Properties 类表示了一个持久的属性集。Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串。
特点
a)该集合不能写泛型
b)可以持久化的属性集。键值可以存储到集合中,也可以存储到硬盘、U盘等
c)可以和IO流有关的技术结合使用
- 可以使用Properties集合中的方法store,把集合中的临时数据,持久化写入到硬盘中存储
- 可以使用Properties集合中的load方法,把硬盘中保存的文件(键值对),读取到集合中使用
使用Properties集合存储数据,遍历取出Properties集合中的数据
Properties是一个双列集合,key和value默认都是字符串
Properties集合有一些操作字符串的特有方法
Object setProperty(String key, String value) 调用 Hashtable 的方法 put
String getProperty(String key) 用指定的键在此属性列表中搜索属性
Set<String> stringPropertyNames() 返回此属性列表中的键集,其中该键及其对应值是字符串,如果在主属性列表中未找到同名的键,则还包括默认属性列表中不同的键。
一些方法
 store方法
store方法
使用store方法把集合中的数据持续写入到硬盘中存储
void store(OutputStream out, String comments) 以适合使用load(InputStream) 方法加载到 Properties 表中的格式,将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输出流。
void store(Writer writer, String comments) 以适合使用 load(Reader) 方法的格式,将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输出字符。
参数的含义:
这两个方法的第一个参数表示的是什么流
第二个参数 String comments的作用是:注释,用来解释说明保存的文件是做什么用的,但是不能使用中文,因为涉及到了编码,默认是unicode编码,使用中文可能会产生乱码,一般使用空字符串来占位
使用步骤:
创建Properties集合对象,添加数据
创建字节输出流/字符输出流对象,构造方法中绑定要输出的目的地
使用Properties集合中的方法store,把集合中的临时数据,持久化写入到硬盘中存储
释放资源
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 创建Properties集合对象,添加数据final Properties prop = new Properties();prop.setProperty("迪丽热巴", "168");prop.setProperty("古力娜扎", "168");prop.setProperty("马儿扎哈", "168");// 创建字节输出流/字符输出流对象,构造方法中绑定要输出的目的地final FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:\\a.txt");// 使用Properties集合中的方法store,把集合中的临时数据,持久化写入到硬盘中存储prop.store(fw, "");// 释放资源fw.close();}
注意:
① 得到的文本的第一行井号后面就是我们添加的注释
② 第二行的系统默认事件是Properties集合在使用store方法后自己添加的
如果注释使用的是中文的话:
代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建Properties集合对象,添加数据
final Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("迪丽热巴", "168");
prop.setProperty("古力娜扎", "168");
prop.setProperty("马儿扎哈", "168");
// 创建字节输出流/字符输出流对象,构造方法中绑定要输出的目的地
final FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:\\a.txt");
// 使用Properties集合中的方法store,把集合中的临时数据,持久化写入到硬盘中存储
