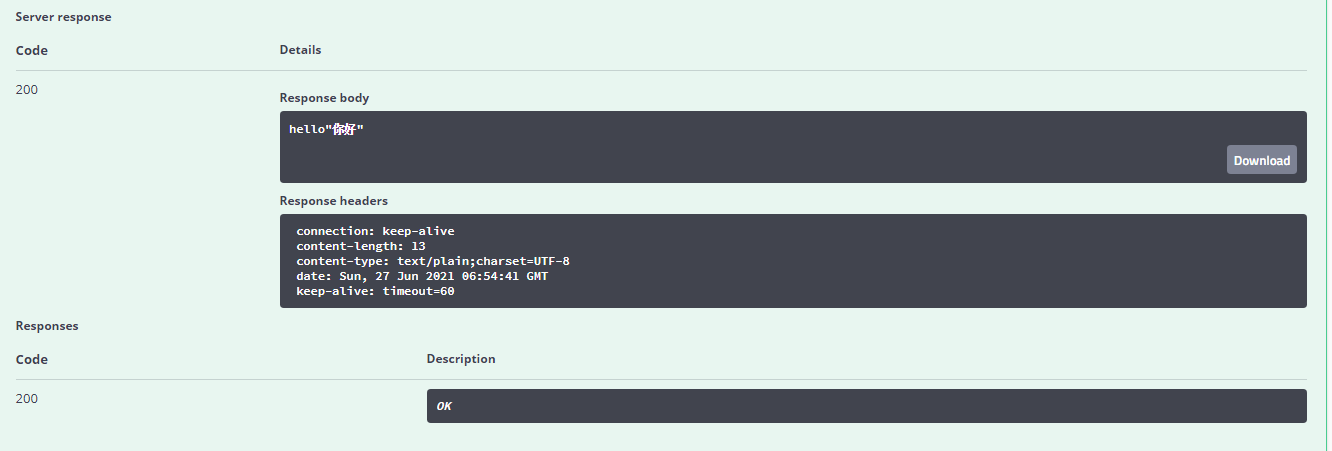
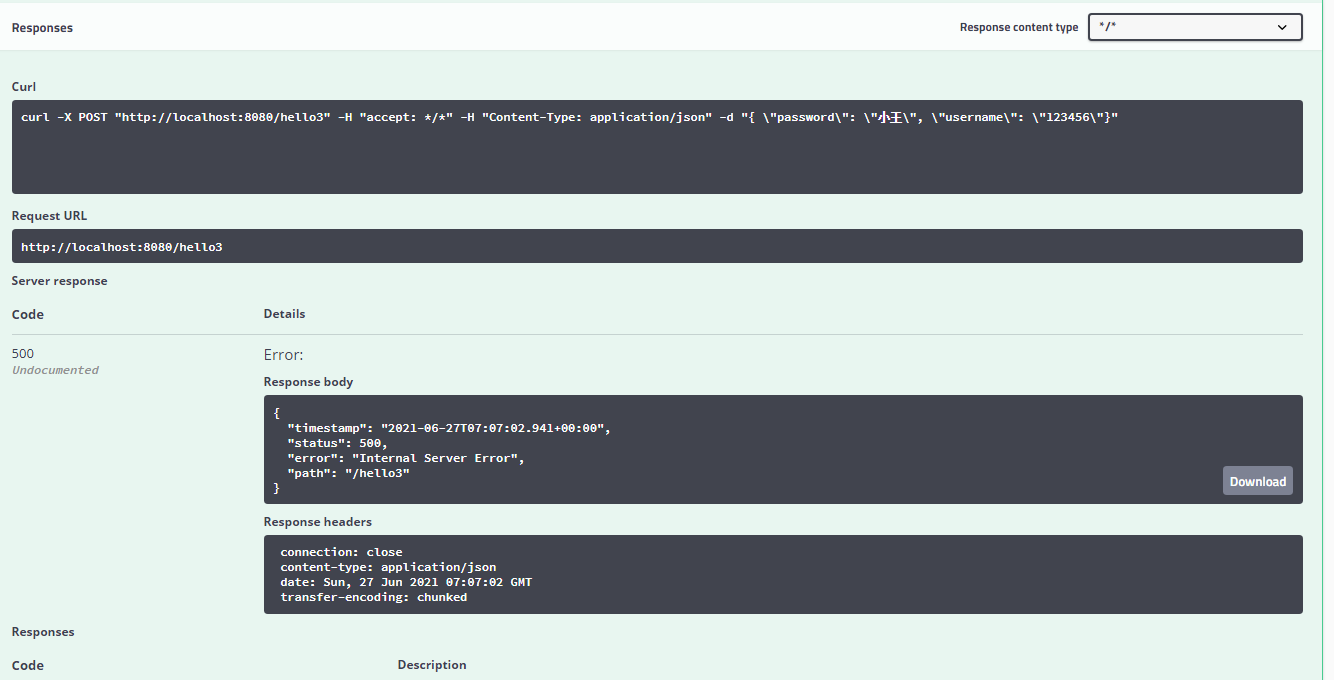
我们新建一个API接口 hello3 传入User
@ApiOperation("hello控制类")@PostMapping(value = "/hello3")public User hello3(@ApiParam("用户名") @RequestBody User