文件
文件介绍
常见的文件操作
创建文件
方式一
public static void main(String[] args) {File newFile2 = new File("d:\\news2.txt"); //一个 \ 为转义字符try {newFile2.createNewFile(); //会抛出一个异常 ,返回值是一个布尔值System.out.println("文件创建成功");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
注意这里的File对象,只是一个对象,只有在执行createNewFile方法,才会真正创建文件。
方式二
public static void main(String[] args) {File newFile1 = new File("d:\\","news2.txt"); //注意不能写成d,可以写成d:/try {newFile1.createNewFile(); //会抛出一个异常System.out.println("文件创建成功");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
方式三(不常用)
public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("d:\\");File newFile3 = new File(file,"news3.txt");try {newFile3.createNewFile();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
其它常用方法
public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("d:\\news1.txt");System.out.println(file.getName()); //获取文件名 news1.txtSystem.out.println(file.getParent()); //文件父级目录 d:\System.out.println(file.length()); // 文件大小(字节)System.out.println(file.exists()); // 文件是否存在 (因为上面已经创建所以为T)System.out.println(file.isFile()); // 是不是一个文件 TSystem.out.println(file.isDirectory()); //是不是一个目录 F}
删除
public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("d:\\news1.txt");if(!file.exists()){System.out.println("d:\\nes1.txt");}else{if(file.delete()){ // delete删除文件System.out.println("删除成功");}else{System.out.println("删除失败");}}}
创建一级目录
public static void main(String[] args) {// 注意在Java里目录(文件夹)也算是文件File file = new File("d:\\demo02");if(file.exists()){System.out.println("文件夹存在");}else{file.mkdir(); //创建单极目录,当然mkdirs也行}}
创建多级目录
public static void main(String[] args) {// 注意在Java里目录(文件夹)也算是文件File file = new File("d:\\demo02\\demo03");if(file.exists()){System.out.println("文件夹存在");}else{file.mkdirs(); //创建多级目录}}
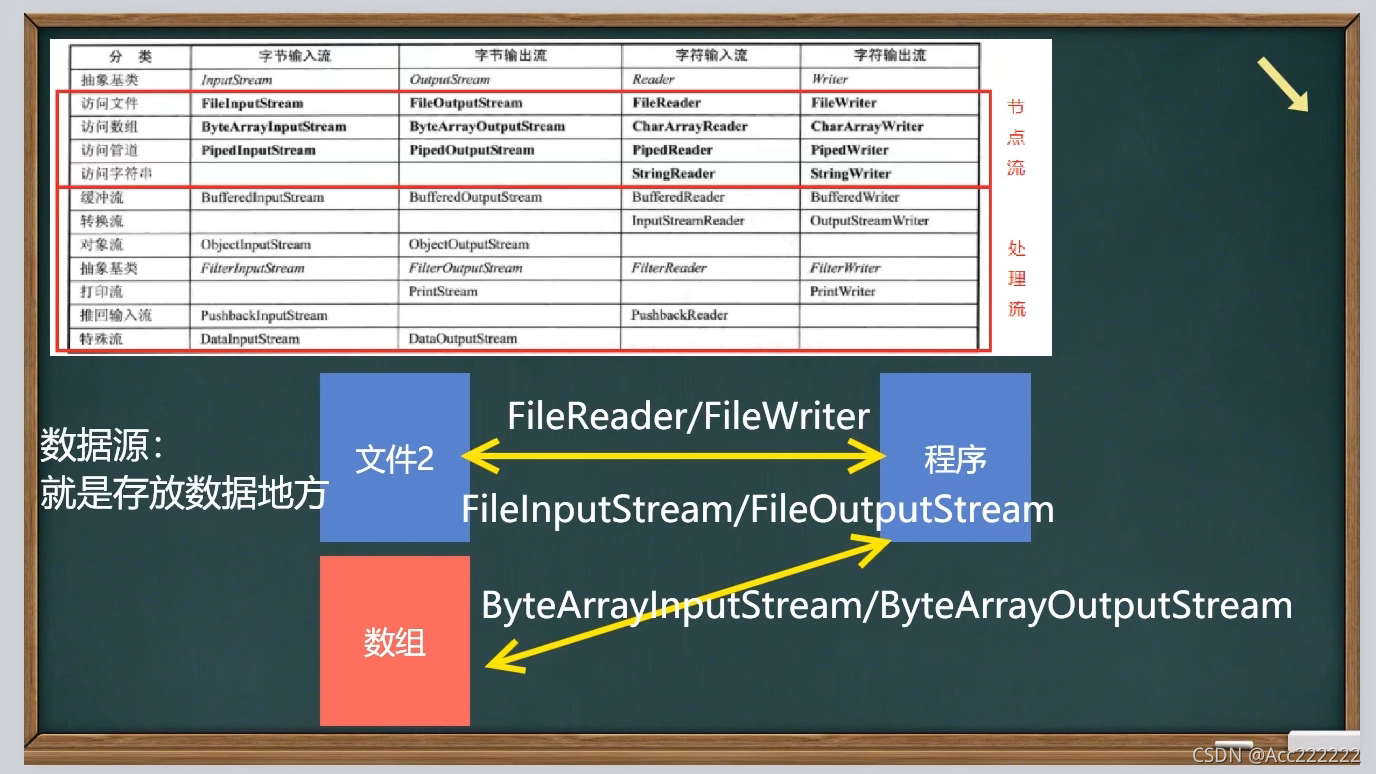
IO流
原理

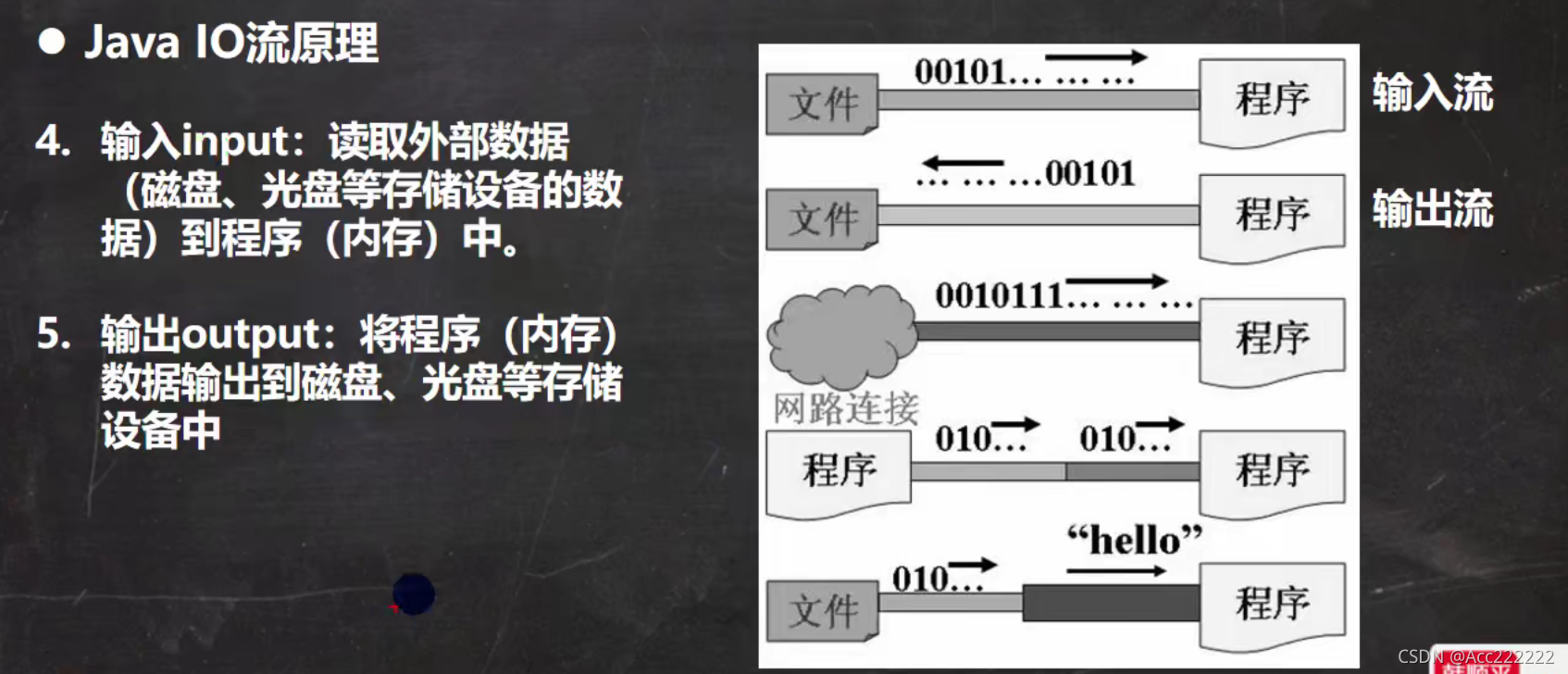
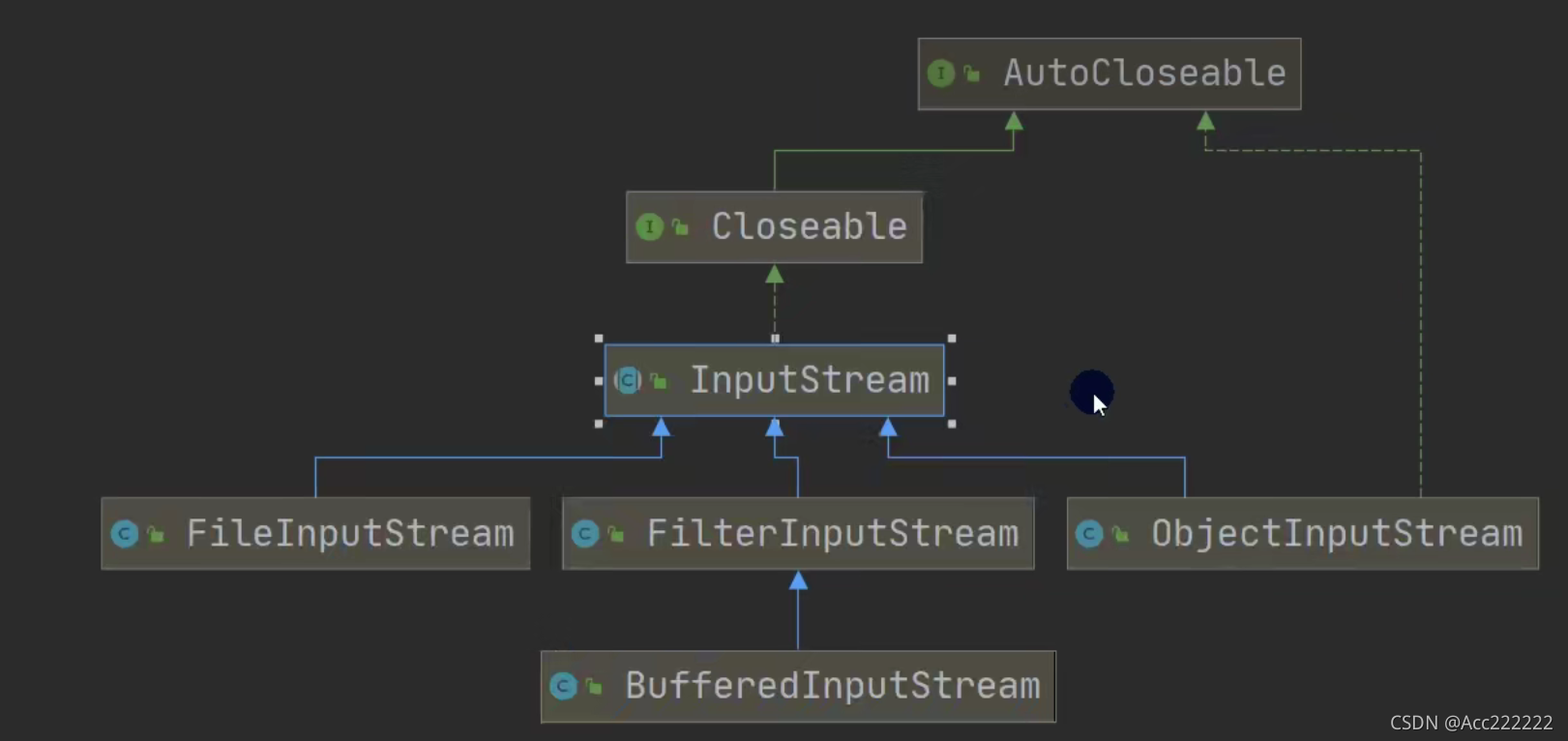
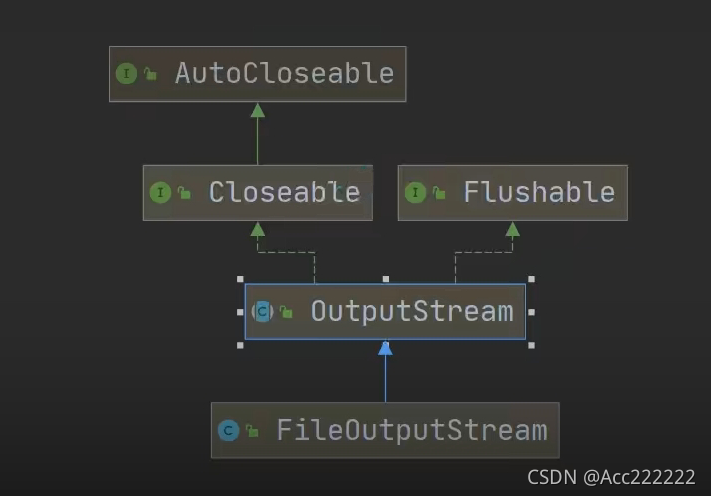
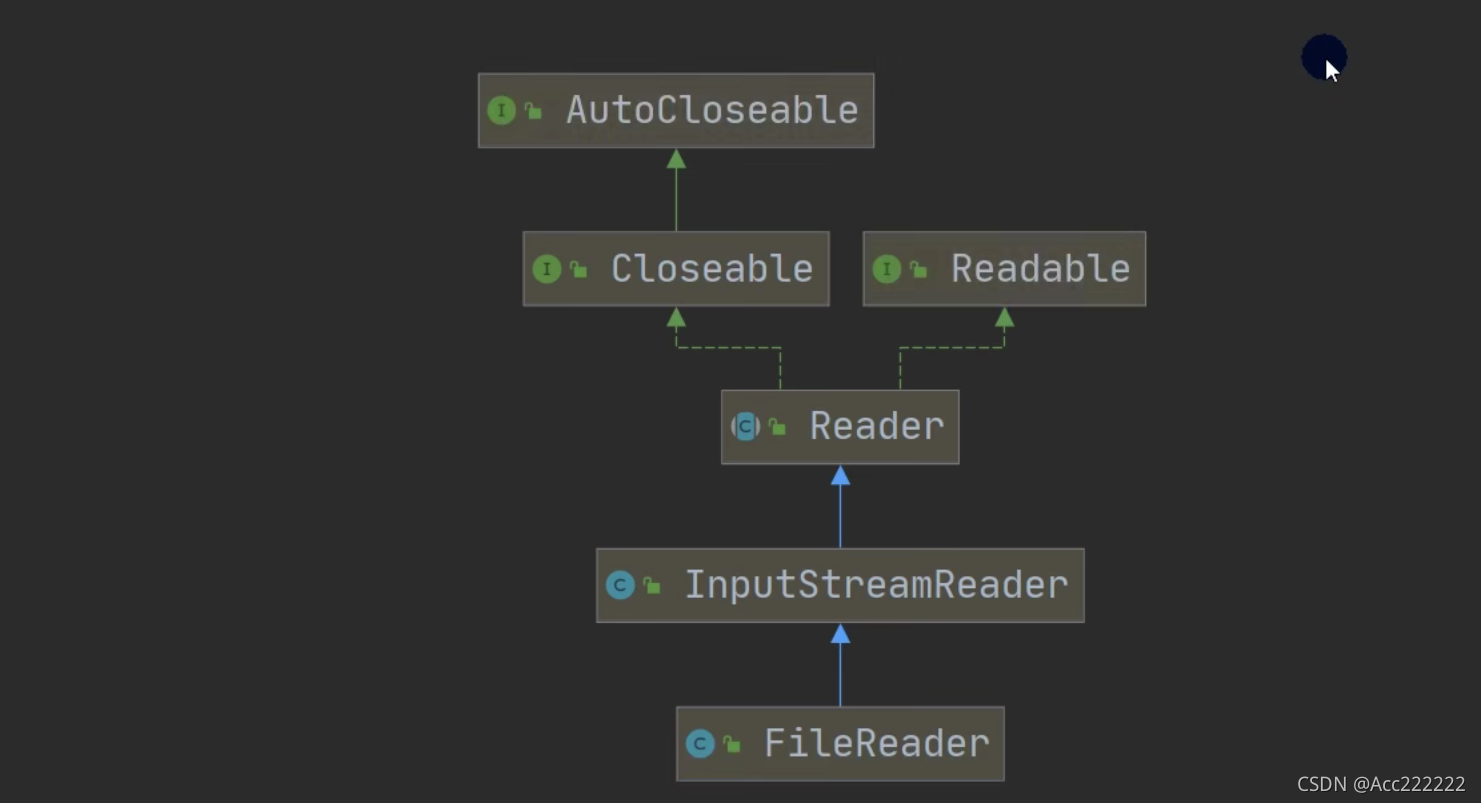
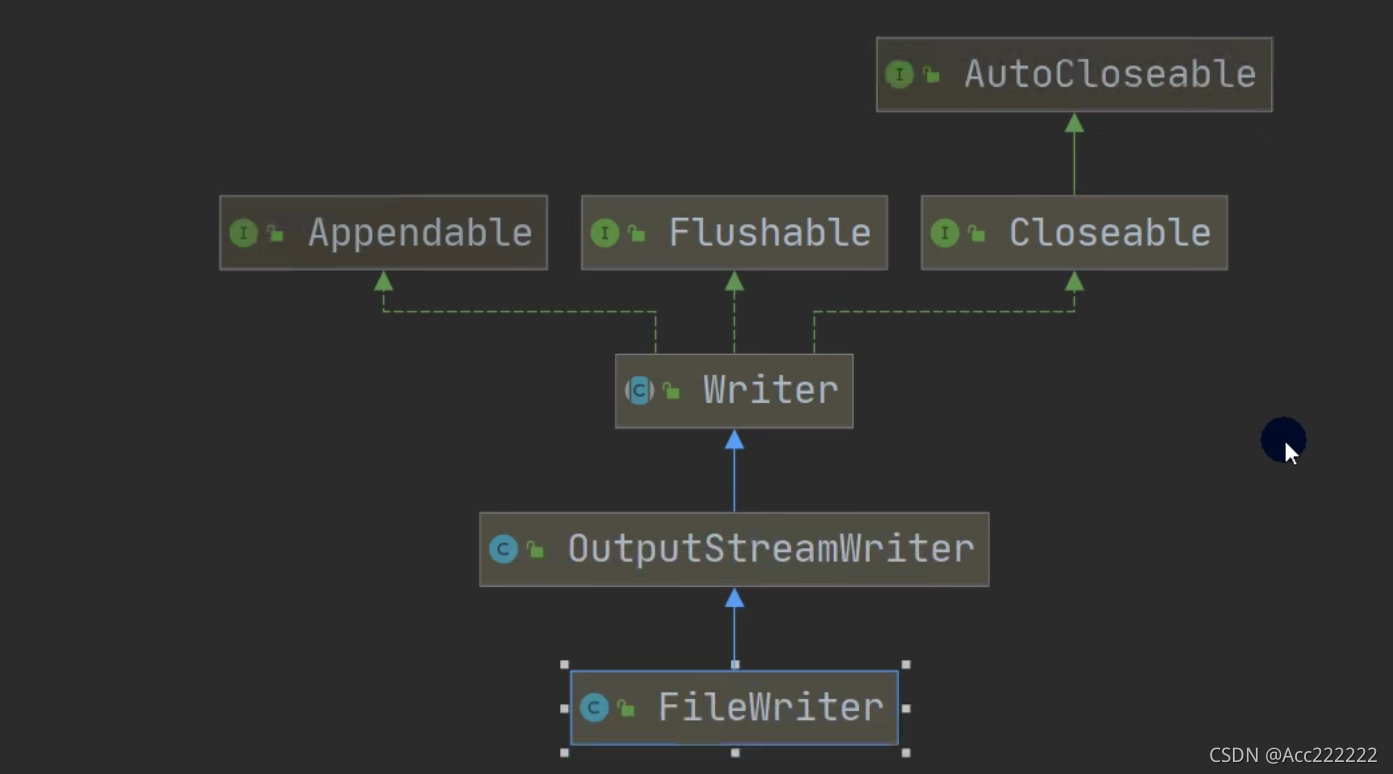
注:1. Java的IO流总共涉及40多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从上面的四个抽象基类派生的。