prop.store(fw, "这里是注释!");
// 释放资源
fw.close();
}
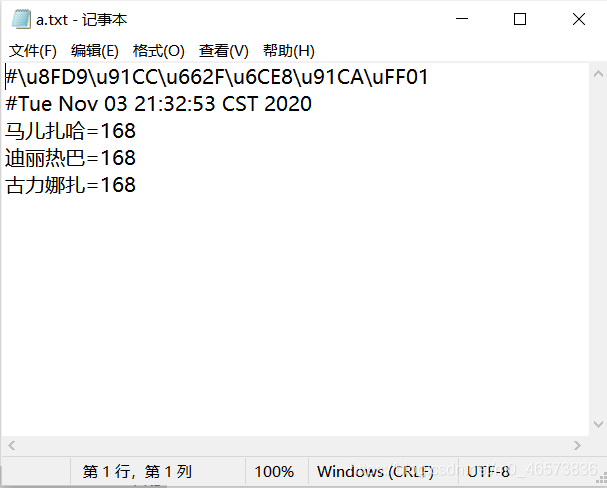
第一行注释位置就出现了乱码
load方法
用来把硬盘中保存的文件(键值对),读取到集合中使用
void load(InputStream inStream) 从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)
void load(Reader reader)按简单的面向行的格式从输入字符流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)
参数的含义:
1、 InputStream inStream:字节输入流,不能读取含有中文的键值对
2、Reader reader:字符输入流,能读取含有中文的键值对
使用步骤:
创建Properties集合对象
使用Properties集合对象中的方法load读取保存键值对的文件
遍历Properties集合
注意:
存储键值对的文件当中,键与值默认的连接符号可以使用等号,空格等其他符号
存储键值对的文件当中,可以使用井号进行注释,备注是的键值对不会在被读取
存储键值对的文件当中,键与值默认都是字符串,不用再加引号
举例示范:
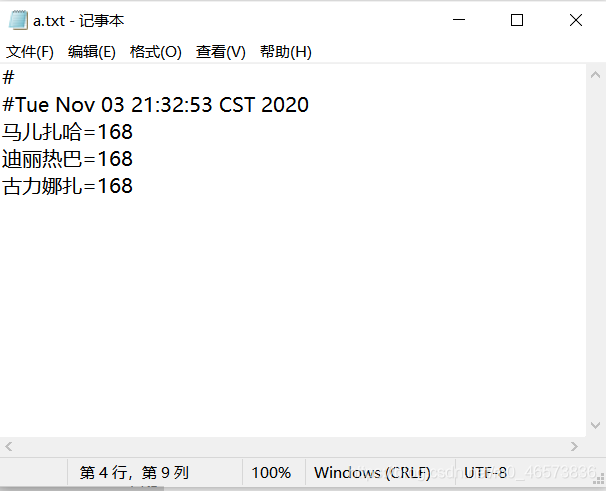
已知a.txt中的内容为
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建Properties集合对象
Properties prop = new Properties();
// 2. 使用Properties集合对象中的方法load读取保存键值对的文件
prop.load(new FileReader("d:\\a.txt"));
// 3. 遍历Properties集合
// 将key值存入set集合当中
Set<String> set = prop.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : set) {
// 通过key值找到value
final String value = prop.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key+ "=" +value);
}
}
得到的结果如下: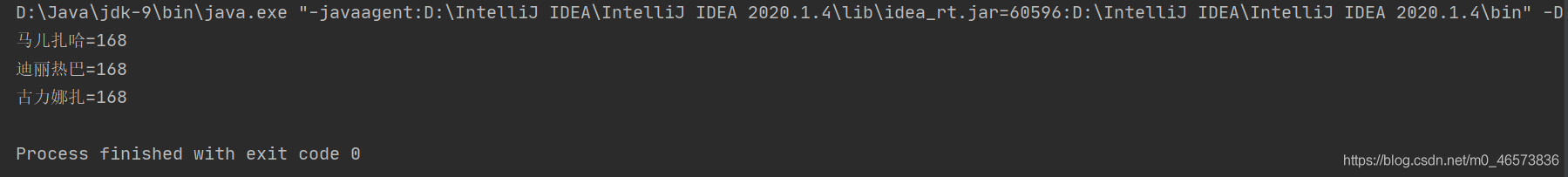
如果使用的是字节流读取的话会乱码如图所示: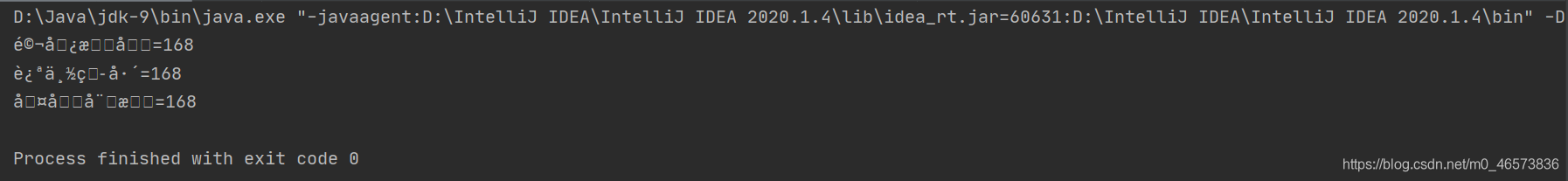
方法综合
//Object setProperty(String key, String value)
@Test
public void test_01(){
Properties pro = new Properties();
pro.setProperty("a","123");
pro.setProperty("b","123");
pro.setProperty("c","123");
System.out.println(pro);
}
// String getProperty(String key) 用指定的键在此属性列表中搜索属性。
@Test
public void test_02(){
Properties pro = new Properties();
pro.setProperty("a","123");
pro.setProperty("b","123");
pro.setProperty("c","123");
String v = pro.getProperty("a");
System.out.println(v);
}
//void load(InputStream inStream) 从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)
@Test
public void test_03() throws Exception{
Properties pro = new Properties();
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("c:\\pro.properties");
//调用方法load,传入输入流
pro.load(in);
//关闭流
in.close();
System.out.println(pro);
}