user ){System.out.println(user.username);System.out.println(user.password);return user;}}
我们进入Swagger hello3的界面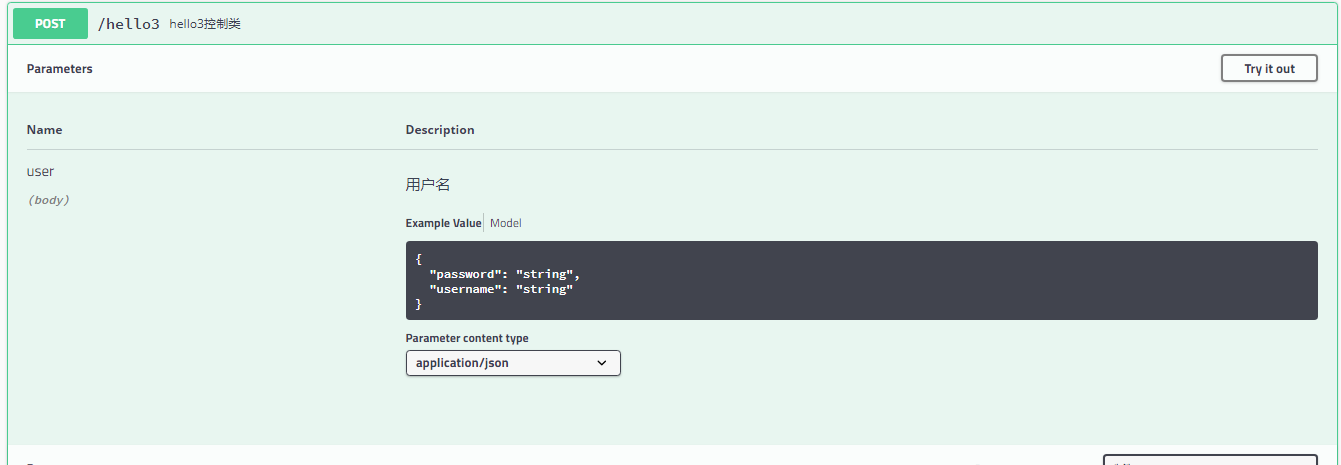
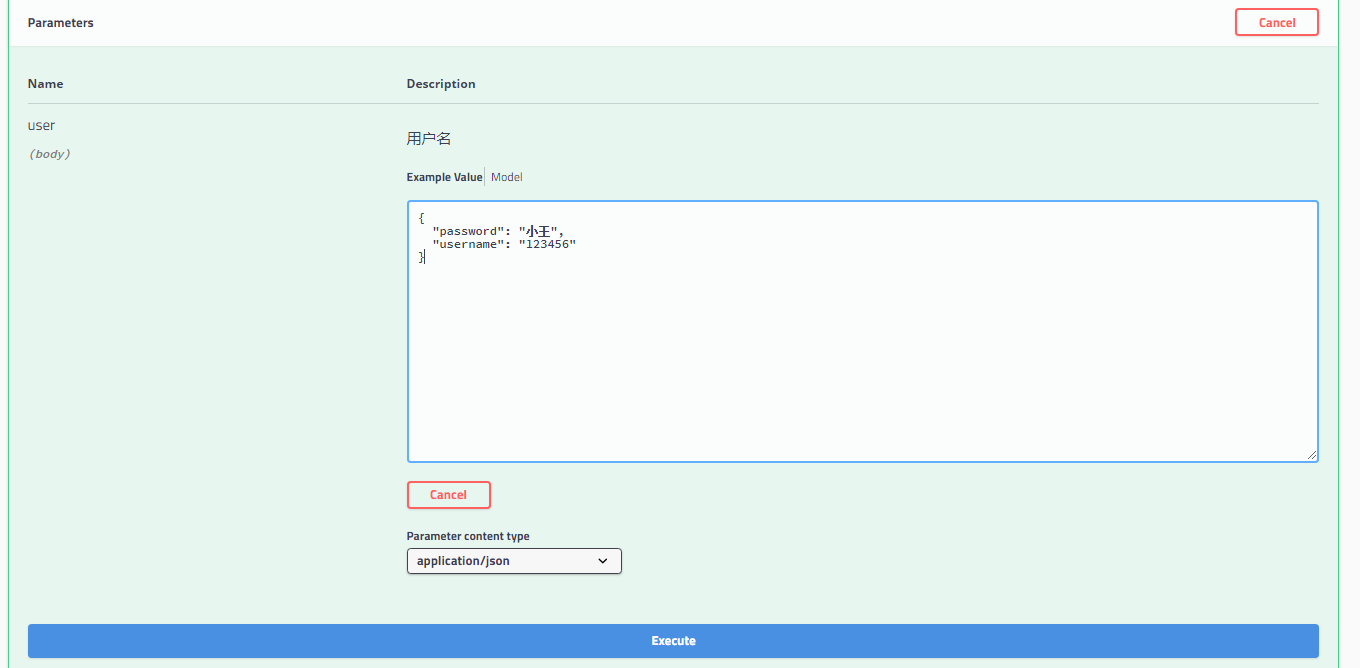
点击Try it out 传值
将password “小王”