2. 由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀。
流与文件的类似关系:
类图
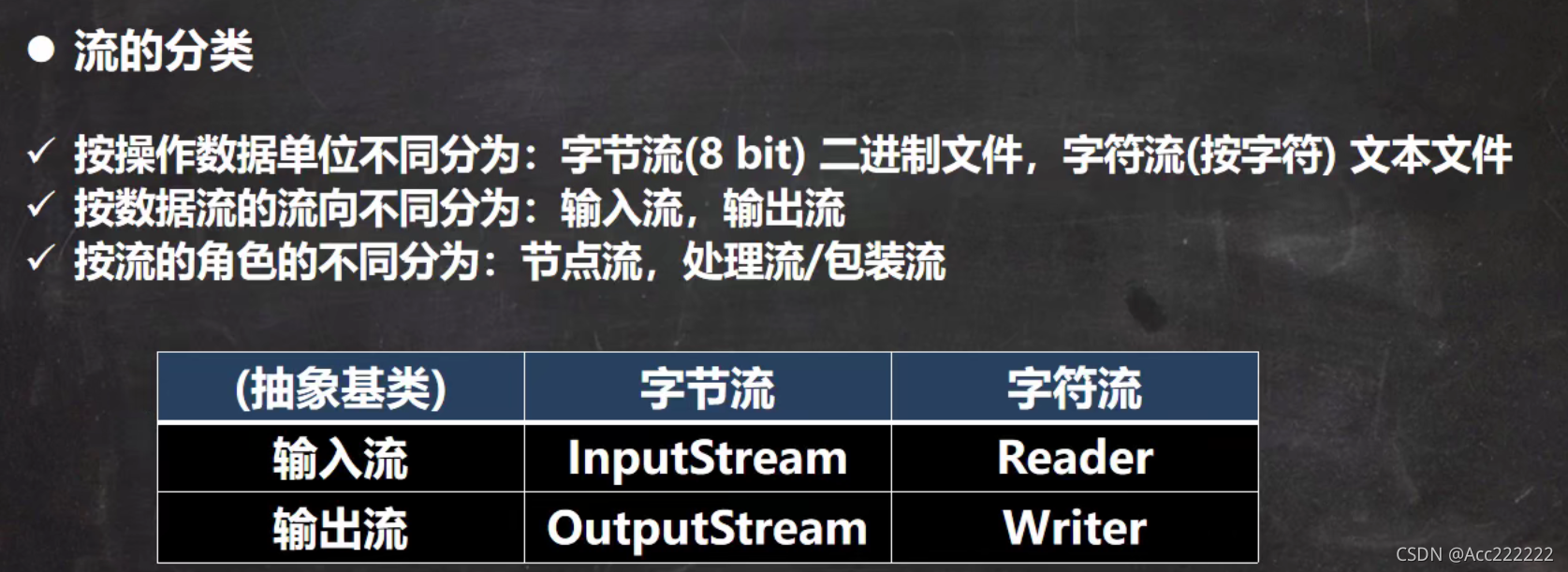
InputStream
OutStream
Reader
Writer
节点流和处理流
节点流图解
包装流图解
对包装流的模拟
class BufferReader_{ //这个就是个包装类private Reader_ reader_; //包装了一个Reader_类型的属性public Test(Reader_ reader_) {this.reader_ = reader_;} //构造器public static void main(String[] args) {BufferReader_ test = new BufferReader_(new StringReader_());//根据多态可以传入各种 节点流test.reader_.readString(); //调用相关方法}}abstract class Reader_{public void readFile(){}public void readString(){}} //定义抽象类,后面在调用时,用动态绑定机制class FileReader_ extends Reader_{ //文件读取类@Overridepublic void readFile(){System.out.println("对文件进行读取");}}class StringReader_ extends Reader_{ //字符串读取类@Overridepublic void readString() {System.out.println("对字符串进行读取");}}
也可以在 BufferReader_中 添加各种读取方法:
public void readFiles(int num){for(int i=0;i<num;i++){reader_.readFile();}}
FileInputStream
用read读取单个字节 read()
