备忘录
// 斐波那契数列及其优化function fibonacci(n) { if (n < 1) throw new Error('参数错误'); if (n === 1 || n === 2) return 1; return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);}function memo(fn) { let obj = {}; return function(n) { if (obj[n] === undefined) obj[n] = fn(n); return obj[n]; }}
滚动数组方式
const fibo = n => { // 判断输入的值是否有效,也可以抛出异常 if (typeof n !== 'number' || !n) return 0; let arr = [1, 1]; if (n > 2) { // 仅当n大于2时需要替换arr中的值 // 循环的时候将上一次末尾的值替换掉头部的值,而尾部的值则等于上一次数组中两项之和 for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) arr = [arr[1], arr[0] + arr[1]]; return arr[1]; // n项的值 } return 1;}
3、斐波那契数列通项公式
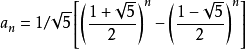
let fib = n => Math.round( (Math.pow((1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2, n) - Math.pow((1 - Math.sqrt(5)) / 2, n)) / Math.sqrt(5) );
4、矩阵乘法 (高级)
let fib=n=> n <= 0 ? 0 : martix22_mul( [[0, 1], [1, 0]], martix22_pow([[0, 1], [1, 1]], n - 1) )[0][1];let martix22_mul = (x, y) => [ [ x[0][0] * y[0][0] + x[0][1] * y[1][0], x[0][0] * y[0][1] + x[0][1] * y[1][1] ], [x[1][0] * y[0][0] + x[1][1] * y[1][0], x[1][0] * y[0][1] + x[1][1] * y[1][1]]];let martix22_pow = (x, n) => { let r = [[1, 0], [0, 1]]; let v = x; while (n) { if (n % 2 == 1) { r = martix22_mul(r, v); n -= 1; } v = martix22_mul(v, v); n = n / 2; } return r;};
推理过程:https://www.jianshu.com/p/adca358b6ec2