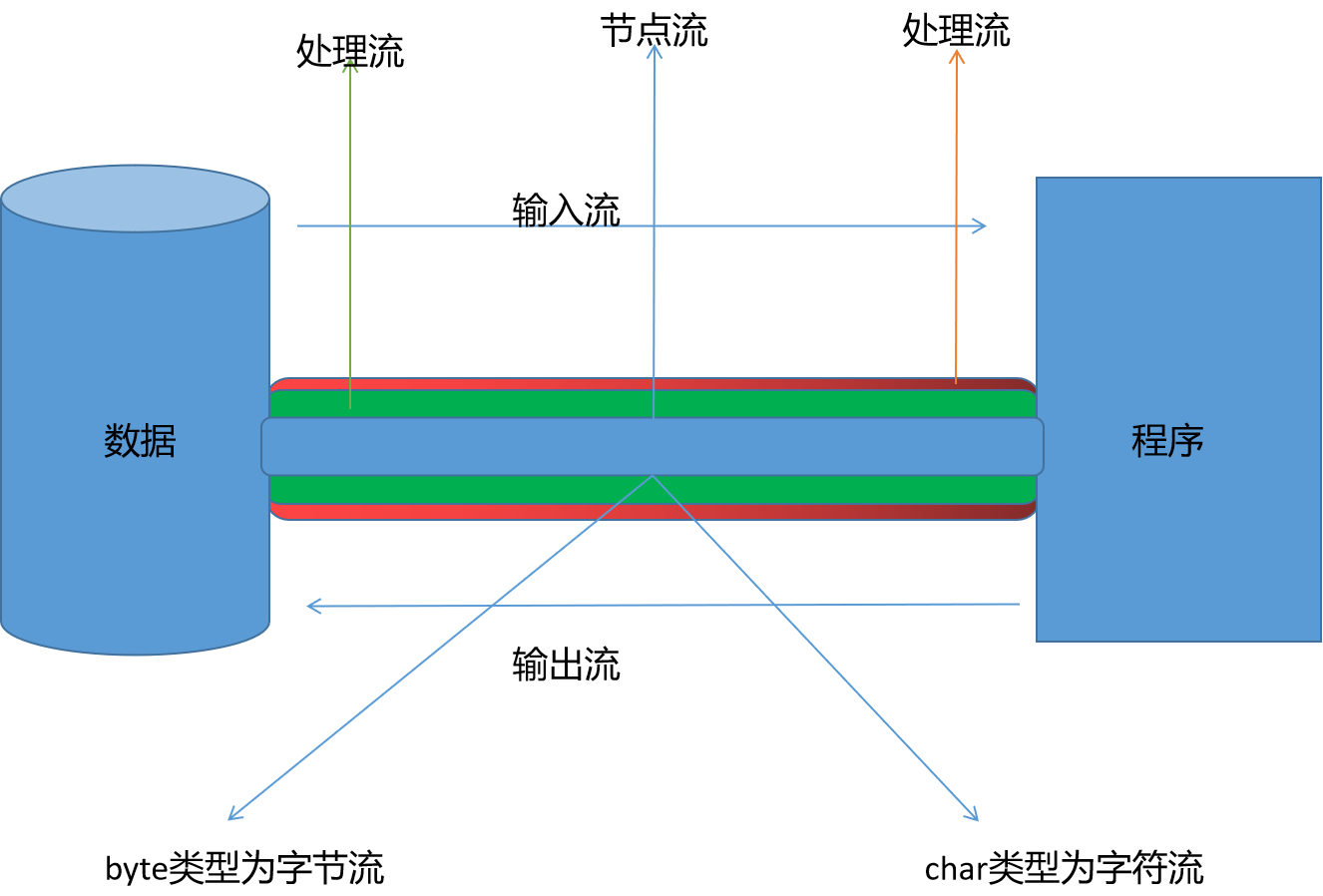
一、流分类
- 根据流的数据单位(类型) 可以分为 字节流 8bit(byte)、字符流 16bit(char)
- 字节流输入流 inputStream
- 字节流输出流 outPutStream
- 字符流输入流 reader
- 字符流输出流 writer
- 根据流的流向 可以分为 输入流、输出流
- 根据流的角色 可以分为节点流、处理流
- 直接作用在数据上的流称为节点流
- 包裹节点流的流称为处理流
二、重点掌握流
| 分类 | 字节输入流 | 字节输出流 | 字符输入流 | 字符输出流 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽象基类 | InputStream | OutputStream | Reader | Writer |
| 访问文件 | FileInputStream | FileOutputStream | FileReader | FileWriter |
| 访问数组 | ByteArrayInputStream | ByteArrayOutputStream | CharArrayReader | CharArrayWriter |
| 访问管道 | PipedInputStream | PipedOutputStream | PipedReader | PipedWriter |
| 访问字符串 |
|
| StringReader | StringWriter | | 缓冲流 | BufferedInputStream | BufferedOutputStream | BufferedReader | BufferedWriter | | 转换流 |
|
| InputStreamReader | OutputStreamWriter | | 对象流 | ObjectInputStream | ObjectOutputStream |
|
| |
| FilterInputStream | FilterOutputStream | FilterReader | FilterWriter | | 打印流 |
|
PrintStream |
|
PrintWirter |
| 推回输入流 |
|
|
|
| | 特殊流 |
|
|
|
|
/*** @author:LYY 创建时间:2022/5/9* io流操作*/public class FileReaderTest {/*** 对象流* 序列化对象和反序列化* 当person对象序列化到person.dat文件中 并实现反序列化*/@Testpublic void objectInputStreamAndObjectOutputStreamTest() {// 1. 实例化File文件对象File file = new File("person.dat");// 要被序列化的对象Person person = new Person("张胜男", 15);// 2. 创建序列化对象(输出对象流:ObjectOutputStream)ObjectOutputStream oos = null;// 2. 创建反序列化对象(输入对象流:ObjectInputStream)ObjectInputStream ois = null;try {// 3. 序列化对象(将对象输出到硬盘)oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));oos.writeObject(person);// 清空缓冲空间oos.flush();// 4. 反序列化对象(将硬盘中保存的对象重新获取到内存)ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));Object object = ois.readObject();System.out.println(object);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 关闭反序列化对象if (ois != null) {try {ois.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 关闭序列化对象if (oos != null) {try {oos.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}/*** 标准输入输出流和打印流*/@Testpublic void systemTest() {// 标准输入流 从键盘输入InputStream in = System.in;// 标准输出流 默认输出到控台PrintStream out = System.out;PrintWriter printWriter = null;try {// 创建打印流//printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(new File("hello.txt")));FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("hello.txt");// 重写标准输出流// printWriter.print("你好!");// 重新设置打印流System.setOut(new PrintStream(fileOutputStream));System.out.print("boolean");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//printWriter.close();}}/*** 转换流读取文件写出文件* 1. 读取文件时 读取文件的转换流编码格式必须与文件格式一致* 2. 