public static void main(String[] args) { //用read读取单个字节int readData = 0; //注意这里,readData初始化为int类型,因为读入的是字符码FileInputStream fis = null; //不初始化会报错try {//创建 FileInputStream对象,用于读取文件fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\test1.txt");//从该输入流读取一个字节的数据,如果没有输入可用,此方法返回-1,表示读取完毕while((readData = fis.read()) != -1){ //持续读入System.out.print((char)readData); //输出时转换为char类型}} catch (IOException e) {//IOException包括一切IO异常,用别的read和FileInputStream只能管一个e.printStackTrace();} finally {//关闭文件流,释放资源try {fis.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
但是这种方法不适用于汉字的读取,因为在UTF-8中,一个汉字是由二到三个字符码编成的,如果按字节读取,会导致乱码。
用read方法读取多个字节:read(byte[]) 每次能读取byte数组容量(N)个字节
public static void main(String[] args) {int readLen;byte[] buf = new byte[8]; //一次读取8个字节FileInputStream fis = null; //不初始化会报错try {//创建 FileInputStream对象,用于读取文件fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\test1.txt");//从该输入流读取一个字节的数据,如果没有输入可用,此方法返回-1,表示读取完毕while((readLen = fis.read(buf)) != -1){ //如果读取正常,返回实际读取的字节数System.out.print(new String(buf,0,readLen));//注意不能用buf.length,会有额外字节}} catch (IOException e) {//IOException包括一切IO异常,用别的read和FileInputStream只能管一个e.printStackTrace();} finally {//关闭文件流,释放资源try {fis.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
