7.1 CountDownLatch
让一些线程阻塞直到另一些线程完成一系列操作后才被唤醒
CountDownLatch 主要有两个方法,当一个或多个线程调用 await 方法时,调用线程会被阻塞。其它线程调用 countDown 方法会将计数器减 1(调用 countDown 方法的线程不会阻塞),
当计数器的值变为零时,因调用 await 方法被阻塞的线程会被唤醒,继续执行。
package s02.e07;public class CountDownLatchDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t上完自习,离开教室");}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t*****************班长最后关门走人");}}
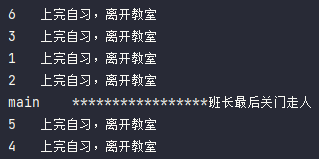
不使用 CountDownLatch,main 线程不会最后执行
package s02.e07;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;public class CountDownLatchDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6);for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t上完自习,离开教室");countDownLatch.countDown();}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}countDownLatch.await();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t*****************班长最后关门走人");}}
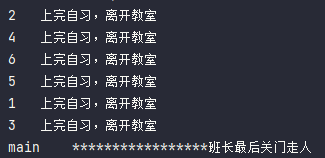
使用 CountDownLatch 后,main 线程最后执行
package s02.e07;import lombok.Getter;public enum CountryEnum {ONE(1, "齐"), TWO(2, "楚"), THREE(3, "燕"), FOUR(4, "赵"), FIVE(5, "魏"), SIX(6, "韩");@Getterprivate Integer retcode;@Getterprivate String retMessage;CountryEnum(Integer retcode, String retMessage) {this.retcode = retcode;this.retMessage = retMessage;}public static CountryEnum forEach_CountryEnum(int index) {CountryEnum[] myArray = CountryEnum.values();for (CountryEnum element : myArray) {if (index == element.getRetcode()) {return element;}}return null;}}
package s02.e07;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;public class CountDownLatchDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6);for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 国,被灭");countDownLatch.countDown();}, CountryEnum.forEach_CountryEnum(i).getRetMessage()).start();}countDownLatch.await();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t*****************秦帝国,一统华夏");}}
7.2 CyclicBarrier
CyclicBarrier 的字面意思是可循环(Cyclic)使用的屏障(Barrier)。它要做的事情是,让一组线程到达一个屏障(也可以叫同步点)时被阻塞,直到最后一个线程到达屏障时,屏障才会开门,所有被屏障拦截的线程才会继续干活,线程进入屏障通过 CyclicBarrier 的 await() 方法。
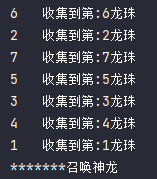
package s02.e07;import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;public class cyclicBarrierDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// CyclicBarrier( int parties,Runnable barrierAction)CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(7, () -> {System.out.println("*******召唤神龙");});for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) {final int tempInt = i;new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t收集到第:" + tempInt + "龙珠");try {cyclicBarrier.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}}}
7.3 Semaphore
信号量主要用于两个目的,一个是用于多个共享资源的互斥使用,另一个用于并发线程数的控制。
package s02.e07;import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class SemaphoreDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3); // 模拟3个停车位for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { // 模拟6部汽车new Thread(() -> {try {semaphore.acquire();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t抢到车位"); // 门暂停一会儿线程try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t停车3秒后离开车位");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {semaphore.release();}}, String.valueOf(i)).start();}}}
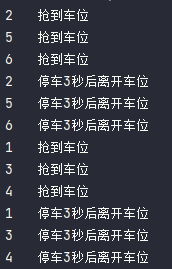
semaphore 使用完后要释放,以便下一个等候的线程进入