写出文件时 写出文件的转换流可以自定义文件编码 不指定则默认系统设置的编码格式*/@Testpublic void inputStreamReaderAndOutputStreamWriterTest() {// 1. 实例化File对象File inFile = new File("hello.txt");File outFile = new File("hello1.txt");// 2. 创建转换流对象// 将读入的字节流 转为 字符流InputStreamReader isr = null;// 将写出的字符流 转为 字节流OutputStreamWriter osw = null;try {// 3. 实例化转换流对象// 实例化输入转换流isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(inFile));// 实例输出转换流// osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(outFile));// 可以指定写出文件的编码格式osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(outFile),"gbk");char[] chars = new char[1024];int len;// 读取文件while ((len = isr.read(chars)) != -1) {// 写出文件osw.write(chars, 0, len);}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 4. 关闭转换流if (osw != null) {try {osw.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}if (isr != null) {try {isr.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}/*** 使用缓冲流(BufferedInputStream)实现文件的复制*/@Testpublic void bufferedInputStreamAndBufferedOutputStreamTest() {// 1. 实例化file对象// 实例化要读取的文件File inputStreamJpg = new File("preview.jpg");String user = System.getProperty("user.name");// 实例化要输出的文件File outputStream = new File("C:\\Users\\" + user + "\\Desktop",inputStreamJpg.getName());// 2. 实例化输入流(FileInputStream)和输出流(FileOutputStream)FileInputStream input = null;FileOutputStream output = null;// 3. 实例化处理流(缓冲流)// 实例化输入流BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = null;// 实例化输出流BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = null;try {// 赋值输入节点流input = new FileInputStream(inputStreamJpg);// 赋值输出节点流output = new FileOutputStream(outputStream);// 赋值输入缓冲流bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(input);// 赋值输出流缓冲流bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(output);byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];// 记录每次读取的字节个数int len;while ((len = bufferedInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {// 写出文件到硬盘bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 4. 关闭缓冲输出流和缓冲输入流// 关闭处理流的同时 节点流也会关闭if (bufferedOutputStream != null) {try {bufferedOutputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}if (bufferedInputStream != null) {try {bufferedInputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}/*** 使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream实现文件的复制*/@Testpublic void fileInputStreamAdnFileOutputStreamTest() {// 1. 实例化file对象// 实例化要读取的文件File inputStreamJpg = new File("preview.jpg");String user = System.getProperty("user.name");System.out.println(user);// 实例化要输出的文件File outputStream = new File("C:\\Users\\" + user + "\\Desktop",inputStreamJpg.getName());System.out.println(outputStream);// 2. 