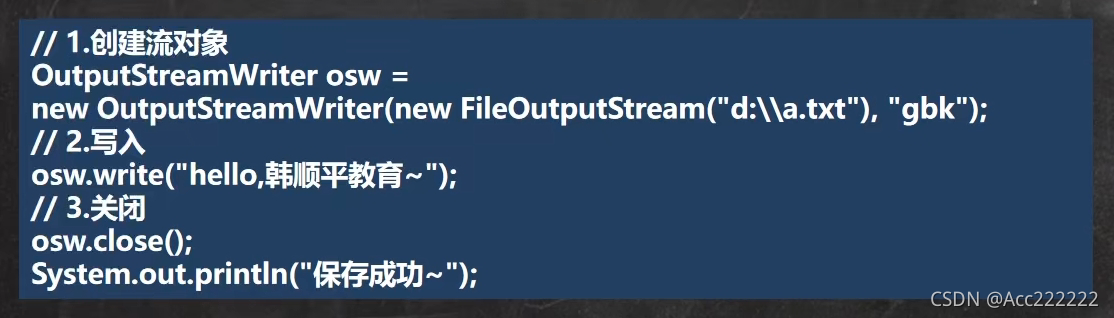
FileOutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) {String filePath = "d:\\a.txt";//如果不存在这个文件,会自动创建FileOutputStream fos = null;String str = "Hello,world!";try {fos = new FileOutputStream(filePath);// fos.write('a'); 输入一个字符// 写入字符串方法:str.getBytes() 可以把 字符串-> 字节数组fos.write(str.getBytes());fos.write(str.getBytes(),2,3);//从索引为2的地方开始追加3个字节。} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {fos.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
注:1. write(byte[] b,int off,int len){} 将len个字节从off索引开始写入文件。
2. new FileOutputStream(filePath) 这样的创建方式会把写入的内容覆盖原来的内容。
3. new FileOutputStream(filePath,true) 这样的创建方式,当写入内容会追加到文件后面。
4. FileOutputStream和FileInputStream都是字节处理流,可以处理二进制文件和文本文件。
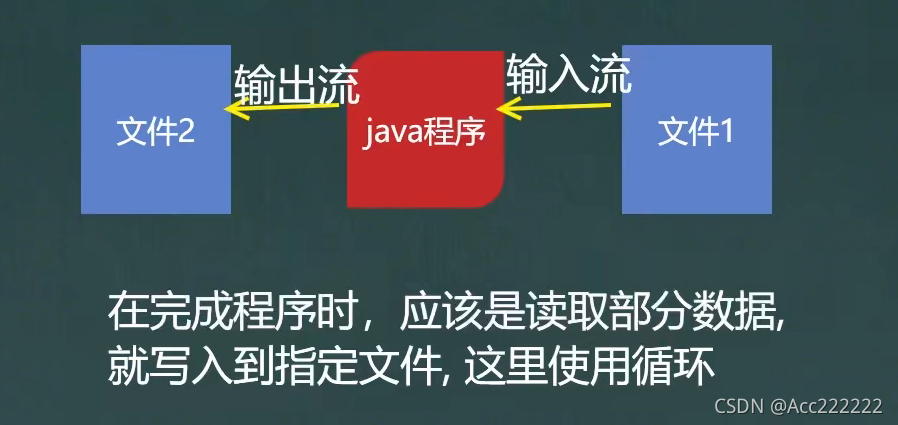
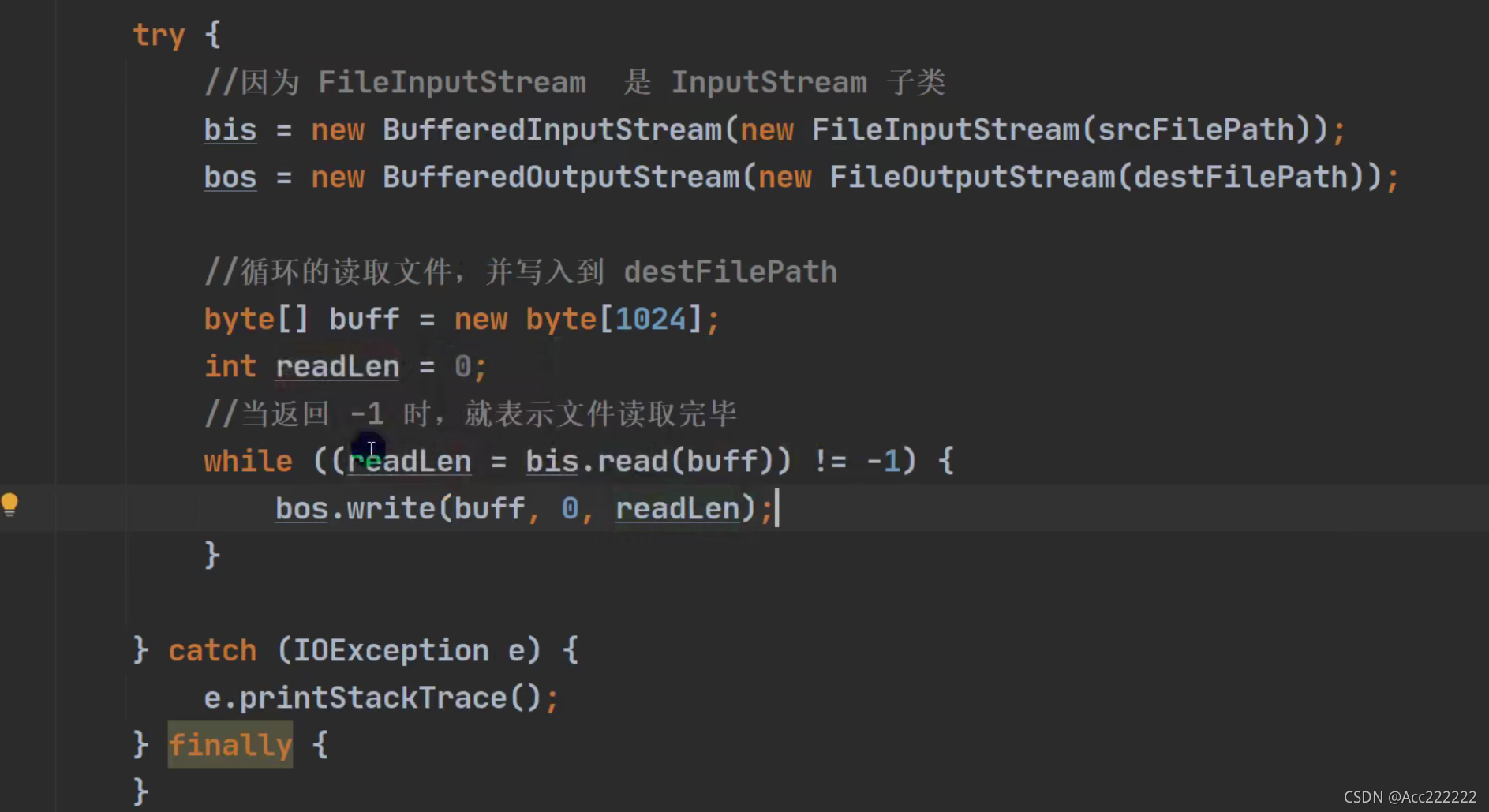
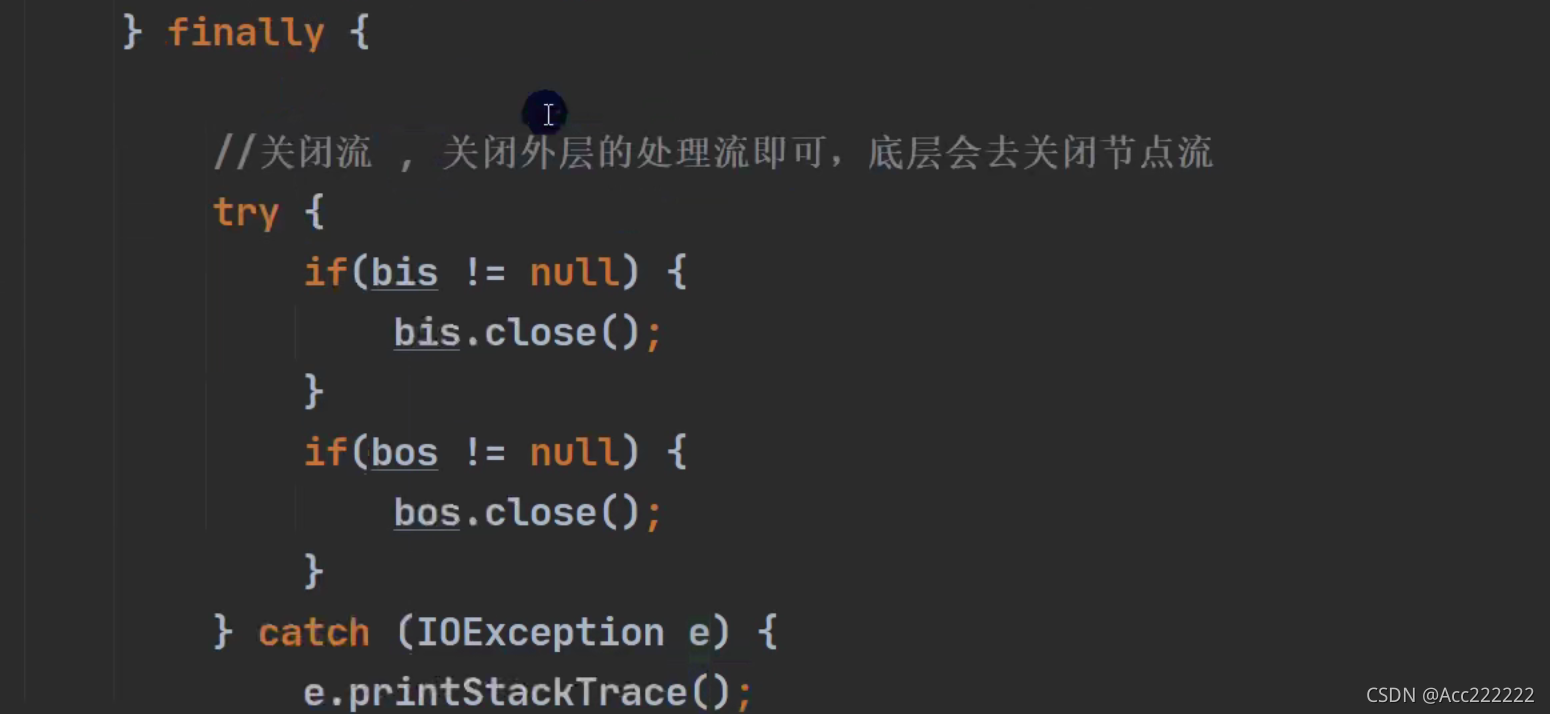
复制一个文件(图像等)
