需求:使用简单模式完成消息传递
步骤:
① 创建工程(生成者、消费者)
② 分别添加依赖
③ 编写生产者发送消息
④ 编写消费者接收消息
1)创建工程
2)添加依赖
<dependencies><!--rabbitmq java 客户端--><dependency><groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId><artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId><version>5.6.0</version></dependency></dependencies><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><version>3.8.0</version><configuration><source>1.8</source><target>1.8</target></configuration></plugin></plugins></build>
3) 编写生产者发送消息
/*** 发送消息*/public class Producer_HelloWorld {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {//1.创建连接工厂ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();//2. 设置参数factory.setHost("172.16.98.133");//ip 默认值 localhostfactory.setPort(5672); //端口 默认值 5672factory.setVirtualHost("/itcast");//虚拟机 默认值/factory.setUsername("heima");//用户名 默认 guestfactory.setPassword("heima");//密码 默认值 guest//3. 创建连接 ConnectionConnection connection = factory.newConnection();//4. 创建ChannelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();//5. 创建队列Queue/*queueDeclare(String queue, boolean durable, boolean exclusive, boolean autoDelete, Map<String, Object> arguments)参数:1. queue:队列名称2. durable:是否持久化,当mq重启之后,还在3. exclusive:* 是否独占。只能有一个消费者监听这队列* 当Connection关闭时,是否删除队列*4. autoDelete:是否自动删除。当没有Consumer时,自动删除掉5. arguments:参数。*///如果没有一个名字叫hello_world的队列,则会创建该队列,如果有则不会创建channel.queueDeclare("hello_world",true,false,false,null);/*basicPublish(String exchange, String routingKey, BasicProperties props, byte[] body)参数:1. exchange:交换机名称。简单模式下交换机会使用默认的 ""2. routingKey:路由名称3. props:配置信息4. body:发送消息数据*/String body = "hello rabbitmq~~~";//6. 发送消息channel.basicPublish("","hello_world",null,body.getBytes());//7.释放资源channel.close();connection.close();}}
4) 编写消费者接收消息
public class Consumer_HelloWorld {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {//1.创建连接工厂ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();//2. 设置参数factory.setHost("172.16.98.133");//ip 默认值 localhostfactory.setPort(5672); //端口 默认值 5672factory.setVirtualHost("/itcast");//虚拟机 默认值/factory.setUsername("heima");//用户名 默认 guestfactory.setPassword("heima");//密码 默认值 guest//3. 创建连接 ConnectionConnection connection = factory.newConnection();//4. 创建ChannelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();/*basicConsume(String queue, boolean autoAck, Consumer callback)参数:1. queue:队列名称2. autoAck:是否自动确认3. callback:回调对象*/// 接收消息Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){/*回调方法,当收到消息后,会自动执行该方法1. consumerTag:标识2. envelope:获取一些信息,交换机,路由key...3. properties:配置信息4. body:数据*/@Overridepublic void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {System.out.println("consumerTag:"+consumerTag);System.out.println("Exchange:"+envelope.getExchange());System.out.println("RoutingKey:"+envelope.getRoutingKey());System.out.println("properties:"+properties);System.out.println("body:"+new String(body));}};channel.basicConsume("hello_world",true,consumer);//关闭资源?不要}}
小结 :
上述的入门案例中其实使用的是如下的简单模式: 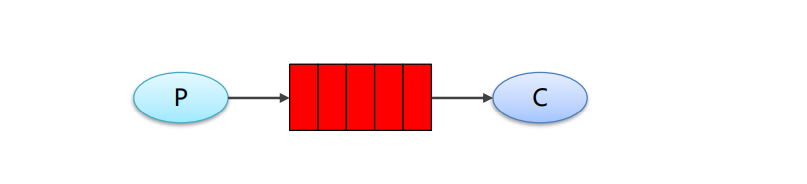
在上图的模型中,有以下概念:
- P:生产者: 也就是要发送消息的程序
- C:消费者:消息的接收者,会一直等待消息到来
- queue:消息队列,图中红色部分。类似一个邮箱,可以缓存消息;生产者向其中投递消息,消费者从其中取出消息