实例化输入流(FileInputStream)和输出流(FileOutputStream)FileInputStream input = null;FileOutputStream output = null;try {// 实例化输入流input = new FileInputStream(inputStreamJpg);// 实例化输出流output = new FileOutputStream(outputStream);byte[] bytes = new byte[100];// 记录每次读取的字节个数int len;while ((len = input.read(bytes)) != -1) {// 写出文件到硬盘output.write(bytes,0,len);}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 4. 关闭输出流和输入流try {if (output != null) {output.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {if (input != null) {input.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}/*** 将内存中的数据写到硬盘中*/@Testpublic void fileWriterTest() {// 1. 实例化File对象File file = new File("hello.txt");FileWriter writer = null;try {// 2. 实例化输出流FileWriter对象// 默认文件不存在 输出流自动创建 若文件已经存在 则覆盖 可以通过设置关闭是否覆盖已存在的文件writer = new FileWriter(file);// 3. 调用输出方法 将数据写入到硬盘中writer.write("你好,世界!\n");writer.write("hello world!");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 4. 关闭try {writer.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}/*** 读取文件到内存中*/@Testpublic void readerTest02() {// 1. 创建要的读取的file对象File fileJpg = new File("preview.jpg");File fileTxt = new File("preview.txt");// 2. 创建对应流对象FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;FileReader fileReader = null;try {// 实例化流对象fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(fileJpg);fileReader = new FileReader(fileTxt);char[] chars = new char[5];int c;// fileReader.read(chars) 该方法返回读取的字符数 末尾返回-1while ((c = fileReader.read(chars)) != -1) {// 正确的// String str = new String(chars, 0, c);// System.out.print(str);// 错误的// for (char aChar : chars) {// System.out.print(aChar);// }// 正确的for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) {System.out.print(chars[i]);}}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 4. 关闭对应流对象try {if (fileInputStream != null) {fileInputStream.close();}if (fileReader != null) {fileReader.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}/*** 读取文件到内存中*/@Testpublic void readerTest01() {// 1. 创建要的读取的file对象File fileJpg = new File("preview.jpg");File fileTxt = new File("preview.txt");// 2. 创建对应流对象FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;FileReader fileReader = null;try {// 实例化流对象fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(fileJpg);fileReader = new FileReader(fileTxt);int c;while ((c = fileReader.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char)c);}} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 4. 关闭对应流对象try {if (fileInputStream != null) {fileInputStream.close();}if (fileReader != null) {fileReader.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
```