public static void main(String[] args) {FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; //输入流FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; //输出流try {fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\test2.txt");fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\test1.txt");byte[] b = new byte[1024]; //边读边写int len;while((len = fileInputStream.read(b)) != -1){fileOutputStream.write(b,0,len); //不能用b,因为可能有没有用到的空间}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {try {fileOutputStream.close();fileInputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
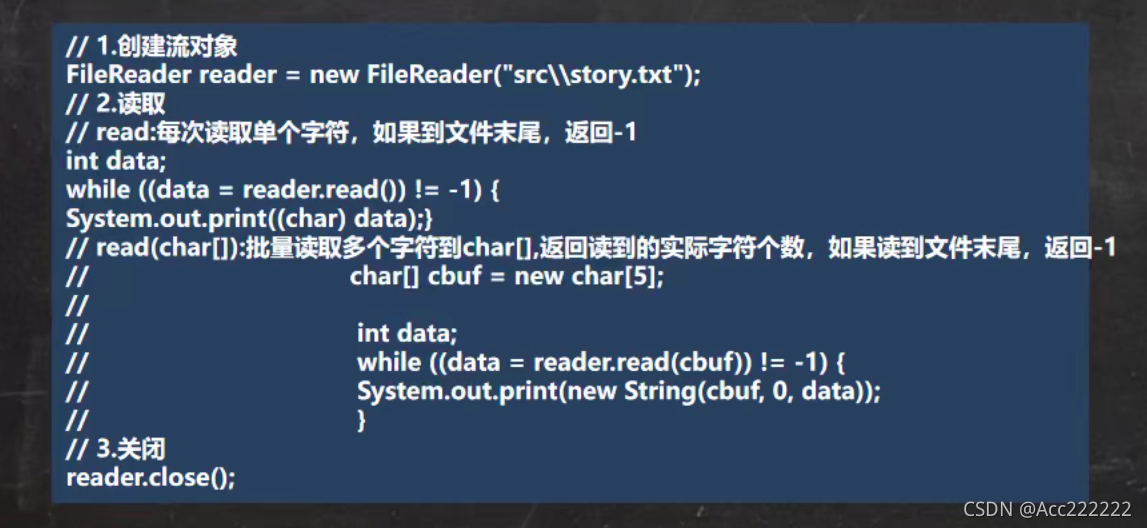
FileReader
FileWriter

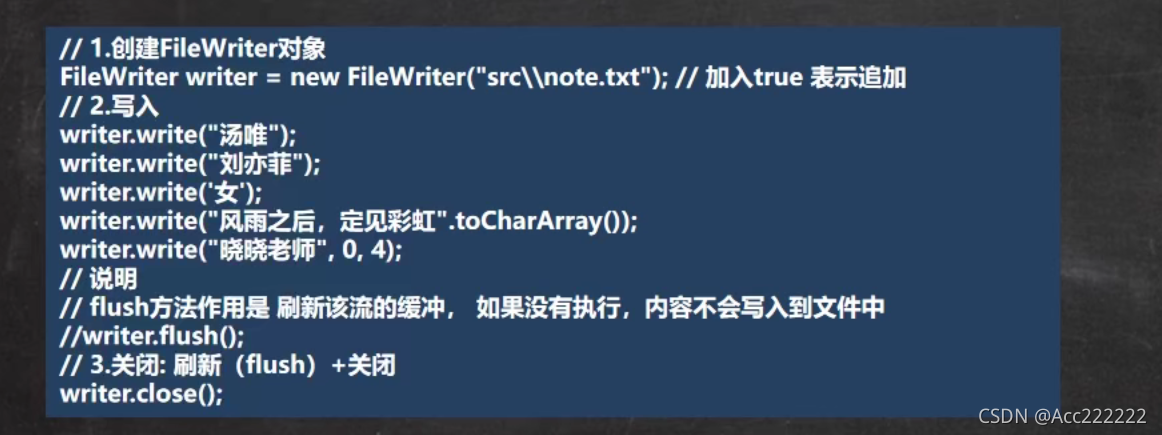
FileWriter和FileReader是节点流中的字符流,处理字符,不能处理二进制文件,只能处理文本文件。
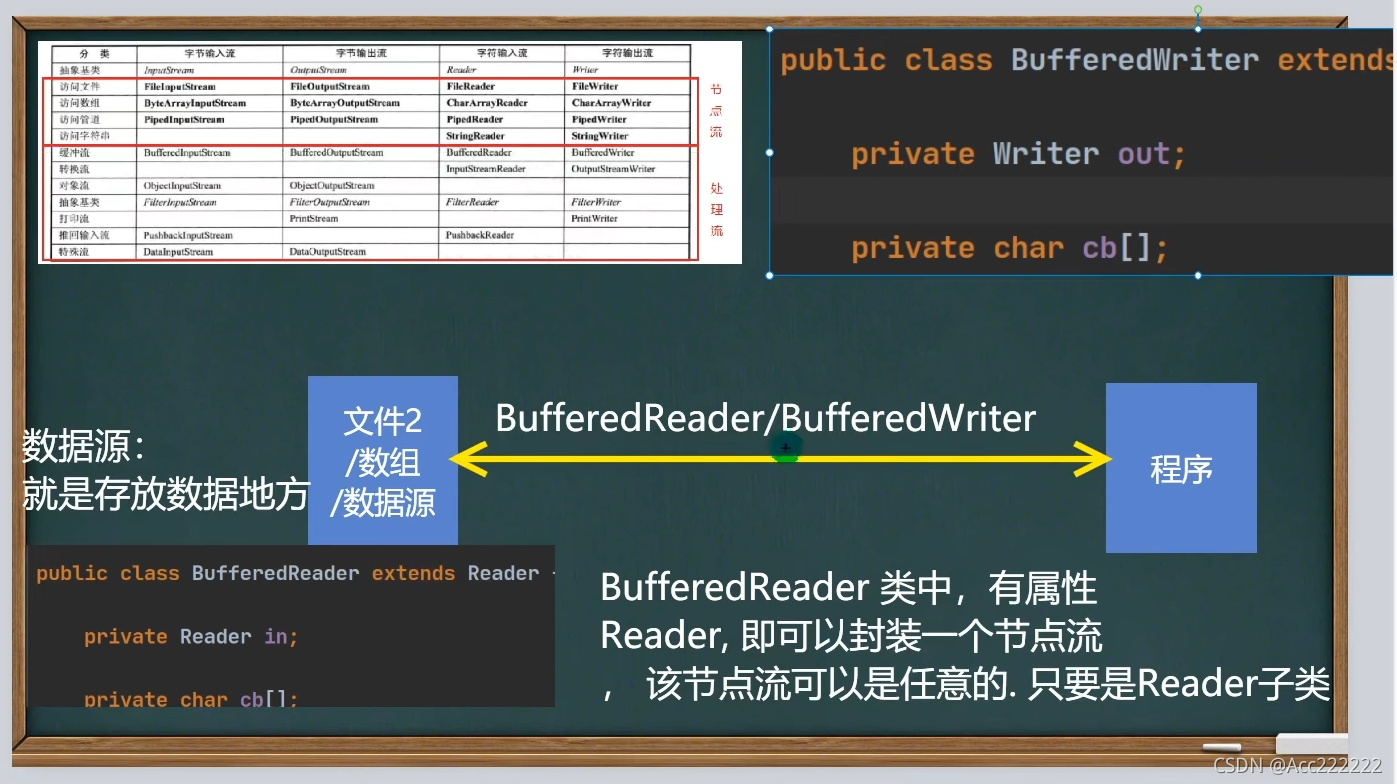
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
Buffered和Object IO流都属于包装流。
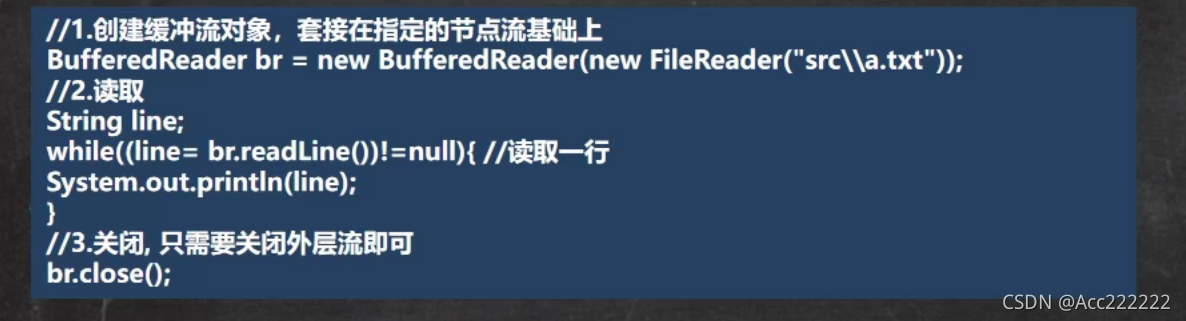
注:1. readLine方法读取一行,读取完毕返回null。
2. BufferedReader的关闭只需要关闭包装流,节点流在包装流关闭后会自动关闭。
注:
new FileWriter(filePath,true); //表示以追加的方式写入new FileWriter(filePath); // 表示以覆盖的方式写入
BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter 是安装字符操作。不要去操作二进制文件(声音,视频,doc等),可能造成文件损坏。
