一、Error异常 java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题. 一般不编写针对性的代码节能型处理
二、Exception异常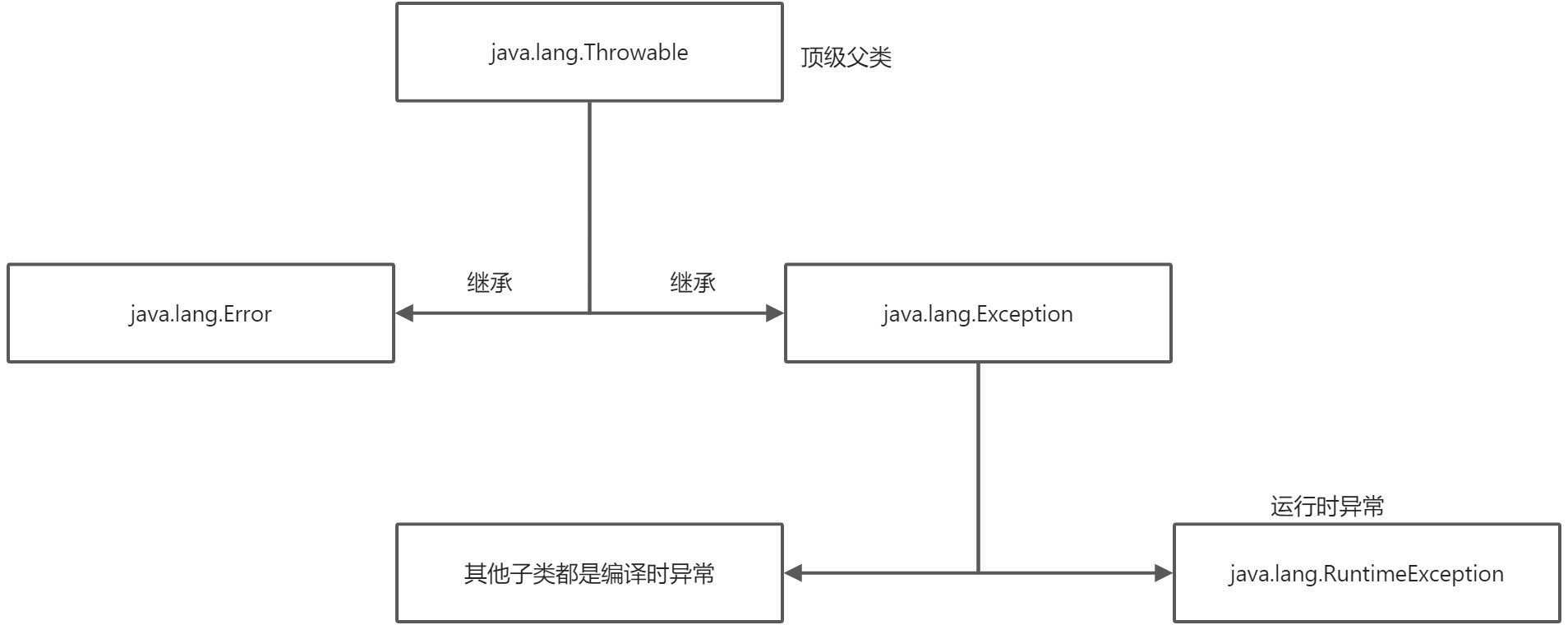
三、常见异常 — 运行时异常
/*** 空指针* NullPointerException*/@Testpublic void getNullException(){int [] arr = null;System.out.println(arr[0]);}/** 数组下标越界* ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException*/@Testpublic void getIndexOfBoundsException() {int[] arr = new int[]{1, 5, 3, 5};System.out.println(arr[4]);}/*** 数值转换异常* NumberFormatException*/@Testpublic void getNumberFormatException(){String a = "a";int b = Integer.parseInt(a);}
四、异常的处理方式:try—catch—finally
- try结构包裹可能存在异常的代码
- try结构中出现异常后 与catch结构中的异常类型进行匹配 匹配成功后 进入处理
- catch结构可以同时存在多个
- catchi结构中的异常类型存在父子关系时 必须子类在前方 反之随意
- 使用try—catch—finally处理编译时异常, 编译通过后 运行时仍有可能会出现
- finally 可选的 一定会被执行的 即使前方存在return
- throws 向上抛出异常
- throws处理异常时 子类重写父类方法时 向上抛出时 异常类型不大于父类的异常类型(否则可能发生类转换异常)
如果父类被重写的方法中没有throws 则子类只能使用try—catch处理异常
@Testpublic void getNumberFormatException(){// try 包裹可能出现异常的代码try {String a = "a";int b = Integer.parseInt(a);// catch 捕获出现对应类型的异常 随后进入catch结构} catch (NumberFormatException e) {// 输出错误信息 e.getMessage()System.out.println(e.getMessage());// 打印栈追踪错误信息e.printStackTrace();// 可以存在多个catch结构} catch (NullPointerException e) {// 异常类型之间存在父子关系时,一定要子类异常在前方 反之随意} catch (Exception e) {}}
五、throw 手动抛出异常