username:“123456”
发送给后端
在后端控制台上打印username 和password的值并且返回给前端user对象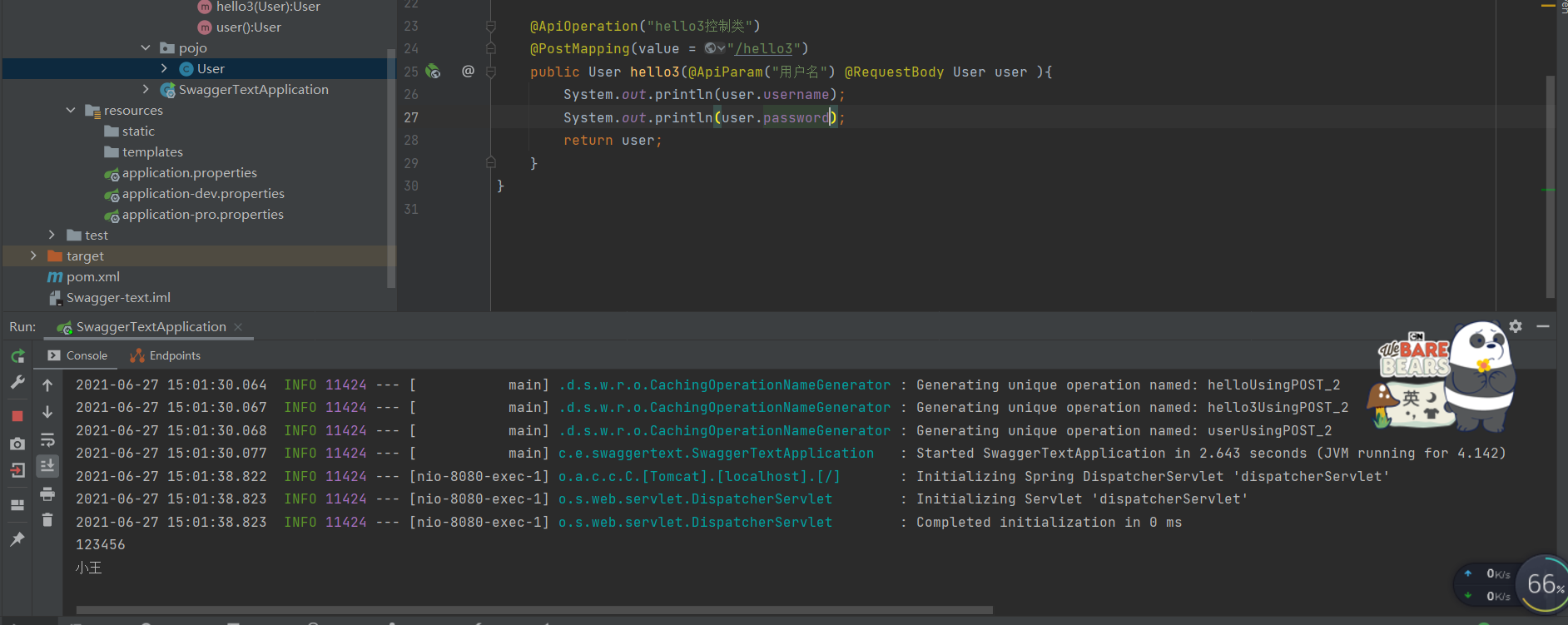
可以看出前端response的值为user对象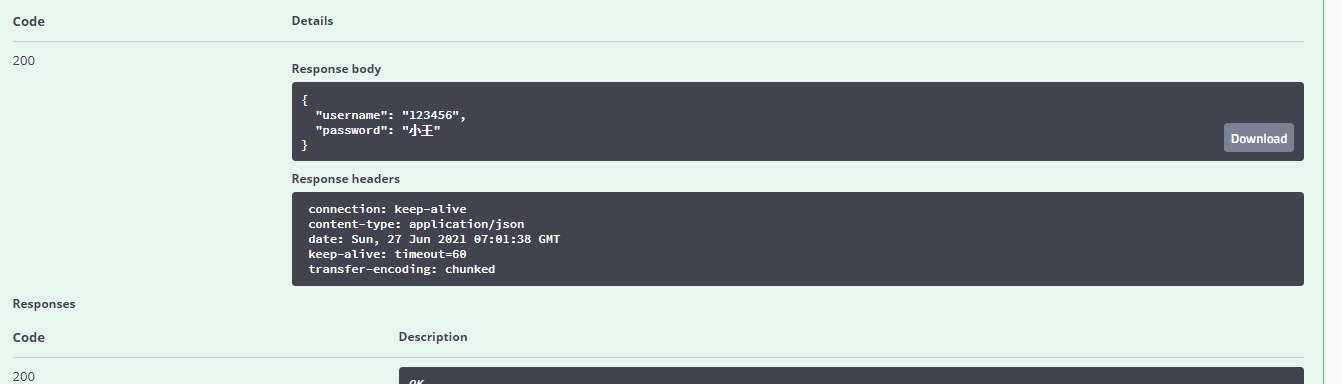
code返回200为成功
我们现在测试一下500的错误
在后端中写入 int i=5/0;
public User hello3(@ApiParam("用户名") @RequestBody User user ){int i = 5/0;System.out.println(user.username);System.out.println(user.password);return user;}
总结
1.我们可以使Swagger给一些比较难理解的属性或者接口,增加注释信息,
2.接口文档实时更新
3.可以在线测试