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
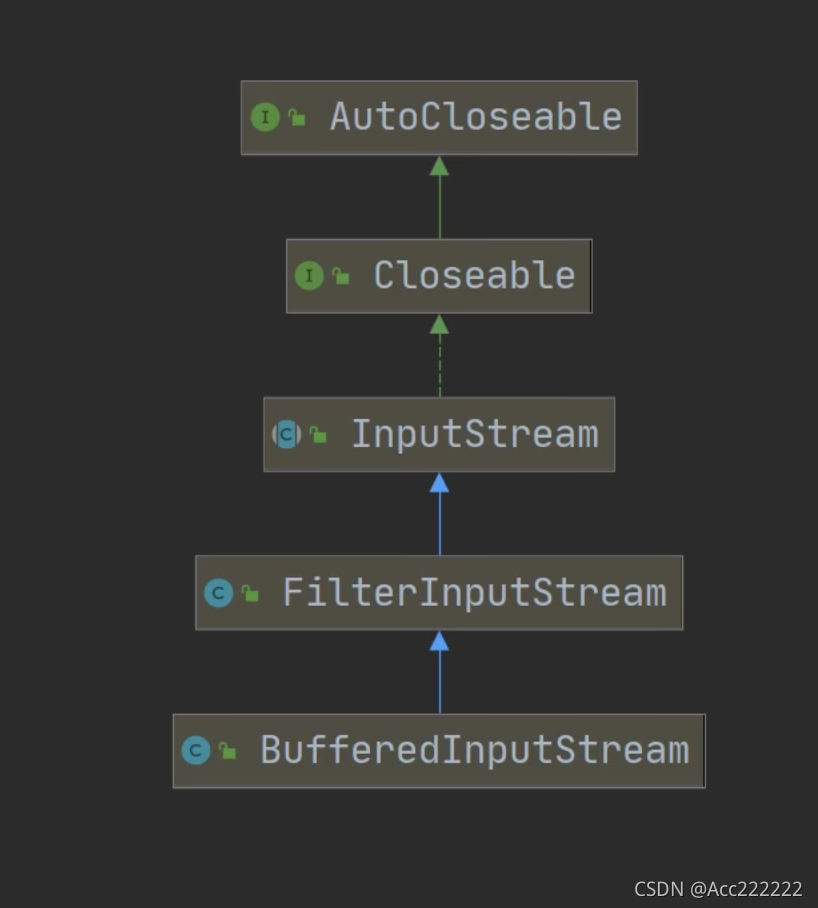

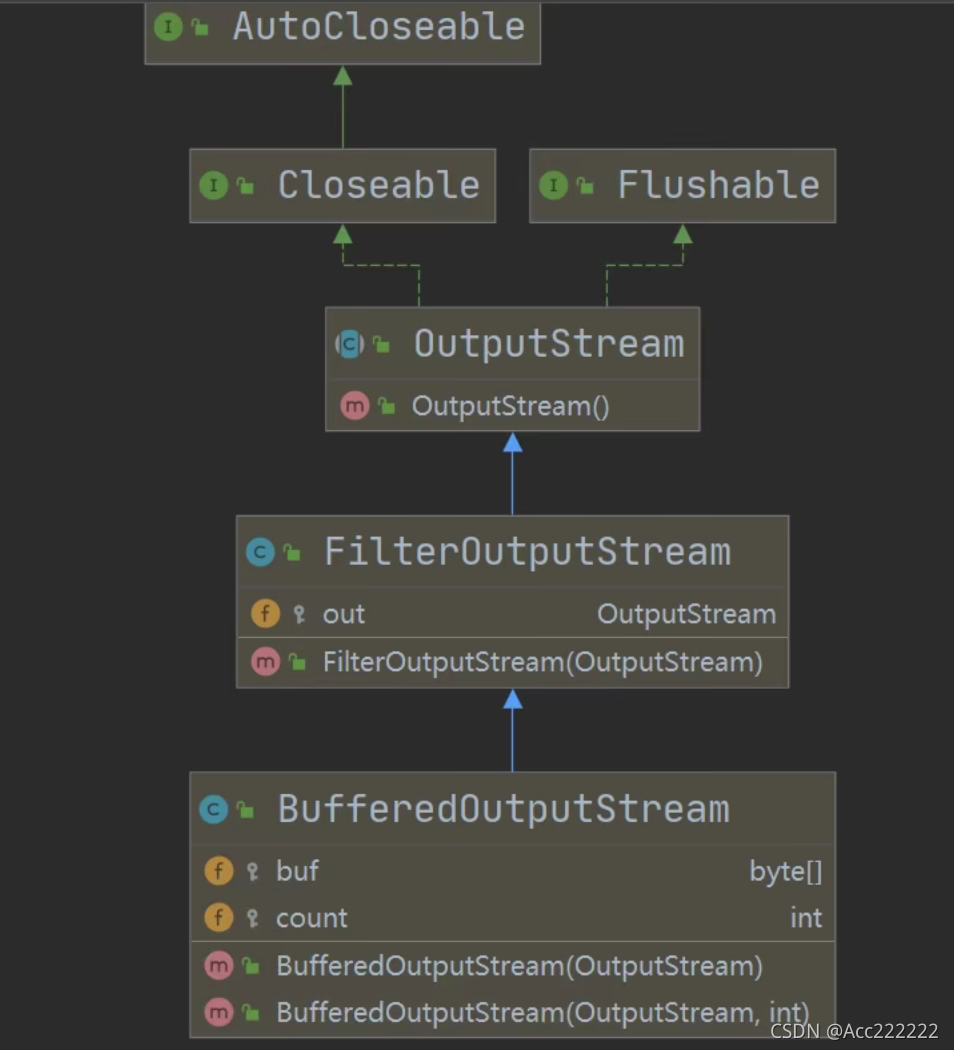
前面的Buffered使用writer和reader,这个Buffered使用 FileInputStream和FileOutputStream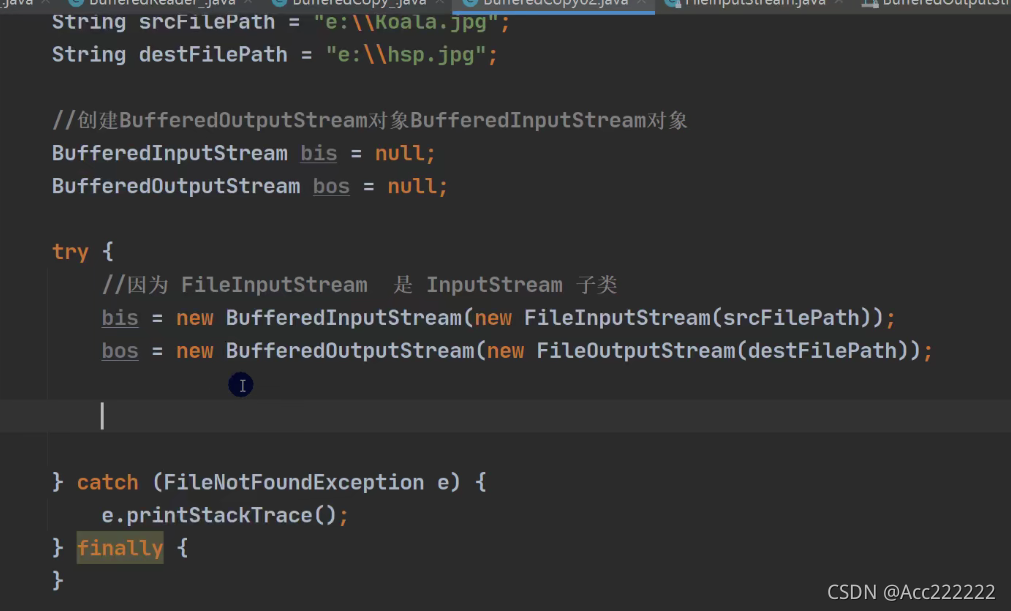
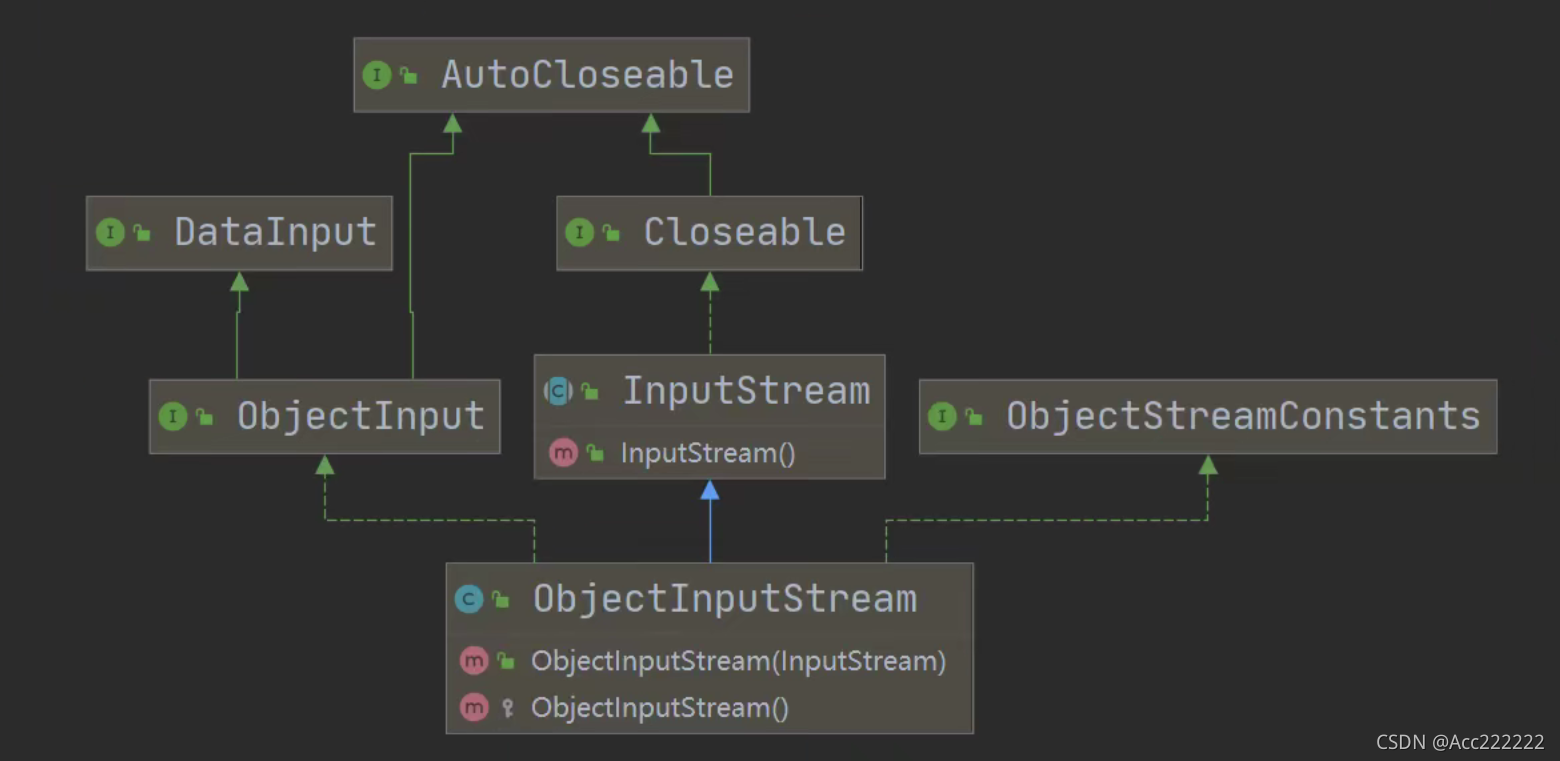
ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream
假如说我们只想把”10”这个数存到文件里,那么只是保存值,用不上ObjectInputStream。但如果想把值和数据类型都保存,比如Dog类或者”int a = 10”,那么就需要用到了。

ObjectOutputStream提供 序列化功能。 ObjectInputStream提供 反序列化功能。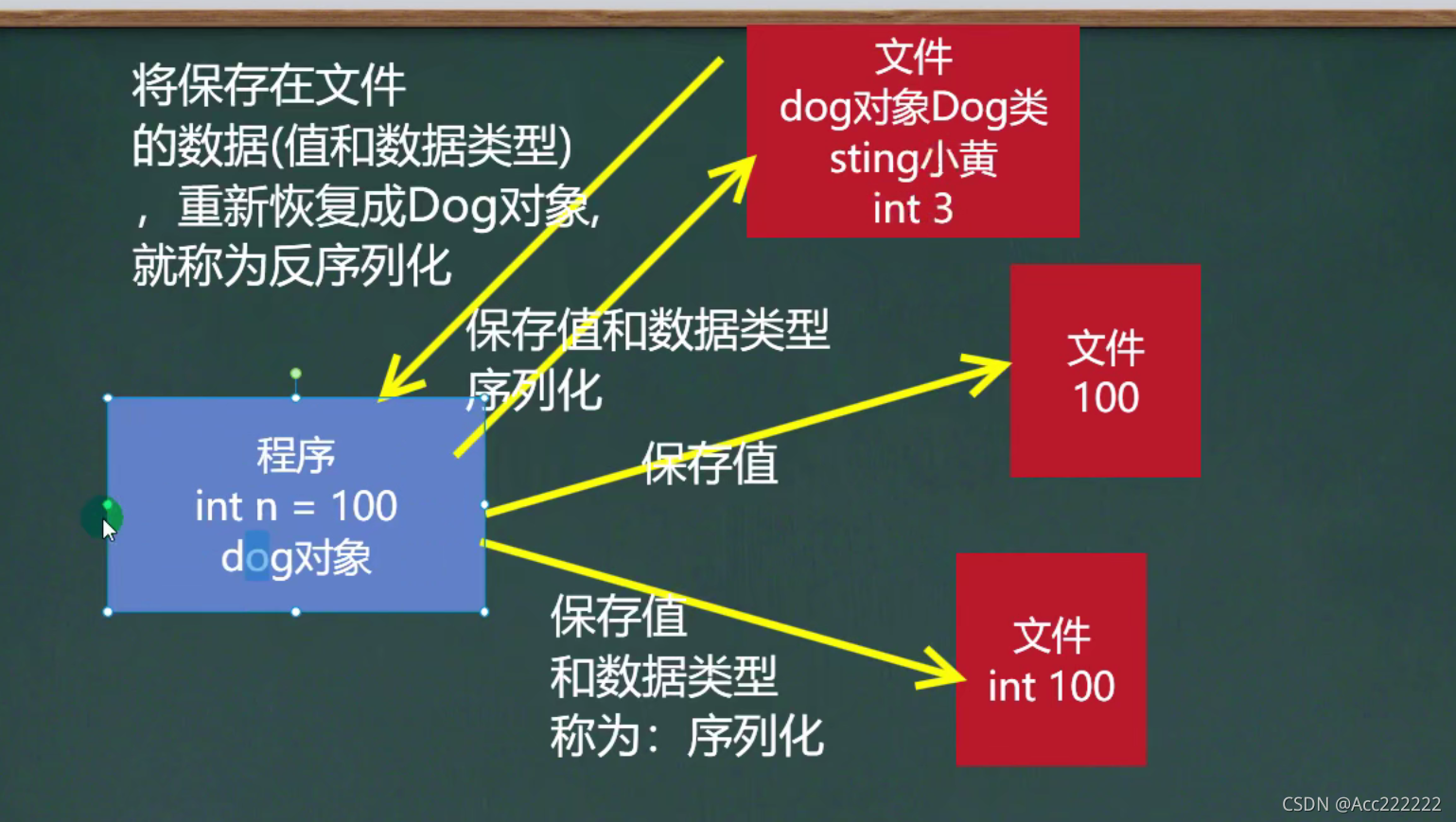

注:Dog类需要实现Serializable接口
class Dog implements Serializable{ ... }


值得注意的是:1. 读取顺序必须和write顺序一致。 2. 读取自定义类时,这个类需要能被访问到。
3. ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream都是只关闭外流就可以了。

标准输入输出流
public final static InputStream in = null;public final static PrintStream out = null;
System.in 编译类型:InputStream,运行类型:BufferedInputStream。表示的是标准输入 键盘
System.out 编译类型:PrintStream,运行类型:PrintStream。 表示的是标准输入 显示器
转换流
默认情况下,读取文件是按照UTF-8编码,如果文件按照别的方式编码,就很容易读取到乱码。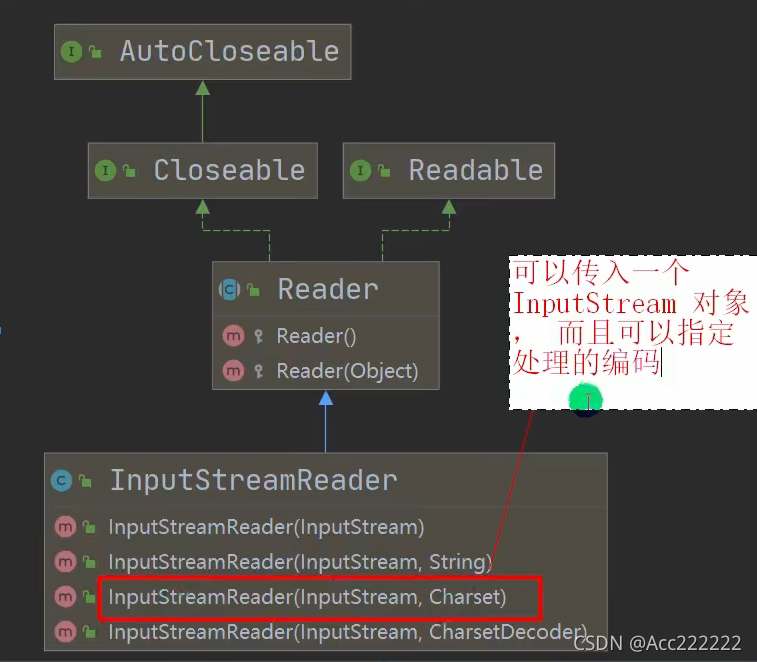


包装:其实就是转换。
String filePath = "d:\\a.txt";InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath,"gbk"));//注意文件编码格式是啥,就转化成啥格式BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); //包装转换流,转换成字符流String s = br.readLine();br.close(); //关闭外层流
打印流
只有输出流,没有输入流。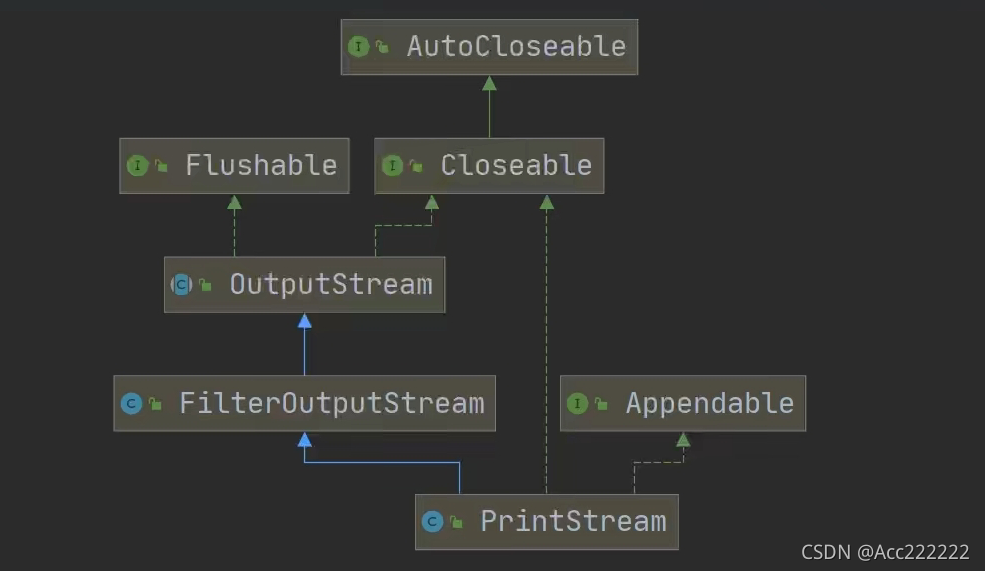

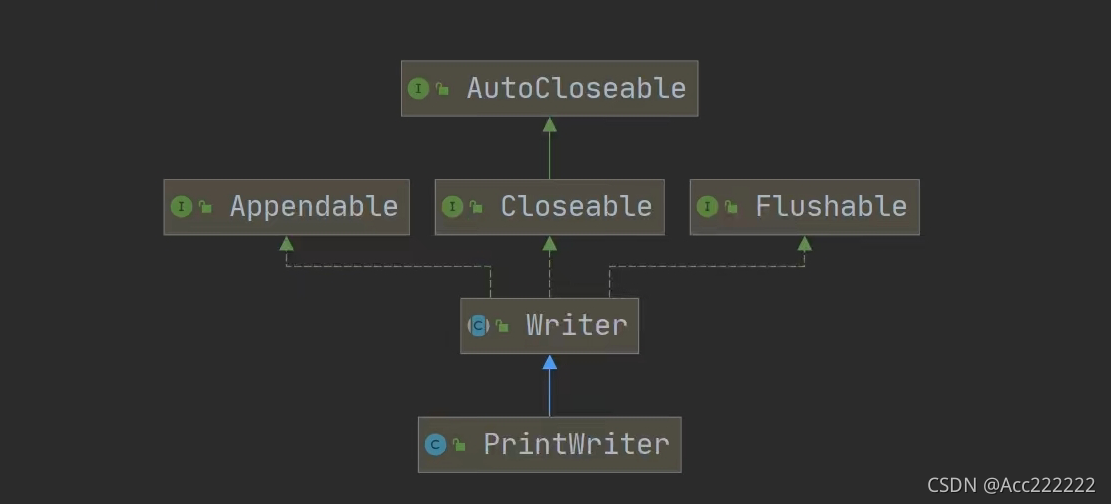

PrintStream out = new PrintStream(System.out);out.println("hello");out.write("你好,世界".getBytes());//print底层调用的是write,所以可以直接调用write进行打印out.close(); //注意由于out是System.out,这个一结束,sout就不能用了System.out.println("wowowo"); //无法输出
PrintStream out2 = new PrintStream("d:\\a.txt");System.setOut(out2);//修改打印流输出的位置System.out.println("1111"); //输出到文件当中
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("d:\\a.txt");PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(fileWriter);printWriter.print("hello,world!!!!!!");printWriter.flush();//printWriter.close(); //flush或者close调用一个,才能输入进去}
Properties

注:键值对不需要有空格,值不需要用引号引起来,值的默认类型是String。


store方法的第二个参数是注释,null表示没有注释。在store方法中,如果没有这个文件就是创建,如果有这个文件就是修改。